0 引言
岩心观察和薄片鉴定是识别火山岩岩性最直观、准确的方法,受成本和取心技术的限制,无法获取连续的井下岩性资料[13]。对此诸多学者研究发现运用地层元素测井(ECS、LithScaner等)[14]和成像测井(FMI、EMI等)[15]可以较好地识别火山岩储层岩性,但这两种方法成本较高,没有大规模使用。常规测井资料可以间接反映地层岩性,且具有纵向分辨率高、数据连续、获取方便的特点,被广泛运用于岩性识别领域[16]。运用常规测井资料识别火山岩岩性的方法主要有常规交会图版法、多参数分步交会法和机器学习算法。常规交会图版法是通过选取对火山岩岩性敏感的测井曲线,制作交会图识别岩性[17],优点是操作简单、便捷,但识别精度低,适用性较差。多参数分步交会法是利用不同的测井参数组合识别火山岩岩性,识别精度相较于常规交会图版法有所提高[18],但对测井数据的深度挖掘能力较差。机器学习算法作为新方法技术被国内外学者广泛应用于岩性识别方面[19⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓-26],取得良好效果。支持向量机、深度信任网络DBN、GBDT、LD-AFSA是近几年广泛应用于火山岩岩性识别并取得良好效果的机器学习模型[27⇓⇓⇓⇓-32],不仅节省了大量人力资源,而且有效地提高了对储层岩性的识别精度[33]。遗憾的是这些机器学习模型需要调整的参数较多,且多采用单一学习算法。
为此,本文采用一种集成学习算法识别火山岩岩性。首先,总结分析滴西地区不同火山岩岩性的薄片和钻井资料;其次,通过二维、三维交会图优选对火山岩岩性敏感性较好的测井曲线作为特征参数;最后,通过网格搜索和正交试验法确定模型最优参数组合,提高模型识别精度,建立准噶尔盆地滴西井区石炭系火山岩岩性的智能识别模型。
1 研究区概况
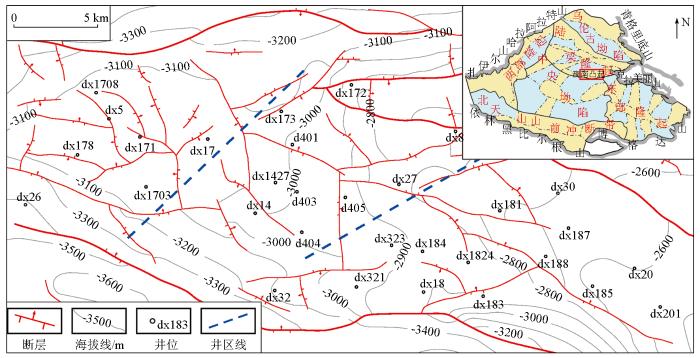
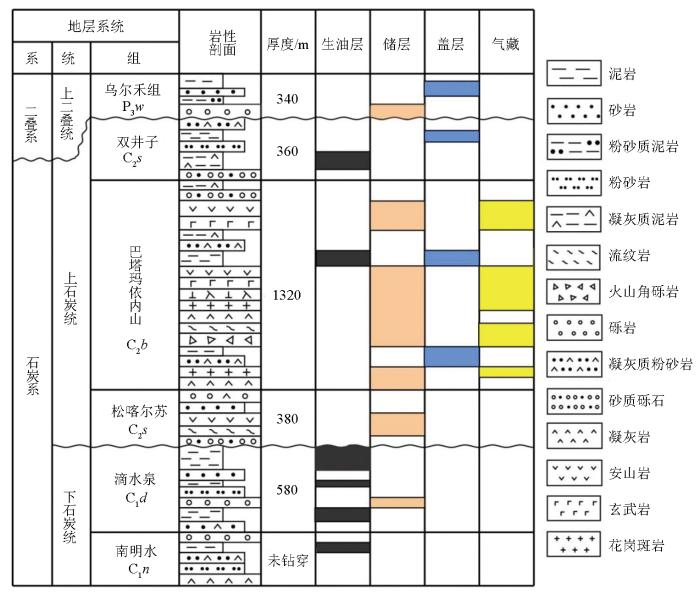
克拉美丽气田位于准噶尔盆地滴南凸起的西部、东边与克拉美丽山相连、东道海子以北、滴水泉凹陷以南[34⇓⇓-37],自东往西可分为3个井区,分别为滴西18井区、滴西14井区和滴西17井区(图1)。石炭系火山岩是研究区一个重要的勘探层系[38⇓-40],钻井揭示研究区石炭系自上而下依次划分为上石炭统双井子组、巴塔玛依内山组和松喀尔苏组及下石炭统滴水泉组和南明水组(图2),其中巴塔玛依内山组的火山岩是重要的储集层,不同井区的岩性迥异[41],滴西14井区主要发育以中—酸性爆发相为主的火山碎屑岩,主要有凝灰质角砾岩、安山质角砾岩和玄武质角砾岩;滴西17井区主要发育基性熔岩,常见安山岩、玄武岩及安山玄武质—玄武质熔岩;滴西18井区以酸性侵入岩为主,主要包括花岗斑岩、二长玢岩[42]。
图1
图2
图2
研究区岩性地层综合柱状图
Fig.2
Comprehensive column chart of lithology and stratigraphy in the study area
2 岩性划分
表1 不同岩性岩石薄片和钻井取心分布统计
Table 1
| 岩性标签 | 岩性 | 岩石 薄片数 | 占比/% | 钻井取心累 计长度/m | 占比/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 凝灰岩 | 185 | 31.04 | 74.8 | 17.72 |
| 2 | 二长玢岩 | 38 | 6.38 | 11.52 | 2.73 |
| 3 | 花岗斑岩 | 86 | 14.43 | 125 | 29.61 |
| 4 | 安山岩 | 93 | 15.60 | 68.96 | 16.34 |
| 5 | 玄武岩 | 95 | 15.94 | 97.83 | 23.18 |
| 6 | 霏细岩 | 7 | 1.17 | 3.98 | 0.94 |
| 7 | 流纹岩 | 17 | 2.85 | 0.89 | 0.21 |
| 8 | 霏细斑岩 | / | / | 6.4 | 1.52 |
| 0 | 火山角砾岩 | 61 | 10.23 | 23.13 | 5.48 |
| 10 | 其他 | 14 | 2.35 | 9.6 | 2.27 |
3 随机森林方法原理
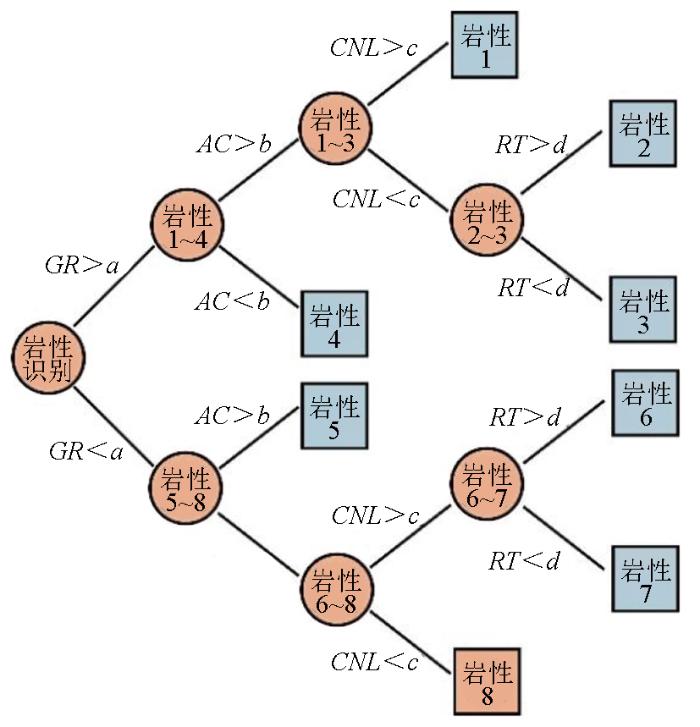
3.1 决策树算法
图3
步骤1:通过对数据收集建立岩性识别数据库,数据库中每一个样本都有一组测井参数(自然伽马、声波时差、补偿中子及地层真电阻率测井)和一种岩性(凝灰岩、二长玢岩、花岗斑岩、安山岩、玄武岩、霏细岩、流纹岩及霏细斑岩);
步骤2:通过对岩性识别数据库的学习,得到合理的测井参数和划分岩性的界限,每一次划分都可能直接得到最终结果;
步骤3:建立好的决策树模型能够对新出现的样本进行准确的岩性识别。
本次研究采用的决策树算法为ID3,该算法以信息熵Ent(D)为基础,以信息增益Gain(D,a)为准则对样本进行分类:
式中:D为样本数据集;Cm为第m类样本数量;Ent(D)为信息熵,Ent(D)越小,样本的复杂程度越低,越容易划分,Ent(D)越大,样本越复杂,越不易划分;Ent(D|a)为条件熵,Ent(D|a)越小,分类效果越好;Gain(D,a)为信息增益,Gain(D,a)越大,属性特征a对样本数据集划分的效果最好。
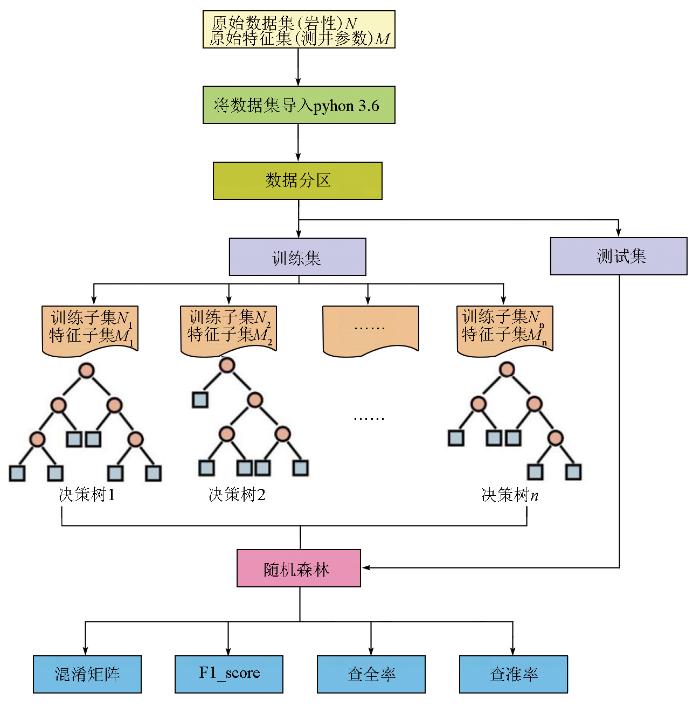
3.2 随机森林算法
图4
步骤1:将原始数据集N(岩性)和原始特征集M(测井参数)导入Python 3.6 并按一定比例随机划分为训练集和测试集,训练集是用于训练调整岩性识别模型,以提高模型对岩性样本的识别精度,测试集是用于验证评价已训练好的岩性识别模型;
步骤2:在训练集中随机抽取n个训练样本子集,每抽取得到一个训练样本子集Mn,将该训练样本子集Mn放回,再抽取下一个训练样本子集Mn+1,直至得到n个训练样本子集M;
步骤3:每棵决策树都是由训练样本子集经过单独训练得到,且它们之间互不相关;
步骤4:使用测试集验证评价已训练好的岩性识别模型,评价参数有F1_score、查准率及查全率。
4 实验结果与分析
4.1 数据预处理
4.1.1 数据准备
本次研究采用来自滴西井区14口井在3 500~4 200 m之间的常规测井资料和岩心数据,目的层为石炭系巴塔玛依内山组,共优选出1 977个样本数据。将样本数据随机划分出25%作为测试集,剩余75%作为训练集。使用1、2、3、4、5、6、7和8的岩性标签来分别对应凝灰岩、二长玢岩、花岗斑岩、安山岩、玄武岩、霏细岩、流纹岩和霏细斑岩8种主要岩性。表2展示了不同火山岩岩性的样本分布。
表2 数据集中不同岩性样本分布统计
Table 2
| 岩性标签 | 岩性 | 样本数 | 占比/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 凝灰岩 | 654 | 33.08 |
| 2 | 二长玢岩 | 160 | 8.09 |
| 3 | 花岗斑岩 | 539 | 27.26 |
| 4 | 安山岩 | 214 | 10.82 |
| 5 | 玄武岩 | 215 | 10.88 |
| 6 | 霏细岩 | 42 | 2.12 |
| 7 | 流纹岩 | 106 | 5.36 |
| 8 | 霏细斑岩 | 47 | 2.38 |
| / | 汇总 | 1977 | / |
4.1.2 数据标准化
式中:Xs为标准化后的数据;Xmin为测井参数最小值;Xmax为测井参数最大值;X为测井参数值。
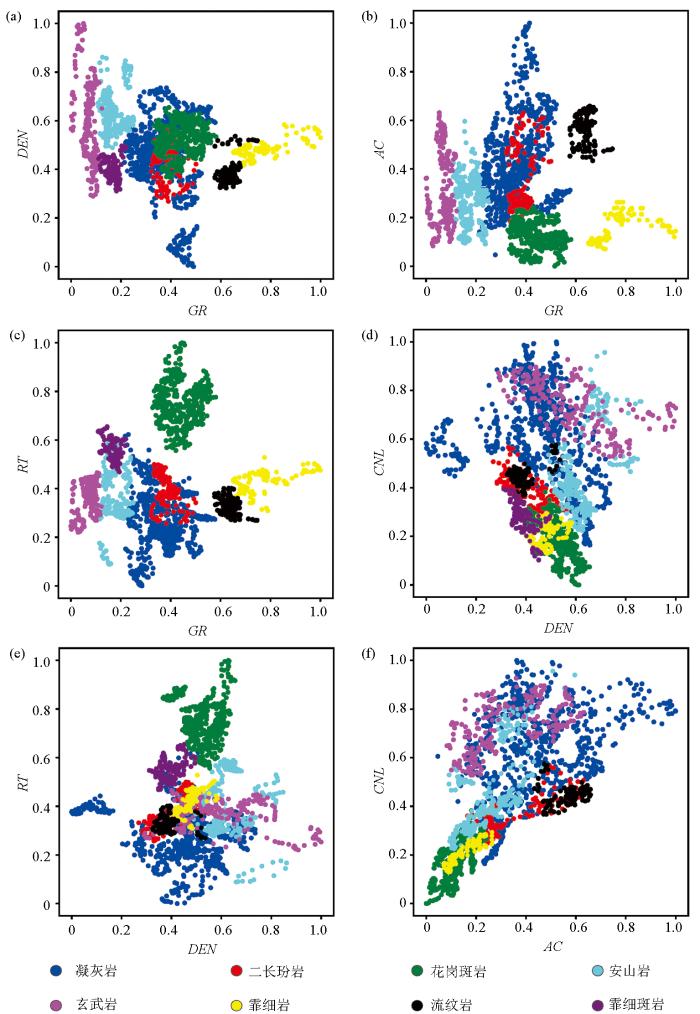
4.1.3 测井参数选取
图5
图5
不同测井参数二维岩性识别交会
Fig.5
Cross plot of 2D lithology identification with different logging parameters
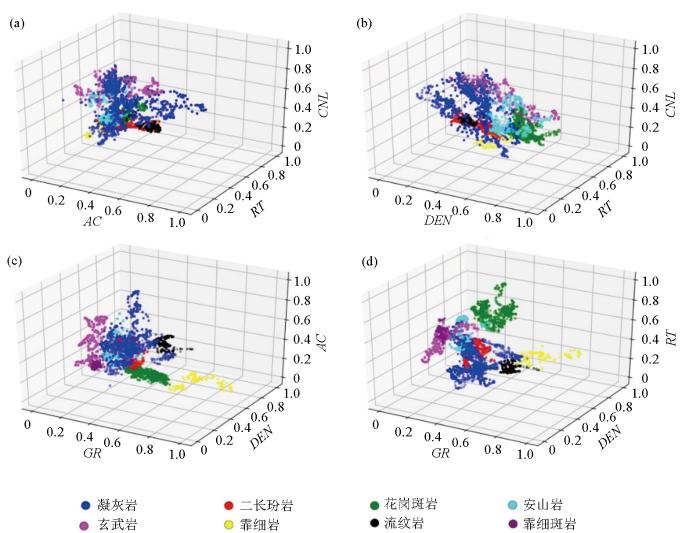
图6
图6
不同测井参数三维岩性识别交会
Fig.6
Intersection diagram of 3D lithology identification with different logging parameters
4.2 实验过程
4.2.1 模型参数调优
为了得到最佳的岩性识别模型预测能力,需要对模型进行参数优选,参数优选的不恰当致使模型难以拟合良好,从而降低模型的分类准确性。因此,选取恰当的模型参数,对岩性识别、模型的准确性起到至关重要的作用。本研究模型参数优选采取网格搜索法,但因样本数量较多,计算量大,所以将网格搜索法与正交试验法相结合以减少计算量,提高模型运算速度。
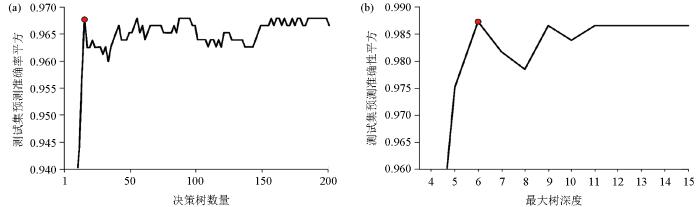
模型参数调优可以有效地提高随机森林模型的岩性识别准确性,随机森林模型主要是对最大树深度、迭代次数、叶子结点最小样本数,以及内部节点再划分所需最小样本数的4个参数进行调优。决策树的数量表示模型的迭代次数控制模型的复杂性,理论上决策树数量越多,模型就越复杂,模型准确性就越高,但实际的模型训练中,模型准确性随着决策树数量增大到一定程度则难以再发生较为明显的增长。本文对决策树数量优化的搜索范围为[2~230],步长为2。训练过程如图7a,当决策树数量达到14时,模型的准确性达到最好,继续增大决策树数量,模型的性能没有明显的增长。对于最大树深度,该参数取值过大会使模型过拟合,过小会导致模型欠拟合。本文对最大树深度优化的搜索范围为[3~15],步长为1。训练过程如图7b,当最大树深度达到6时,模型准确性达到最大,继续增大最大树深度,模型的性能没有明显的增长。如表3所示最优的最大树深度、迭代次数、叶子结点最小样本数,以及内部节点再划分所需最小样本数分别为6、14、1、4。
图7
表3 随机森林算法参数调优
Table 3
| 参数 | 搜索范围 | 步长 | 最优值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 迭代次数 | 2~230 | 2 | 14 |
| 内部节点再划分所需最小样本数 | 2~50 | 2 | 4 |
| 叶子结点最小样本数 | 1~50 | 1 | 1 |
| 最大树深度 | 3~15 | 1 | 6 |
4.2.2 评价标准
本研究针对随机森林模型所使用的评价标准为查准率、查全率和Fl_score。查准率为预测为a类岩性且预测正确的样本占所有预测为a类岩性的比例。查全率为预测为a类岩性且预测正确的样本占所有真正为a类岩性的比例。Fl_score为前两者的调和平均数。各评价指标的公式如下:
式中:A为查准率;Ra为预测为a类且预测正确的样本;Fa1为预测为a类但预测错误的样本;Rc为查全率;Fa2为预测为其他类但实际为a类的样本。
4.3 结果分析
4.3.1 单点预测结果分析
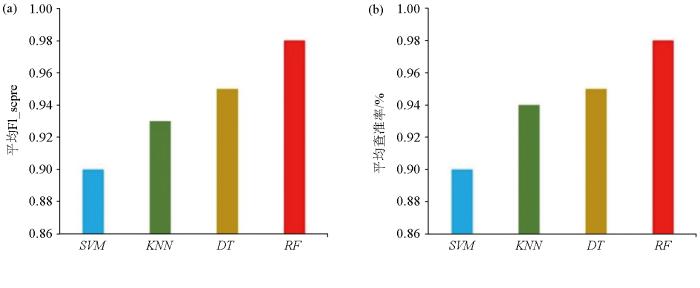
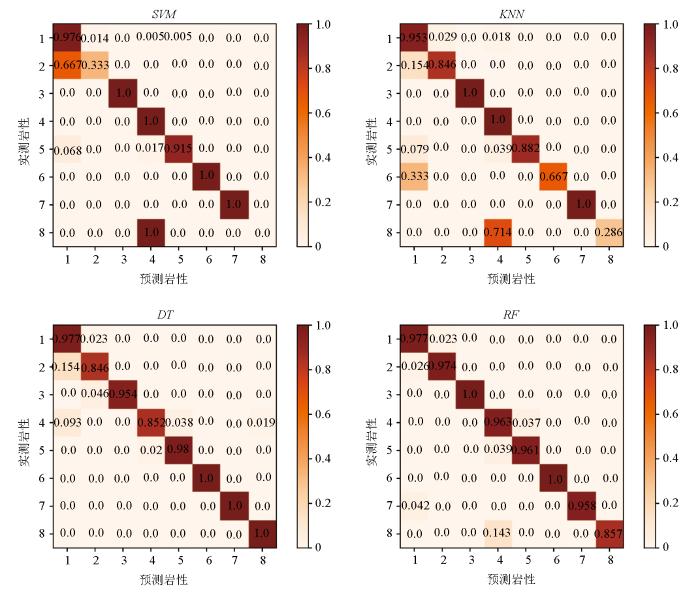
模型参数调优后,为了验证已经建立好的岩性识别模型分类效果,需要使用测试集。将随机森林(RF)与支持向量机(SVM)、决策树(DT)、K-近邻算法(KNN)比较来评价模型对岩性的识别性能(图8)。可以看出,SVM的岩性识别平均查准率和平均Fl_score都是最低的,为0.90;RF的平均查准率为98%,平均Fl_score为0.98,均高于SVM、KNN和DT。由此可知,RF的岩性识别性能要高于其他3个岩性识别模型。
图8
图8
不同模型岩性识别结果对比
Fig.8
Comparison of different lithology identification results
由图9和表4可知,不同模型对各岩性的岩性识别效果不同。RF是4种岩性识别模型性能最高的,其对凝灰岩、花岗斑岩、安山岩、玄武岩、霏细岩和流纹岩的Fl_score都在0.95以上,并且主要是将霏细斑岩错分为安山岩,流纹岩错分为凝灰岩;DT的岩性识别效果仅次于RF,其对凝灰岩、花岗斑岩、玄武岩、霏细岩和流纹岩的Fl_score都在0.95以上,且主要是将二长玢岩错分为凝灰岩,安山岩错分为凝灰岩和玄武岩;KNN对花岗斑岩和流纹岩的Fl_score为1,其余岩性的Fl_score都在0.95以下,且主要将霏细斑岩错分为安山岩,霏细岩和二长玢岩错分为凝灰岩;SVM的火山岩岩性识别能力最低,对二长玢岩和霏细斑岩的Fl_score都在0.5以下,且主要将霏细斑岩错分为安山岩,二长玢岩错分为凝灰岩。
图9
图9
不同岩性识别模型混淆矩阵
Fig.9
Comparison of confusion matrix for different lithology identification models
表4 不同模型的岩性识别Fl_score
Table 4
| 岩性标签 | 岩性 | SVM | KNN | DT | RF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 凝灰岩 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.98 |
| 2 | 二长玢岩 | 0.48 | 0.86 | 0.80 | 0.94 |
| 3 | 花岗斑岩 | 1 | 1 | 0.98 | 1 |
| 4 | 安山岩 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.95 |
| 5 | 玄武岩 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.96 |
| 6 | 霏细岩 | 1 | 0.80 | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | 流纹岩 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.98 |
| 8 | 霏细斑岩 | 0 | 0.44 | 0.93 | 0.92 |
4.3.2 单井连续预测评价
表5 不同井随机森林模型的岩性识别结果
Table 5
| 井号 | 岩性识别长度 /m | 岩石薄片 | 钻井取心 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 识别正确/块 | 识别错误/块 | 准确性/% | 识别正确/m | 识别错误/m | 准确性/% | ||
| dx182 | 400 | 41 | 22 | 65.08 | 7.18 | 3.5 | 67.23 |
| dx183 | 270 | 17 | 1 | 94.44 | 12.56 | 5.12 | 71.04 |
| dx402 | 80 | 8 | 2 | 80.00 | 16.93 | - | 100.00 |
| dx17 | 20 | 9 | 1 | 90.00 | 8.7 | - | 100.00 |
| dx172 | 100 | 17 | 2 | 89.47 | 7.48 | - | 100.00 |
| 统计 | 870 | 92 | 28 | 76.67 | 52.85 | 8.62 | 85.98 |
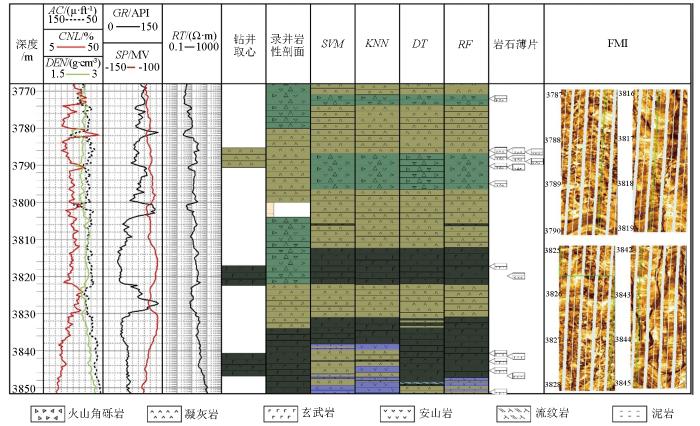
图10为dx402井的实际岩性识别结果。可以看出RF、DT、KNN、SVM算法都能较好地识别火山岩岩性,且描述精度明显高于录井岩性,但随机森林岩性识别模型的识别准确性更高、稳定性更好,在一定程度上提高了火山岩岩性识别效果。
图10
图10
dx402井不同火山岩岩性识别模型分类结果对比
Fig.10
Comparison of classification results from different volcanic rock lithology identification models for well dx402
5 结论
本文通过结合钻井取心、岩石薄片确定了研究区主要发育的岩性。基于常规测井资料建立二维、三维交会图版,优选对研究区火山岩敏感性较高的测井曲线。进一步在网格搜索和正交试验法优化模型参数组合的基础上,建立了研究区火山岩岩性的智能识别模型,并识别了研究区火山岩储层岩性,取得了良好应用效果,并得到以下结论:
1)准噶尔盆地滴西地区石炭系火山岩储层主要发育8种岩性,分别为凝灰岩、二长玢岩、花岗斑岩、安山岩、玄武岩、霏细岩、流纹岩和霏细斑岩。
2)自然伽马、声波时差、补偿中子和地层电阻率曲线,对准噶尔盆地滴西地区石炭系火山岩具有良好的检测能力。
3)网格搜索和正交试验法能够很大程度上提高模型参数调优的效率。实例结果表明:随机森林模型能够很好地识别研究区火山岩储层岩性,其识别准确性要高于决策树、支持向量机和KNN算法。
参考文献
基于岩性分类的火山岩储层流体识别方法——以克拉美丽气田石炭系火山岩为例
[J].
Study on fluid identification method of volcanic reservoir based on lithology classification:A case study of carboniferous volcanic rocks in kelameigasfield
[J].
裂缝充填矿物和蚀变晕对火山岩储集层流体作用的指示——以克拉美丽气田滴西地区为例
[J].
Fracture fillings and alteration halo in volcanic reservoirs as indicator of fluid activities in the dixi area in the kelameili gas field,Junggar Basin,northwestern China
[J].
火山岩地震储层学
[J].
Volcanic seismic reservoir
[J].
Mixing ratios quantitative assessment of source-mixed gas reservoirs by carbon isotope analysis in Dinan Uplift,Junggar Basin,China
[J].
Quantitative characterization of fracture-pore distribution and effects on production capacity of weathered volcanic crust reservoirs:Insights from volcanic gas reservoirs of the Dixi Area,Junggar Basin,Western China
[J].
火成岩油气储层特征及形成浅析
[J].
Analysis on features and formation of igneous reservoirs
[J].
Effects of weathering and fracturing on the physical properties of different types of volcanic rock:Implications for oil reservoirs of the Zhongguai relief,Junggar Basin,NW China
[J].
A study on water saturation predictions in igneous reservoirs based on the relationship between the transverse relaxation time and the resistivity index
[J].
Lithology identification of igneous rocks based on XGboost and conventional logging curves,a case study of the eastern depression of Liaohe Basin
[J].
Probabilistic logging lithology characterization with random forest probability estimation
[J].
A major discovery in Permian volcanic rock gas reservoir exploration in the Sichuan Basin and its implications
[J].
CT-based 3D pore-fracture network analysis of volcanic reservoirs of Lower Cretaceous Yingcheng Formation in southern Songliao Basin,China:Impact on natural gas migration
[J].
王府断陷火石岭组火山岩岩性及岩相识别
[J].
Identification of volcanics reservoir lithology and lithofacies in Huoshiling Formation of Wangfu fault depression
[J].
基于元素俘获谱测井计算火山岩储集层孔隙度的方法
[J].
Method for calculation of volcanic reservoir porosity based on ECS log
[J].
速度优化与建模技术在德惠断陷火山岩成像中的应用
[J].
Application of velocity optimization and modeling technology in volcanic rock imaging in Dehui fault depression
[J].
基于常规测井资料的火山岩岩性识别方法研究——以渤海海域中生界为例
[J].
Study on volcanic lithology identification methods based on the data of conventional well logging data:A case from Mesozoic volcanic rocks in Bohai Bay Area
[J].
准噶尔盆地西泉地区石炭系火山岩岩性测井识别
[J].
Lithology identification of carboniferous volcanic rock with logging data in xiquan area,Junggar Basin
[J].
基于常规测井的火成岩岩性识别方法——以准噶尔盆地西北缘红车断裂带石炭系火成岩储层为例
[J].
Lithology identification method of igneous rock based on conventional logging—Takingcarboniferous igneous rock reservoir of Hongche fault zone in northwest margin of Junggar Basin as an example
[J].
Methods for identifying complex lithologies from log data based on machine learning
[J].
地震储层学在准噶尔盆地火山岩油气勘探中的应用——以乌夏地区为例
[J].
Application of seismic reservoir to volcanic reservoir exploration in Wuxia Area of Junggar Basin
[J].
Feature-depth smoothness based semi-supervised weighted extreme learning machine for lithology identification
[J].
Log facies identification in carbonate reservoirs using multiclass semi-supervised learning strategy
[J].
A framework of active learning and semi-supervised learning for lithology identification based on improved naive Bayes
[J].
Prediction of reservoir quality using well logs and seismic attributes analysis with an artificial neural network:A case study from Farrud Reservoir,Al-Ghani Field,Libya
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.jappgeo.2018.09.013
[本文引用: 1]

This paper presents an innovative technique that aims to predict the quality of a petroleum reservoir using Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) analysis of seismic, well logs and core data. A supervised Probabilistic Neural Network (PNN) was deployed to predict several reservoir properties, one at a time, through training and validation of the PNN to determine the seismic attributes that best fit a measured property in the well logs. The validated PPN models accurately converted the available 3D seismic data into shale volume, porosity, permeability and water saturation cubes. In addition, these predicted reservoir properties were integrated to define various reservoir grades using K-means Clustering algorithm of unsupervised classification ANN. This technique is applied to Al-Ghani Field and four grades of reservoir quality were classified as very good, good, bad, and very bad and their spatial distributions were displayed. The highest reservoir grade is characterized by good porosity and permeability and significantly low water saturation. Such information is highly valuable for optimum reservoir management and well placement. This not only maximizes reservoir profitability through production schemes, but also minimizes uncertainties in drilling, production, injection, and modeling processes. In addition, adopting the proposed methodology would decrease costs in well logging programs and improve the sweeping efficiency of water flooding operations. (C) 2018 Elsevier B.V.
Key factors controlling deep Carboniferous volcanic reservoirs in the east slope of Mahu Sag,Junggar Basin,NW China
[J].
Machine learning approaches for petrographic classification of carbonate-siliciclastic rocks using well logs and textural information
[J].
Research and application of logging lithology identification for igneous reservoirs based on deep learning
[J].
Volcanic lithology identification based on parameter-optimized GBDT algorithm:A case study in the Jilin Oilfield,Songliao Basin,NE China
[J].
A variational inequality approach with SVM optimization algorithm for identifying mineral lithology
[J].
Rock type classification based on petrophysical,geochemical,and core imaging data using machine and deep learning techniques
[J].
Petrophysical rock typing based on deep learning network and hierarchical clustering for volcanic reservoirs
[J].
Data-driven lithology prediction for tight sandstone reservoirs based on new ensemble learning of conventional logs:A demonstration of a Yanchang member,Ordos Basin
[J].
基于随机森林算法的泥页岩岩相测井识别
[J].
Identification of shale lithofacies by well logs based on random forest algorithm
[J].
火山岩岩性、岩相识别方法——以准噶尔盆地滴南凸起火山岩为例
[J].
DOI:10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.10.1808
[本文引用: 1]

准确识别火山岩岩性和岩相是进行火山机构重建及地震相刻画的基础。火山岩岩性复杂且变化快,其变化不同于砂岩分布变化服从于沉积规律,而是与火山建造和喷发期次等因素直接相关,造成目前无成熟的预测模型和较强规律性可以遵循预测。选择准噶尔盆地滴南凸起火山岩为研究对象,总结出适应火山岩复杂岩性岩相识别的技术方法,即首先利用测井、岩心等基础资料建立关键岩性电性识别图版,落实井点硬数据的岩性纵向分布;其次,建立不同岩性的地震响应特征;第三,在地震波阻抗二次刻画岩性分布范围的约束下,应用数学概率和变差函数分析技术对岩性进行精细刻画;最后,结合测井响应特征进行测井相与地震相的综合标定,建立典型的火山机构地质、测井、地震相模式,为火山岩机构识别提供依据。
Identification methods of volcanic lithology,lithofacies:Taking the volcanic rocks of Dinan alient in the Junggar Basin as an instance
[J].
Geochemical characteristics,origin,and mechanism of differential accumulation of natural gas in the carboniferous kelameili gas field in Junggar Basin,China
[J].
三位一体火山岩预测技术的建立及应用——以新僵克拉美丽气田为例
[J].
Establishment and application of trinity interpretation technology on volcanic rock:A case study of the Kelamieli gas field in Xinjiang
[J].
裂缝充填矿物和蚀变晕对火山岩储集层流体作用的指示——以克拉美丽气田滴西地区为例
[J].
Fracture fillings and alteration halo in volcanic reservoirs as indicator of fluid activities in the dixi area in the kelameili gas field,Junggar Basin,northwestern China
[J].
准噶尔盆地滴西地区石炭系火山岩储层次生孔隙的岩相学特征及主控因素
[J].
Petrography characteristics and main controlling factors of secondary pores in Carboniferous volcanic reservoir in Dixi Area,Junggar Basin
[J].
准噶尔盆地克拉美丽地区石炭系天然气来源
[J].
DOI:10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2020.04.018
[本文引用: 1]

在分析准噶尔盆地克拉美丽地区石炭系2套烃源岩地球化学特征基础上,结合天然气组成及其伴生凝析油单体烃碳同位素特征,探讨了克拉美丽地区石炭系天然气来源问题。准噶尔盆地克拉美丽地区石炭系天然气主要为湿气,其中克拉美丽气田天然气为高成熟的腐殖型气,五彩湾气田天然气主要为成熟—高成熟的腐殖型气。根据烃源岩生烃潜力评价和热模拟实验分析,研究区石炭系松喀尔苏组下段与滴水泉组烃源岩以Ⅲ型腐殖型为主,少量Ⅱ型有机质,成熟度达到成熟—高成熟阶段,具备较好的生气潜力。在高温(440~560 ℃)热解阶段,2套石炭系烃源岩生成的天然气碳同位素值与克拉美丽地区天然气的碳同位素值较为一致,在600 ℃温度时,烃源岩总产气率大于150 kg/t<sub>TOC</sub>,具有较强的生气能力。正构烷烃碳同位素组成特征显示克拉美丽地区石炭系气藏天然气及伴生凝析油主要为滴水泉组烃源岩及松喀尔苏组下段烃源岩混源。
Source of Carboniferous natural gas in Kelameili Area,Junggar Basin
[J].
准噶尔盆地陆东—五彩湾地区石炭系火山岩油气藏成藏影响因素研究
[J].
Influencing factors of Carboniferous volcanic reservoir in Ludong-Wucaiwan Area,Junggar Basin
[J].
克拉美丽气田滴西地区石炭系火山岩储层成岩作用及孔隙演化
[J].
Diagenesis and pore evolution of Carboniferous volcanic reservoirs in Dixi Area,Kelameili Gas Field
[J].
基于电成像测井的火山岩裂缝分布定量表征——以准噶尔盆地滴西地区石炭系为例
[J].
DOI:10.7623/syxb201810005
[本文引用: 1]

火山岩油气藏与裂缝有关,利用电成像测井资料,建立了火山岩裂缝的定量表征方法,对滴西地区石炭系火山岩裂缝"点"、"线"、"面"分布规律进行了研究。利用电成像测井资料精细解释了岩性和裂缝,并确定了裂缝参数的计算方法,获得了裂缝发育程度及分布特征。研究发现,中—高角度构造缝是石炭系主要裂缝类型;基性熔岩和酸性侵入岩中裂缝发育率、裂缝层密度明显高于角砾岩和凝灰岩,是裂缝发育的主要场所;单层厚度小于15 m,裂缝易发育,呈现"单段式"发育模式,裂缝层密度大、裂缝发育率高;单层厚度大于15 m,裂缝较难发育,且集中分布在岩性体顶部和底部,呈现"三段式"或"二段式"发育模式,整体裂缝层密度小、裂缝发育率低,但局部高;风化壳可以促进紧邻岩性体中裂缝发育,改变发育模式。裂缝在纵向上主要分布在石炭系风化壳顶面以下250 m内,且向深部裂缝发育程度逐渐减小,而平面上断层附近是裂缝层密度、裂缝发育率的高值区,且沿断层呈趋势分布。
Quantitative characterization of volcanic fracture distribution based on electrical imaging logging:A case study of Carboniferous in Dixi Area,Junggar Basin
[J].
DOI:10.7623/syxb201810005
[本文引用: 1]

There is certain relationship between volcanic hydrocarbon reservoirs and fractures, while fracture distribution laws are macroscopically characterized by seismic attributes. A quantitative characterization method of volcanic fractures is established on a basis of electrical imaging logging to study the "point", "linear" and "planar" distribution laws of Carboniferous volcanic fractures in Dixi area. This method is applied to perform the fine interpretation of lithology and fractures using electrical imaging logging data, define the calculation method of fracture parameters, and obtain the fracture development level and distribution characteristics. The study shows that the tectonic fractures with median-high angle are dominant in Carboniferous. Meanwhile, basic lava and acidic intrusive rocks have higher fracture development rate and density than volcanic breccia and tuff, and are the main place for the development of fractures. In case of the single-layer thickness less than 15 m, fractures are prone to develop, characterized with "single-section" development mode, large density of fracture layer and high fracture development rate. In case of the single-layer thickness greater than 15 m, fractures are difficult to develop, mainly concentrated at the top and bottom of lithological body, characterized with the "tri-section" or "bi-section" development pattern, overall small density of fracture layer, low fracture development rate and high local rate. In the meantime, the weathering crust can promote the development of fractures in the adjacent lithological body and change the development pattern. Fractures are mainly distributed vertically at the depth of 250 meters under the top of Carboniferous weathering crust; the deep fracture development degree is gradually declined. However, on the horizontal level, the vicinity of faults is the high-value zone of fracture layer density and development rate, distributed in the trend towards fault.
准噶尔盆地克拉美丽气田滴西14井区石炭系蚀变凝灰岩储层热液作用过程及时限
[J].
Hydrothermal process and duration of carboniferous altered tuff reservoir in well dixi 14 area of kelameili gas field(Junggar basin),NW China
[J].
滴南凸起区石炭系火山岩岩性特征及其意义
[J].
Characteristics and significance of Carboniferous volcanic rocks in Dinan uplift
[J].
克拉美丽气田火山岩岩性测井识别技术研究
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2016.05.016
[本文引用: 1]

准确、有效的岩性识别是火山岩油气藏勘探评价的关键。以克拉美丽气田石炭系火山岩为例,在薄片鉴定和岩心分析基础上,应用常规测井曲线建立岩性识别图版,发现岩性之间存在严重交叉和重叠现象,影响岩性识别的准确性。为了修正直接图版法的识别误差,采用对应分析法分析测井响应与岩性的相关性,发现自然伽马、补偿中子、地层真电阻率曲线对岩性最为敏感,进一步计算出各曲线点到各岩性点的距离,并以距离的倒数作为权重系数对岩性识别图版进行校正,最后采用最短欧氏距离归属法识别火山岩岩性。将识别结果与有薄片鉴定岩性的6口井累计2 240 m井段进行对比,岩性解释符合率达89.2%,取得了良好的应用效果。
Study on lithology identification of igneous rocks in Kelameili Gasfield by well logging
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2016.05.016
[本文引用: 1]

Effective lithology identification for igneous rocks is the key to the evaluation of igneous reservoirs.On the basis of core analysis and thin slice analysis,log responses of various igneous rocks was studied and a lithologic identification plate of igneous rocks in Kelameili Gasfield,Junggar Basin based on conventional well logs was established.It was found that there are many crossing and overlapping between the different lithologies on the plates,which affected the accuracy of lithology identification.Thus,in order to correct the error of direct plate approach,the relationship between log responses and lithologies of igneous rocks was analyzed by correspondence analysis.It was found that the GR,CNL and RD curves are the most sensitive for lithologies of igneous rocks.The distance between various logs points and lithologic points was then calculated respectively.Regard the reciprocal of distance as the weight coefficient,the lithologic identification plates were calibrated.Lastly,based on the calibrated plates,lithologies of igneous rocks were identified with the shortest Euclidean distance method.The identification results were compared with the thin slice analysis in 6 wells added up to 2240 meters well sections and the lithology interpretation coincidence rate is as high as 89.2%,which has achieved good application effect.
火山岩岩性测井识别方法研究——以准噶尔盆地火山岩为例
[J].
Logging identification method of volcanic rock lithology:A case study from volcanic rock in Junggar Basin
[J].
红车断裂带石炭系火山岩岩性岩相特征分析及储层识别
[J].
Lithology and lithofacies characteristics analysis and reservoir identification of Carboniferous volcanic rocks in Hongche fault zone
[J].
基于改进随机森林的火山岩测井岩性识别
[J].
Lithology identification of volcanic logging based on improved random forest
[J].
基于随机森林的K-近邻算法划分火成岩岩性
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2021.06.008
[本文引用: 1]

针对火成岩油气藏火成岩岩性划分难,岩性划分准确率受薄片鉴定样本数量影响大的问题,利用随机森林(RF)算法分析不同的测井曲线与火成岩岩性相关性,再利用K-近邻(KNN)算法划分小样本薄片鉴定情况下的火成岩岩性。将研究成果应用于川西地区二叠系火成岩地层,结果表明:测井曲线与岩性相关程度从高到低依次为GR、R<sub>t</sub>、DEN、CNL、AC;KNN算法划分火成岩岩性,k取值受分类数量和训练样本数量2个因素控制,样本数量较小时后者影响程度大于前者;k为3时,24个火成岩训练样本(5种岩性)KNN法回判准确率为87.5%,14个火成岩(5种岩性)测试样本测试准确率为92.5%。对比图版划分火成岩岩性,KNN算法受人为影响小,参数调节简便。该研究对小样本情况下火成岩岩性划分有重要指导意义。
Classification of igneous rock lithology with K-nearest neighbor algorithm based on random forest (RF-KNN)
[J].
基于随机森林算法的塔然高勒地区测井数据岩性识别
[J].
Random forest algorithm based lithology identification of geophysical logging data in tarangaole area
[J].
基于随机森林的矿压预测方法
[J].
Mine pressure prediction method based on random forest
[J].
Modeling and testing landslide hazard using decision tree
[J].
A data-driven shale gas production forecasting method based on the multi-objective random forest regression
[J].
Integrated lithology identification based on images and elemental data from rocks
[J].
Comparison of supervised and unsupervised approaches for mudstone lithofacies classification:Case studies from the Bakken and Mahantango-Marcellus Shale,USA
[J].
Data-driven diagenetic facies classification and well-logging identification based on machine learning methods:A case study on Xujiahe tight sandstone in Sichuan Basin
[J].