0 引言
时频分析是一类用于处理非平稳信号的方法,它主要关注信号在时域和频域上的能量分布,以实现噪声分析、定位、剔除或压制。当前主要时频分析方法包括基于短时傅里叶变换(STFT)、连续小波变换(CWT)、匹配追踪时频分析和S变换等[7-8]。研究中采用基于广义S变换的时频分析。其中,1946年,学者Gabor提出一种重要的时频分析方法——Gabor变换,以研究非平稳信号在局部范围内的振幅和相位特征为目标[9]。后来,Potter[10]将Gabor变换进一步发展,于1947年提出短时傅里叶变换,成为非平稳信号振幅谱、相位谱的常用分析工具。短时傅里叶变换通过使用移动窗函数来计算不同时刻的时频信息,并将非平稳信号视为一系列短时平稳信号的叠加[11]。然而,该方法存在一些限制,如使用固定的窗函数导致时频分辨率不可调节,除非重新选择窗函数。这意味着短时傅里叶变换缺乏自适应性,不适用于具有不同宽度的窗函数情况。
研究采用复杂介质等效化对待的方式,即将复杂缝洞体系等效为相同体积的均质地质体,分别由岩石骨架和总孔隙体积组成。以断控“板状”油藏的空间特征为分析目标,通过改进广义S变换的时频分析方法提取目标处时频道集能量包络线并获取等效斜率趋势,并联合实钻数据对复杂缝洞体系水体发育进行综合分析,探索出断控“板状”油藏油柱高度地震识别的有效方法。
1 方法原理
一般情况,油气藏厚度(油柱或气柱高度)越大,地震波传播衰减和散射反射的影响就越大,频率衰减的特征越容易被捕获和识别。因断控储层沿断裂带走向展布,不同尺度断裂—裂缝向深层延展,同时输导油气向上聚集成藏,进而形成非规则形态的“板状”油藏。基于这类油藏的独特性质,采用复杂介质等效化对待的方式,通过相对较大时窗分析取时频分析数据中的最大共性特征,进而弥补由于油藏埋藏深度大导致利用地震资料识别储层内含油气性描述精度提升因难的不足。
1.1 改进的广义S变换
式中:τ为时间平移因子。
Stockwell等[12]从低频信号变化相对平稳且周期相对较大,以及高频信号变化剧烈且周期相对较小的角度出发,对Gabor变换进行了改进,提出了S变换:
由于方程(2)中的S变换调节时窗函数宽度的参数比较单一,无法很灵活地适应实际信号的振幅和相位随时间和频率变化的特征。因此,一些学者在S变换的基础上进行了改进和发展,提出了广义S变换[11]:
式中:a>0,b≥0。
假设有:
则,实信号x(t)的广义S变换在频率域实现的表达式可表示为:
假设有实信号x0(τ,t),τ为常数,t为时间变量且x0(τ,t)=x(t)w1(t-τ,f),则有
X0(τ,f)=
于是:
假设:
图1
本文基于地震数据开展断裂带板状油藏内油水界面预测的研究思路主体分为三步:第一步,基于地震数据开展时频能量包络分析并获得高频衰减的时间厚度;第二步,对研究区储层顶面进行刻画,得到沿断裂分布的储层顶面构造图;第三步,利用沿断裂分布的储层顶面构造累加预测的油层厚度获得断裂带油水界面深度。
1.2 模型验证
为进一步论证利用基于广义S变换的时频分析方法对断缝体油藏油层厚度预测的可行性,建立地质模型开展粘弹性波动方程正演模拟,然后基于正演的地震数据开展基于广义S变换的时频分析。
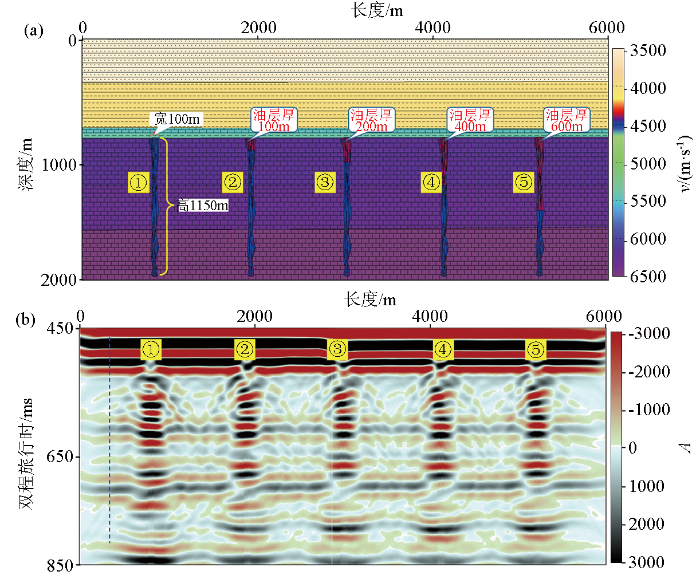
建立地质模型时,综合考虑研究区碳酸盐岩断缝体地震特征、野外露头特征以及研究区内钻井、测井资料,建立符合该区断缝体实际特征的地质模型(图2a)。地质模型设计时完全参考实际钻井揭示的地层参数(深埋>6 000 m),断裂带上覆地层和围岩模型完全按测井真实地层速度和地层厚度进行速度建模。模型中,断缝体高1 150 m,宽100 m,断缝体里充填的主要为流体和灰岩角砾。含油气段纵波速度为4 400 m/s,横波速度为2 531 m/s,密度为2.47 g/cm3,吸收因子Qp为4、Qs为1.78;储层内含水段的等效纵波速度为4 500 m/s,等效横波速度为2 835 m/s,等效密度为2.55 g/cm3,吸收因子Qp和Qs不填参数。断裂缝体周围致密灰岩纵波速度为 6 200~6 500 m/s。图2a中第①个“板状”条带断缝体设计为全含水模型,第②、③、④、⑤个条带断缝体油层厚度分别为100、200、400、600 m。
图2
图2
不同油层厚度的断缝体油藏地质模型(a)和正演模拟成果数据的地震剖面(b)
Fig.2
Geological model of fractured reservoir with different oil layer thicknesses(a) and forward modeling results profile(b)
数值模拟时,为了能更真实模拟地下断控油藏地震波场特征,采用基于粘弹波动方程开展正演。图2b为断缝体正演数据的偏移成果剖面,从图中可以看出,正演出的地震剖面上断缝体均为纵向强振幅反射,5条断缝体正演地震特征很相近,特别是第②~第⑤断缝体正演地震特征基本一致,难以从地震上识别出断缝体的油层高度。
图3
图3
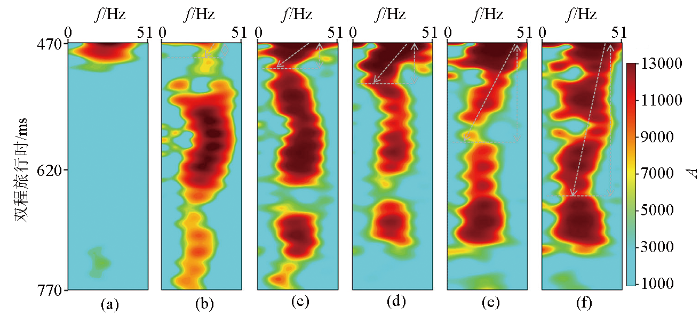
不同地质体正演地震数据时频道集剖面对比
a—
Fig.3
Comparison of time-frequency gathers for forward seismic data of different geological bodies
a—blue dashed line position in
表1 时频分析预测的模型油层厚度对照统计
Table 1
| 序号 | 模型油层 厚度/m | 频谱衰减 高度/ms | 预测油层 厚度/m | 误差/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 6 | 18 | — |
| 2 | 100 | 28 | 84 | 16 |
| 3 | 200 | 60 | 180 | 10 |
| 4 | 400 | 130 | 390 | 2.5 |
| 5 | 600 | 195 | 585 | 2.5 |
2 应用实例
2.1 地质背景
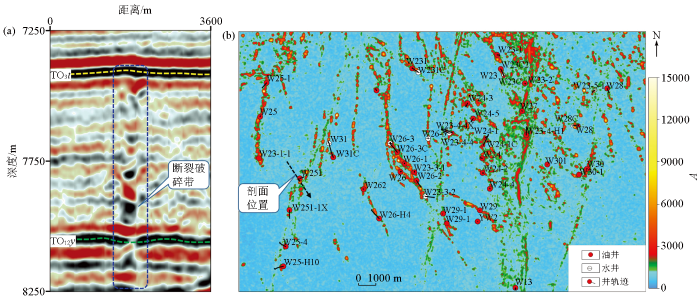
研究区位于中国西北部塔里木盆地北部,为塔里木河泛滥平原,地势相对平坦,地表海拔930~950 m。地下目标层位于塔北隆起轮南低凸起向南倾入北部坳陷的斜坡区域(图4)。学者研究表明,研究区奥陶系一间房组—鹰山组碳酸盐岩地层内部的原生孔隙基本消失殆尽,以断裂破碎作用等次生孔隙为主(大于95%),储集空间主要为次生溶蚀及构造破裂作用形成的孔、洞与裂缝[14]。针对走滑断裂破碎带的钻探结果表明,断裂破碎带的横向储集体结构非常的复杂,其钻井、录井、测井特征表现出明显的差异性(表2)。鉴于断控缝洞体系的空间复杂性,采用适当大小的时间窗口分析策略将缝洞体系等效为相同体积条件下的均质地质体,分别由岩石骨架和总孔隙体积(裂缝、孔隙、洞穴)组成。基于此开展地球物理特征的分析及有效信号的提取识别。
图4
表2 走滑断裂破碎带不同横向结构钻井、录井、测井特征识别
Table 2
| 储集体结构 | 地震反射特征 | 测井特征 | 实钻特征 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 电阻率/(Ω·m) | 密度/(g·cm-3) | 声波时差/(m·μs-1) | 钻井情况 | 钻时/(min·m-1) | ||
| 裂缝—基岩段 | 连续状 | 2 000以上 | 2.7~2.8 | 50 | 见气测 | 25~40 |
| 裂缝—孔洞段 | 弱连续杂乱 | 500~2 000 | 2.5~2.6 | 40~50 | 漏失无放空 | 13~25 |
| 断层角砾段 | 串珠 | 40~2 000 | 2.5~2.6 | 35~45 | 漏失量较大或钻遇放空 | 5~12 |
研究区内断控缝洞储层因经过多期次断裂活动及局部溶液沿断裂破碎带的扩溶作用,形成非规则的复杂缝洞系统,缝—孔—洞等储层组合类型复杂多样。这种碳酸盐岩优质储层多为不同数量的波谷—波峰组合而成的强能量反射[15-16]。因储层受控于断裂作用,其纵向呈现条带状杂乱反射(强能量反射—弱能量反射交织成带)的特征、储层横向分布呈现沿断裂展布的条带特点(图5)。由于断裂破碎具有差异性且断裂发育具有分段性,沿走滑断裂缝洞储层纵横向的非均质性,造成同一条断裂油气富集差异非常大,高产井、低产井、失利井分布规律不清。因此,通过开展地球物理方法针对走滑断裂破碎带内部储层的油层厚度进行有效探测,进而指导该区下步井位部署和油气高效开发。
图5
图5
垂直断裂破碎带地震剖面特征(a)和研究区奥陶系振幅属性(b)
Fig.5
Seismic profile characteristics of vertical fault fractured-zone(a) and amplitude attribute map of Ordovician in the study area(b)
2.2 油柱高度识别与分析
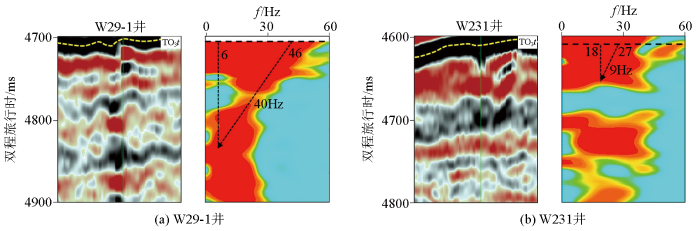
研究区内,W29-1井自投入生产以来,已累计产油量超19 万t,该井进入奥陶系一间房灰岩地层垂直厚度为31 m。油田油藏研究人员结合钻井、油气生产动态数据确定的油层厚度为190 m。基于本文方法获得的时频道集剖面显示,121 ms时间范围内,频率由46 Hz衰减至6 Hz(图6a),衰减幅度40 Hz。根据灰岩段平均速度6 000 m/s,预测频率衰减段厚度315 m。W231井为研究区内北部一口评价井,对井段6 247.08~6 314.8 m用8 mm油嘴求产,油压3.1 MPa,套压13.58 MPa,折算日产水量为212.08 m3,产出水的氯根含量为57 500 ppm,累产水551.79 m3,测试结论为水层;对井段6 369.00~6 564.40 m,6 mm油嘴放喷排液,油压1.60~1.44 MPa,日排液79.06 m3,测试累计排液315.76 m3,产出水的氯根含量为61 892~68 745 ppm,无油气。油田油藏研究人员给定油层厚度近似为0 m。基于本文方法获得的时频道集剖面显示,22 ms时间范围内,频率由27 Hz衰减至18 Hz(图6b),衰减幅度9 Hz。小幅度衰减特征反映地震波于目标点储层段的衰减特征,并非明显油柱面时频差异。
图6
图6
过井地震剖面和时频道集剖面对比
Fig.6
Comparison of cross well seismic profiles and time-frequency profiles
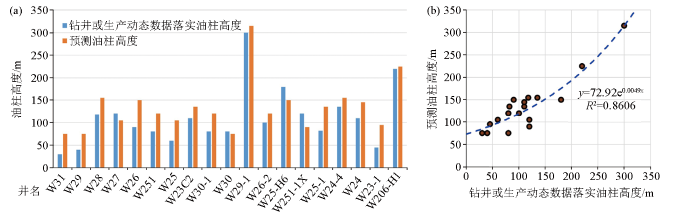
利用本文方法对该区油田油藏研究人员已确定的油层厚度数据的19口井进行分析,预测的油柱高度与根据井动态数据预测的油柱高度存在良好的一致性(图7a),预测油柱高度整体有偏大的趋势。为此,研究中建立油藏研究人员已确定的油层厚度数据与本文方法预测油柱高度数据之间的关系,两者相关度达到0.860 6。当实际油柱高度大于等于150 m时,地震预测呈1∶1的关系;当实际油柱高度小于150 m时,地震预测结果稍偏大,实际油柱高度为地震预测结果的0.587 7倍。因此需要对油柱高度进行校正,进而获取更准确的油水界面参数。
图7
图7
研究区钻井油柱高度(a)和本文方法预测的油层厚度(b)对比
Fig.7
Comparison between the drilling oil column height in the study area(a) and the predicted oil layer thickness using this method(b)
图8
图8
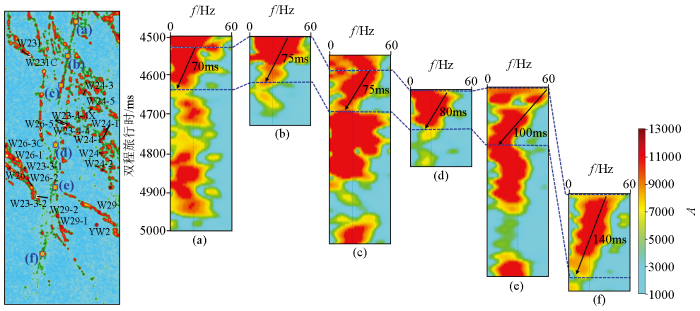
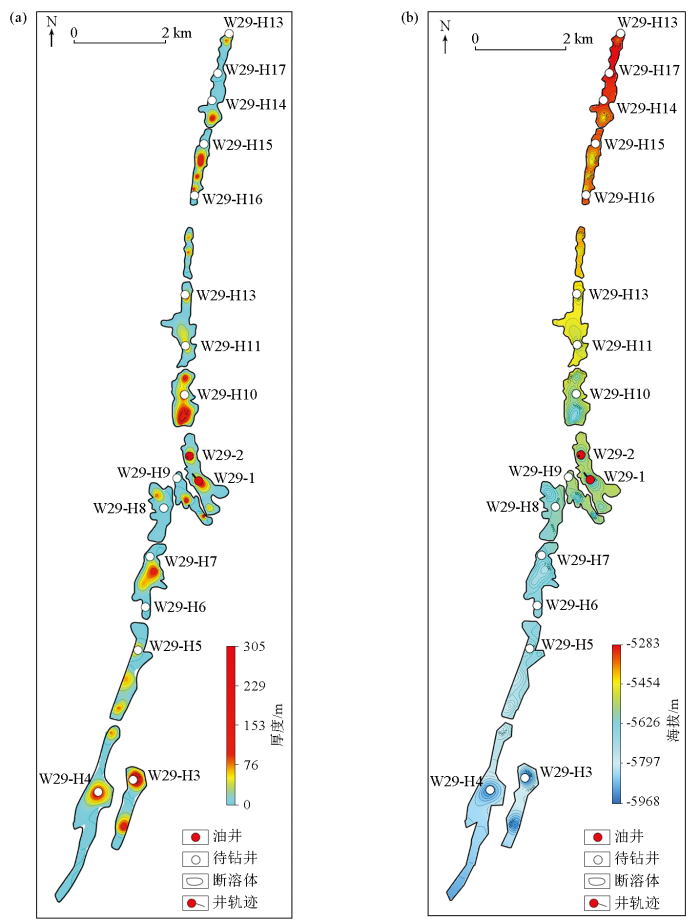
研究区内某断裂破碎带油层厚度预测对比
Fig.8
Comparison chart of oil layer thickness prediction for a fractured zone in the study area
图9
图9
研究区内某断裂破碎带预测油层厚度平面(a)和油水界面平面(b)
Fig.9
Plan view of predicted oil layer thickness in a fractured zone(a) and the OWC(b)
3 结论
1)针对走滑断控“板状”油藏的地震地质特点,研究了应用基于广义S变换的时频分析方法,利用了基于时频特征包络分析方法实现断控油藏的油柱高度的有效预测,并应用钻井信息约束实现沿断裂破碎带的油藏内部油水界面的工业化成图。
2)在塔里木盆地富满油田某区的实际应用表明,研究区内油柱高度整体表现北小南大的特点。当实际油柱高度大于或等于150 m时,地震预测与实际误差明显较小;当实际油柱高度小于150 m时,地震预测结果稍偏大,需要进行校正。
3)该方法预测精度与地震资料品质相关,优良资料品质区可取得更佳效果。通过正演地震数据和野外地震数据的应用,方法具有较好的稳定性,可快速推广至具有类似地质特征的区域。
致谢
本研究的完成和推广应用,得益于东方物探公司和塔里木油田公司相关专家的指导和地震数据的允许使用,得益于西南石油大学张固澜教授的精心指教,在此一并表示感谢。
参考文献
超深断控缝洞型储层迭代反演方法——以富满油田为例
[J].
Iterative inversion method for ultradeep fault-controlled fracture-vug reservoirs:A case study of the Fuman oilfield,Tarim Basin
[J].
塔里木盆地富满油田成藏地质条件及勘探开发关键技术
[J].
DOI:10.7623/syxb202108001
[本文引用: 1]

塔里木盆地超深层海相碳酸盐岩油气资源丰富,已发现中国最大的风化壳型油田和最大的凝析气田,但勘探开发长期局限在古隆起及斜坡部位。近年来,随着勘探上突破"古隆起控油、斜坡富集"的传统理论认识以及地震、钻井与开发配套技术进步,在坳陷区发现了超深层(大于7 500 m)走滑断裂断控型油田——富满油田。富满油田的勘探开发实践与研究表明:(1)走滑断裂的发育不仅沟通了深层下寒武统烃源岩,而且控制了中奥陶统碳酸盐岩缝洞体储层的发育,并与上奥陶统巨厚泥岩构成了优越的走滑断裂断控型油气成藏体系;(2)油气沿走滑断裂破碎带呈条带状差异分布,具有圈闭类型特殊、油柱高度大、油品性质好、单井产量高等特点;(3)发现三级石油地质储量达4×10<sup>8</sup>t,石油资源量达10×10<sup>8</sup>t,开发高效井多,快速建成了原油产量达160×10<sup>4</sup>t/a的产能。通过持续攻关,逐步形成了沙漠区超深层高密度宽方位三维地震采集、弱走滑断裂刻画、碳酸盐岩破碎带圈闭评价、高效井位部署、超深层钻完井等配套技术,支撑了超深层复杂断控型碳酸盐岩油藏的规模与效益勘探开发。
Geological conditions for hydrocarbon accumulation and key technologies for exploration and development in Fuman oilfield,Tarim Basin
[J].
DOI:10.7623/syxb202108001
[本文引用: 1]

Tarim Basin has enriched oil and gas resources in ultra-deep marine carbonate rocks, where China's largest weathering crust-type oil reservoir and largest condensate gas reservoir have been discovered. However, the oil and gas exploration and development have been conducted only in palaeohighs and slopes for a long time. In recent years, with breakthroughs in the traditional theoretical understanding of "oil accumulation controlled by palaeohighs and enrichment in slopes" and advances in the supporting technologies of seismic exploration, drilling and development, Fuman oilfield, the ultra-deep (over 7 500 m) strike-slip fault-controlling oilfield, has been discovered in the depression area. Exploration and development practice and studies of the Fuman oilfield show the following results. First, the developed strike-slip faults not only cut through the deep Lower Cambrian source rocks, but also control the development of Middle Ordovician carbonate cavity-fracture reservoirs, and constitute a superior petroleum accumulation system under the control of strike-slip faults together with the huge thick Upper Ordovician mudstone. Second, the oil and gas show a stripe-shaped differential distribution along the strike-slip fractured zone, characterized by special trap type, large oil column height, good oil property, and high single-well production. Third, the predicted geological reserves of oil are up to 4×10<sup>8</sup>t, the amount of oil resources is 10×10<sup>8</sup>t, and there are many efficient development wells. The oil productivity of 160×10<sup>4</sup>t/a has been rapidly achieved. Through continuous research, the supporting technologies such as ultra-deep, high-density and wide-azimuth 3D seismic acquisition, characterization of weak strike-slip faults, evaluation of traps in carbonate fractured zone, efficient well location deployment, ultra-deep drilling and completions have been gradually established in the desert area, providing supports for the large-scale and efficient exploration and development of the ultra-deep complex fault-controlling carbonate reservoirs.
塔里木盆地超深层走滑断裂带的地震识别方法
[J].
Seismic identification method of ultra-deep strikeslip fault zones in Tarim Basin
[J].
断溶体油藏注采井网构建方法
[J].
Constructing optimum injection-production well pattern for fault-karst reservoirs
[J].
双相介质油气检测技术在塔河油田白垩系舒善河组的应用
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2022.05.015
[本文引用: 1]

塔河油田西部白垩系舒善河组砂岩具有良好的油气显示和勘探开发潜力。受制于单砂体厚度薄、砂泥互层频繁、沉积微相变化快等特点,以往常用的“振幅找油”技术存在一定的多解性,储层和流体分布预测难度大。在A井区进行了双相介质油气检测技术的探索性应用研究,在对已知油气层进行精确标定和层位解释的基础上开展了多时窗频谱分析试验,确定了最佳时窗和高、低频敏感段。因油气层是典型的双相介质,对应的地震波具有“低频能量增强,高频能量衰减”的特性,低频段与高频段的能量之比可以较好地反映地层中油气的富集程度,同时兼顾频谱中频段相对凸起的特征。应用结果表明,A井区的检测结果与已知油气井的符合率约为94.4%,高于振幅属性72.2%的符合率,说明该技术在本研究区是适用的,再结合其它成果进行综合分析,可更准确地预测潜在的有利目标区。
Application of dual-phase medium oil and gas detection technology in Cretaceous Shushanhe formation of Tahe Oilfield
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2022.05.015
[本文引用: 1]

Abstract: The sandstone of the Cretaceous Shushanhe formation in the western Tahe Oilfield has oil and gas that show considerable potential for exploration and development.The commonly applied amplitude oil search method cannot be used in this formation due to its thin sand,frequent sand and mud interbed,and rapid changes in its sedimentary microfacies,so accurately predicting reservoir and fluid distribution in this area is difficult.To more accurately their distribution,we exploratively applied two-phase medium oil and gas detection technology in the A well area of the Tahe Oilfield.Based on an accurate well-seismic calibration and horizon interpretation of the known oil and gas reservoirs,we conducted a multiwindow spectrum analysis test,through which we determined the optimal time window and sensitive high- and low-cut frequency bands.Because the oil and gas reservoir is a typical dual-phase medium,the corresponding seismic waveforms have the typical characteristics:low-frequency energy enhancement and high-frequency energy attenuation.The energy ratio of the low- and high-frequency bands qualitatively reflected the degree of oil and gas enrichment in the formation.By examining the results obtained with the fluid detection technique,we found that the coincidence rate between the fluid detection results of the A well area and known oil wells was 94.4%,which is higher than the coincidence rate of the amplitude attribute of 72.2%,proving the effectiveness of the method in detecting fluid and that it can be used to predict favorable oil-bearing reservoirs.
油气检测多技术联合在B油田的应用研究
[J].
The application of multi-seismic hydrocarbon detection technology to gas identification in B oilfield
[J].
时频域变分模态分解地震资料去噪方法
[J].
Seismic data de-noising method based on VMD in time-frequency domain
[J].
基于分频相干体的蚂蚁追踪技术在塔河油田断裂刻画中的应用
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2020.02.012
[本文引用: 1]

利用全频带常规蚂蚁追踪技术刻画断裂易出现横向连续性不强或平面断裂格局不明显的现象,造成断裂刻画与井间动态响应匹配度低。提出了基于匹配追踪频谱分解的分频相干体技术,并改进常规蚂蚁追踪技术流程,以提高断裂刻画精度。首先,以原始全频带地震数据为基础,采用匹配追踪频谱分解技术生成一系列分频体,并利用倾角导向滤波提高分频体的信噪比;然后,采用本征相干计算方法获得不同中心频率的分频相干体,对照不同分频剖面及目的层相干切片优选出某一分频相干体;最后对二次去噪后的分频相干体应用蚂蚁追踪技术并结合井区动静态资料,反复调整追踪参数,获得分频蚂蚁体。在此过程中,合理的频谱分解和去噪处理可提高中小尺度断裂的分辨率,本征相干计算和精调参数的蚂蚁追踪可提高中小尺度断裂的识别效果。将此技术应用于塔河油田T井区碳酸盐岩储层的中小尺度断裂识别,结果表明,相较于常规技术,该技术对断裂的刻画精度高,刻画结果与井间动态连通关系匹配性好,与地质认识吻合度高。
Application of an ant-tracking technique based on spectral decomposition to fault characterization
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2020.02.012
[本文引用: 1]

The conventional ant-tracking technique applied to fault characterization often results in weak transverse continuity or unobvious plane fracture patterns.It also leads to a poor matching relationship between the characterized faults and the inter-well dynamic response.To solve these issues,we proposed an improved ant-tracking technique based on matching-tracking spectral decomposition and improved the conventional workflow of ant-tracking.Firstly,the full spectral-band seismic data were decomposed into a series of frequency-divided data,and the dip steering filtering method was used to improve the signal-to-noise ratio of the initial seismic data.Then,the intrinsic coherence of seismic data in different frequency bands were calculated and extracted.We compared the profiles and the coherent slices of the target layer from different single-frequency data,so as to optimize the required coherent data.In addition,the data after further noise reduction were tracked by artificial ants,and the appropriate ant-tracking parameters were repeatedly adjusted based on dynamic or static data.Finally,dividing-frequency ant data were obtained by the aforementioned ant-tracking process.The resolution for medium-and small-scale fracture identification was improved through denoising and reasonable spectral decomposition.Furthermore,the effect of fault identification was enhanced by the ant-tracking parameters determination and intrinsic coherence calculation.This method was applied to the identification of medium-and small-scale faults in carbonate reservoirs in well area T in Tahe Oilfield.The results showed that the so-identified faults were consistent with the inter-well dynamic connectivity and geological interpretation.
Theory of communication
[J].
Localization of the complex spectrum:The S-transform
[J].
多频解释软件的数据存储与显示
[C]//
Data storage and display of multifrequency interpretation software
[C]//
走滑断裂对碳酸盐岩储层和油气藏的控制作用——以塔里木盆地北部坳陷为例
[J].
Control effect of strike-slip faults on carbonate reservoirs and hydrocarbon accumulation:A case study of the northern depression in the Tarim Basin
[J].
哈拉哈塘地区缝洞集合体地震特征研究
[J].
Study on seismic characteristics of fracture cave assembly in Halahatang area
[J].
Ultradeep fractured-vuggy reservoir characteristic identification based on well data constrained seismic linear discriminant analysis
[J].