0 引言
石南地区油气成藏具有“连片含油、优质储层控藏、立体式含油”的特点[6⇓⇓⇓-10],在继续立足侏罗系勘探开发的基础上,应该不断加强对白垩系底砾岩储层空间展布特征的认识。该套储集层系纵向厚度变化大,横向变化快,储集空间刻画难度大。为了进一步查明白垩系底砾岩的空间展布特征及其地质主控因素,查明优质储层的空间展布规律,实现进一步的增储上产、扩大油田规模,本次研究充分利用2015年采集的三维地震资料,在地震地质层位精细标定解释的基础上,确定白垩系底砾岩在地震剖面和测井曲线上的响应特征,采用地震层位层拉平及拟波阻抗储层反演相结合的技术,系统开展了白垩系清水河组一段的古地貌恢复与储层精细反演,刻画出石南地区白垩系清水河组底砾岩的空间展布特征,厘定其发育规律和地质主控因素,为油田的勘探开发提供了充分的科学部署依据。
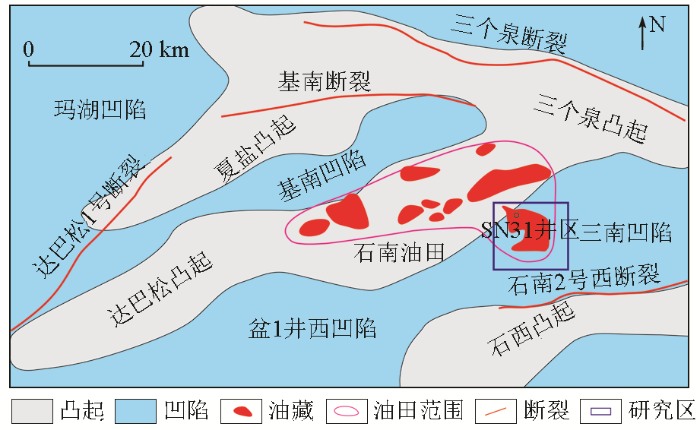
1 区域地质概况
图1
2 三维地震资料与地震反射特征
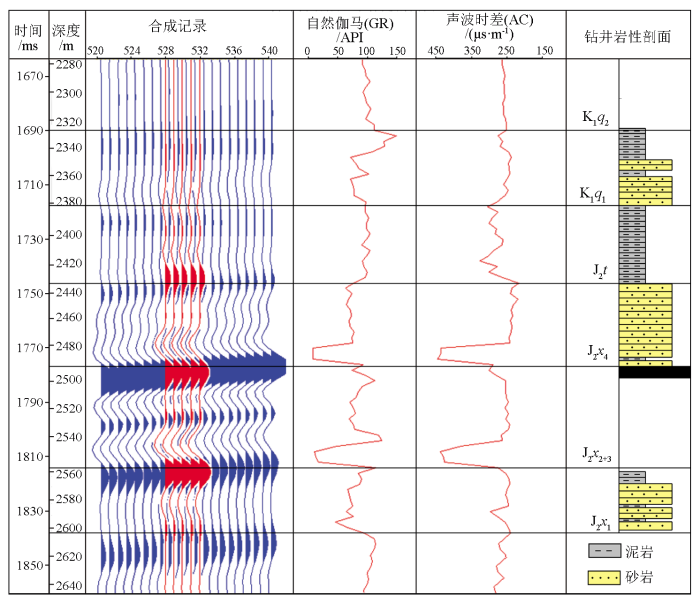
本次研究采用2015年底采集的地震资料,覆盖次数达408次,满覆盖面积达500 km2,面元为12.5 m×12.5 m。该三维地震部署的主要目的是落实侏罗系西山窑组(J2x)、头屯河组(J2t)及白垩系清水河组(K1q)的钻探目标及高效储量,有效频宽为9~64 Hz。地震剖面上波阻特征、地层接触关系清晰,侏罗系、白垩系同相轴横向连续性好,信噪比较高,合成记录与地震波组匹配关系良好(图2),地震资料质量基本能够满足该区精细构造解释及岩性目标识别。经测井曲线归一化处理、地震—地质统层、井震精确标定,主要地震反射层的特征如下。
图2
图2
SHI103井单井合成记录标定剖面
Fig.2
Calibration profile of single well synthesis record of SHI103 well
K1q底:相当于白垩系底界,是一个区域不整合面,与下伏侏罗系呈不整合接触关系。与地质界面对应的反射波组部位为波谷,反射能量中等,波组能量中等。地层表现为较中高频、较连续的地震反射特征,整体看连续性好,波组特征较为稳定。
J2t1底:相当于头屯河组底界,与下伏西山窑组呈上超不整合接触关系。
J2x4底:相当于侏罗系西山窑组四段底界。与地质界面对应的反射波组部位为波峰,反射能量较强,地震反射能量变化不大;频率普遍具中—高频特征。
J2x1底:相当于侏罗系西山窑组底界,与地质界面对应的反射波组部位为波峰,反射能量较强,地震反射能量变化不大;频率普遍具中—高频特征,整体看连续性好,易追踪。
3 古地貌恢复及对沉积的控制作用
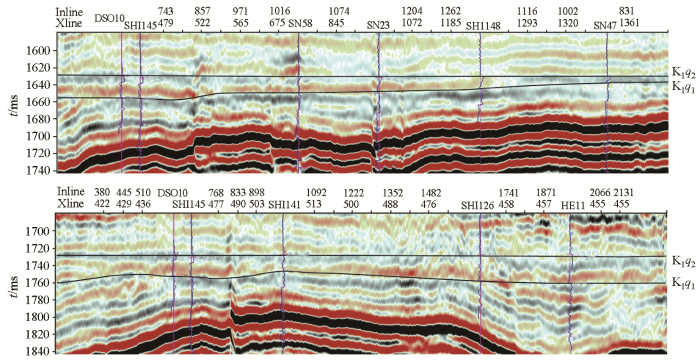
图3
图3
石南地区白垩系清水营组地震剖面
Fig.3
Seismic profile of the Cretaceous Qingshuiying Formation in the Shinan area
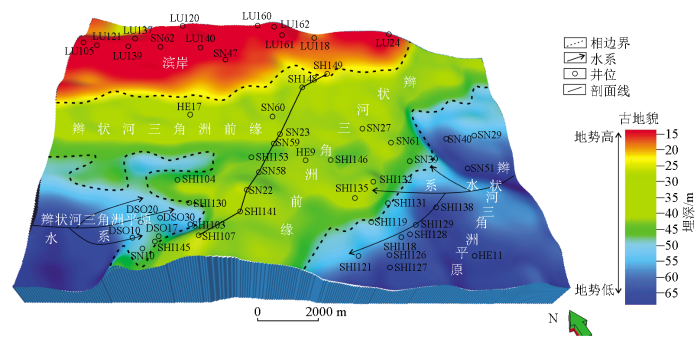
第一步,依据区域钻井、测井、录井资料开展精细井震标定,在地质分层约束下进行白垩系清水河组一段顶、底三维地震层位全区闭合追踪,完成白垩系清水河组一段时间域厚度图。第二步,利用标定井时深关系建立精确速度场,分别针对白垩系清水河组一段顶、底地震层位进行时深转换,从而得到白垩系清水河组一段顶、底两层深度域构造图,利用两者海拔高程之差完成白垩系清水河组一段深度域厚度图。第三步,对局部深度域厚度进行井震优化校正,以消除软件算法存在的系统误差,获得精准的深度域厚度图。最终,利用残余厚度法获得白垩系清水河组一段沉积期古地貌(图4)。
图4
图4
石南地区白垩系清水河组沉积期古地貌与沉积相叠合结果
Fig.4
Paleogeomorphological and sedimentary facies map of the Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation sedimentary period in the Shinan area
从图4上看,白垩系清水河组一段沉积前,古地貌特征总体表现为北部高、南部低,中部高、东西低的特点。根据地形的起伏特征可以划分为古隆起、微古隆起和沉积凹陷3个古地貌单元,古地貌特征控制着清水河组厚度的区域变化。古隆起位于研究区北部,沉积厚度较薄,沉积地层厚度介于15~20 m;沉积凹陷位于研究区南部,沉积厚度较大,沉积地层厚度介于50~65 m。南部的沉积凹陷又被近SN向的微古隆起进一步划分为东西次洼,次洼的地层沉积厚度介于20~50 m。结合钻井结果发现,石南地区白垩系清水河组一段的区域沉积特征主要受控于沉积前的古地形、地貌,该时期区域上物源主要来自于研究区的东西方向。在研究区南部古地貌相对低洼处,主要接受了早期的冲积扇沉积体系,发育厚度较大的大套底砾岩,而此时研究区北部古地貌相对较高的部位尚未接受沉积。随着湖盆底形的扩张,沉积盆地进一步发展,水体逐渐淹没研究区中部的微古隆起,微古隆起的高部位逐渐接受沉积,主要发育一套辫状河前缘沉积,砂体相对分选较好,储层物性好。目前的钻井主要都位于古地貌相对较高的部位,也是油气富集成藏的最有利区带。在研究区北部微地貌最高的古隆起部位,随着湖盆的进一步扩张,最后才接受沉积,岩性主要为一套滨岸相的细砂岩、粉砂岩,泥质含量较高,储层物性相对较差,主
要起着岩性圈闭的侧向封堵作用。研究区SN向微古隆起分割了东西物源,在中部微地貌的相对较高部位,东西物源交汇,形成了一条近SN向的有利储集相带。受控于白垩系沉积前的古地貌格局,微古隆起斜坡带是砂体的主要尖灭带,也是岩性油气藏形成的有利区带。
4 储层识别与应用效果分析
4.1 储层识别
为准确落实清水河组一段底砾岩及优质储层的空间展布特征,在宏观古地貌特征精细刻画的指导下,针对研究区面积大、钻井资料较少、储层横向与纵向分布规律不清楚等关键地质问题,开展了对目标层——石南地区白垩系清水河组一段储层的综合预测。
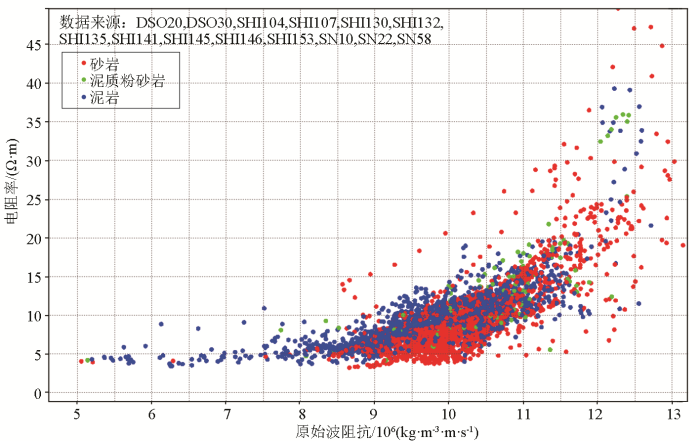
一般情况下,原始波阻抗是叠后储层预测首选敏感参数曲线。但通过对石南地区重点井目标层录井、测井资料及原始波阻抗曲线的对比分析,发现该区的原始波阻抗曲线无法有效区分储层与非储层,不能直接用于砂砾岩储层预测(图5)。
图5
图5
石南地区白垩系清水河组岩性—电阻率—原始波阻抗交汇图
Fig.5
Lithology-resistivity-original wave impedance intersection analysis diagram of Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation in Shinan area
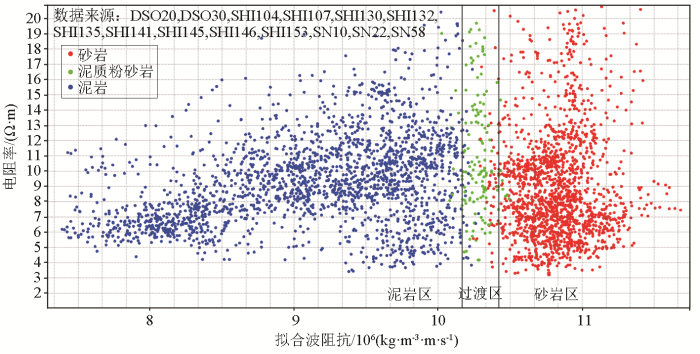
为了精细刻画砂体的空间展布特征,进一步对该区重点钻井进行了岩石物理分析。综合研究区自然伽马、自然电位、电阻率、密度、声波时差等多条测井曲线,发现自然伽马曲线(GR)对于目标层砂泥岩区分效果最为明显:泥岩主要表现为高GR分布特征,砂岩主要为中低GR分布,二者之间的分界线能够较好地区分储层与非储层。因此,优选自然伽马(GR)曲线为该区白垩系清水河组一段岩性识别的敏感曲线,融入自然伽马曲线(GR)高频信息,纳入声波时差曲线量纲,利用拟声波阻抗反演方法,开展该区储层综合预测[22⇓⇓⇓-26]。拟合波阻抗反演方法可以有效区分研究区储层与非储层(图6):砂岩区的阻抗值域高于11 000 g/cm3·m/s,泥岩区的阻抗值域低于10 700 g/cm3·m/s,阻抗值域在10 700~11 000 g/cm3·m/s之间为砂泥岩过渡区。
图6
图6
石南地区白垩系清水河组岩性—电阻率—自然伽马(GR)拟声波阻抗交汇图
Fig.6
Lithology-resistivity-natural gamma (GR) mimic wave impedance intersection analysis of Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation in the Shinan area
4.2 应用效果分析
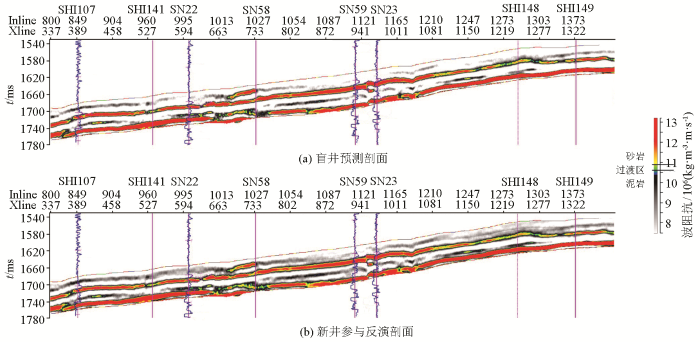
图7
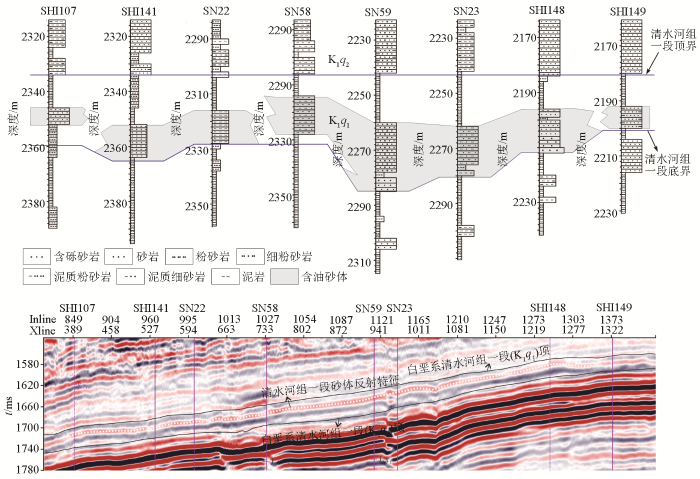
以过SHI107—SHI141—SN22—SN58—SN59—SN23—SHI148—SHI149的白垩系清水河组一段剖面为例(图8),详细分析拟声波阻抗反演方法的反演效果。该剖面上SHI107储层发育较薄,属于典型的“泥包砂”型组合结构,与邻井SHI141、SN22砂体错落叠置,SN58—SN59—SN23—SHI148为同一期砂体,砂体的主体部位位于SN58—SN59—SN23之间,SHI148位于砂体的高部位,砂体有减薄的趋势。
图8
图8
石南地区典型联井砂体对比及地震剖面
Fig.8
Comparison chart of typical joint wells in the Shinan area
从井震标定结果可知,石南地区三维地震资料保真性较高,尤其对白垩系清水河组一段砂泥岩响应特征具有很好的表征,砂岩区主要对应于中强波谷反射,泥岩区主要对应于中弱反射或波峰反射特征。原始地震剖面3个井区砂体之间叠置尖灭,剖面特征清楚,与钻井剖面上井间的对应关系较好。
综上所述,通过此次拟声波阻抗储层预测,落实了不同砂体尖灭点或尖灭特征,明确了该区岩性油藏的空间展布,解剖了复杂的油水关系,推进了SHI148井位部署及突破(试油获纯油层)。这是继SN31井区清水河组岩性油藏勘探获得突破之后岩性油气藏勘探的又一个新领域,为石南斜坡区清水河组一段评价产能新区块提供了技术支持。该储层预测方法成功验证后,又进一步指导了石南南斜坡SHI107井区岩性识别与刻画,支撑了SHI107井区评价井位部署工作(图7b)。
5 结论
1)白垩系沉积时期古地貌恢复和储层拟合波阻抗反演相结合是预测石南地区有利沉积相带和有利储层空间展布的有效技术方法组合。
2)石南地区白垩系清水河组一段沉积时期,古地貌总体呈现北高南低、东西分带的特点,沉积空间展布明显受控于古地貌。古地貌低部位沉积序列完整,底部发育底砾岩,向上逐渐过渡为砂岩、泥岩,古地貌高部位缺失底砾岩,主要发育以泥岩为主的沉积,研究区中部的南北向微古隆起带是储层发育的有利地区。
3)自然伽马测井曲线对于石南地区白垩系清水河组砂泥岩识别比较明显,优选自然伽马曲线拟合波阻抗反演方法进行储层反演预测,反演结果剖面岩性尖灭点清楚,砂体叠置关系明确,对于古地貌刻画的岩性油气藏发育有利区带优质储层的纵、横向展布特征具有较好的预测作用,这已在后期勘探开发井位部署中得到了很好的验证。
参考文献
准噶尔盆地腹部低凸起带油气成藏研究
[J].
Hydrocarbon accumulation of low uplift belt in central Junggar Basin
[J].
准噶尔盆地白垩系底砾岩与油气成藏的关系
[J].
Relationship between Cretaceous basal conglomerate and oil/gas reservoiring in the Junggar Basin
[J].
准噶尔盆地石南地区清水河组一段成岩特征及其油气意义
[J].准噶尔盆地石南地区清水河组一段广泛发育砂岩和砂砾岩沉积,成岩作用复杂,成岩作用是影响储层发育的重要因素。通过大量岩石薄片、铸体薄片、扫描电镜、X 射线衍射分析,并结合岩心观察、物性数据和测井数据,对清水河组一段储层的成岩作用特征进行研究,并分析了砂岩和砂砾岩储层成岩特征的区别。研究认为,石南地区清一段储层主要经历了压实、胶结和溶蚀三大成岩作用,其成岩阶段主要为早成岩B 期,局部处于中成岩A 期。压实作用是清一段砂岩储层物性损失的主要因素;而砂砾岩因刚性砾石格架的支撑作用使得压实相对较弱,成岩流体得以大量流经其原生孔隙,并进行大面积胶结,胶结作用是影响其物性的主要因素。溶蚀作用是改善储层物性的重要因素,砂岩储层主要因斜长石颗粒的溶蚀而产生粒内溶孔,砂砾岩储层则因方解石胶结物溶蚀而产生粒间溶孔和剩余粒间孔。溶蚀流体为二叠系烃源岩成熟过程中产生的酸性流体。石南地区清一段储层共划分出强压实相、强胶结相、中强压实中胶结相、中压实弱胶结相和中强压实弱溶蚀相5 类成岩相类型,且以中强压实中胶结相为主。该地区地势高部位中压实弱胶结成岩相的河道砂岩(如夏盐8 井区),以及断层发育区中强压实弱溶蚀成岩相的砂砾岩(如石西12、石南44、石南31 井区)可形成较好储层。
Diagenetic characteristics of the first member of Qingshuihe Formation in Shinan area,Junggar Basin,and its petroleum significance
[J].In the First Member of Qingshuihe Formation (Qing 1 Member) in Shinan area, the Junggar Basin, sandstones and glutenites are widely developed with complex diagenesis, which is an important factor affecting reservoir development. Based on analysis of thin sections, cast thin sections, scanning electron microscope (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD), together with core observation, physical property data and log data, the diagenetic characteristics of the Qing 1 Member reservoirs were studied and the differences of diagenetic characteristics between sandstone and glutenite reservoirs were analyzed. It is shown that the Qing 1 Member reservoirs experienced three diagenesis, i.e., compaction, cementation and dissolution, and they were mainly at Period B of early diagenesis and locally at Period A of middle diagenesis. Compaction is the major factor leading to the physical property loss of Qing 1 Member sandstone reservoirs. In glutenites, however, compaction was relatively weak due to the support of rigid gravels, so a large amount of diagenetic fluids flowed through its primary pores and were cemented in a large area. Therefore, cementation is the main factor affecting the physical properties of glutenites. Dissolution is an important factor for the improvement of reservoirs. In sandstone reservoirs, intragranular dissolved pores are produced by the dissolution of plagioclase grains. And in glutenite reservoirs, intergranular dissolved pores and residual intergranular pores are formed by the dissolution of calcite cement. Dissolution fluid is the acidic fluid generated during the maturation of the Permian source rocks. Five types of diagenetic facies are identified in the Qing 1 Member reservoirs in Shinan area, including strong compaction facies, strong cementation facies, mediumstrong compaction and medium cementation facies, medium compaction and weak cementation facies, and medium-strong compaction and weak dissolution facies. The medium-strong compaction and medium cementation facies is predominant. In this area, favorable reservoirs may exist in the channel sandstones of medium compaction and weak cementation facies at the structural highs (e.g. Xiayan 8 well block) and the glutenites of medium-strong compaction and weak dissolution facies in fault development zones (e.g. Shixi 12, Shinan 44 and Shinan 31 well blocks).
玛湖凹陷源上砾岩大油区形成分布与勘探实践
[J].
Discovery,distribution and exploration practice of large oil provinces of above-source conglomerate in Mahu Sag
[J].
准噶尔盆地莫西庄—永进地区白垩系清水河组地貌演化及沉积响应
[J].
Geomorphic evolution and sedimentary response of Cretaceous Qingshuihe formation in moxizhuang-yongjin area,Junggar Basin
[J].
准噶尔盆地白垩系岩相古地理
[J].
Lithofacies paleogeography of the Cretaceous in the Junggar Basin
[J].
准噶尔盆地石南地区清水河组沉积层序演化分析
[J].
Sedimentary sequence evolution analysis of Qingshuihe formation in Shinan area of Junggar Basin
[J].
准噶尔盆地夏盐凸起石南31井区下白垩统清水河组一段物源分析
[J].
Provenance analysis of the member 1 of lower Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation in SN31 well area in Xiayan uplift of Junggar Basin
[J].
准噶尔盆地石南31井区下白垩统清水河组一段辫状河三角洲相及沉积演化
[J].
Braided fluvial delta facies and sedimentary evolution of the member 1 of Qingshuihe Formation of lower Cretaceous in Shinan 31 wellblock,Junggar Basin
[J].
准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷白垩系清水河组低位体系域充填模式及油气勘探意义
[J].
Filling model of lowstand system tract of Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation in Fukang Sag in Junggar Basin and its significance on petroleum exploration
[J].
准噶尔盆地腹部缓坡型岩性地层油气藏成藏控制因素分析
[J].
Controlling factors of reservoir formation in ramp-type lithostratigraphic reservoir in hinterland of Junggar Basin
[J].
准噶尔盆地石南地区清水河组一段层序地层特征
[J].
Sequence stratigraphic characteristics of the first member of Qingshuihe formation in Shinan area,Junggar Basin
[J].
准噶尔盆地石南地区清水河组油气成藏条件
[J].
Conditions of oil and gas accumulation in Qingshuihe formation of Shinan area,Junggar Basin
[J].
准噶尔盆地白垩系储集层特征
[J].
Characteristics of Cretaceous reservoir rocks in Junggar Basin
[J].
准噶尔盆地SN31井区白垩系清一段一砂组沉积相及储层主控因素分析
[J].
Fine analysis of sedimentary facies and main controlling factors of reservoir in the first sand group of 1st member of Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation in SN31 well area of Junggar Basin
[J].
古地貌恢复方法综述
[J].
Review on methods of paleo-geomorphologic restoration
[J].
准噶尔盆地车排子凸起白垩系层序—古地貌耦合控砂机制与砂体预测
[J].
Coupling mechanism for sand control and sand body prediction of Cretaceous sequence and paleogeomorphology in the Chepaizi Uplift,Junggar Basin
[J].
古地貌对沉积体系和沉积微相的控制作用分析——以准噶尔盆地腹部白垩系清水河组为例
[J].
Controlling effect of paleogeomorphology on sedimentary system and sedimentary microfacies:A case study of Cretaceous Qingshuihe formation in the hinterland of Junggar Basin
[J].
A seismic geomorphology study of the fluvial and lacustrine-delta facies of the Cretaceous Quantou-Nenjiang Formations in Songliao Basin,China
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.01.017 URL [本文引用: 1]
Restoration of paleokarst geomorphology of sinian dengying formation in Sichuan Basin and its significance,SW China
[J].DOI:10.1016/S1876-3804(15)30021-5 URL [本文引用: 1]
Provenance of the Paleogene Colton Formation (Uinta Basin) and Cretaceous-Paleogene provenance evolution in the Utah foreland:Evidence from U-Pb ages of detrital zircons,paleocurrent trends,and sandstone petrofacies
[J].DOI:10.1130/GES00763.1 URL [本文引用: 1]
三角洲水下分流河道砂体地震预测方法研究——以塔河油田三叠系河道砂岩为例
[J].
A study of seismic prediction method of underwater distributary channel sandbody in delta:A case study of the Tahe Oilfied
[J].
油气检测多技术联合在B油田的应用研究
[J].
The application of multi-seismic hydrocarbon detection technology to gas identification in B oilfield
[J].
基于叠前同时反演的致密砂岩储层预测及含气性识别——以苏里格S区块为例
[J].
Prediction and identification of gas-bearing properties of tight sandstone reservoirs through simultaneous pre-stack inversion:A case study of block S in Sulige gas field
[J].
准噶尔盆地腹部白垩系清水河组清一段高分辨率层序地层特征及岩性油气藏预测
[J].
High-resolution sequence stratigraphic characteristic and lithological reservoir prediction of section,of Qingshuihe formation in the central of Junggar Basin
[J].
多属性融合定量储层预测方法研究与应用——以廊固凹陷杨税务潜山为例
[J].
Application of multi-attribute fusion in quantitative prediction of reservoirs:A case study of Yangshuiwu buried hill in Langgu Sag
[J].