0 引言
在我国滨海城市地下工程建设中,断层、孤石及其他不良地质体是影响工程进展的重要因素。经多年地质勘查研究,工作区域中的大型断裂构造往往已得到揭露,次生断裂和破碎带成为新一轮工程勘查的重点。而对于花岗岩长期风化过程中形成的孤石,由于其形状、尺寸、埋藏及分布较为随机,使之成为勘查工作的难点[1]。在这些问题揭露的过程中,钻探是最直观、可靠的方法,但受成本限制,钻孔间距极有可能远大于勘探目标尺寸,难以精确判定目标体的空间位置[2]。断层、孤石与围岩间存在物性差异,为地球物理方法提供了应用的前提。多年来,许多种地球物理方法已经被用于工程地质勘查,产生了较好的应用效果[3⇓⇓⇓-7]。每种地球物理方法对工作环境的适应性各异,为了实现精细探测目的,综合地球物理探测成为目前常用的技术手段[8⇓-10]。由于地表覆盖层电性对许多地球物理方法的探测效果可产生影响,因此覆盖层因素也成为方法选择的依据之一[11]。堤坝隐患探测和煤矿超前探测等理论研究表明,通过建立目标体模型,利用正反演手段获得探测目标体的直流电场特征,可以有效指导探测工作实践[12⇓-14]。为此,针对滨海城市施工环境与地质特点,本文聚焦高密度电阻率法,开展了直流电场三维有限差分数值模拟研究;针对建立的不同地电模型,研究了覆盖层和孤石因素对高密度电阻率探测效果的影响,为青岛市地铁5号线地质构造探测方法选择提供了依据。
1 基础理论
直流电场满足的微分方程为[15]:
式(1)可以写成
式中:U为电位;f为点电流源;I为电流强度;σ为介质电导率;δ为狄拉克函数;r和rA分别为场点和场源坐标。采用文献[15]中的模型剖分方法对目标体模型进行网格剖分,求解微分方程(式(2))获得模拟空间内任一点的电位,在数值模拟结果转化为视电阻率方面,高密度电阻率法采用对称四极公式。
2 数值模拟
图1
表1 模型参数
Table 1
| 序号 | 描述 | 参数 | 电阻率等参数数值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 第一层介质,素填土、粉质粘土、淤泥质粉质 粘土、含淤泥粉细砂、中细砂 | ρ1 | 10、50、100、200、500 W×m |
| h1 | 5、10、15、20 m | ||
| 2 | 第二层介质,强风化花岗岩、强风化煌斑岩 | ρ2 | 300 W×m |
| h2 | (30~h1)m | ||
| 3 | 第三层介质,中微风化花岗岩、中微风化煌斑岩 | ρ3 | 1000 W×m |
| h3 | 90 m | ||
| 4 | 断裂 | ρf1 | 50 W×m |
| 5 | 构造破碎带 | ρf2 | 100 W×m |
| 6 | 孤石 | ρr | 5000 W×m |
| h | 0、10、30、50 m | ||
| d | 10、20、30、40 m |
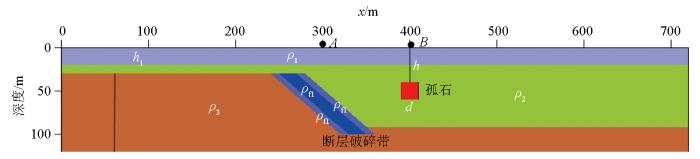
2.1 覆盖层电阻率变化
图2
图2
覆盖层电阻率变化高密度电阻率反演剖面
Fig.2
Inversed resistivity sections for different overburden resistivity
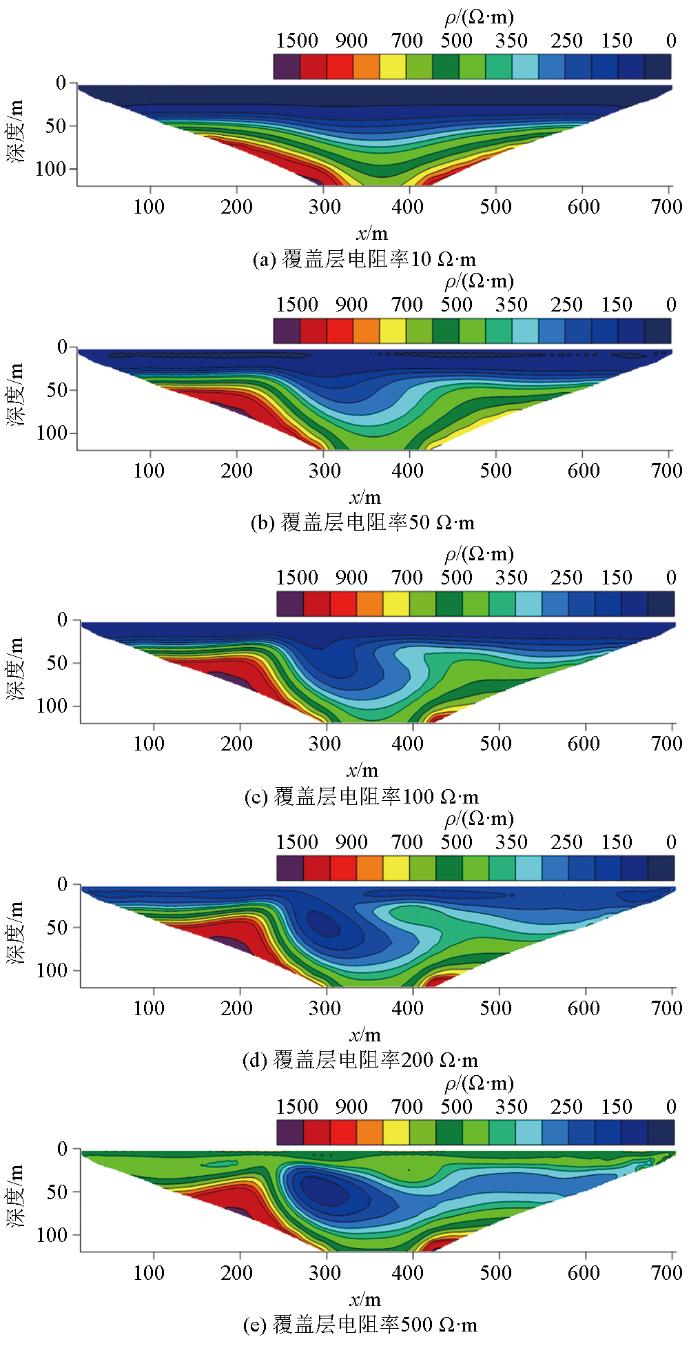
图3
图3
覆盖层电阻率不同时的电阻率曲线
Fig.3
Resistivity curves of different overburden resistivity
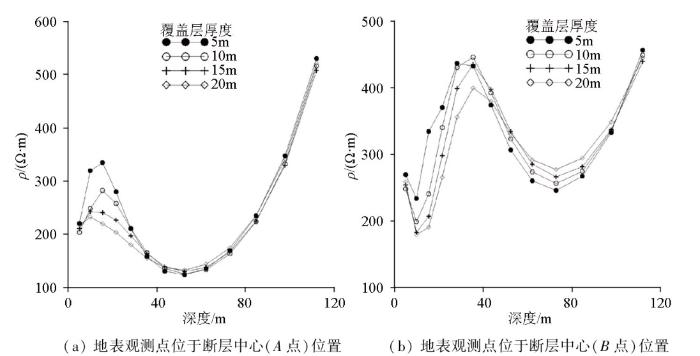
2.2 覆盖层厚度变化
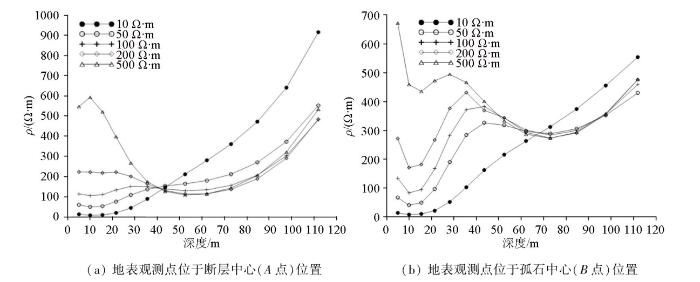
根据覆盖层厚度与目标体的相对大小,建立了4种覆盖层厚度模型。覆盖层厚度分别为5、10、15和20 m,覆盖层电阻率为200 W×m,其余参数保持不变。在完成正演计算后,采用Res2Dinv反演软件对数据进行反演,得到反演剖面如图4所示。从图中可以看出覆盖层厚度变大时,对断层破碎带的探测影响较小,当厚度达到20 m时断层和孤石仍然可以得到分辨,但孤石的电场响应强度稍微降低。
图4
图4
覆盖层厚度变化高密度电阻率反演剖面
Fig.4
Inversed resistivity sections for different overburden thicks
图5
图5
覆盖层厚度不同时的电阻率曲线
Fig.5
Resistivity curves with different thickness of covering layer
综合上述分析可以发现,覆盖层与探测目标的电阻率差异大小是决定覆盖层影响的主要因素。对于低阻断层破碎带,覆盖层电阻率越高,破碎带的响应越突出。覆盖层对孤石探测的主要影响因素为覆盖层电阻率,覆盖层厚度对探测结果影响相对较小。
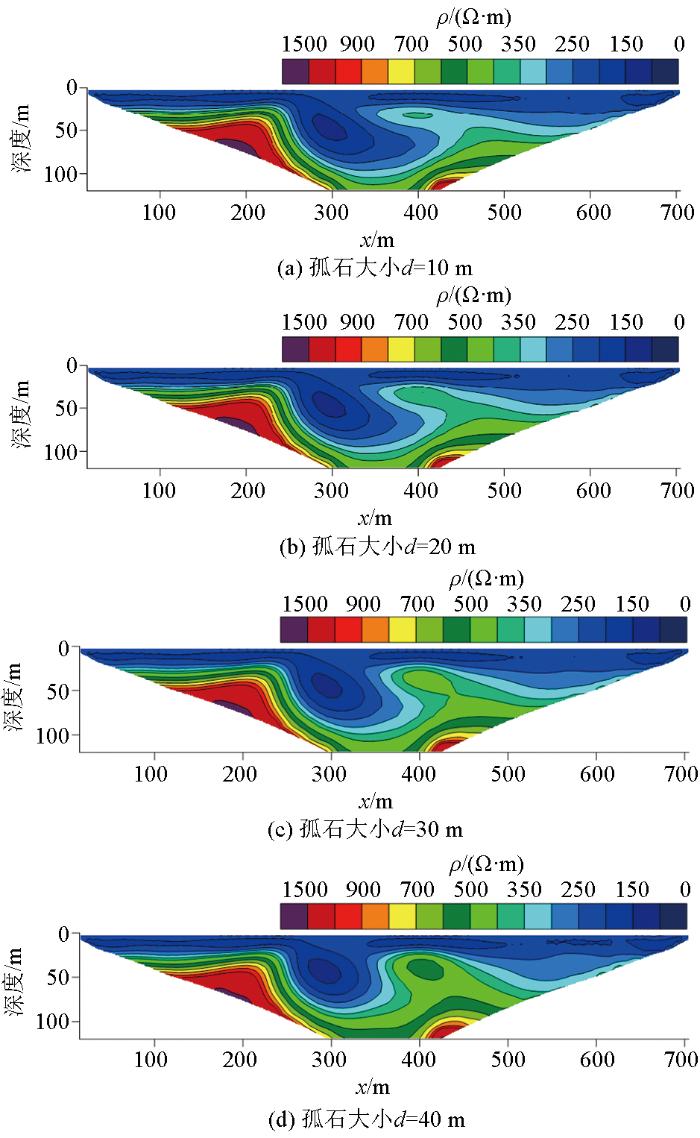
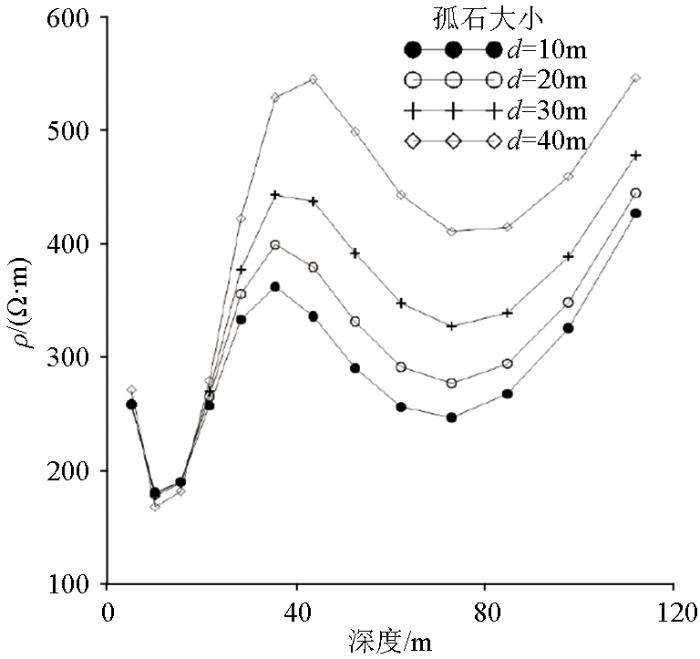
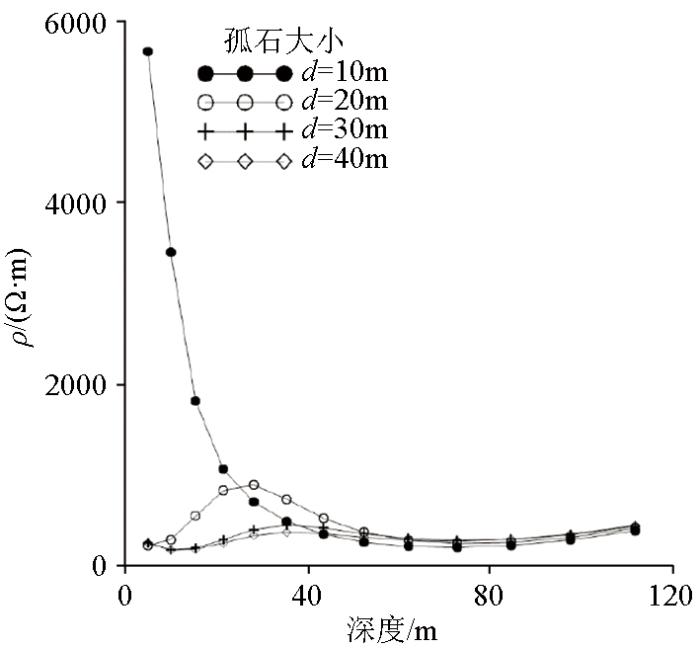
2.3 孤石尺寸变化
图6
图6
孤石尺寸不同时高密度电阻率反演剖面
Fig.6
Inversed resistivity sections for different boulder sizes
图7
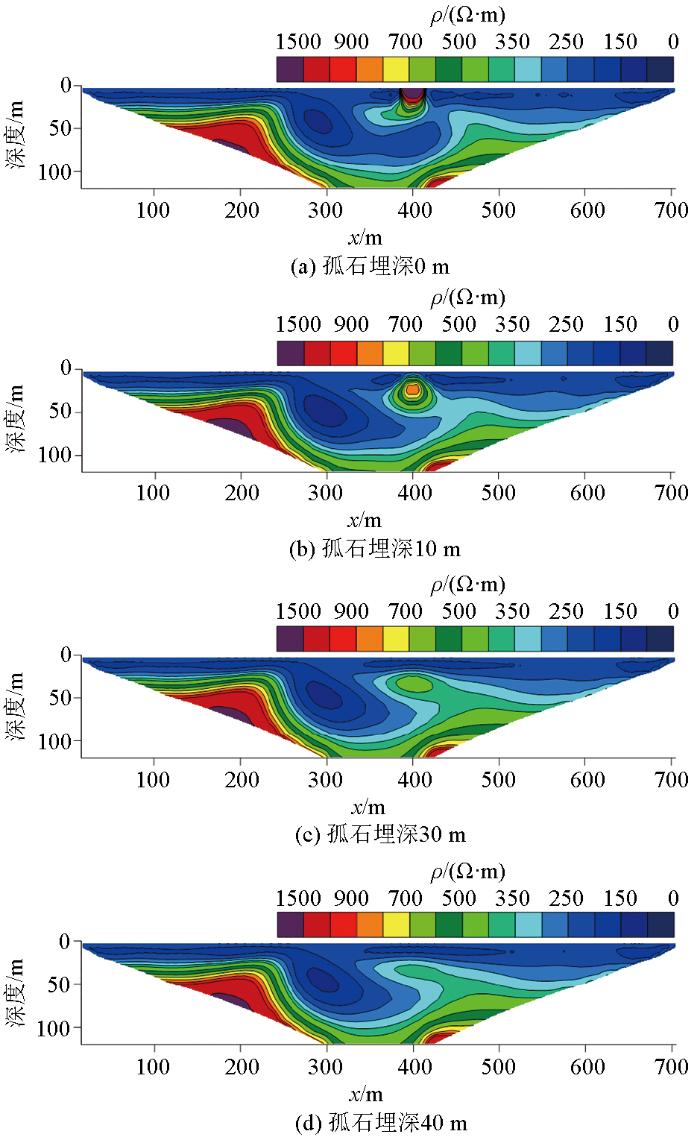
2.4 孤石埋深变化
图8
图8
孤石埋深不同时高密度电阻率反演剖面
Fig.8
Inversed resistivity sections for different boulder depth
图9
图9
孤石埋深不同时的电阻率曲线
Fig.9
Resistivity curves of boulders with different buried depths
3 应用实例
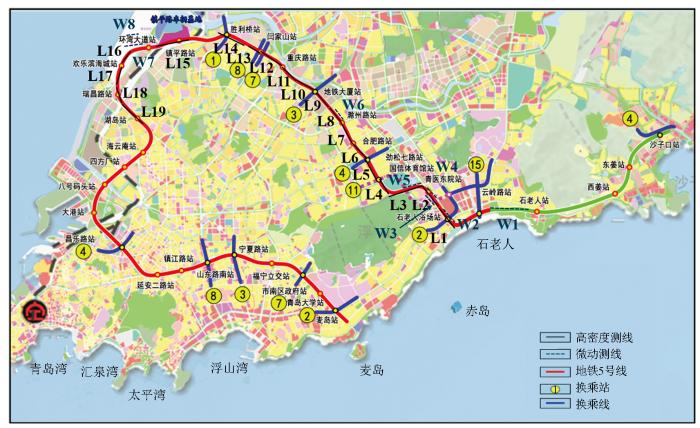
青岛市地铁5号线湖岛站至云岭路站主要位于胶州湾东岸李沧区,区内构造主要受沧口断裂、劈石山—浮山所断裂及王哥庄—山东头断裂影响。次生断裂、破碎带以及区内广泛分布的孤石对地铁施工产生重大影响,严重时会导致施工工作面喷涌、塌方。因此,精确查明区域基岩、断裂构造及其他不良地质体分布特征,对地铁工程勘查尤为重要。为了查明地铁线路下方地质情况,沿地铁线附近布设了19条高密度测线(图10),总长12 280 m。测量装置为温纳装置,电极间距10 m,电极数为1 247个。
图10
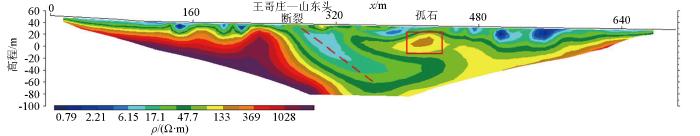
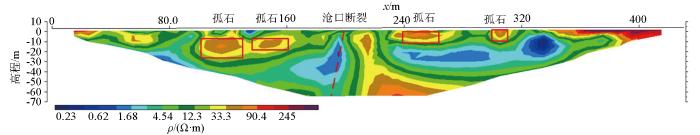
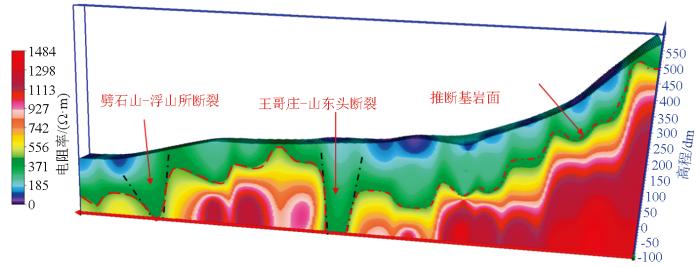
图11和图12分别为L5和L16线高密度电阻率反演剖面。L5和L16线长分别为720 m和440 m,沿线地形较平缓,地表为绿化带,接地条件较好。在L5线水平方向250~320 m处视电阻率等值线向下延伸,存在高阻与低阻的过渡带以及视电阻率较低异常带。根据已知资料,280~320 m处低阻异常带为王哥庄—山东头断裂南段,推测250~280 m处为构造破碎带。在水平方向410~430 m、高程20 m处存在一个孤立的高阻区,经验证为一个较大规模的孤石(图11)。根据测区的电阻率特征与断裂、孤石之间的对应关系,推测出L16线断裂和地质体情况如图12所示,该测线孤石较多,断裂构造主要为沧口断裂南端。L5线结果验证了本文高密度电阻率正演模拟的正确性。
图11
图12
图13
4 结论
针对我国滨海城市普遍存在的断层破碎带和孤石地质勘查问题,开展了覆盖层影响和目标体电性特征正反演研究,并以探测实例验证了研究成果的有效性。取得主要结论如下:
1)在复杂地质条件下开展高密度电阻率法勘探应用,根据工作区地质结构特点建立地电模型,采用正反演手段提前获得探测目标的电性特征和影响因素,可以为探测工作实施和资料处理解释提供帮助。
2)覆盖层电性和厚度对高密度电阻率法的探测结果产生直接影响,探测目标与覆盖层的电性差异是决定目标体响应强度和覆盖层影响大小的主要因素。
3)在中高阻覆盖条件下,浅部孤石的电性特征最为明显,容易分辨,埋藏较深的孤石电性响应减弱,但仍然能得到有效辨识。
参考文献
盾构地铁隧道孤石探测方法及研究展望
[J].
Detection method and research prospect of boulder detection in shield subway tunnel
[J].
二维微动剖面探测“孤石”:以深圳地铁7号线为例
[J].
Mapping spherically weathered “Boulders” using 2D microtremor profiling method:A case study along subway line 7 in Shenzhen
[J].
等值反磁通瞬变电磁法在轨道交通勘探中的应用
[J].
The application of opposing coils transient electromagnetic method to exploration of rail transit
[J].
温纳装置探测孤石深度影响因素及其数值模拟研究
[J].
Influencing factors and numerical simulation of wenner device for detecting boulder depth
[J].
球状孤石在探地雷达探测成果中的表现特征
[J].
The performance characteristic of spherical boulder in the georadar detection
[J].
基于跨孔电阻率CT的地铁盾构区间孤石探测方法及物理模型试验研究
[J].
Boulder detection method for metro shield zones based on cross-hole resistivity tomography and its physical model tests
[J].
微动探测:地层分层和隐伏断裂构造探测的新方法
[J].
Microtremor survey method:A new geophysical method for dividing strata and detecting the buried fault structures
[J].
微动探测技术在地层结构研究中的应用——以福州滨海新城核心区为例
[J].
Application of microtremor survey method in the study of stratum structure:A case study of Binhai New Town,Fuzhou City
[J].
综合物探方法在蚌埠隆起金多金属矿勘查中的应用——以怀远双沟勘查区为例
[J].
Application of comprehensive geophysical survey in Bengbu uplift gold polymetallic ore exploration:a case study of Huaiyuan Shuanggou exploration area
[J].
综合物探方法在地铁孤石探测中的应用研究
[J].
Application of integrated geophysical method to detection of boulder in subway shield zone
[J].
基于对偶加权后验误差估计的2.5维直流电阻率自适应有限元正演
[J].
2.5D direct current resistivity adaptive finite-element numerical modeling based on dual weighted posteriori error estimation
[J].
基于非结构网格三维有限元堤坝隐患时移特征分析
[J].
Time-lapse characteristics analysis of hidden dangers of three-dimensional finite element levees based on unstructured grids
[J].
直流电阻率法与工作面透明化
[J].
Direct current resistivity method and the transparency of mining face
[J].