0 引言
在野外数据采集过程中,受到地形、地貌、仪器故障等因素的限制,地震勘探数据在空间方向上常呈现不规则采样,导致地震波场信息不完整,从而出现空间假频现象,影响高分辨率地震勘探的准确性[1 -2 ] 。此外,即使按照传统的奈奎斯特定理进行理想采样,但在后续的某些地震处理方法中,地震数据仍存在采样不足的情况,难以满足特定处理方法的要求,在这种情况,需要发展快速高精度叠前数据重建方法,重建出高密度地震数据,以减轻地震数据采样不足对后续处理方法的影响。
目前主要存在5类地震数据重建方法。第一类是基于滤波器的方法,这类方法通过插值滤波来实现数据重建,但对于不均匀网格采样的数据,规则化处理可能导致较大误差。第二类是波场延拓方法[3 ] ,这类方法需要利用地下信息,但由于地下结构的先验信息通常不明确且计算量巨大,难以应用于实际工作中。第三类是快速降秩方法[4 -5 ] ,该类方法将插值问题转化为图像填充问题,速度快,参数简单,但在非均匀网格采样下有不规则缺失数据现象,在反假频能力方面也存在一定不足。第四类是稀疏变换的方法,该类方法将地震数据从时间域转换到变换域,利用变换域的信号特征进行插值;这一类方法无需先验地下信息,可以重建规则和不规则的缺失地震道,计算速度快,精度高。第五类是人工智能重建方法[6 ] ,根据地震数据本身的特征进行自我学习,从而恢复缺失道信息,如:有监督学习、无监督学习、自监督学习等。
由于不规则采样数据产生的混叠噪声较少,因此重建不规则采样数据的难度低于重建规则采样数据的难度[7 ] 。针对不规则数据的重建,稀疏促进重建是应用最为广泛的方法之一。压缩感知理论提供了一个很好的机会来解决地震数据重建问题,指出可以用低于奈奎斯特采样率的非自适应测量来处理信号,将地震数据重建问题转化为稀疏优化问题,利用稀疏变换来区分有用信号和缺失信号[8 ] 。目前,对于稀疏变换的研究已取得了大量成果,如早期的傅里叶变换[9 ] 、小波变换[10 ] ,以及众多具有更好方向表示能力的类小波变换:Contourlet变换、Curvelet变换[11 -12 ] 、Shearlet变换等[13 -14 ] 。Shearlet变换是一种与多尺度和多分辨率分析密切相关的多维函数逼近方法[15 ] ,该变换的基函数可以通过膨胀、剪切和平移构造在频域中逐层细分,从而使得其比小波变换更为稀疏。值得一提的是,该变换的分解方向数量和支撑基的规模没有明确限制。现如今Curvelet变换已被广泛应用于地震数据重建和去噪领域,但Shearlet变换在地震数据处理领域中尚未得到广泛应用。
在所有数据插值算法中,凸集投影算法(POCS)因其高效率和高性能的优势而被广泛应用于图像重建和不规则数据绘制[16 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -21 ] 。Gao等[22 ] 结合傅里叶变换与POCS算法对不规则地震数据进行插值。基于傅里叶变换重建能较好地处理近似线性同相轴的地震数据,但处理非线性同相轴的效果不佳。Curvelet变换[23 ] 有局部化识别能力,于是被用于地震数据重建。张华等[12 ] 基于Curvelet变换和POCS算法,通过对时间切片处理实现三维地震数据重建。
在前人研究基础上,本文采用Shearlet变换基作为稀疏表示基,对地震数据进行二维随机欠采样,并通过POCS算法对时间切片进行重建,在时间域实现了基于Shearlet变换的三维地震数据重建,这种方法降低了地震数据的维数,提高了计算效率,节省内存空间。研究结果表明,Shearlet变换相较于Curvelet变换不仅运算速度更快,而且重建效果更好。
1 理论原理
1.1 压缩感知基本理论
由完整地震数据d 和实测数据y 组成的地震正演模型可以表示为
(1) y =Md ,
式中:y ∈Rn d ∈RN N 、n 为数据维度,且N >n ;M 为随机采样矩阵。
S 为一种稀疏变换,且有S H S =I ,则d 在变换域中的稀疏表示为
(2) y =Ax 且A =MS H ,
式中,S H 是S 的共轭转置矩阵。地震数据重建问题就是把实际采集的数据d 重建回完整的数据y ,这是一个欠定的反演问题。获得稀疏表示后,该问题可以转化为L 0 范数最小化问题:
(3) x ~ m i n x 0 s.t. y=Ax 。
式中:x ~ [24 ] ,即可求得唯一解。地震勘探中,所使用的随机采样矩阵(数据缺失位置对应元素为0,采集的数据对应元素为1)能满足以上条件。这时,求解L 0 范数最小化问题等价于求解L 1 范数最小化问题,这样就转化为一个线性规划凸优化问题:
(4) x ~ m i n x 1 s.t. y=Ax;
(5) x ~ m i n x ‖ y - A x ‖ 2 2 1 ;
(6) d ~ H x ~
1.2 Shearlet变换基本理论
稀疏变换是压缩感知的一个主要环节,其中Shearlet变换是一种多维函数稀疏表示方法,具有比曲波更敏感的方向性和更稀疏的表现形式。当维度为2时,shearlet系统的形式为
(7) S H ( ψ ) = { ψ i , j , k ( x ) = | d e t A | i / 2 ψ ( S j A i x - k ) : i , j ∈ Z , k ∈ Z 2 } ,
式中:ψ ∈ L 2 ( R 2 ) ψ i , j , k ( x ) Ai 为各向异性膨胀矩阵;Sj 为剪切矩阵;i 、j 、k 分别为尺度参数、剪切参数和平移参数,对∀i >0,j ∈R,有:
(8) Ai = i 0 0 i j = 1 j 0 1
另外,对于任意ξ =(ξ 1 ,ξ 2 )∈R2 ,ξ 1 ≠0,ψ 满足:
(9) ψ ^ ( ξ ) = ψ ^ 1 ( ξ 1 ) ψ ^ 2 ξ 2 ξ 1 ,
式中:ψ ^ ψ 的傅里叶变换;ψ ^ 1 C ∞ (R)且suppψ ^ 1 - 2 , - 1 2 1 2 , 2 ψ ^ 2 C ∞ (R)且suppψ ^ 2 ψ 、各向异性膨胀矩阵Ai 和剪切矩阵Sj 可以得到Shearlet系统:
(10) { ψ i , j , k ( x ) = i - 3 / 4 ψ ( A i - 1 S j - 1 ( x - k ) ) : i ∈ R + , j ∈ R , s ∈ R 2 } 。
1.3 POCS算法
由压缩感知理论得到,利用随机欠采样可以将信号的重建问题转化为去噪问题。本文采用凸集投影算法进行数据重建,在每次迭代过程中,将空间域的地震数据转换到变换域,通过设置阈值保留有效信号,然后把有效信号进行反剪切波变换,最后把原始待重建的地震数据置换到反剪切波后的数据中。反复重复以上步骤,直到缺失的地震数据得到最佳恢复,迭代公式为
(11) d ~ k + 1 = y + ( I - M ) S H T λ k S d ~ k 。
式中:S 表示稀疏变换;y 为缺失数据;d ~ k T λ k
(12) T λ k ( x ) = 1 , | x k | ≥ λ k ; 0 , | x k | < λ k 。
(13) ‖Sy ‖∞ =λ 1 >λ 2 >…λk …>ε ,
其中,ε 是几乎为零的最小阈值,其大小和数据中噪声的能量有关;λk 为第k 次迭代后的阈值,可以根据阈值模型选择λk 。为了使计算速度更快,本文引用以指数形式e - x [12 ] :
(14) λ k = m · e x p k - 1 N - 1 ( l n ε - l n m )
式中:m =|Sy |max ,表示稀疏变换系数绝对值的最大值。
2 模型数据重建试验
为了评价地震数据重建后的质量,本文定义的信噪比(SNR)公式为
(15) S N R = 20 l g ( ‖ d 0 ‖ 2 / ‖ d - d 0 ‖ 2 ) ,
式中:d 0 为原始数据;d 为重建后的数据。SNR 值越高,表示重建结果与原始数据越接近,效果越好。
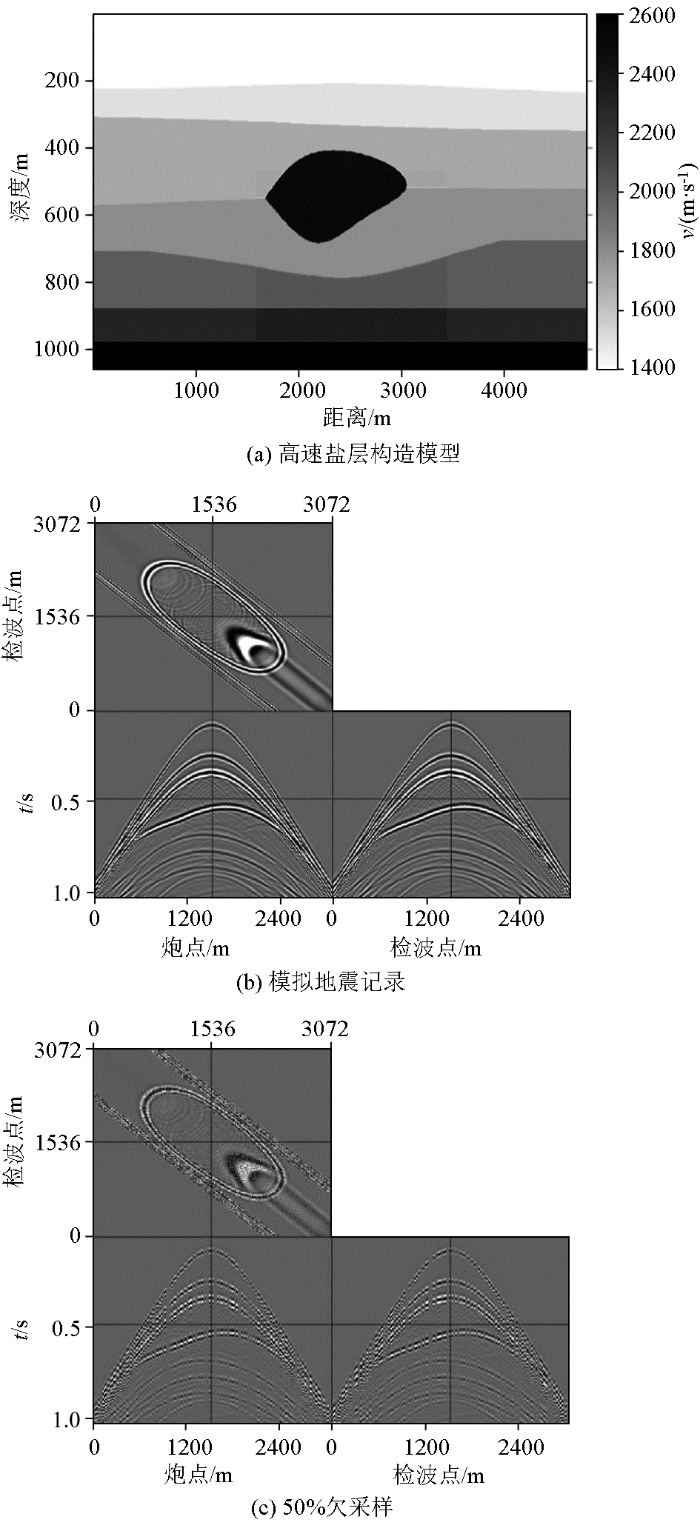
为了恢复缺失的地震数据、提高数据质量,以满足后续处理、反演和解释工作的要求,进行叠前数据重建是不可缺少的一环。首先设计如图1a 所示的速度模型,该模型由沉积物层包围的高速盐层组成;然后使用声波方程有限差分法进行模拟,从而得到一个理论的合成数据,并将其按检波器、炮点和时间采样点方向排列成三维数据体,如图1b 所示。该合成的数据包括256炮,每一炮有256个检波器,炮间距与检波距都为12 m。其中每个检波器都包含256个时间采样点,时间采样间隔为4 ms,采样时长为1.024 s。图1c 为50%二维随机欠采样记录,抽取共炮点第128炮(1 536 m),共检波器第128道(1 536 m),时间0.48 s进行展示。
图1
图1
合成数据及相应速度模型
Fig.1
Synthesize data and corresponding speed model
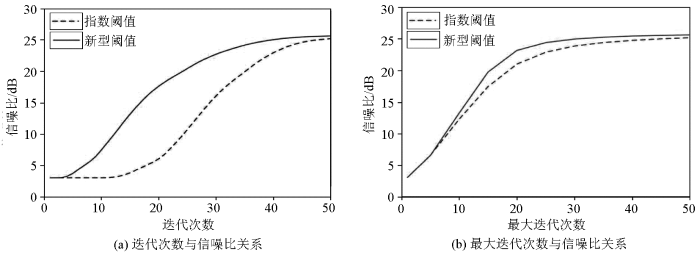
阈值模型的选择影响算法的收敛速度。为了比较本文方法在不同模型下的运算效果,随机抽取任意一时间切片进行计算。图2a 为最大迭代次数固定为50次、迭代次数与两种阈值模型重建后的信噪比关系图,图2b 为不同的最大迭代次数、两种不同阈值模型重建后的信噪比曲线。从图2 中可以看出,无论是固定迭代次数还是不同的最大迭代次数,两者在迭代次数为50时均已收敛,但新型阈值模型的收敛速度更具有优势,在迭代次数少的情况下,重建后的信噪比更高。因此,在后续的模型试验中,选择新型阈值模型和迭代次数为50次进行数据重建试验。
图2
图2
指数和新型阈值模型的重建信噪比曲线
Fig.2
Reconstructed SNR curves of the index and the new threshold model
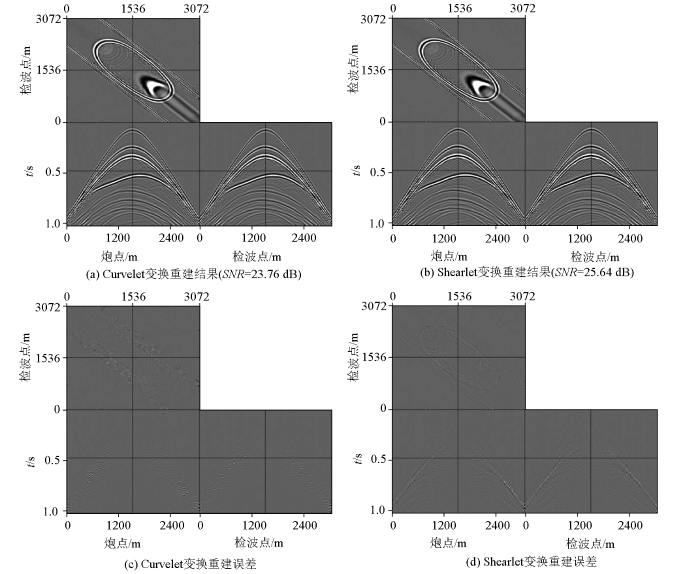
本文采用50%随机欠采样的地震数据进行重建。图3a~d 分别为基于Curvelet变换和Shearlet 变换的重建结果以及重建后与完整数据的误差,工程方法重建后的SNR 分别为23.76 dB和25.64 dB。重建结果表明:两种方法都获得了较好的插值结果,相比之下,基于Shearlet变换重建后的同相轴恢复得更完整,重建误差更小,信噪比更高。值得一提的是,Shearlet变换相比Curvelet变换,仅需一半的时间就完成了数据的重建,大大提高了重建速度。
图3
图3
Curvelet变换和Shearlet变换重建结果及其误差
Fig.3
The reconstructed results and error by Curvelet and Shearlet
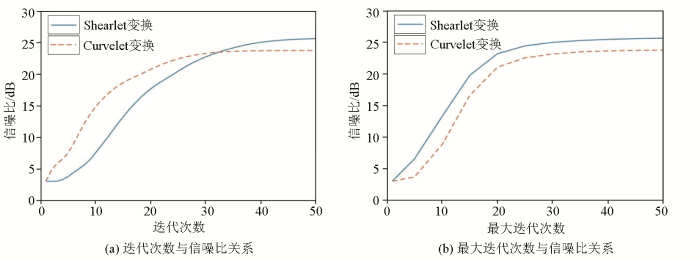
图4a 为最大迭代次数固定为50次、迭代次数与重建后的信噪比关系曲线,可以看出:在初期基于Curvelet变换重建的收敛速度快、信噪比较高,但后期收敛慢;在第32次迭代后的迭代过程中,基于Shearlet变换重建后的精度更高。图4b 为计算不同最大迭代次数与重建后的信噪比关系曲线,可以发现在1~50的最大迭代次数中,Shearlet变换的重建效果都优于Curvelet变换。经对比,信噪比达到23 dB时,Curvelet变换要迭代30次,而Shearlet仅需要迭代20次即可,所用的时间更少,在效率上更具有优势,这说明Shearlet变换具有一定的实际意义。
图4
图4
Curvelet变换和Shearlet变换重建信噪比曲线
Fig.4
Reconstructed SNR curves by Curvelet and Shearlet
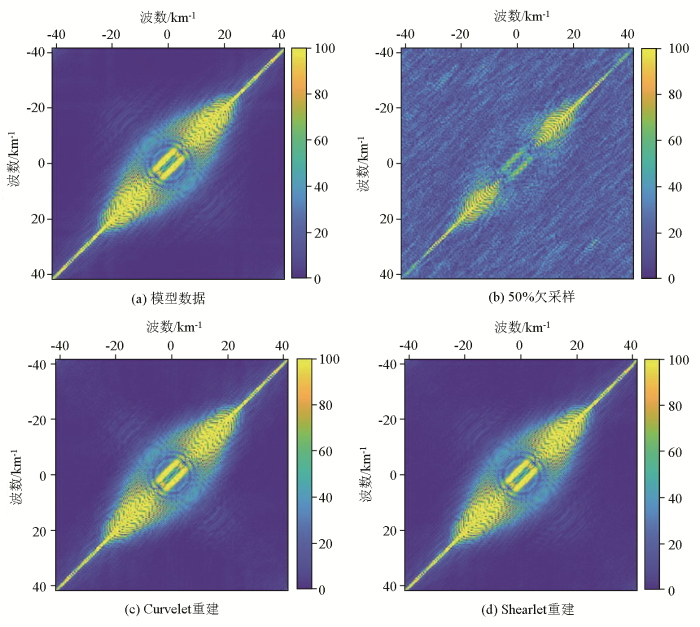
图5a~d 分别为图1b~c 和图3a~b 对应时间切片的f-k频谱图,可以看到由于随机缺失的存在,原始时间切片的能量发生了泄露,导致在整个频谱中出现类似随机噪声出现的采样噪声。经过重建后有效波的能量更加集中,有了更明显的收敛,不相干的随机噪声得到了有效压制。基于Shearlet变换重建后的频谱与原始时间切片的频谱的相似度更高,几乎无差别。
图5
图5
二维随机欠采样重建结果f-k谱
Fig.5
f-k spectrum of 2D random under-sampling reconstruction results
为了更好地从细节处对比两种变换方法的重建效果,从重建后的三维数据中提取2条单道曲线进行对比。图6 是炮点为第90道、检波器为第60道和炮点为第60道、检波器为第94道的重建前后对比曲线,时窗为0~0.8 s。可以看到两种变换重建后与原始数据的单道曲线都吻合较好,都具有良好的插值精度。
图6
图6
重建结果与误差的单道显示
1—原始记录;2—Curvelet变换重建曲线;3—Shearlet变换重建曲线;4—Curvelet变换的误差曲线;5—Shearlet变换的误差曲线
Fig.6
Single channel display of reconstruction results and errors
1—original record;2—Curvelet reconstruction results;3—Shearlet reconstruction results;4—Curvelet errors; 5—Shearlet errors
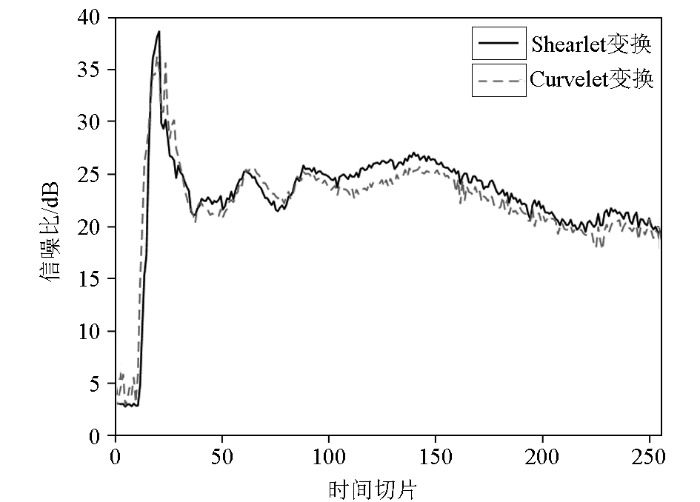
为了更加直观地对比两种变换方法在时间方向上的重建结果,图7 给出了在50%欠采样率下,逐时间切片(4 ms一个切片)的重建后的信噪比。可以发现:在1~36和60~80时间切片中,基于Curvelet变换方法重建的信噪比略高;在其余时间切片中,基于Shearlet变换方法的重建精度略高。即经过对比,占比76.92%的基于Shearlet的时间切片重建效果略高于基于Curvelet变换方法的。
图7
图7
Curvelet变换和Shearlet变换重建结果和各时间切片信噪比
Fig.7
Reconstruction results of curved and shear wave bases and SNR of each time slice
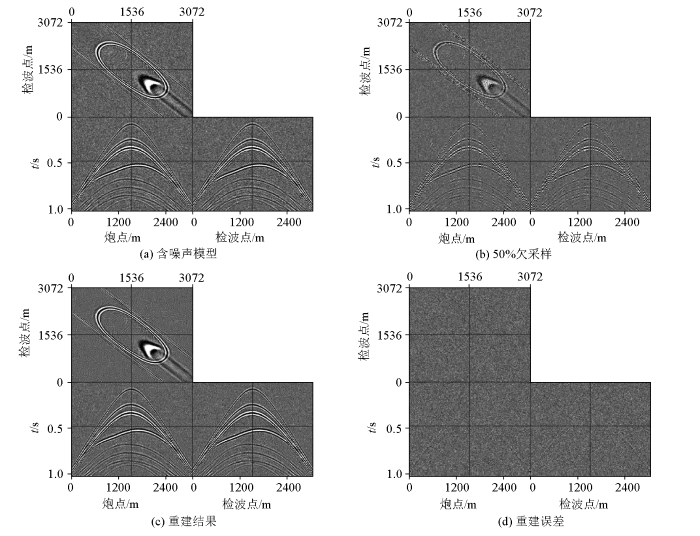
通常实测地震数据中都含有噪声,因此本文检验了基于Shearlet变换在随机欠采样下用POCS重建算法的抗噪声能力。在图1b 模型中加入高斯随机噪声进行抗噪声地震数据重建试验(图8 )。经对比可以发现,重建后的有效波同相轴几乎相同,损失的有效信息较少,数据的重建效果较好,说明Shearlet变换重建方法有着不错的抗噪声能力,可以进行实际地震资料的数据处理。
图8
图8
含噪声数据二维随机欠采样重建结果及其误差
Fig.8
Reconstruction results of two-dimensional random under-sampling of noisy data and its error diagram
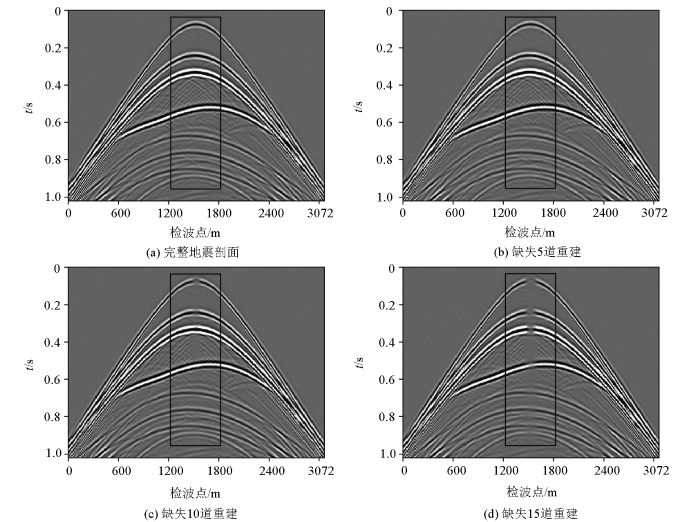
为了检验本文方法对于连续缺失不同地震道数据的重建效果,从三维地震数据抽取128炮进行处理(图9a ),并以128道(1 536 m)为中心点,分别连续缺失5、10和15道,然后采用本文方法进行重建。由图9 分析可得,连续缺失5道时所有同相轴能完好重建,连续缺失10道时重建效果相对较好,但当缺失道数为15道时,重建后的同相轴不完整,特别是能量较弱的缺失道,重建误差相对较大。
图9
图9
连续缺失地震道重建
Fig.9
Continuous missing seismic trace reconstruction
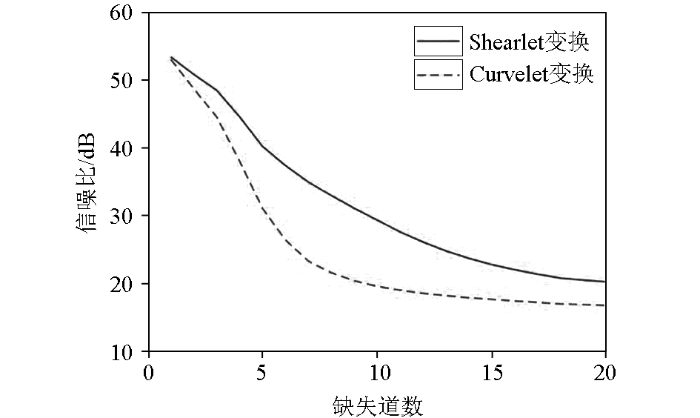
为了进一步测试本文方法与Curvelet的重建效果,将图9a 连续缺失2~20道,然后分别使用Curvelet和Shearlet变换方法进行重建,重建后的信噪比曲线如图10 所示。可以看到:随着连续缺失道增多,两种方法重建后的信噪比都是逐渐降低,且变化趋势一致,但相比较而言,本文方法重建后的信噪比更高,表明重建效果更佳。综合图9 与图10 的结果可以推断,本文方法对于连续缺失10道以内的地震数据可以有效地重建出来。
图10
图10
连续缺失地震道数与重建后信噪比曲线
Fig.10
Continuous missing trace number and reconstructed SNR
3 实测数据应用
实测数据为某海上二维高密度地震资料,道间距为25 m,采样率为4 ms,180道接收,检波点和炮点移动一个检波器的距离。把检波器、炮点和时间采样点方向排列成三维数据体,截取了其中的180道、180炮和采样长度为2 s的数据体进行计算,由于在时间方向上采样是连续不断的,为了加快计算速度,把三维数据体在时间方向上进行切片处理。
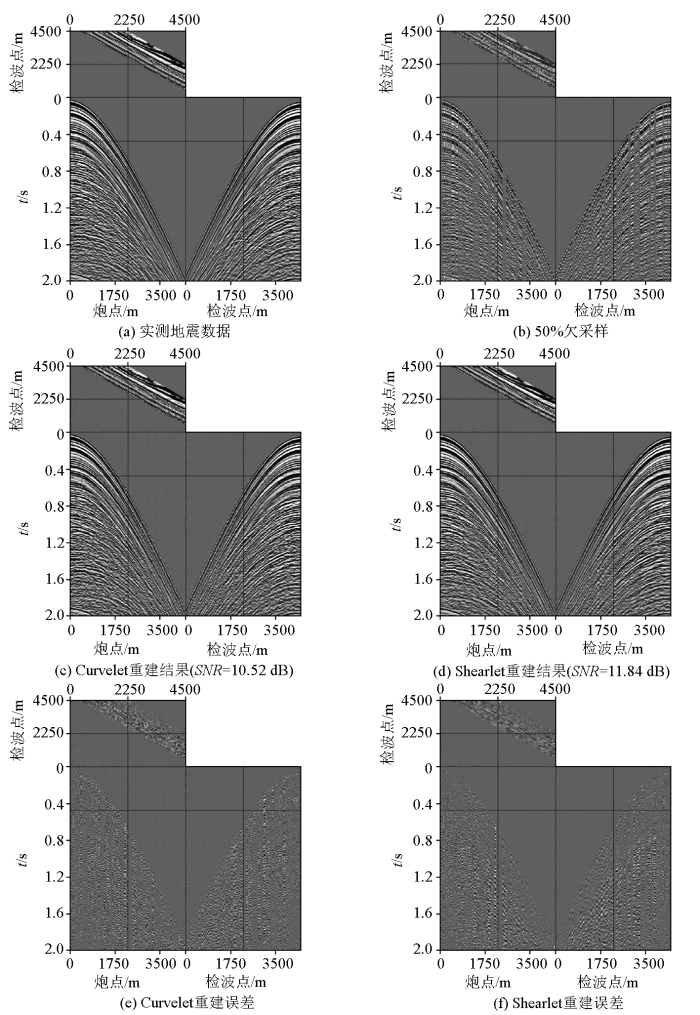
图11a 为共炮点距离和共检波点距离为2 250 m、时间切片为0.48 s的实际采样数据,图11b 为实际采样数据的50%二维随机欠采样;然后利用POCS算法迭代计算进行数据重建(图11c~f )。可以看出:在50%欠采样下,基于Shearlet变换重建后的局部细节恢复得更好、误差更小,在精度上略优于Curvelet变换方法;在计算速度方面,Shearlet变换比Curvelet变换的计算速度快一倍。这表明当处理大量的地震数据时,本文所提出的方法更具有优势。
图11
图11
实测数据重建结果
Fig.11
Reconstruction results of measured data
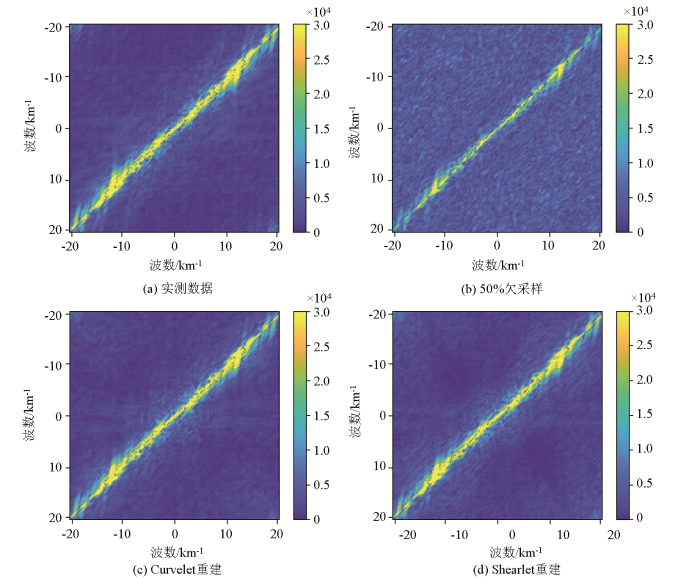
图12 为图11a~d 时间切片的f-k频谱图。图12b 出现了能量泄露的迹象,产生了白色噪点,经过重建后有效波的能量有了明显的收敛。经对比,基于Curvelet变换重建后的频谱图还存在少量的噪点,而基于Shearlet变换重建后的频谱更接近于原始的实际采样数据。
图12
图12
实测数据重建结果f-k谱
Fig.12
f-k spectrum of reconstructed measured data
4 结论
基于压缩感知理论的知识框架,在随机欠采样情况下运用Shearlet变换和凸集投影算法进行了三维地震数据重建。通过模型试验、加入随机噪声实验、最大连续缺失道重建试验和实际数据应用,验证了基于Shearlet变换相较于Curvelet变换在地震数据重建中表现更优,从重建后的剖面、误差剖面和f-k频谱图等对比观察,基于Shearlet变换的精度略高。
从计算效率上看,基于Shearlet变换的重建速度比Curvelet变换快一倍,但在处理更大数据体时,计算效率仍然是个挑战。未来需要发展其他快速算法或者在频率域中进行快速计算,在保证精度的前提下进一步提高计算速度。
在实际勘探中,可以利用目标测区的地质先验信息,因此,下一步的研究工作将采用基于先验信息的采样方式。本文方法是基于均匀网格情形,然而在实际采样工作中常常遇到复杂地形情况,均匀网格不一定适用。因此,未来的研究方向之一是发展基于非均匀Shearlet变换的三维地震数据重建方法,以应对实际采样工作中遇到的挑战。
参考文献
View Option
[1]
霍志周 , 熊登 , 张剑锋 . 地震数据重建方法综述
[J]. 地球物理学进展 , 2013 , 28 (4 ):1749 -1756 .
[本文引用: 1]
Huo Z Z Xiong D Zhang J F . The overview of seismic data reconstruction methods
[J]. Progress in Geophysics , 2013 , 28 (4 ):1749 -1756 .
[本文引用: 1]
[2]
孟小红 , 郭良辉 , 张致付 , 等 . 基于非均匀快速傅里叶变换的最小二乘反演地震数据重建
[J]. 地球物理学报 , 2008 , 51 (1 ):235 -241 .
[本文引用: 1]
Meng X H Guo L H Zhang Z F , et al . Reconstruction of seismic data with least squares inversion based on nonuniform fast Fourier transform
[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics , 2008 , 51 (1 ):235 -241 .
[本文引用: 1]
[3]
Naghizadeh M Sacchi M D . Beyond alias hierarchical scale curvelet interpolation of regularly and irregularly sampled seismic data
[J]. Geophysics , 2010 , 75 (6 ):WB189 -WB202 .
[本文引用: 1]
[4]
Gao J J Sacchi M D Chen X H . A fast reduced-rank interpolation method for prestack seismic volumes that depend on four spatial dimensions
[J]. Geophysics , 2013 , 78 (1 ):V21 -V30 .
[本文引用: 1]
[5]
Ma J W . Three-dimensional irregular seismic data reconstruction via low-rank matrix completion
[J]. Geophysics , 2013 , 78 (5 ):V181 -V192 .
[本文引用: 1]
[6]
蒋润 , 李振春 , 孙小东 . 人工智能地震数据重建方法现状分析
[J]. 地球物理学进展 , 2023 , 38 (5 ):2047 -2062 .
[本文引用: 1]
Jiang R Li Z C Sun X D . Recent research status of seismic data reconstruction by artificial intelligence methods
[J]. Progress in Geophysics , 2023 , 38 (5 ):2047 -2062 .
[本文引用: 1]
[7]
Yang P L Gao J H Chen W C . Curvelet-based POCS interpolation of nonuniformly sampled seismic records
[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics , 2012 , 79 :90 -99 .
[本文引用: 1]
[8]
Chen Y K Chen X H Wang Y F , et al . The interpolation of sparse geophysical data
[J]. Surveys in Geophysics , 2019 , 40 (1 ):73 -105 .
DOI:10.1007/s10712-018-9501-3
[本文引用: 1]
Geophysical data interpolation has attracted much attention in the past decades. While a variety of methods are well established for either regularly sampled or irregularly sampled multi-channel data, an effective method for interpolating extremely sparse data samples is still highly demanded. In this paper, we first review the state-of-the-art models for geophysical data interpolation, focusing specifically on the three main types of geophysical interpolation problems, i.e., for irregularly sampled data, regularly sampled data, and sparse geophysical data. We also review the theoretical implications for different interpolation models, i.e., the sparsity-based and the rank-based regularized interpolation approaches. Then, we address the challenge for interpolating highly incomplete low-dimensional data by developing a novel shaping regularization-based inversion algorithm. The interpolation can be formulated as an inverse problem. Due to the ill-posedness of the inversion problem, an effective regularization approach is very necessary. We develop a structural smoothness constraint for regularizing the inverse problem based on the shaping regularization framework. The shaping regularization framework offers a flexible way for constraining the model behavior. The proposed method can be easily applied to interpolate incomplete reflection seismic data, ground penetrating radar data, and earthquake data with large gaps and also to interpolate sparse well-log data for preparing high-fidelity initial model for subsequent full-waveform inversion.
[9]
Zwartjes P Gisolf A . Fourier reconstruction with sparse inversion
[J]. Geophysical Prospecting , 2007 , 55 (2 ):199 -221 .
[本文引用: 1]
[10]
郭刚明 , 时立彩 , 高生军 , 等 . 小波变换在地震资料处理中的应用效果分析
[J]. 石油物探 , 2003 , 42 (2 ):237 -239 ,270.
[本文引用: 1]
通过分析传统傅里叶变换、窗口傅里叶变换和小波变换的各自特点, 指出了传统傅里叶变换和窗口傅里叶变换的不足, 以及小波变换可对信号任意时刻的任何细节进行细致分析和精细处理的优势。利用小波变换对地震信号进行分频处理, 分别计算不同频段的数据体, 校正后再进行小波重建, 经过分频动校正和分频静校正, 来减少不同频率校正量存在的误差影响, 达到提高信号分辨率的目的。
Guo G M Shi L C Gao S J , et al . Application of wavelet transform in seismic data processing
[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petrole , 2003 , 42 (2 ):237 -239 ,270.
[本文引用: 1]
[11]
王本锋 , 陈小宏 , 李景叶 , 等 . POCS联合改进的Jitter采样理论曲波域地震数据重建
[J]. 石油地球物理勘探 , 2015 , 50 (1 ):20 -28 ,13 -14 .
[本文引用: 1]
Wang B F Chen X H Li J Y , et al . Seismic data reconstruction based on POCS and improved Jittered sampling in the curvelet domain
[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting , 2015 , 50 (1 ):20 -28 ,13 -14 .
[本文引用: 1]
[12]
张华 , 陈小宏 . 基于jitter采样和曲波变换的三维地震数据重建
[J]. 地球物理学报 , 2013 , 56 (5 ):1637 -1649 .
[本文引用: 3]
Zhang H Chen X H . Seismic data reconstruction based on jittered sampling and curvelet transform
[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics , 2013 , 56 (5 ):1637 -1649 .
[本文引用: 3]
[13]
Liu J C Chou Y X Zhu J J . Interpolating seismic data via the POCS method based on shearlet transform
[J]. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering , 2018 , 15 (3 ):852 -876 .
[本文引用: 1]
[14]
Kong D H Peng Z M . Seismic random noise attenuation using shearlet and total generalized variation
[J]. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering , 2015 , 12 (6 ):1024 -1035 .
[本文引用: 1]
[15]
Guo K H Kutyniok G Labate D . Sparse multidimensional representations using anisotropic dilation and shear operators
[J]. Wavelets and Splines , 2006 :189 -201 .
[本文引用: 1]
[16]
Tekalp A M Ozkan M K Sezan M I . High-resolution image reconstruction from lower-resolution image sequences and space-varying image restoration
[C]// [Proceedings] ICASSP-92:1992 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,Speech,and Signal Processing . March 23-26,1992 ,San Francisco,CA,USA.IEEE, 1992 :169 -172 .
[本文引用: 1]
[17]
Stark H Oskoui P . High-resolution image recovery from image-plane arrays,using convex projections
[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A,Optics and Image Science , 1989 , 6 (11 ):1715 -1726 .
[本文引用: 1]
[18]
Youla D C Webb H . Image restoration by the method of convex projections:Part 1 theory
[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging , 1982 , 1 (2 ):81 -94 .
PMID:18238261
[本文引用: 1]
A projection operator onto a closed convex set in Hilbert space is one of the few examples of a nonlinear map that can be defined in simple abstract terms. Moreover, it minimizes distance and is nonexpansive, and therefore shares two of the more important properties of ordinary linear orthogonal projections onto closed linear manifolds. In this paper, we exploit the properties of these operators to develop several iterative algorithms for image restoration from partial data which permit any number of nonlinear constraints of a certain type to be subsumed automatically. Their common conceptual basis is as follows. Every known property of an original image f is envisaged as restricting it to lie in a well-defined closed convex set. Thus, m such properties place f in the intersection E(0) = E(i) of the corresponding closed convex sets E(1),E(2),...EE(m). Given only the projection operators PE(i) onto the individual E(i)'s, i = 1 --> m, we restore f by recursive means. Clearly, in this approach, the realization of the P(i)'s in a Hilbert space setting is one of the major synthesis problems. Section I describes the geometrical significance of the three main theorems in considerable detail, and most of the underlying ideas are illustrated with the aid of simple diagrams. Section II presents rules for the numerical implementation of 11 specific projection operators which are found to occur frequently in many signal-processing applications, and the Appendix contains proofs of all the major results.
[19]
Ozkan M K Tekalp A M Sezan M I . POCS-based restoration of space-varying blurred images
[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing , 1994 , 3 (4 ):450 -454 .
PMID:18291942
[本文引用: 1]
We propose a new method for space-varying image restoration using the method of projection onto convex sets (POCS). The formulation allows the use of a different blurring function at each pixel of the image in a computationally efficient manner. We illustrate the performance of the proposed approach by comparing the new results with those of the ROMKF method on simulated images. We also present results on a real-life image with unknown space-varying out-of-focus blur.
[20]
Patti A J Sezan M I Murat Tekalp A . Superresolution video reconstruction with arbitrary sampling lattices and nonzero aperture time
[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing , 1997 , 6 (8 ):1064 -1076 .
PMID:18282997
[本文引用: 1]
Printing from an NTSC source and conversion of NTSC source material to high-definition television (HDTV) format are some of the applications that motivate superresolution (SR) image and video reconstruction from low-resolution (LR) and possibly blurred sources. Existing methods for SR image reconstruction are limited by the assumptions that the input LR images are sampled progressively, and that the aperture time of the camera is zero, thus ignoring the motion blur occurring during the aperture time. Because of the observed adverse effects of these assumptions for many common video sources, this paper proposes (i) a complete model of video acquisition with an arbitrary input sampling lattice and a nonzero aperture time, and (ii) an algorithm based on this model using the theory of projections onto convex sets to reconstruct SR still images or video from an LR time sequence of images. Experimental results with real video are provided, which clearly demonstrate that a significant increase in the image resolution can be achieved by taking the motion blurring into account especially when there exists large interframe motion.
[21]
Bregman L M . The method of successive projection for finding a common point of convex sets
[J]. Dokl.akad.nauk Sssr , 1965 , 6 (3 ):487 -490 .
[本文引用: 1]
[22]
Gao J J Chen X H Li J Y , et al . Irregular seismic data reconstruction based on exponential threshold model of POCS method
[J]. Applied Geophysics , 2010 , 7 (3 ):229 -238 .
[本文引用: 1]
[23]
Candès E Demanet L Donoho D , et al . Fast discrete curvelet transforms
[J]. Multiscale Modeling & Simulation , 2006 , 5 (3 ):861 -899 .
[本文引用: 1]
[24]
Candes E J Wakin M B . An introduction to compressive sampling
[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine , 2008 , 25 (2 ):21 -30 .
[本文引用: 1]
地震数据重建方法综述
1
2013
... 在野外数据采集过程中,受到地形、地貌、仪器故障等因素的限制,地震勘探数据在空间方向上常呈现不规则采样,导致地震波场信息不完整,从而出现空间假频现象,影响高分辨率地震勘探的准确性[1 -2 ] .此外,即使按照传统的奈奎斯特定理进行理想采样,但在后续的某些地震处理方法中,地震数据仍存在采样不足的情况,难以满足特定处理方法的要求,在这种情况,需要发展快速高精度叠前数据重建方法,重建出高密度地震数据,以减轻地震数据采样不足对后续处理方法的影响. ...
地震数据重建方法综述
1
2013
... 在野外数据采集过程中,受到地形、地貌、仪器故障等因素的限制,地震勘探数据在空间方向上常呈现不规则采样,导致地震波场信息不完整,从而出现空间假频现象,影响高分辨率地震勘探的准确性[1 -2 ] .此外,即使按照传统的奈奎斯特定理进行理想采样,但在后续的某些地震处理方法中,地震数据仍存在采样不足的情况,难以满足特定处理方法的要求,在这种情况,需要发展快速高精度叠前数据重建方法,重建出高密度地震数据,以减轻地震数据采样不足对后续处理方法的影响. ...
基于非均匀快速傅里叶变换的最小二乘反演地震数据重建
1
2008
... 在野外数据采集过程中,受到地形、地貌、仪器故障等因素的限制,地震勘探数据在空间方向上常呈现不规则采样,导致地震波场信息不完整,从而出现空间假频现象,影响高分辨率地震勘探的准确性[1 -2 ] .此外,即使按照传统的奈奎斯特定理进行理想采样,但在后续的某些地震处理方法中,地震数据仍存在采样不足的情况,难以满足特定处理方法的要求,在这种情况,需要发展快速高精度叠前数据重建方法,重建出高密度地震数据,以减轻地震数据采样不足对后续处理方法的影响. ...
基于非均匀快速傅里叶变换的最小二乘反演地震数据重建
1
2008
... 在野外数据采集过程中,受到地形、地貌、仪器故障等因素的限制,地震勘探数据在空间方向上常呈现不规则采样,导致地震波场信息不完整,从而出现空间假频现象,影响高分辨率地震勘探的准确性[1 -2 ] .此外,即使按照传统的奈奎斯特定理进行理想采样,但在后续的某些地震处理方法中,地震数据仍存在采样不足的情况,难以满足特定处理方法的要求,在这种情况,需要发展快速高精度叠前数据重建方法,重建出高密度地震数据,以减轻地震数据采样不足对后续处理方法的影响. ...
Beyond alias hierarchical scale curvelet interpolation of regularly and irregularly sampled seismic data
1
2010
... 目前主要存在5类地震数据重建方法.第一类是基于滤波器的方法,这类方法通过插值滤波来实现数据重建,但对于不均匀网格采样的数据,规则化处理可能导致较大误差.第二类是波场延拓方法[3 ] ,这类方法需要利用地下信息,但由于地下结构的先验信息通常不明确且计算量巨大,难以应用于实际工作中.第三类是快速降秩方法[4 -5 ] ,该类方法将插值问题转化为图像填充问题,速度快,参数简单,但在非均匀网格采样下有不规则缺失数据现象,在反假频能力方面也存在一定不足.第四类是稀疏变换的方法,该类方法将地震数据从时间域转换到变换域,利用变换域的信号特征进行插值;这一类方法无需先验地下信息,可以重建规则和不规则的缺失地震道,计算速度快,精度高.第五类是人工智能重建方法[6 ] ,根据地震数据本身的特征进行自我学习,从而恢复缺失道信息,如:有监督学习、无监督学习、自监督学习等. ...
A fast reduced-rank interpolation method for prestack seismic volumes that depend on four spatial dimensions
1
2013
... 目前主要存在5类地震数据重建方法.第一类是基于滤波器的方法,这类方法通过插值滤波来实现数据重建,但对于不均匀网格采样的数据,规则化处理可能导致较大误差.第二类是波场延拓方法[3 ] ,这类方法需要利用地下信息,但由于地下结构的先验信息通常不明确且计算量巨大,难以应用于实际工作中.第三类是快速降秩方法[4 -5 ] ,该类方法将插值问题转化为图像填充问题,速度快,参数简单,但在非均匀网格采样下有不规则缺失数据现象,在反假频能力方面也存在一定不足.第四类是稀疏变换的方法,该类方法将地震数据从时间域转换到变换域,利用变换域的信号特征进行插值;这一类方法无需先验地下信息,可以重建规则和不规则的缺失地震道,计算速度快,精度高.第五类是人工智能重建方法[6 ] ,根据地震数据本身的特征进行自我学习,从而恢复缺失道信息,如:有监督学习、无监督学习、自监督学习等. ...
Three-dimensional irregular seismic data reconstruction via low-rank matrix completion
1
2013
... 目前主要存在5类地震数据重建方法.第一类是基于滤波器的方法,这类方法通过插值滤波来实现数据重建,但对于不均匀网格采样的数据,规则化处理可能导致较大误差.第二类是波场延拓方法[3 ] ,这类方法需要利用地下信息,但由于地下结构的先验信息通常不明确且计算量巨大,难以应用于实际工作中.第三类是快速降秩方法[4 -5 ] ,该类方法将插值问题转化为图像填充问题,速度快,参数简单,但在非均匀网格采样下有不规则缺失数据现象,在反假频能力方面也存在一定不足.第四类是稀疏变换的方法,该类方法将地震数据从时间域转换到变换域,利用变换域的信号特征进行插值;这一类方法无需先验地下信息,可以重建规则和不规则的缺失地震道,计算速度快,精度高.第五类是人工智能重建方法[6 ] ,根据地震数据本身的特征进行自我学习,从而恢复缺失道信息,如:有监督学习、无监督学习、自监督学习等. ...
人工智能地震数据重建方法现状分析
1
2023
... 目前主要存在5类地震数据重建方法.第一类是基于滤波器的方法,这类方法通过插值滤波来实现数据重建,但对于不均匀网格采样的数据,规则化处理可能导致较大误差.第二类是波场延拓方法[3 ] ,这类方法需要利用地下信息,但由于地下结构的先验信息通常不明确且计算量巨大,难以应用于实际工作中.第三类是快速降秩方法[4 -5 ] ,该类方法将插值问题转化为图像填充问题,速度快,参数简单,但在非均匀网格采样下有不规则缺失数据现象,在反假频能力方面也存在一定不足.第四类是稀疏变换的方法,该类方法将地震数据从时间域转换到变换域,利用变换域的信号特征进行插值;这一类方法无需先验地下信息,可以重建规则和不规则的缺失地震道,计算速度快,精度高.第五类是人工智能重建方法[6 ] ,根据地震数据本身的特征进行自我学习,从而恢复缺失道信息,如:有监督学习、无监督学习、自监督学习等. ...
人工智能地震数据重建方法现状分析
1
2023
... 目前主要存在5类地震数据重建方法.第一类是基于滤波器的方法,这类方法通过插值滤波来实现数据重建,但对于不均匀网格采样的数据,规则化处理可能导致较大误差.第二类是波场延拓方法[3 ] ,这类方法需要利用地下信息,但由于地下结构的先验信息通常不明确且计算量巨大,难以应用于实际工作中.第三类是快速降秩方法[4 -5 ] ,该类方法将插值问题转化为图像填充问题,速度快,参数简单,但在非均匀网格采样下有不规则缺失数据现象,在反假频能力方面也存在一定不足.第四类是稀疏变换的方法,该类方法将地震数据从时间域转换到变换域,利用变换域的信号特征进行插值;这一类方法无需先验地下信息,可以重建规则和不规则的缺失地震道,计算速度快,精度高.第五类是人工智能重建方法[6 ] ,根据地震数据本身的特征进行自我学习,从而恢复缺失道信息,如:有监督学习、无监督学习、自监督学习等. ...
Curvelet-based POCS interpolation of nonuniformly sampled seismic records
1
2012
... 由于不规则采样数据产生的混叠噪声较少,因此重建不规则采样数据的难度低于重建规则采样数据的难度[7 ] .针对不规则数据的重建,稀疏促进重建是应用最为广泛的方法之一.压缩感知理论提供了一个很好的机会来解决地震数据重建问题,指出可以用低于奈奎斯特采样率的非自适应测量来处理信号,将地震数据重建问题转化为稀疏优化问题,利用稀疏变换来区分有用信号和缺失信号[8 ] .目前,对于稀疏变换的研究已取得了大量成果,如早期的傅里叶变换[9 ] 、小波变换[10 ] ,以及众多具有更好方向表示能力的类小波变换:Contourlet变换、Curvelet变换[11 -12 ] 、Shearlet变换等[13 -14 ] .Shearlet变换是一种与多尺度和多分辨率分析密切相关的多维函数逼近方法[15 ] ,该变换的基函数可以通过膨胀、剪切和平移构造在频域中逐层细分,从而使得其比小波变换更为稀疏.值得一提的是,该变换的分解方向数量和支撑基的规模没有明确限制.现如今Curvelet变换已被广泛应用于地震数据重建和去噪领域,但Shearlet变换在地震数据处理领域中尚未得到广泛应用. ...
The interpolation of sparse geophysical data
1
2019
... 由于不规则采样数据产生的混叠噪声较少,因此重建不规则采样数据的难度低于重建规则采样数据的难度[7 ] .针对不规则数据的重建,稀疏促进重建是应用最为广泛的方法之一.压缩感知理论提供了一个很好的机会来解决地震数据重建问题,指出可以用低于奈奎斯特采样率的非自适应测量来处理信号,将地震数据重建问题转化为稀疏优化问题,利用稀疏变换来区分有用信号和缺失信号[8 ] .目前,对于稀疏变换的研究已取得了大量成果,如早期的傅里叶变换[9 ] 、小波变换[10 ] ,以及众多具有更好方向表示能力的类小波变换:Contourlet变换、Curvelet变换[11 -12 ] 、Shearlet变换等[13 -14 ] .Shearlet变换是一种与多尺度和多分辨率分析密切相关的多维函数逼近方法[15 ] ,该变换的基函数可以通过膨胀、剪切和平移构造在频域中逐层细分,从而使得其比小波变换更为稀疏.值得一提的是,该变换的分解方向数量和支撑基的规模没有明确限制.现如今Curvelet变换已被广泛应用于地震数据重建和去噪领域,但Shearlet变换在地震数据处理领域中尚未得到广泛应用. ...
Fourier reconstruction with sparse inversion
1
2007
... 由于不规则采样数据产生的混叠噪声较少,因此重建不规则采样数据的难度低于重建规则采样数据的难度[7 ] .针对不规则数据的重建,稀疏促进重建是应用最为广泛的方法之一.压缩感知理论提供了一个很好的机会来解决地震数据重建问题,指出可以用低于奈奎斯特采样率的非自适应测量来处理信号,将地震数据重建问题转化为稀疏优化问题,利用稀疏变换来区分有用信号和缺失信号[8 ] .目前,对于稀疏变换的研究已取得了大量成果,如早期的傅里叶变换[9 ] 、小波变换[10 ] ,以及众多具有更好方向表示能力的类小波变换:Contourlet变换、Curvelet变换[11 -12 ] 、Shearlet变换等[13 -14 ] .Shearlet变换是一种与多尺度和多分辨率分析密切相关的多维函数逼近方法[15 ] ,该变换的基函数可以通过膨胀、剪切和平移构造在频域中逐层细分,从而使得其比小波变换更为稀疏.值得一提的是,该变换的分解方向数量和支撑基的规模没有明确限制.现如今Curvelet变换已被广泛应用于地震数据重建和去噪领域,但Shearlet变换在地震数据处理领域中尚未得到广泛应用. ...
小波变换在地震资料处理中的应用效果分析
1
2003
... 由于不规则采样数据产生的混叠噪声较少,因此重建不规则采样数据的难度低于重建规则采样数据的难度[7 ] .针对不规则数据的重建,稀疏促进重建是应用最为广泛的方法之一.压缩感知理论提供了一个很好的机会来解决地震数据重建问题,指出可以用低于奈奎斯特采样率的非自适应测量来处理信号,将地震数据重建问题转化为稀疏优化问题,利用稀疏变换来区分有用信号和缺失信号[8 ] .目前,对于稀疏变换的研究已取得了大量成果,如早期的傅里叶变换[9 ] 、小波变换[10 ] ,以及众多具有更好方向表示能力的类小波变换:Contourlet变换、Curvelet变换[11 -12 ] 、Shearlet变换等[13 -14 ] .Shearlet变换是一种与多尺度和多分辨率分析密切相关的多维函数逼近方法[15 ] ,该变换的基函数可以通过膨胀、剪切和平移构造在频域中逐层细分,从而使得其比小波变换更为稀疏.值得一提的是,该变换的分解方向数量和支撑基的规模没有明确限制.现如今Curvelet变换已被广泛应用于地震数据重建和去噪领域,但Shearlet变换在地震数据处理领域中尚未得到广泛应用. ...
小波变换在地震资料处理中的应用效果分析
1
2003
... 由于不规则采样数据产生的混叠噪声较少,因此重建不规则采样数据的难度低于重建规则采样数据的难度[7 ] .针对不规则数据的重建,稀疏促进重建是应用最为广泛的方法之一.压缩感知理论提供了一个很好的机会来解决地震数据重建问题,指出可以用低于奈奎斯特采样率的非自适应测量来处理信号,将地震数据重建问题转化为稀疏优化问题,利用稀疏变换来区分有用信号和缺失信号[8 ] .目前,对于稀疏变换的研究已取得了大量成果,如早期的傅里叶变换[9 ] 、小波变换[10 ] ,以及众多具有更好方向表示能力的类小波变换:Contourlet变换、Curvelet变换[11 -12 ] 、Shearlet变换等[13 -14 ] .Shearlet变换是一种与多尺度和多分辨率分析密切相关的多维函数逼近方法[15 ] ,该变换的基函数可以通过膨胀、剪切和平移构造在频域中逐层细分,从而使得其比小波变换更为稀疏.值得一提的是,该变换的分解方向数量和支撑基的规模没有明确限制.现如今Curvelet变换已被广泛应用于地震数据重建和去噪领域,但Shearlet变换在地震数据处理领域中尚未得到广泛应用. ...
POCS联合改进的Jitter采样理论曲波域地震数据重建
1
2015
... 由于不规则采样数据产生的混叠噪声较少,因此重建不规则采样数据的难度低于重建规则采样数据的难度[7 ] .针对不规则数据的重建,稀疏促进重建是应用最为广泛的方法之一.压缩感知理论提供了一个很好的机会来解决地震数据重建问题,指出可以用低于奈奎斯特采样率的非自适应测量来处理信号,将地震数据重建问题转化为稀疏优化问题,利用稀疏变换来区分有用信号和缺失信号[8 ] .目前,对于稀疏变换的研究已取得了大量成果,如早期的傅里叶变换[9 ] 、小波变换[10 ] ,以及众多具有更好方向表示能力的类小波变换:Contourlet变换、Curvelet变换[11 -12 ] 、Shearlet变换等[13 -14 ] .Shearlet变换是一种与多尺度和多分辨率分析密切相关的多维函数逼近方法[15 ] ,该变换的基函数可以通过膨胀、剪切和平移构造在频域中逐层细分,从而使得其比小波变换更为稀疏.值得一提的是,该变换的分解方向数量和支撑基的规模没有明确限制.现如今Curvelet变换已被广泛应用于地震数据重建和去噪领域,但Shearlet变换在地震数据处理领域中尚未得到广泛应用. ...
POCS联合改进的Jitter采样理论曲波域地震数据重建
1
2015
... 由于不规则采样数据产生的混叠噪声较少,因此重建不规则采样数据的难度低于重建规则采样数据的难度[7 ] .针对不规则数据的重建,稀疏促进重建是应用最为广泛的方法之一.压缩感知理论提供了一个很好的机会来解决地震数据重建问题,指出可以用低于奈奎斯特采样率的非自适应测量来处理信号,将地震数据重建问题转化为稀疏优化问题,利用稀疏变换来区分有用信号和缺失信号[8 ] .目前,对于稀疏变换的研究已取得了大量成果,如早期的傅里叶变换[9 ] 、小波变换[10 ] ,以及众多具有更好方向表示能力的类小波变换:Contourlet变换、Curvelet变换[11 -12 ] 、Shearlet变换等[13 -14 ] .Shearlet变换是一种与多尺度和多分辨率分析密切相关的多维函数逼近方法[15 ] ,该变换的基函数可以通过膨胀、剪切和平移构造在频域中逐层细分,从而使得其比小波变换更为稀疏.值得一提的是,该变换的分解方向数量和支撑基的规模没有明确限制.现如今Curvelet变换已被广泛应用于地震数据重建和去噪领域,但Shearlet变换在地震数据处理领域中尚未得到广泛应用. ...
基于jitter采样和曲波变换的三维地震数据重建
3
2013
... 由于不规则采样数据产生的混叠噪声较少,因此重建不规则采样数据的难度低于重建规则采样数据的难度[7 ] .针对不规则数据的重建,稀疏促进重建是应用最为广泛的方法之一.压缩感知理论提供了一个很好的机会来解决地震数据重建问题,指出可以用低于奈奎斯特采样率的非自适应测量来处理信号,将地震数据重建问题转化为稀疏优化问题,利用稀疏变换来区分有用信号和缺失信号[8 ] .目前,对于稀疏变换的研究已取得了大量成果,如早期的傅里叶变换[9 ] 、小波变换[10 ] ,以及众多具有更好方向表示能力的类小波变换:Contourlet变换、Curvelet变换[11 -12 ] 、Shearlet变换等[13 -14 ] .Shearlet变换是一种与多尺度和多分辨率分析密切相关的多维函数逼近方法[15 ] ,该变换的基函数可以通过膨胀、剪切和平移构造在频域中逐层细分,从而使得其比小波变换更为稀疏.值得一提的是,该变换的分解方向数量和支撑基的规模没有明确限制.现如今Curvelet变换已被广泛应用于地震数据重建和去噪领域,但Shearlet变换在地震数据处理领域中尚未得到广泛应用. ...
... 在所有数据插值算法中,凸集投影算法(POCS)因其高效率和高性能的优势而被广泛应用于图像重建和不规则数据绘制[16 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -21 ] .Gao等[22 ] 结合傅里叶变换与POCS算法对不规则地震数据进行插值.基于傅里叶变换重建能较好地处理近似线性同相轴的地震数据,但处理非线性同相轴的效果不佳.Curvelet变换[23 ] 有局部化识别能力,于是被用于地震数据重建.张华等[12 ] 基于Curvelet变换和POCS算法,通过对时间切片处理实现三维地震数据重建. ...
... 其中,ε 是几乎为零的最小阈值,其大小和数据中噪声的能量有关;λk 为第k 次迭代后的阈值,可以根据阈值模型选择λk .为了使计算速度更快,本文引用以指数形式 e - x [12 ] : ...
基于jitter采样和曲波变换的三维地震数据重建
3
2013
... 由于不规则采样数据产生的混叠噪声较少,因此重建不规则采样数据的难度低于重建规则采样数据的难度[7 ] .针对不规则数据的重建,稀疏促进重建是应用最为广泛的方法之一.压缩感知理论提供了一个很好的机会来解决地震数据重建问题,指出可以用低于奈奎斯特采样率的非自适应测量来处理信号,将地震数据重建问题转化为稀疏优化问题,利用稀疏变换来区分有用信号和缺失信号[8 ] .目前,对于稀疏变换的研究已取得了大量成果,如早期的傅里叶变换[9 ] 、小波变换[10 ] ,以及众多具有更好方向表示能力的类小波变换:Contourlet变换、Curvelet变换[11 -12 ] 、Shearlet变换等[13 -14 ] .Shearlet变换是一种与多尺度和多分辨率分析密切相关的多维函数逼近方法[15 ] ,该变换的基函数可以通过膨胀、剪切和平移构造在频域中逐层细分,从而使得其比小波变换更为稀疏.值得一提的是,该变换的分解方向数量和支撑基的规模没有明确限制.现如今Curvelet变换已被广泛应用于地震数据重建和去噪领域,但Shearlet变换在地震数据处理领域中尚未得到广泛应用. ...
... 在所有数据插值算法中,凸集投影算法(POCS)因其高效率和高性能的优势而被广泛应用于图像重建和不规则数据绘制[16 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -21 ] .Gao等[22 ] 结合傅里叶变换与POCS算法对不规则地震数据进行插值.基于傅里叶变换重建能较好地处理近似线性同相轴的地震数据,但处理非线性同相轴的效果不佳.Curvelet变换[23 ] 有局部化识别能力,于是被用于地震数据重建.张华等[12 ] 基于Curvelet变换和POCS算法,通过对时间切片处理实现三维地震数据重建. ...
... 其中,ε 是几乎为零的最小阈值,其大小和数据中噪声的能量有关;λk 为第k 次迭代后的阈值,可以根据阈值模型选择λk .为了使计算速度更快,本文引用以指数形式 e - x [12 ] : ...
Interpolating seismic data via the POCS method based on shearlet transform
1
2018
... 由于不规则采样数据产生的混叠噪声较少,因此重建不规则采样数据的难度低于重建规则采样数据的难度[7 ] .针对不规则数据的重建,稀疏促进重建是应用最为广泛的方法之一.压缩感知理论提供了一个很好的机会来解决地震数据重建问题,指出可以用低于奈奎斯特采样率的非自适应测量来处理信号,将地震数据重建问题转化为稀疏优化问题,利用稀疏变换来区分有用信号和缺失信号[8 ] .目前,对于稀疏变换的研究已取得了大量成果,如早期的傅里叶变换[9 ] 、小波变换[10 ] ,以及众多具有更好方向表示能力的类小波变换:Contourlet变换、Curvelet变换[11 -12 ] 、Shearlet变换等[13 -14 ] .Shearlet变换是一种与多尺度和多分辨率分析密切相关的多维函数逼近方法[15 ] ,该变换的基函数可以通过膨胀、剪切和平移构造在频域中逐层细分,从而使得其比小波变换更为稀疏.值得一提的是,该变换的分解方向数量和支撑基的规模没有明确限制.现如今Curvelet变换已被广泛应用于地震数据重建和去噪领域,但Shearlet变换在地震数据处理领域中尚未得到广泛应用. ...
Seismic random noise attenuation using shearlet and total generalized variation
1
2015
... 由于不规则采样数据产生的混叠噪声较少,因此重建不规则采样数据的难度低于重建规则采样数据的难度[7 ] .针对不规则数据的重建,稀疏促进重建是应用最为广泛的方法之一.压缩感知理论提供了一个很好的机会来解决地震数据重建问题,指出可以用低于奈奎斯特采样率的非自适应测量来处理信号,将地震数据重建问题转化为稀疏优化问题,利用稀疏变换来区分有用信号和缺失信号[8 ] .目前,对于稀疏变换的研究已取得了大量成果,如早期的傅里叶变换[9 ] 、小波变换[10 ] ,以及众多具有更好方向表示能力的类小波变换:Contourlet变换、Curvelet变换[11 -12 ] 、Shearlet变换等[13 -14 ] .Shearlet变换是一种与多尺度和多分辨率分析密切相关的多维函数逼近方法[15 ] ,该变换的基函数可以通过膨胀、剪切和平移构造在频域中逐层细分,从而使得其比小波变换更为稀疏.值得一提的是,该变换的分解方向数量和支撑基的规模没有明确限制.现如今Curvelet变换已被广泛应用于地震数据重建和去噪领域,但Shearlet变换在地震数据处理领域中尚未得到广泛应用. ...
Sparse multidimensional representations using anisotropic dilation and shear operators
1
2006
... 由于不规则采样数据产生的混叠噪声较少,因此重建不规则采样数据的难度低于重建规则采样数据的难度[7 ] .针对不规则数据的重建,稀疏促进重建是应用最为广泛的方法之一.压缩感知理论提供了一个很好的机会来解决地震数据重建问题,指出可以用低于奈奎斯特采样率的非自适应测量来处理信号,将地震数据重建问题转化为稀疏优化问题,利用稀疏变换来区分有用信号和缺失信号[8 ] .目前,对于稀疏变换的研究已取得了大量成果,如早期的傅里叶变换[9 ] 、小波变换[10 ] ,以及众多具有更好方向表示能力的类小波变换:Contourlet变换、Curvelet变换[11 -12 ] 、Shearlet变换等[13 -14 ] .Shearlet变换是一种与多尺度和多分辨率分析密切相关的多维函数逼近方法[15 ] ,该变换的基函数可以通过膨胀、剪切和平移构造在频域中逐层细分,从而使得其比小波变换更为稀疏.值得一提的是,该变换的分解方向数量和支撑基的规模没有明确限制.现如今Curvelet变换已被广泛应用于地震数据重建和去噪领域,但Shearlet变换在地震数据处理领域中尚未得到广泛应用. ...
High-resolution image reconstruction from lower-resolution image sequences and space-varying image restoration
1
1992
... 在所有数据插值算法中,凸集投影算法(POCS)因其高效率和高性能的优势而被广泛应用于图像重建和不规则数据绘制[16 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -21 ] .Gao等[22 ] 结合傅里叶变换与POCS算法对不规则地震数据进行插值.基于傅里叶变换重建能较好地处理近似线性同相轴的地震数据,但处理非线性同相轴的效果不佳.Curvelet变换[23 ] 有局部化识别能力,于是被用于地震数据重建.张华等[12 ] 基于Curvelet变换和POCS算法,通过对时间切片处理实现三维地震数据重建. ...
High-resolution image recovery from image-plane arrays,using convex projections
1
1989
... 在所有数据插值算法中,凸集投影算法(POCS)因其高效率和高性能的优势而被广泛应用于图像重建和不规则数据绘制[16 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -21 ] .Gao等[22 ] 结合傅里叶变换与POCS算法对不规则地震数据进行插值.基于傅里叶变换重建能较好地处理近似线性同相轴的地震数据,但处理非线性同相轴的效果不佳.Curvelet变换[23 ] 有局部化识别能力,于是被用于地震数据重建.张华等[12 ] 基于Curvelet变换和POCS算法,通过对时间切片处理实现三维地震数据重建. ...
Image restoration by the method of convex projections:Part 1 theory
1
1982
... 在所有数据插值算法中,凸集投影算法(POCS)因其高效率和高性能的优势而被广泛应用于图像重建和不规则数据绘制[16 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -21 ] .Gao等[22 ] 结合傅里叶变换与POCS算法对不规则地震数据进行插值.基于傅里叶变换重建能较好地处理近似线性同相轴的地震数据,但处理非线性同相轴的效果不佳.Curvelet变换[23 ] 有局部化识别能力,于是被用于地震数据重建.张华等[12 ] 基于Curvelet变换和POCS算法,通过对时间切片处理实现三维地震数据重建. ...
POCS-based restoration of space-varying blurred images
1
1994
... 在所有数据插值算法中,凸集投影算法(POCS)因其高效率和高性能的优势而被广泛应用于图像重建和不规则数据绘制[16 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -21 ] .Gao等[22 ] 结合傅里叶变换与POCS算法对不规则地震数据进行插值.基于傅里叶变换重建能较好地处理近似线性同相轴的地震数据,但处理非线性同相轴的效果不佳.Curvelet变换[23 ] 有局部化识别能力,于是被用于地震数据重建.张华等[12 ] 基于Curvelet变换和POCS算法,通过对时间切片处理实现三维地震数据重建. ...
Superresolution video reconstruction with arbitrary sampling lattices and nonzero aperture time
1
1997
... 在所有数据插值算法中,凸集投影算法(POCS)因其高效率和高性能的优势而被广泛应用于图像重建和不规则数据绘制[16 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -21 ] .Gao等[22 ] 结合傅里叶变换与POCS算法对不规则地震数据进行插值.基于傅里叶变换重建能较好地处理近似线性同相轴的地震数据,但处理非线性同相轴的效果不佳.Curvelet变换[23 ] 有局部化识别能力,于是被用于地震数据重建.张华等[12 ] 基于Curvelet变换和POCS算法,通过对时间切片处理实现三维地震数据重建. ...
The method of successive projection for finding a common point of convex sets
1
1965
... 在所有数据插值算法中,凸集投影算法(POCS)因其高效率和高性能的优势而被广泛应用于图像重建和不规则数据绘制[16 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -21 ] .Gao等[22 ] 结合傅里叶变换与POCS算法对不规则地震数据进行插值.基于傅里叶变换重建能较好地处理近似线性同相轴的地震数据,但处理非线性同相轴的效果不佳.Curvelet变换[23 ] 有局部化识别能力,于是被用于地震数据重建.张华等[12 ] 基于Curvelet变换和POCS算法,通过对时间切片处理实现三维地震数据重建. ...
Irregular seismic data reconstruction based on exponential threshold model of POCS method
1
2010
... 在所有数据插值算法中,凸集投影算法(POCS)因其高效率和高性能的优势而被广泛应用于图像重建和不规则数据绘制[16 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -21 ] .Gao等[22 ] 结合傅里叶变换与POCS算法对不规则地震数据进行插值.基于傅里叶变换重建能较好地处理近似线性同相轴的地震数据,但处理非线性同相轴的效果不佳.Curvelet变换[23 ] 有局部化识别能力,于是被用于地震数据重建.张华等[12 ] 基于Curvelet变换和POCS算法,通过对时间切片处理实现三维地震数据重建. ...
Fast discrete curvelet transforms
1
2006
... 在所有数据插值算法中,凸集投影算法(POCS)因其高效率和高性能的优势而被广泛应用于图像重建和不规则数据绘制[16 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -21 ] .Gao等[22 ] 结合傅里叶变换与POCS算法对不规则地震数据进行插值.基于傅里叶变换重建能较好地处理近似线性同相轴的地震数据,但处理非线性同相轴的效果不佳.Curvelet变换[23 ] 有局部化识别能力,于是被用于地震数据重建.张华等[12 ] 基于Curvelet变换和POCS算法,通过对时间切片处理实现三维地震数据重建. ...
An introduction to compressive sampling
1
2008
... 式中: x ~ [24 ] ,即可求得唯一解.地震勘探中,所使用的随机采样矩阵(数据缺失位置对应元素为0,采集的数据对应元素为1)能满足以上条件.这时,求解L 0 范数最小化问题等价于求解L 1 范数最小化问题,这样就转化为一个线性规划凸优化问题: ...