0 引言
关于该领域的研究,前人做了大量的探索[6⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-12],王香文等[6]利用不同反演方法得到的数据体进行比对解释,进行了薄层的高精度预测;张向君等[7]利用深度学习方法,通过优选惩罚因子及核函数参数,提高储层预测精度;刁新东等[8]基于地震正演分析,在层序约束下开展多属性分析,进行砂体反射特征研究;魏敏等[9]利用拓频地震资料进行波形指示反演,预测薄层的平面分布和厚度;赵宝银等[10]采用基于叠前地质统计学反演的低渗油藏优质储层综合预测方法,提高了储层预测精度;王光付等[11]利用宽频地震波形约束,通过优化相控非线性反演算法和流程,提高了薄砂层的预测精度。任宪军等[12]通过分频迭代反演,利用不同频段、尺度地震信息逐级传递,优化反演结果,提高储层预测精度。上述研究偏向于通过物探技术手段的改进来实现薄层的预测,无法满足轮南地区强非均质薄层高精度预测的需要。
在前人研究的基础上,本文提出了基于沉积相约束的叠前地质统计学反演方法。该方法以沉积岩石学、地震层序地层学为指导,从地震、地质两方面开展综合研究;在等时层序追踪解释结果的基础上,开展目标砂体的地震相特征分析,并结合井上实钻数据明确目标砂体的宏观沉积规律,以此为约束,构建岩相模型,约束叠前地质统计学反演过程;实际应用结果表明,该方法在提高非均质薄储层纵向分辨率的同时,大幅降低了横向上的不确定性,预测结果与井上实钻结果和生产动态数据吻合程度高,能够为开发井网优化调整和滚动评价方向提供指导。
1 非均质薄储层预测方法
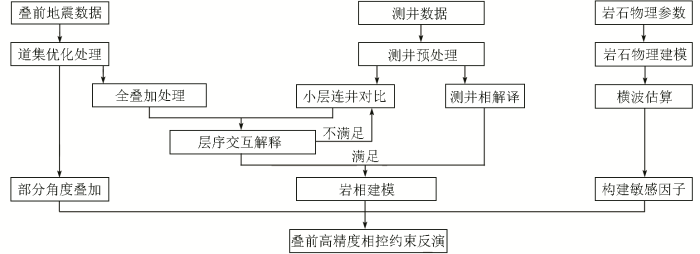
轮南三叠系属陆相三角洲沉积体系[13⇓⇓-16],轮南三叠系TII0薄砂层是近年来滚动研究的重点,储层埋深大(4 500~5 000 m),横向相变快,具有很强的非均质性,整体为“泥厚、砂薄”的沉积特征;空间连续性差;属于超薄储层,远超地震有效分辨率极限,常规方法难以精确落实储层展布特征。近年来研究区新采集的高密度三维地震资料,有效频带范围6~65 Hz,主频35 Hz,有效频带内,平均信噪比约为5,并且具有较为齐全的钻井、测井和生产数据资料,满足开展叠前相控约束反演的条件。根据研究区资料情况以及目的层地质特点制定了针对性的技术流程,在完成道集优化叠加处理、精细小层连井对比、地震地质层序交互解释、岩相建模以及敏感因子重构等关键环节的基础上,开展叠前相控约束反演,实现对陆相非均质薄储层的高精度预测(图1)。
图1
图1
陆相非均质薄储层预测技术流程
Fig.1
Technical flow chart of continental heterogeneous thin reservoir prediction
1.1 目的层段地震相解释
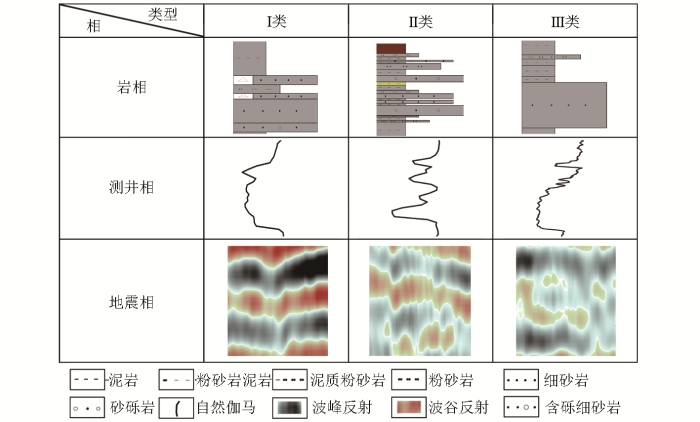
基于高密度地震资料,通过地震地质综合研究,利用岩相、测井相和地震相的差异,建立了三叠系TII0砂体的识别图版(图2),共有3种不同的砂体沉积类型:Ⅰ类砂体,TII油组块状主砂体发育,稳定泥岩隔层之上发育TII0砂体,GR曲线形态为箱型,地震剖面为连续中强反射特征,该类型TII0砂体沉积受控于TII主砂体空间展布;Ⅱ类砂体,TII主砂体向湖相变为席状砂沉积,砂地比明显降低,GR曲线形态以钟形和指状为主,地震为不连续弱反射特征;Ⅲ类砂体,整体呈“泥包砂”沉积特征,GR曲线为指状,地震为复波、亚连续、弱反射特征。
图2
图2
TII0小层砂体岩相—测井相—地震相识别图版
Fig.2
Lithofacies,logging facies and seismic facies identification chart of TII0 small layer sand body
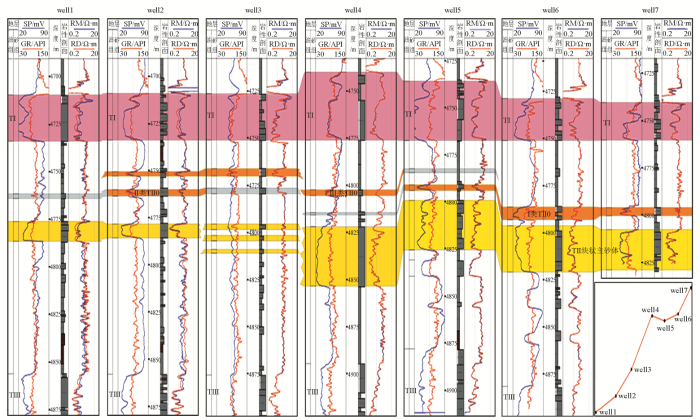
图3
图3
轮南三叠系TII0小层多期砂体叠置模式连井对比剖面
Fig. 3
Correlation profile of Wells connected by multi stage sand uperposition model of TII0 small layer in Lunnan Triassic system
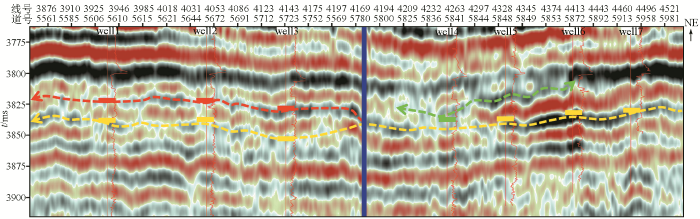
图4
图4
轮南三叠系TII0小层多期砂体叠置模式对应的地震解释方案
Fig.4
Seismic interpretation scheme corresponding to multi-stage sand body superposition model of TII0 small layer in Lunnan Triassic system
图5
图5
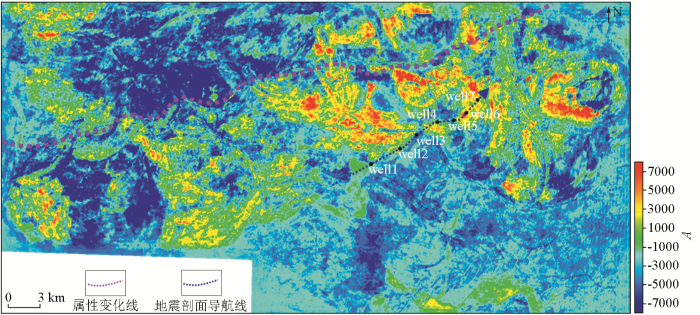
轮南三叠系TII0小层Ⅰ期砂体解释方案沿层地震均方根振幅属性平面
Fig.5
Seismic RMS amplitude attribute map of Triassic TII0 Phase Ⅰ sand body interpretation scheme in Lunnan System
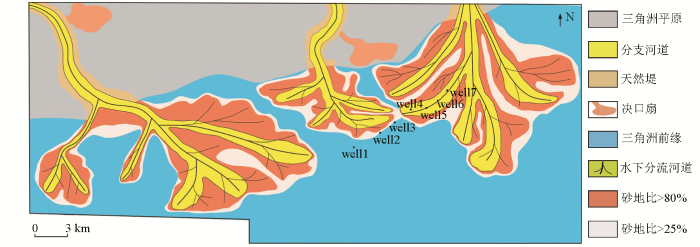
结合钻井认识,编制了Ⅰ期TII0砂体沉积相图,主体为三角洲沉积体系,缓坡之上为三角洲平原亚相,发育主河道和决口扇等沉积微相;缓坡之下为三角洲前缘亚相,发育水下分流河道、分流间湾、前缘席状砂等沉积微相(图6),沉积相带从宏观上反应了不同期砂体的分布规律,可作为砂体空间展布特征预测的约束条件,为精细落实储层发育细节提供指导。
图6
图6
轮南及周缘三叠系TII0小层沉积相平面
Fig.6
Sedimentary facies plan of TII0 small layer in the south and surrounding Triassic
1.2 叠前地质统计学反演
图7
图7
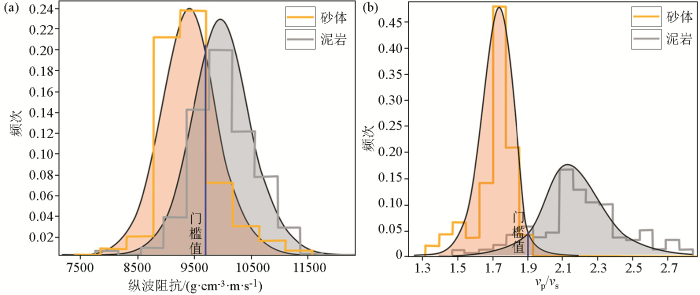
岩石物理特征分析
a—砂泥岩纵波阻抗统计直方图;b—砂泥岩纵横波速度比统计直方图
Fig.7
Analysis of rock physical characteristics
a—statistical histogram of P-wave impedance of sand-mudstone;b—statistical histogram of P-S velocity ratio of sand-mudstone
为此,本文采用叠前地质统计学反演方法[17],求取纵横波速度比。为提高反演方法的稳定性和反演结果的可靠性,在似然函数p(d|rp,rs,rd)的基础上,加入相控先验约束项pm(rp,rs,rd),得到最终后验概率密度分布函数:
式中:
式中:d为地震记录,rp、rs、rd分别为纵、横波阻抗反射系数和密度反射系数,下标m代表岩相,当m=1时,p1(rp)、p1(rs)、p1(rd)分别为砂岩背景中,纵横波速度及密度反射系数对应的概率密度分布函数;当m=0时,p0(rp)、p0(rs)、p0(rd)分别为泥岩背景中,纵、横波速度及密度反射系数对应的概率密度分布函数。岩相模型是以沉积相研究成果为约束,在层序框架内,分别设置各沉积相对应的砂岩和泥岩概率值,进行模拟得到。其中,岩相概率值可利用测井解释结果进行统计。在轮南地区,三叠系水下分流河道、河口坝、分流间湾微相发育砂岩的概率分别为96%、81%和27%,模拟得到的岩相模型见图8。
图8
为得到所估参数的后验概率分布p(rp,rs,rd|d),利用Metropolis-Hasting算法来生成马尔科夫链,进行迭代反演。
图9
图9
不同方法模拟结果对比
a,b,c—常规地质统计学不同随机路径模拟结果;d,e,f—相控地质统计学不同随机路径模拟结果
Fig.9
Comparison of simulation results of different methods
a,b,c—results of conventional geostatistical simulation of different random paths; d,e,f—simulation results of different random paths by phased geostatistics
2 实际应用效果分析
利用新的相控约束叠前地质统计学方法,其反演结果的分辨率和储层预测精度较高。
2.1 反演效果
图10
图10
不同方法反演剖面对比
a—常规反演剖面;b—叠前相控地质统计学反演剖面
Fig.10
Comparison of inversion profiles with different methods
a—conventional inversion profile;b—pre-stack phase controlled geostatistical inversion profile
2.2 反演评价
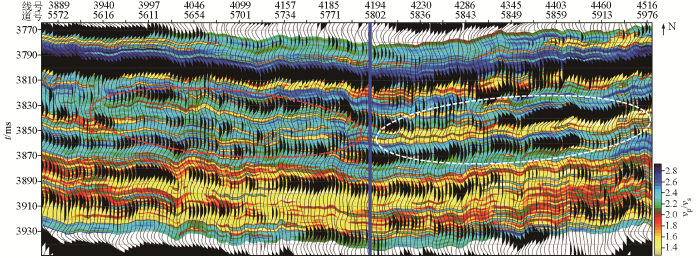
通过叠前相控地质统计学反演结果叠合地震波形进行分析(图11),蓝色竖线两侧存在明显差异,右侧白色椭圆范围内,地震为连续中强反射,反演结果显示该区域内块状主砂体发育,Ⅰ期TII0砂体位于主砂体之上,受主砂体沉积范围的控制;左侧红色椭圆范围内,地震为不连续弱反射,主砂体相变为席状砂特征,砂体发育细节与地震波形之间有良好的匹配关系。
图11
图11
叠前相控地质统计学反演结果与地震波形叠合剖面
Fig.11
Pre-stack phase controlled geostatistics inversion results and seismic waveform superimposed profile
图12
图12
叠前反演效果验证井分析
a—well8过井反演剖面;b—well8实测与反演提取曲线对比;c—well9过井反演剖面;d—well9实测与反演提取曲线对比
Fig.12
Pre-stack inversion effect verification well analysis diagram
a—well8 cross well inversion profile;b—well8 comparison of measured and inversion extraction curves; c—well9 cross well inversion profile; d—well9 comparison of measured and inversion extraction curves
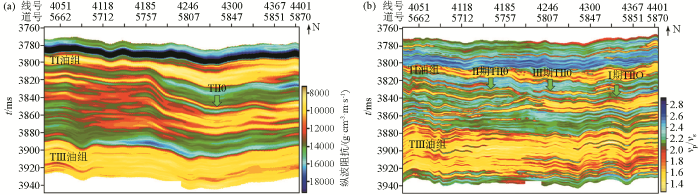
2.3 复杂井分析
图13
图13
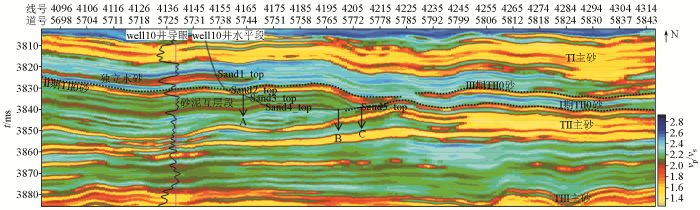
沿well10井轨迹方向叠前相控地质统计学反演剖面
Fig.13
Pre-stack phase-controlled geostatistical inversion profile along the direction of well10 trajectory
图14
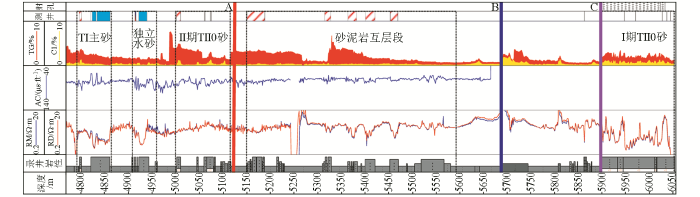
利用叠前反演数据进行分析发现,well10井导眼实钻(图13中黑色GR曲线)与反演结果吻合程度高,侧钻过程中,在独立水砂之下钻遇了Ⅱ期TII0砂体,但是,由于砂体相变快,厚度变化较大,工程上追踪钻进难度大,轨迹很快下探至砂泥岩互层段,在水平轨迹上的A点标识位置处进行了第二次轨迹调整,期间钻遇多套薄砂体,砂泥岩频繁交互,储层钻遇率低,在钻至B点标识位置处进行了第三次轨迹调整,开始向Ⅰ期TII0主砂体方向钻进,至C点标识位置处钻遇Ⅰ期TII0砂体,在TII0油藏主体区获得了油气,反演结果揭示了各套薄储层的空间展布特征和相互关系,与井上实钻结果吻合程度高,能够为后续开发井位部署和井网优化提供指导。
3 结论
1)以沉积相为约束,建立岩相概率体,并将其作为先验信息,约束叠前地质统计学反演过程,既可提高反演结果对储层的辨识能力及分辨率,又能降低砂体平面预测的多解性,适用于陆相非均质薄储层预测。
2)将叠前相控地质统计学反演应用于塔里木盆地轮南油田,实现了对轮南三叠系陆相非均质储层的精细表征,反演结果与井上实钻结果及生产动态相吻合,能够为开发井位部署和井网优化调整提供支撑,奠定了轮南三叠系岩性油藏高效开发的地质基础。
参考文献
塔里木盆地轮南低凸起构造特征及演化
[J].
Structure features and its evolution of Lunnan low uplift,the Tarim Basin
[J].
物理调整油气藏的类型与成藏机制研究——运用三维荧光定量研究塔里木盆地轮南三叠系油气藏调整机制
[J].
The research of types and formation mechanism of physical adjustment reservoirs:Applying the three-dimensional fluorescence quantitative to study on the adjustment mechanism of Triassic oil and gas reservoirs in the Lunnan area,Tarim Basin
[J].
塔里木盆地喜马拉雅晚期油气藏调整与改造
[J].
Adjustment and alteration of hydrocarbon reservoirs during the late Himalayan period,Tarim Basin,NW China
[J].
中国海相盆地的形成与演化
[J].
Formation and evolution of marine basins in China
[J].
塔北隆起轮南低凸起断裂构造特征与形成演化
[J].
DOI:10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2020.04.014
[本文引用: 1]

轮南低凸起是塔里木台盆区油气勘探的重点地区,发育一系列受控于断裂的缝洞型油气藏。目前对该区断裂研究多是针对某一区块的研究,亟需进行全区系统梳理。基于轮南低凸起大量三维地震资料,采用断裂构造解析方法,开展研究区断裂类型、构造特征与形成演化分析。结果表明:轮南低凸起发育逆冲断裂、走滑断裂、张扭断裂3类断裂。逆冲断裂分布在研究区西北部、中部轮南地区,既有沿层滑脱型,也有基底卷入型逆冲断裂。走滑断裂是研究区主要的断裂类型,剖面上表现为高陡直立、正花状、半花状3种构造样式,平面上发育线性延伸、棋盘格式、辫状构造、马尾状构造4种构造样式,沿走向具有明显的分段性。张扭断裂主要分布在上古生界、中-新生界,断裂规模较小,剖面上呈阶梯状、堑垒式或负花状,平面上大多沿深层走滑断裂、逆断裂呈雁列式、斜列式展布。利用断层上下构造样式差异、卷入断裂构造变形地层时代、生长指数3种方法分别判定走滑断裂、逆冲断裂、张扭断裂活动期次,揭示研究区断裂演化主要经历中加里东期、早海西期、晚海西—印支期、燕山—早喜马拉雅期4期演化,断裂演化具有一定的继承性。
Structural characteristics and evolution process of faults in the Lunnan low uplift,Tabei Uplift in the Tarim Basin,NW China
[J].
DOI:10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2020.04.014
[本文引用: 1]

The Lunnan low uplift of the Tabei Uplift is a hotspot for oil and gas exploration in the Tarim Basin, in which a series of fractured-vuggy oil and gas reservoirs controlled by faults are found. At present, the faults in the study area are mostly studied in a certain block, which needs to be systematically hackled in the whole study area. Based on a large number of three-dimensional seismic data, the method of fault structure analysis is adopted to analyze the types, structural features, and formation and evolution processes of faults in the study area. The results show that: There are three types of faults, such as reverse faults, strike-slip faults, and transtensional faults. The reverse faults are distributed in the northwest of the study area and central Lunnan areas. There are both detachment thrust faults and basement-involved thrust faults. Strike-slip fault is the main fault type in the study area. Three kinds of structural styles are developed on the profile, which are high-steep style, positive flower, and semi-flower. Four kinds of structural styles are developed on the plane, which are linear extension, chess board format, braided structure, and horsetail structure. The strike-slip fault has obvious segmentation along the strike. The transtensional faults are mainly small, which are distributed in the Mesozoic and Cenozoic. The transtensional faults are stepped, grabbed or negative flower on the profile. On the surface, most of them are arranged in the form of en echelon along the strike-slip faults or the reverse faults. Three methods are used to reveal the evolutionary history of strike-slip faults, reverse faults, and transtensional faults respectively, which are the differences of upper and lower fault structure styles, the age of strata deformed by faults and growth index. The faults have undergone 4 stages, which are the middle Caledonian, the early Hercynian, the late Hercynian-Indochina, and the Yanshan-early Himalayan. The fault evolution has certain inheritance.
地质统计学反演技术在薄储层预测中的应用
[J].
Application of geostatistical inversion to thin reservoir prediction
[J].
基于支持向量机的交互检验储层预测
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2018.04.014
[本文引用: 2]

基于统计学习理论的支持向量机(support vector machine,SVM)是有限样本情况下的机器学习方法,具有严格的理论基础,能较好地解决小样本、非线性、高维数和局部极小点等问题。在地震储层预测中,影响支持向量机应用效果的主要因素在于惩罚因子及核函数参数的设置,其值设置过小或过大,都会使估计函数的泛化能力变差,降低储层预测精度。为提高支持向量机在储层预测中的应用效果,将已知样本随机划分为若干组,依次选其中的一组作为检验样本,其余样本作为学习样本,交互检验惩罚因子及核函数参数对储层预测精度的影响;优选惩罚因子及核函数参数,提高支持向量机储层预测精度。通过实际资料应用,验证了方法的有效性。
Reservoir prediction through cross-validation based on support vector machine
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2018.04.014
[本文引用: 2]

<p> A support vector machine (SVM) based on statistical learning theory is a machine learning method for a limited sample size.It has a strict theoretical basis and could also solve problems related to small samples,nonlinearity,high dimensions,and local minima.In seismic reservoir prediction,the main factor affecting the excellent performance of the SVM is the setting of the penalty factor and the kernel function parameter.If the value is set too small or too large,the generalization capability of the estimation function will degrade and the accuracy of reservoir prediction will be reduced.Therefore,the known samples were randomly divided into several groups,and one of them was selected as the test sample,and the remaining samples were used as the learning sample,to cross-validate the effect of the penalty factor and the kernel function parameter on the accuracy of reservoir prediction.Next,optimizing the selected penalty factor and kernel function parameters was carried out to improve the accuracy of reservoir prediction based on SVM.An application example is given to verify the effectiveness of the method.</p>
三角洲水下分流河道砂体地震预测方法研究——以塔河油田三叠系河道砂岩为例
[J].
A study of seismic prediction method of underwater distributary channel sandbody in delta:A case study of the Tahe oilfied
[J].
波形指示反演在准中庄3工区薄储层预测中的应用
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2021.04.013
[本文引用: 2]

薄储层预测是油气勘探开发的难点,准噶尔盆地中部庄3工区三工河组砂岩属于典型的深埋储层,其中二二亚段砂体厚度薄、横向变化快,非均质性强。为解决薄储层预测问题,需要对薄储层地震资料进行拓频处理。采用混合相位子波反褶积技术,以信噪比谱为参考,测井曲线为监督,拓宽地震频带,提高主频,并利用拓频后的地震资料进行高分辨率波形指示反演,预测储层砂体平面展布情况和厚度。针对岩性横向变化快、非均质性强的难题,在砂体厚度预测的基础上进行孔隙度模拟,将砂体厚度预测结果和孔隙度预测结果叠合显示,明确储层物性变化规律。结果表明,波形指示反演得到的储层预测结果有效提高了纵、横向分辨率,成功预测了砂体边界、砂体厚度以及砂体物性,预测的砂体厚度与已知钻井结果吻合程度较高,同时也符合研究区的沉积规律,为钻探目标的优选以及开发评价提供了重要依据。
Application of a seismic motion inversion method for thin reservoir prediction in the Zhuang-3 block of the Central Junggar Basin
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2021.04.013
[本文引用: 2]

<p> Thin reservoir prediction is a prevalent issue that limits oil and gas exploration and development.The Sangonghe Formation in the Zhuang-3 block in the central Junggar Basin is a typical deep sandstone reservoir.The sand layers in the second sub-member are thin and characterized by high lateral spatial variability and pronounced heterogeneity.To better identify these thin reservoirs,the seismic data were first processed by expanding the frequency band through the mixed-phase wavelet deconvolution method.This method uses the signal-to-noise ratio spectrum as a reference and well data for validation to broaden the seismic frequency band and improve the main frequency.The expanded seismic data were then used for high-resolution seismic motion inversion to predict the plane and profile of the reservoir sand body.In view of the lateral variability and heterogeneity,porosity inversion was performed based on sand body thickness prediction.Then,the thickness prediction map and porosity inversion map were overlapped to clarify the characteristics of reservoir physical properties.The results showed that seismic motion inversion effectively improved the vertical and lateral resolutions of the reservoir.The boundary,thickness,and physical properties of the reservoir sand could be predicted satisfactorily.In fact,the prediction results were practically coincident with the logging data and with the sedimentary succession of the region.These results provide an important basis for the optimization of drilling targets and the evaluation of the production.</p>
相控叠前地质统计学反演方法在低渗油藏优质储层预测中的应用——以A区沙三段3亚段V油组为例
[J].
Application of facies-controlled prestack geostatistical inversion method in high quality reservoir prediction of low permeability reservoir:A case study of V oil formation of $\mathrm{Es}_{3}^{3}$ in block A
[J].
超薄砂岩储层预测方法研究与应用——以厄瓜多尔安第斯14和17区块为例
[J].
Predication methods of ultra-thin sandstone reservoirs and their application to blocks 14 and 17 in the Andes,Ecuador
[J].
地震分频迭代反演在薄层河道砂体预测中的应用
[J].
Application of seismic frequency-divided iterative inversion in the prediction of thinly laminated channel sand bodies
[J].
轮南油田2井区三叠系储集层精细描述
[J].
Fine characterization of Triassic Reservoir in wellblock No.2 in Lunnan oilfield
[J].
阿克库勒地区三叠系储集层成岩作用
[J].
Diagenesis of Triassic reservoir in Arkekule area,Tarim Basin
[J].
塔里木盆地轮南地区三叠系扇三角洲沉积与储集层研究
[J].
Study on Triassic fan delta sedimention and reservoir in Lunnan area,Tarim Basin
[J].
轮南地区三叠系辫状河三角洲沉积储层特征
[J].
Sedimentary characteristic and physical property of braid delta of Triassic in Lunnan region
[J].