0 引言
实际地下介质充满流体、裂缝及裂隙,因而表现出各向异性特征,这种现象也在实验室和波场测量中被观测到[1],使得各向异性成为地震波场数值模拟中越来越不容忽略的因素。
进行弹性波数值模拟时,得到的混合波场通常同时含有纵波和横波,而在进行地震偏移成像,尤其是弹性波逆时偏移成像时,须将纵、横波解耦,以得到物理意义明确的成像剖面[2]。为此,Alkhalifah[3-4]提出了声学近似假设下的拟声波方程,人为设定沿对称轴方向的横波速度为零,推导出标量形式的四阶微分方程。为了简化方程,提高计算效率,Du等[5]和Zhou等[6]通过不同的降阶方法,推导出不同形式的二阶耦合qP波微分方程。Duveneck等[7]从胡克定律和运动方程出发,推导得到另一种形式的拟声波方程,且其波场具有明确的物理意义。程玖兵等[8-9]推导得到各向异性介质的伪纯模式波动方程,使其在运动学上同弹性波动方程等价。
上述各方法均存在拟声波方程的突出缺点,即当模型参数中有变化较大的倾角和方位角时,会出现不稳定的现象[10]、残留着横波假象[11],或只有在Thomsen参数满足ε≥δ时正演模拟才是稳定的[12]。为了解决此类问题,有学者另辟蹊径,从qP波与qSV波的频散关系出发,直接解耦以构建纯qP波控制方程。要实现qP与qSV波的完全分离,关键在于导出简单、灵活的纯qP波控制方程和设计有效的拟微分求解算法。例如,Du等[5]和Zhang等[13]基于弱各向异性近似和平方根近似,推导出一种纯qP波解耦方程,其表现为时间—波数域形式,能较准确地描述TTI介质中的运动学特征;Zhan等[14]推导了一种新的解耦方程,将P波与SV波完全分离开来,并成功将其应用于逆时偏移中;Xu等[15]提出了一种纯qP波椭圆微分方程,通过将微分方程分解成一个标量算子和一个微分算子,并用椭圆分解方法修正标量算子,达到校正振幅误差的目的;胡书华等[16]则将Xu等[15]二阶微分方程做降阶处理,通过Lebedev交错网格,得到TTI介质下纯qP波的稳定传播;张庆朝等[17]利用近似相速度公式,导出TTI介质三维qP波频散方程及波动方程,并使用伪谱法做正演模拟;顾汉明等[18]将各向异性介质推广到黏声各向异性介质,通过Low-rank方法,实现了黏声各向异性介质纯qP波正演模拟。
纯qP波波动方程中往往存在着拟微分算子,谱方法能够较好地进行求解。伪谱法(pseudo spectral method,PSM)是一种早期发展出来的谱方法[19],其基本思想是通过傅里叶变换方法计算波场对空间的导数,在时间域通过有限差分法计算波场对时间的导数。正因如此,使得伪谱法具有非常高的空间精度,没有误差累积效应和空间频散,是一种较为理想的数值模拟方法。由于伪谱法计算时间导数时采用的是有限差分,使得其具有时间频散,为了解决这一问题,Etgen等[20]提出了伪解析算法,其基本思想是波数域推导时间误差补偿因子并作用于拉普拉斯算子,从而补偿在伪谱法中因时间导数的二阶差分造成的误差,达到进一步提高数值模拟精度的目的;Chu等[21]在Etgen提出的伪解析法的基础上,提出了归一化伪拉普拉斯算子的伪解析法,随后,张衡等[22]将这一方法运用于解耦的TTI介质波动方程中,得到了高精度的地震波场,在时间和空间上能够同时达到Nyquist频率。
本文在前人的研究基础上,将qP波拟微分方程变换到空间—波数域,并通过坐标变换,推导了时间域TTI介质二阶纯qP波波动方程,引入伪解析算法,实现了基于伪解析法的TTI介质纯qP波地震波场正演模拟。通过简单和复杂模型测试,验证了本文方法的正确性及对复杂介质的适用性。
1 时间域TTI介质二阶纯qP波波动方程
为了推导本文的TTI介质纯qP波方程,首先从如下VTI介质qP波标量方程
出发[23]。式中,Q为拟微分算子,其具体表达式为
式中:t为时间坐标;x、y、z为空间坐标;p为地震波场;v0为qP波垂直速度;ε、δ为Thomsen参数。
式(1)控制着VTI介质中qP波的传播,其中所有参数都是随空间变化的,且与混合波场中纵波有着一样的频散关系,即相位相同,能够准确地表征其运动学特征。
将式(1)变换到频率—波数域中有
式中:ω为角频率;kh为水平方向波数,并有
将式(3)改写为
式中:k=(kx,ky,kz)为波数矢量;
将式(4)重新改写为
记椭圆微分算子Se为
则将式(6)变换到时间域有
二维情况下有
式(9)即为二维VTI介质二阶纯qP波方程。从VTI介质转换到TTI介质,可做如下坐标变换[24]:
式中:θ为TTI介质中的极化角;Gx、Gz分别为x、z方向经过坐标旋转后新的一阶微分算子;Hx、Hz分别为x、z方向经过坐标旋转后新的二阶微分算子。
将式(10)代入式(9)中即可得到二维TTI介质纯qP波方程:
式(11)克服了拟声波方程的局限性,消除了伪横波干扰,不受模型参数限制且地震波场能稳定传播,能够准确地表征地震波场的运动学特征。
伪谱法可以很好求解式(11),即有
式中:Δt为时间步长;
式中,
2 伪解析法
在用伪谱法进行数值模拟时,虽然在空间方向能达到一个波长两个采样点的Nyquist谱精度,但波场对时间的导数仍用有限差分方法计算。因此,在时间方向上仍存在时间频散。而另一种谱方法,即伪解析方法(pseudo analytical method,PAM)能够较好地解决上述问题,并且相比于伪谱法,精度能够进一步提高,使得空间和时间方向上均无频散。其主要思想是在波数域通过修正拉普拉斯算子来达到对时间方向上的有限差分离散误差进行补偿的目的。
对于二阶声波方程,有
其二阶时间离散形式有
对上式进行傅里叶变换并利用时移定理有
化简上式并代入ω=v0|k|有
因此,式(17)的伪解析法为
定义归一化伪拉普拉斯(NPL)算子[21]有
则式(17)的NPL伪解析法为
从上式可看出,
故,式(11)的伪解析法格式为
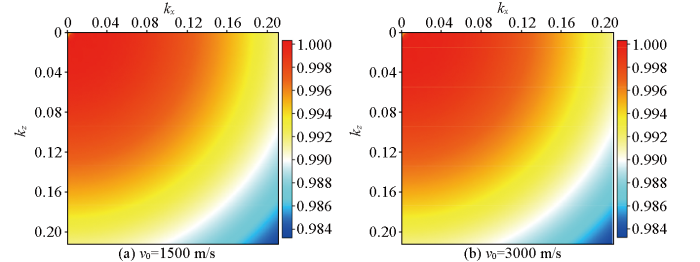
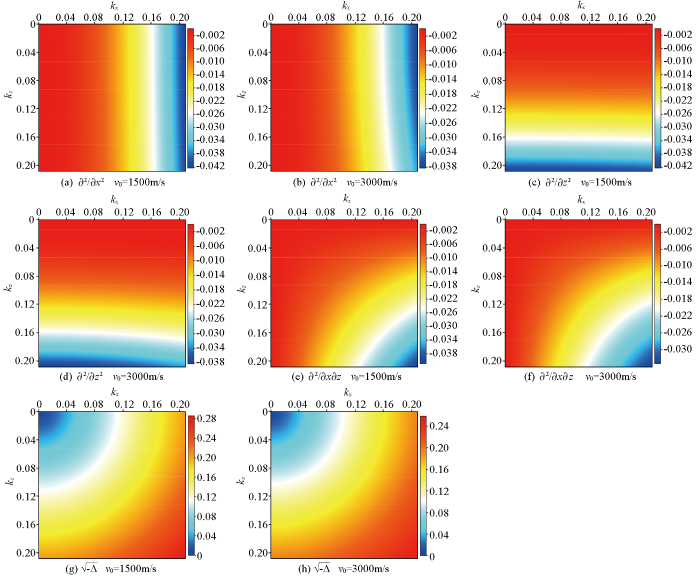
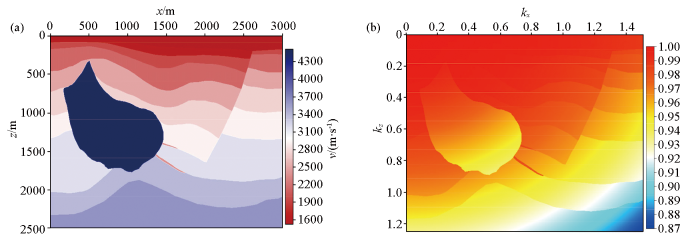
伪解析法能够准确地补偿时间方向二阶差分所造成的误差,得益于其一个重要特性,即归一化伪拉普拉斯算子的空间导数项随速度的变化缓慢,使得其能够较为准确地补偿时间方向上的误差。为了说明其空间导数项随速度变化缓慢的特点,采用速度1 500 m/s和3 000 m/s作为对比,时间步长为0.001 s,选择波数范围为[0,0.21]。图1为不同速度时的归一化伪拉普拉斯(NPL)算子;图2为基于归一化伪拉普拉斯算子的各类空间二阶导数,包括x方向二阶导数、z方向二阶导数、 xz方向混合二阶导数及拟微分算子;图3为基于Hess复杂介质模型的归一化伪拉普拉斯算子。从图1~3中可以发现,归一化伪拉普拉斯算子及各类空间二阶导数均随速度变化缓慢,能够适应较复杂介质。
图1
图2
图2
基于归一化伪拉普拉斯(NPL)算子的空间二阶导数
Fig.2
A second derivative of space based on normalized pseudo-Laplace(NPL) operators
图3
图3
复杂介质模型下的归一化伪拉普拉斯(NPL)算子
a—Hess复杂介质模型;b—Hess模型的NPL
Fig.3
Normalized pseudo-Laplace (NPL) operator under complex media model
a—Hess complex media model;b—NPL for the Hess model
3 模型试算
3.1 均匀模型
为了验证本文构建的二维TTI介质纯qP波方程不受模型参数的限制,且无伪横波干扰,设计了尺寸为2 000 m×2 000 m的均匀介质模型。其空间网格大小为5 m×5 m,时间步长为1 ms,总时间采样点数为1 000,记录长度为1 s;纵波震源位于模型中心,采用主频为25 Hz的Ricker子波震源;边界条件为海绵边界条件;接收排列范围是0~2 000 m,排列深度为750 m,道间距为10 m,共201道接收。其均匀介质弹性参数见表1。
表1 均匀介质模型参数
Table 1
| 介质类型 | v0/(m·s-1) | ρ/(g·cm-3) | ε | δ | θ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 1700 | 2.5 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0° |
| Ⅱ | 1700 | 2.5 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 90° |
| Ⅲ | 1700 | 2.5 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 45° |
| Ⅳ | 1700 | 2.5 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 45° |
| Ⅴ | 1700 | 2.5 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 45° |
图4
图4
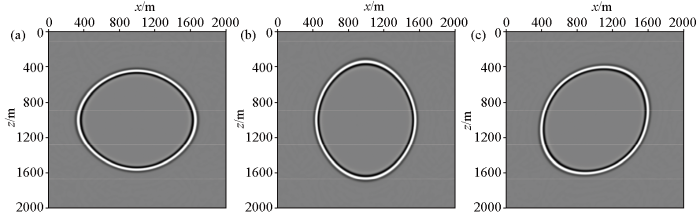
均匀声学TTI介质拟声波方程(上)和纯qP波方程(下)400 ms时刻波场快照
a、d—对应介质类型Ⅲ; b、e—对应介质类型Ⅳ; c、f—对应介质类型Ⅴ
Fig.4
Snapshot of the 400 ms moment wave field for uniform acoustic TTI medium pseudoacoustic wave equation (top) and pure qP wave equation (bottom)
a,d—corresponding media type III;b,e—corresponding media type IV;c,f—corresponding media type V
图5
图5
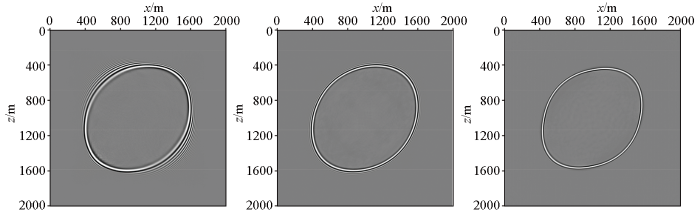
纯qP波方程在均匀各向异性介质中400 ms时刻波场快照
a—介质类型Ⅰ; b—介质类型Ⅱ; c—介质类型Ⅲ
Fig.5
Pure qP wave equation snapshot of the wave field at 400 ms in a homogeneous anisotropic medium
a—media type Ⅰ; b—media type Ⅱ; c—media type Ⅲ
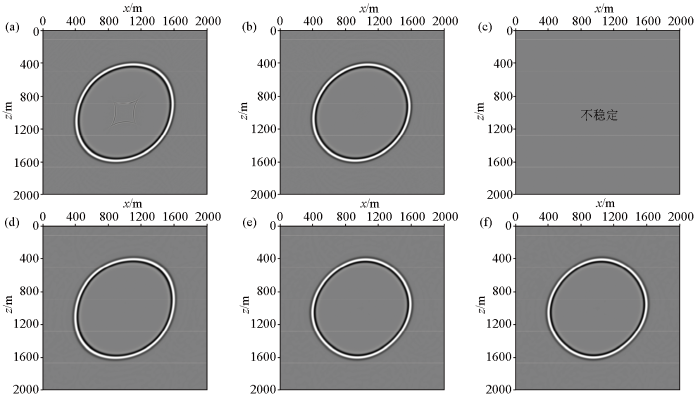
为了说明伪解析法的计算精度,设计了大小为2 000 m×2 000 m的均匀介质TTI模型,空间网格间距为5 m×5 m,时间步长1 ms,采用60 Hz主频的Ricker子波,采用海绵边界条件,纵波震源位于模型中心,模型参数为纵波波速为1 700 m/s,ε=0.25,δ=0.1,θ=45°,由于60 Hz主频的Ricker子波最大频率约为150 Hz,最大纵波速度为1 700 m/s,空间网格间距为5 m,因此一个波长内的采样点数约为1700/150/5=2.2个,基本达到了Nyquist采样定理极限精度的要求。
图6
图6
均匀TTI介质纯qP波350 ms时刻波场快照
a—有限差分法(FDM); b—伪谱法(PSM); c—伪解析法(PAM)
Fig.6
Snapshot of the 350 ms time wave of pure qP wave in uniform TTI medium
a—finite difference method(FDM); b—pseudo spectral method(PSM); c—pseudo analytical method(PAM)
3.2 复杂BP模型
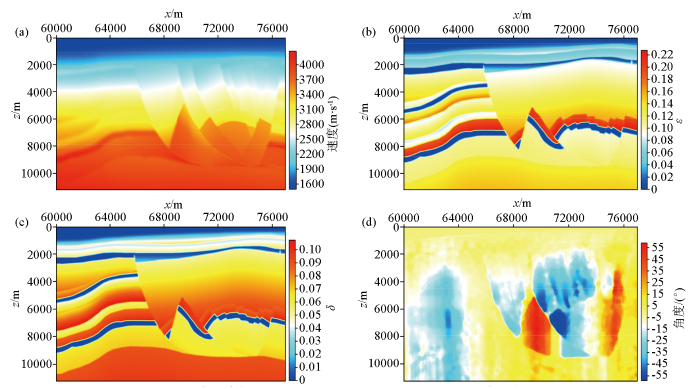
为检验所提方法对倾角剧变复杂介质的稳定性,截取一段倾角变化范围是-55°~55°的二维BP2007声学TTI介质模型进行测试。该模型规模为17 km×11.25 km,空间网格单元为6.25 m×6.25 m,时间步长为5 ms,总时间采样点为1 600,记录长度为8 s,纵波震源位于(68.5 km,0),采用主频为20 Hz的Ricker子波震源,采用海绵边界条件,接收排列范围是0~17 km,排列深度为0,接收点间距为25 m,共681道接收,模型参数见图7。
图7
图7
二维BP2007声学TTI介质模型参数
a—纵波速度v0;b—纵波各向异性参数ε;c—变异系数δ;d—极化角θ
Fig.7
Two-dimensional BP2007 acoustic TTI media model parameters
a—P-wave velocity v0;b—P-wave anisotropy parameters ε;c—variation coefficient δ;d—polarization angle θ
图8
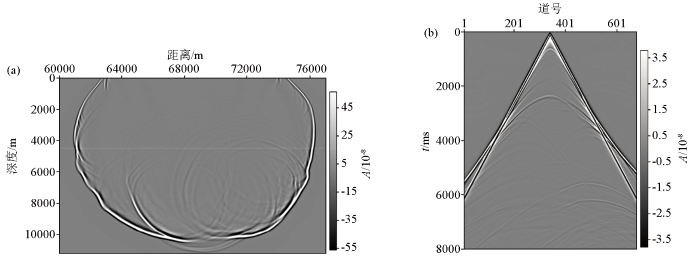
图8
二维BP2007声学TTI介质4 s时刻波场快照(a)及地震记录(b)
Fig.8
Two-dimensional BP2007 acoustic TTI medium 4 s time wave field snapshot(a) and seismic record(b)
4 结论
本文在前人的研究基础上,将qP波拟微分方程变换到空间—波数域,并通过坐标变换,推导了时间域TTI介质二阶纯qP波波动方程,引入伪解析算法,实现了基于伪解析法的TTI介质纯qP波地震波场正演模拟。通过多种模型的测试,得出以下认识和结论:
1)克服了拟声波方程的局限性,消除了伪横波干扰,不受模型参数限制且地震波场能稳定传播,具有较为广泛的应用前景;
2)与其他方法相比(有限差分法及伪谱法),伪解析法能有效提高数值模拟精度;
3)简单及复杂模型测试验证了本文方法的正确性与适用性,能够适应复杂介质,且具有更高的计算精度。
参考文献
Attenuation anisotropy in the linear-slip model: Interpretation of physical modeling data
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.3173806
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This study attempts to validate a mathematical formalism of introducing attenuation into Schoenberg’s linear slip model. This formalism is based on replacing the real-valued weaknesses by complex-valued ones. During an ultrasonic experiment, performed at a central frequency of [Formula: see text] on a plate-stack model with [Formula: see text]-thick Plexiglas™ plates, the velocity and attenuation (inverse of the quality factor [Formula: see text]) of P-, SH-, and SV-waves are measured in directions from 25° to 90° with the symmetry axis for dry and oil-saturated models and loading uniaxial pressures of 2 and [Formula: see text]. The velocity and attenuation data are fitted by the derived theoretical functions. The values of the real and imaginary parts of the complex-valued weaknesses are estimated. Thereal parts of the weaknesses, which have a clear physical meaning (they affect the weakening of the material), are three times larger for the dry model than for the oil-saturated one. The imaginary parts of the weaknesses are responsible for attenuation; their values are an order of magnitude smaller than the real parts. The derived expressions for angle-dependent velocities and attenuations can be used to distinguish between dry and oil-saturated fractures. In particular, the P-wave attenuation function in the symmetry-axis direction (normal to fracture planes) is different in dry and saturated media. The experiment shows that the plate-stack model is inhomogeneous because of the nonuniform pressure distribution, which degrades the experimental results and creates difficulties in the inversion for the complex-valued weaknesses — particularly in joint inversion of P- and S-wave data.
逆时偏移成像技术研究进展
[J].
Progress in reverse time migration imaging
[J].
An acoustic wave equation for anisotropic media
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.1444815
URL
[本文引用: 1]

A wave equation, derived using the acoustic medium assumption for P-waves in transversely isotropic (TI) media with a vertical symmetry axis (VTI media), yields a good kinematic approximation to the familiar elastic wave equation for VTI media. The wavefield solutions obtained using this VTI acoustic wave equation are free of shear waves, which significantly reduces the computation time compared to the elastic wavefield solutions for exploding‐reflector type applications. From this VTI acoustic wave equation, the eikonal and transport equations that describe the ray theoretical aspects of wave propagation in a TI medium are derived. These equations, based on the acoustic assumption (shear wave velocity = 0), are much simpler than their elastic counterparts, yet they yield an accurate description of traveltimes and geometrical amplitudes. Numerical examples prove the usefulness of this acoustic equation in simulating the kinematic aspects of wave propagation in complex TI models.
Acoustic approximations for processing in transversely isotropic media
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.1444361
URL
[本文引用: 1]

When transversely isotropic (VTI) media with vertical symmetry axes are characterized using the zero‐dip normal moveout (NMO) velocity [[Formula: see text]] and the anisotropy parameter ηinstead of Thomsen’s parameters, time‐related processing [moveout correction, dip moveout (DMO), and time migration] become nearly independent of the vertical P- and S-wave velocities ([Formula: see text] and [Formula: see text], respectively). The independence on [Formula: see text] and [Formula: see text] is well within the limits of seismic accuracy, even for relatively strong anisotropy. The dependency on [Formula: see text] and [Formula: see text] reduces even further as the ratio [Formula: see text] decreases. In fact, for [Formula: see text], all time‐related processing depends exactly on only [Formula: see text] and η. This fortunate dependence on two parameters is demonstrated here through analytical derivations of time‐related processing equations in terms of [Formula: see text] and η. The time‐migration dispersion relation, the NMO velocity for dipping events, and the ray‐tracing equations extracted by setting [Formula: see text] (i.e., by considering VTI as acoustic) not only depend solely on [Formula: see text] and η but are much simpler than the counterpart expressions for elastic media. Errors attributed to this use of the acoustic assumption are small and may be neglected. Therefore, as in isotropic media, the acoustic model arising from setting [Formula: see text], although not exactly true for VTI media, can serve as a useful approximation to the elastic model for the kinematics of P-wave data. This approximation can boost the efficiency of imaging and DMO programs for VTI media as well as simplify their description.
Reverse-time migration for tilted TI media
[C]//
An anisotropic acoustic wave equation for modeling and migration in 2D TTI media
[C]//
Acoustic VTI wave equations and their application for anisotropic reverse-time migration
[C]//
各向异性介质qP波传播描述Ⅱ:分离纯模式标量波
[J].
DOI:10.6038/cjg20141025
[本文引用: 1]

在各向异性地震波场中,qP波与qS波常常是耦合在一起的.多分量地震数据处理中一个关键环节就是波型分离(即模式解耦),以纵波成分为主的常规单分量地震数据的成像则需要合理描述标量qP波的传播算子.本文作者曾构建了在运动学上同弹性波动方程等价,动力学上突出标量qP波的伪纯模式波动方程.为了彻底消除qS波残余,本文根据波矢量与qP波偏振矢量之间的偏差,提出从伪纯模式波场提取纯模式标量qP波的方法.数值分析展示了投影偏差算子在波数域和空间域的特征.基于不同复杂程度理论模型的试验结果表明,联合"伪纯模式传播算子"与"投影偏差校正"可为各向异性介质分离模式波场传播过程提供一种简便的描述工具.
Description of qP-wave propagation in anisotropic media,Part II:Separation of pure-mode scalar waves
[J].
各向异性介质qP波传播描述Ⅰ:伪纯模式波动方程
[J].
Description of qP-wave propagation in anisotropic media,Part Ⅰ:Pseudo-pure-mode wave equations
[J].
Stable P-wave modeling for reverse-time migration in tilted TI media
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.3533964
URL
[本文引用: 1]

We present an approach for P-wave modeling in inhomogeneous transversely isotropic media with tilted symmetry axis (TTI media), suitable for anisotropic reverse-time migration. The proposed approach is based on wave equations derived from first principles — the equations of motion and Hooke’s law — under the acoustic TI approximation. Consequently, no assumptions are made about the spatial variation of medium parameters. A rotation of the stress and strain tensors to a local coordinate system, aligned with the TI-symmetry axis, makes it possible to benefit from the simple and sparse form of the TI-elastic tensor in that system. The resulting wave equations can be formulated either as a set of five first-order or as a set of two second-order partial differential equations. For the constant-density case, the second-order TTI wave equations involve mixed and nonmixed second-order spatial derivatives with respect to global, nonrotated coordinates. We propose a numerical implementation of these equations using high-order centered finite differences. To minimize modeling artifacts related to the use of centered first-derivative operators, we use discrete second-derivative operators for the nonmixed second-order spatial derivatives and repeated discrete first-derivative operators for the mixed derivatives. Such a combination of finite-difference operators leads to a stable wave propagator, provided that the operators are designed properly. In practice, stability is achieved by slightly weighting down terms that contain mixed derivatives. This has a minor, practically negligible, effect on the kinematics of wave propagation. The stability of the presented scheme in inhomogeneous TTI models with rapidly varying anisotropic symmetry axis direction is demonstrated with numerical examples.
Shear waves in acoustic anisotropic media
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.1707077
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Acoustic transversely isotropic (TI) media are defined by artificially setting the shear‐wave velocity in the direction of symmetry axis, VS0, to zero. Contrary to conventional wisdom that equating VS0= 0 eliminates shear waves, we demonstrate their presence and examine their properties. Specifically, we show that SV‐waves generally have finite nonzero phase and group velocities in acoustic TI media. In fact, these waves have been observed in full waveform modeling, but apparently they were not understood and labeled as numerical artifacts.
改进的TTI介质纯P波方程正演模拟与逆时偏移
[J].
DOI:10.6038/cjg20170121
[本文引用: 1]

逆时偏移作为一种高精度偏移方法已成为复杂构造成像的重要技术,描述纵波独立传播的延拓方程是各向异性介质逆时偏移的一个关键问题.在对VTI介质几个经典相速度近似公式回顾的基础上,针对常用于描述纯P波的Harlan近似公式在各向异性参数ε较大情况下近似精度较低的问题,本文对Harlan公式中的非椭圆项进行了修正,在非椭圆项前添加了一个与各向异性参数ε有关的修正系数,得到了三种改进型Harlan公式,并以近似精度最高的改进式为基础,推导了TTI介质纯P波方程.针对该伪微分方程,本文利用伪谱法和有限差分法联合实现波场延拓,对于常密度二阶方程,基于中心网格实现;对于一阶应力-速度方程则基于旋转交错网格实现.通过数值试验分析了TTI介质纯P波一阶应力-速度方程的近似精度,并以一阶纯P波方程为基础进行了TTI介质逆时偏移数值模拟试验.结果表明,本文给出的方法能够较准确地描述TTI介质纯P波波场特征,可以应用至各向异性介质逆时偏移.
Numerical simulation and reverse time migration using an improved pure P-wave equation in tilted transversely isotropic media
[J].
A stable TTI reverse time migration and its implementation
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.3554411
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Modeling and reverse time migration based on the tilted transverse isotropic (TTI) acoustic wave equation suffers from instability in media of general inhomogeniety, especially in areas where the tilt abruptly changes. We develop a stable TTI acoustic wave equation implementation based on the original elastic anisotropic wave equation. We, specifically, derive a vertical transversely isotropic wave system of equations that is equivalent to their elastic counterpart and introduce the self-adjoint differential operators in rotated coordinates to stabilize the TTI acoustic wave equations. Compared to the conventional formulations, the new system of equations does not add numerical complexity; a stable solution can be found by either a pseudospectral method or a high-order explicit finite difference scheme. We demonstrate by examples that our method provides stable and high-quality TTI reverse time migration images.
Decoupled equations for reverse time migration in tilted transversely isotropic media
[J].
DOI:10.1190/geo2011-0175.1
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Conventional modeling and migration for tilted transversely isotropic (TTI) media may suffer from numerical instabilities and shear wave artifacts due to the coupling of the P-wave and SV-wave modes in the TTI coupled equations. Starting with the separated P- and SV-phase velocity expressions for vertical transversely isotropic (VTI) media, we extend these decoupled equations for modeling and reverse time migration (RTM) in acoustic TTI media. Compared with the TTI coupled equations published in the geophysical literature, the new TTI decoupled equations provide a more stable solution due to the complete separation of the P-wave and SV-wave modes. The pseudospectral method is the most convenient method to implement these equations due to the form of wavenumber expressions and has the added benefit of being highly accurate and thus avoiding numerical dispersion. The rapid expansion method (REM) in time is employed to produce a broad band numerically stable time evolution of the wavefields. Synthetic results validate the proposed TTI decoupled equations and show that modeling and RTM in TTI media with the decoupled equations remain numerically stable even for models with strong anisotropy and sharp contrasts.
Quasi-P wave propagation with an elliptic differential operator
[C]//
复杂TTI介质稳定的纯qP波波场模拟方法
[J].
Pure quasi-P wave stable simulation in complex TTI media
[J].
TTI介质qP波伪谱法正演模拟
[J].
qP-wave numerical simulation in TTI media with pseudo-spectral method
[J].
基于Low-rank一步法波场延拓的黏声各向异性介质纯qP波正演模拟
[J].
Low-rank one-step wave extrapolation for pure qP-wave forward modeling in viscoacoustic anisotropic media
[J].
Comparison of accurate methods for the integration of hyperbolic equations
[J].
The pseudo-analytical method:Application of pseudo-Laplacians to acoustic and acoustic anisotropic wave propagation
[C]//
Acoustic anisotropic wave modeling using normalized pseudo-laplacian
[C]//
TTI介质伪解析解耦波动方程
[J].
Pseudo-analytical decoupled wave equation for TTI media
[J].
Accurate simulations of pure quasi-P-waves in complex anisotropic media
[J].
DOI:10.1190/geo2014-0242.1
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Reverse time migration (RTM) in complex anisotropic media requires calculation of the propagation of a single-mode wave, the quasi-P-wave. This was conventionally realized by solving a [Formula: see text] system of second-order partial differential equations. The implementation of this [Formula: see text] system required at least twice the computational resources as compared with the acoustic wave equation. The S-waves, an introduced auxiliary function in this system, were treated as artifacts in the RTM. Furthermore, the [Formula: see text] system suffered numerical stability problems at the places in which abrupt changes of symmetric axis of anisotropy exist, which brings more challenges to real data implementation. On the other hand, the Alkhalifah’s equation, which governs the pure quasi-P-wave propagation, was hard to solve because it was a pseudodifferential equation. We proposed a pure quasi-P-wave equation that can be easily implemented within current imaging framework. Our new equation was obtained by decomposing the original pseudodifferential operator into two numerical solvable operators: a differential operator and a scalar operator. The combination of these two operators yielded an accurate phase of quasi-P-wave propagation. Our solution was S-wave free and numerically stable for very complicated models. Because only one equation was required to resolve numerically, the new proposed scheme was more efficient than those conventional schemes that solve the [Formula: see text] second-order differential equations system. For tilted transverse isotropy (TTI) RTM implementation, the required increase of numerical cost was minimal, and we could expect at least a factor of two of improvement of efficiency. We showed the effectiveness and robustness of our method with numerical examples with simple and very complicated TTI models, the SEG Advanced Modeling (SEAM) model. Further extension of our approach to orthorhombic anisotropy or tilted orthorhombic anisotropy was straightforward.
Anisotropic viscoacoustic wave RTM based on second-order quasi-differential equation
[C]//