0 引言
1999,中国地质调查局在全国组织实施1∶25万多目标区域地球化学调查(又称土地质量地球化学调查、农业地质调查)[6]。广西壮族自治区自2007年开始开展1∶25万多目标区域地球化学调查工作,并于2013年在前期1∶25万多目标区域地球化学调查工作的基础上,以县为评价单元开展1∶5万土地质量地球化学评价。本研究依托南宁地区1∶25万多目标区域地球化学调查和南宁市西乡塘区1∶5万土地质量地球化学评价的成果数据,对南宁市区范围内典型农用地土壤重金属元素的累积趋势进行预测,为广西土壤重金属元素的监测、预测、预警提供研究案例。
1 研究区背景
西乡塘区位于广西南宁市区西北部,地处东经107°58'26″~108°21'04″、北纬22°45'40″~23°05'30″,东、西、北面分别与兴宁区、隆安县、扶绥县和武鸣县接壤,南隔邕江与江南区相望,行政区域土地总面积1 298 km2。西乡塘区自2005年3月经国务院批准成立,是南宁市人口最多、建成区人口密度最大的城区。全年气候温热潮湿,阳光充足,雨量充沛,农业资源丰富,已建成多个万亩农产品示范基地,着力发展城郊型现代农业,是广西重要的蔬菜、水果产区。西乡塘区土地利用类型以旱地、水田、果园为主,土壤成土母质包括砂岩砂砾岩类、灰岩白云岩类的残坡积洪冲积物,土壤类型以赤红壤、水稻土、紫色土、石灰岩土、冲积土等为主[7-8]。
2 研究基础
2.1 1∶25万多目标区域地球化学调查
广西壮族自治区地质调查院于2007年开展了南宁地区1∶25万多目标区域地球化学调查,西乡塘区是该调查范围其中的一部分。调查工作技术方法按照《多目标区域地球化学调查规范》(1∶250 000)[9]进行,其中表层土壤采样密度为1个点/km2,采样深度为20 cm,采样时在布设点位周围100 m范围内采集3~5处子样点,等量合成为该点位的样品,将4 km2的4个单点样等量混匀为一个组合样进行分析测试。研究区内表层土壤组合样品(分析测试样品)数为189件。
2.2 1∶5万土地质量地球化学评价
广西壮族自治区三○七核地质大队于2017年开展了西乡塘区1∶5万土地质量地球化学评价,评价工作技术方法按照《土地质量地球化学评价规范》[10]进行,其中表层土壤样以网格(1 km2)为主兼顾图斑的原则布设,充分体现代表性和均匀性,平均采样密度为6.9件/km2,采样深度为20 cm,采样时在布设点周围50 m范围内采集3~5处子样点,等量合成为该点位的样品。研究区内样品数为6 524件,单点样进行分析测试。除了表层土壤样品,按照规范同步采集大气干湿沉降物样品、灌溉水样品、农作物样品、根系土样品、化肥样品、岩石样品等辅助类样品。
2.3 数据质量
表1 表层土壤调查样品分析方法及检出限
Table 1
| 分析 指标 | 要求检 出限 | 1∶25万多目标区域 地球化学调查 | 1∶5万土地质量 地球化学评价 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分析方法 | 实际检出限 | 分析方法 | 实际检出限 | ||
| As | 1.0 | AFS | 0.2 | AFS | 0.2 |
| Cd | 0.03 | GFAAS | 0.02 | ICP-MS | 0.02 |
| Cr | 5 | XRF | 3 | XRF | 2 |
| Hg | 0.0005 | AFS | 0.0004 | AFS | 0.0002 |
| Pb | 2.0 | XRF | 1.5 | XRF | 1.0 |
| pH | 0.10 | ISE | 0.08 | ISE | 0.01 |
注:AFS为原子荧光光谱法;GFAAS为石墨炉原子吸收法;ICP-MS为等离子质谱法;XRF为X射线荧光光谱法;ISE为pH计电极法。As、Cd、Cr、Hg、Pb含量单位为10-6,pH无量纲。
样品分析质量由外部质量控制和内部质量控制组成,同时为评估野外采样质量和分析质量,按照样品总量2%的比例采集重复样,每50个基本样中随机密码插入一个重复样。外部质量控制为每个分析批次(50个号码)样品中密码随机插入4件外部标准控制样品与基本样品同时分析,由负责区域化探样品分析质量的检查组按工作区分别计算单元素合格率、相关系数、F检验值、中位值等测试质量技术指标,并进行总体评估,要求单元素合格率≥90%,相关系数(r)≥0.900。内部质量控制包括准确度、精密度控制、报出率控制、样品分析的重复性检验及异常点重复性检验。国家一级标准物质监控样分析准确度、精密度结果见表2,密码重复样分析结果计算双差,要求相对双差合格率≥85%(详见表3)。
表2 表层土壤调查样品一级标准物质分析准确度、精密度
Table 2
| 指标 | 1∶25万多目标区域地球化学调查 | 1∶5万土地质量地球化学评价 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 准确度 | 精密度 | 合格率 | 准确度 | 精密度 | 合格率 | |||||
| 最小值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 最大值 | |||
| As | -0.013 | 0.023 | 0.007 | 0.042 | 100% | -0.061 | 0.086 | 0.002 | 0.061 | 100% |
| Cd | -0.045 | 0.050 | 0.010 | 0.076 | 100% | -0.096 | 0.090 | 0.003 | 0.080 | 100% |
| Cr | -0.014 | 0.014 | 0.002 | 0.037 | 100% | -0.062 | 0.069 | 0.010 | 0.048 | 100% |
| Hg | -0.008 | 0.040 | 0.006 | 0.046 | 100% | -0.100 | 0.098 | 0.007 | 0.072 | 100% |
| Pb | -0.015 | 0.021 | 0.007 | 0.043 | 100% | -0.097 | 0.085 | 0.009 | 0.069 | 100% |
| pH | 0.01 | 0.10 | 100% | 0.01 | 0.07 | 100% | ||||
注:pH单独计算与标准物质的绝对误差ΔpH。
表3 表层土壤调查重复样合格率统计
Table 3
| 指标 | 1∶25万多目标 区域地球化学调查 | 1∶5万土地 质量地球化学评价 |
|---|---|---|
| As | 93.33% | 97.42% |
| Cd | 86.67% | 92.90% |
| Cr | 98.67% | 100.00% |
| Hg | 86.67% | 94.84% |
| Pb | 98.67% | 98.06% |
| pH | 100.00% | 100.00% |
样品的分析测试由中国地质调查局区域化探样品测试质量监督检查组的专家对测试成果和分析质量进行评审验收。所有样品分析测试全部通过验收,样品分析方法、测试质量均符合或优于规范要求。
3 预测模型构建
3.1 点位数据配对
研究区内两组调查样本的间隔时间为10年,调查范围(样本重叠区域)776 km2。为便于讨论,将研究区内1∶25万多目标区域地球化学调查采集的表层土壤样点数据集称为WA,将1∶5万土地质量地球化学评价采集的全部表层土壤样点数据集称为WB1,二者除了调查比例尺引起的采样密度有差别以外,在采样技术方法、样品加工、野外工作质量监控、样品测试、分析数据验收等关键环节基本一致。
进一步验证WA和WB1两组数据的可比性,首先以1∶25万多目标区域地球化学调查的调查单元(1 km×1 km)为基础,对WA和WB1的样品点位信息进行空间分析,以WA采样点位为中心,在WB1点位中搜索与WA采样点距离最近的点位,并进行两两配对。最终经统计,配对的点位距离在10~300 m之间,88%的点位间距在200 m以内,这就在工作及研究尺度上基本保证了两组样本中每个采样点位100 m范围内采集3~5处子样点的位置是比较接近的。将配对形成的新的数据集称为WB2,共包含697个点位;对WB2进一步处理,即按照WA划定评价单元(2 km×2 km),每4 km2内的配对点数据取平均值,获得数据集WB3,共包含189个点位数据(图1)。
图1
表4 表层土壤调查样点元素含量及pH算术平均值统计
Table 4
| 数据集 | 数据量 | w(As)/10-6 | w(Cd)/10-6 | w(Cr)/10-6 | w(Hg)/10-6 | w(Pb)/10-6 | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
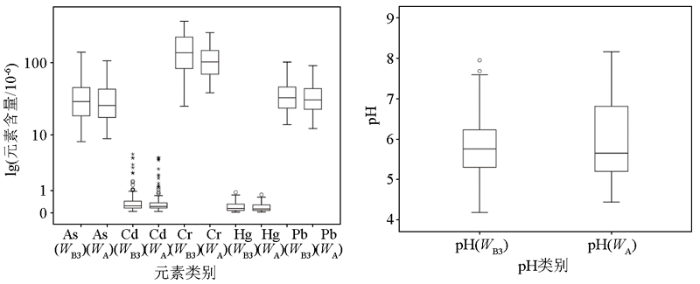
| WA | 189 | 32.71 | 0.448 | 111.50 | 0.194 | 35.18 | 5.97 |
| WB1(全区平均) | 6524 | 37.68 | 0.439 | 154.49 | 0.222 | 37.49 | 5.73 |
| WB2(调查配对点1km2) | 697 | 37.51 | 0.467 | 156.89 | 0.221 | 38.27 | 5.81 |
| WB3(分析配对点4km2) | 189 | 36.47 | 0.456 | 154.31 | 0.218 | 37.78 | 5.82 |
进一步对WB3和WA进行统计比较,从成对数据相关性分析和t检验结果来看(表5),WB3和WA对应元素指标均呈现显著相关(p<0.01),5个重金属元素相关系数达到0.9以上;As、Cr、Hg、Pb的t检验结果p值均小于0.01,说明两组元素含量数据是有显著性差异的,且WB3大于WA,而Cd则差异性不明显。从图2中可看出,两组数据对应的重金属元素含量分布形式基本一致,统计值中算数平均值、几何平均值以及中位值均近似且WB3略大于WA。两组数据的pH值同样呈现显著相关性(p<0.01),但相关系数不高,t检验结果p<0.5显示pH值也出现显著变化,且WB3小于WA;pH值分布形式近似,统计值中算术平均值、几何平均值均为WB3小于WA,中位值出现WB3略大于WA的原因可能为pH值的值域范围较小所致。
表5 WB3和WA中元素含量及pH相关性、t检验统计
Table 5
| 元素 类别 | 样本 数量 | 相关性分析 | t检验 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 相关系数 | Sig. | t | Sig.(双侧) | ||
| As(WB3)-As(WA) | 189 | 0.91** | 0 | 4.86 | 0 |
| Cd(WB3)-Cd(WA) | 189 | 0.91** | 0 | 0.38 | 0.70 |
| Cr(WB3)-Cr(WA) | 189 | 0.92** | 0 | 13.90 | 0 |
| Hg(WB3)-Hg(WA) | 189 | 0.90** | 0 | 4.74 | 0 |
| Pb(WB3)-Pb(WA) | 189 | 0.96** | 0 | 6.67 | 0 |
| pH(WB3)-pH(WA) | 189 | 0.66** | 0 | -2.81 | 0.01 |
注:“**”表示在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关。
图2
因此,WB3点位数据具备与WA的可比性,后续将统一采用WB3代表1∶5万土地质量地球化学评价的一一配对数据。
3.2 预测模型的选择
式中:Wt为预测经历了t年的土壤重金属含量;W0为土壤初始的重金属含量;ΔW为重金属含量的年变化率。
预测的关键是求取土壤重金属含量的年变化率ΔW,本研究选择以下2种预测模型进行比较。
3.2.1 单时段增量模型
式中:ΔW1为该模型2007~2017年的重金属含量的年变化率(kg/(km2·a));WB3为2017年的土壤重金属含量(10-6);WA为2007年的土壤重金属含量(10-6);T为两组数据的间隔时间为10年;Wt为预测经历了t年的土壤重金属含量(10-6);t为预测年限。
3.2.2 输入输出通量模型
相对于漫长的地质历史成壤过程,本研究的调查时间、预测时间均较短,同时限于收集的资料和调查数据,暂不考虑成土风化、土壤侵蚀以及蒸发作用对土壤元素含量的影响,此外广西绝大部分地区已实行秸秆返田,在农作物及秸秆返田方面也考虑农作物籽实(可食用部分)的离田输出。
设W0为土壤重金属初始含量(10-6),Wt为之后某一时点的土壤重金属含量(10-6);Win为一段时间内重金属对土壤的输入通量(kg/km2);Wout为一段时间内重金属离开土壤的输出通量(kg/km2),得到:
式(5)中的(Win- Wout)是土壤重金属元素单位面积的年净累积量,土壤元素在耕作层的净输入通量W可由以下公式计算:
式中:W大气、W灌溉、W化肥分别为输入端各通量(kg/km2),W作物、W排水分别为输出端各通量(kg/km2)。
1)大气干湿沉降
式中:
表6 2017年西乡塘区大气干湿沉降重金属平均输入通量
Table 6
| 端元 | As | Cd | Cr | Hg | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大气 | 0.722 | 0.081 | 0.986 | 0.009 | 1.668 |
2)灌溉水
每年通过灌溉水进入土壤的重金属元素输入量计算公式如下:
式中:
表7 2017年西乡塘区灌溉水重金属平均输入通量
Table 7
| 端元 | As | Cd | Cr | Hg | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灌溉水 | 0.812 | 0.012 | 0.773 | 0.010 | 0.012 |
3)化肥
农田中广泛使用的农用化学品对土壤的污染日趋严重[33],本研究仅讨论施用化肥对土壤的重金属带入量。项目在西乡塘区均匀分布的11家农户中采集了16件当地施用量最大的化肥样品。对土壤的重金属年输入通量计算公式如下:
表8 2017年西乡塘区化肥重金属平均输入通量
Table 8
| 端元 | As | Cd | Cr | Hg | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 化肥 | 0.373 | 0.011 | 0.393 | 0.0003 | 0.185 |
4)农作物
西乡塘区主要的农作物为以水稻为主的粮食类、香蕉为主的水果类和瓜类蔬菜等。根据项目采集的水稻、玉米、香蕉、花生、茄子等240件农作物样品测试结果,计算农作物带出的重金属通量,公式如下:
式中:
表9 2017年西乡塘区农作物重金属平均输出通量
Table 9
| 端元 | As | Cd | Cr | Hg | Pb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 农作物 | 花生 | 0.096 | 0.387 | 0.218 | 0.006 | 0.146 |
| 蔬菜瓜类 | 0.008 | 0.014 | 0.016 | 0.000 | 0.012 | |
| 水稻籽实 | 0.356 | 0.088 | 0.240 | 0.009 | 0.083 | |
| 香蕉 | 0.017 | 0.004 | 0.050 | 0.001 | 0.034 | |
| 玉米 | 0.050 | 0.021 | 0.201 | 0.001 | 0.142 | |
| 按种植面积 加权平均 | 0.030 | 0.015 | 0.051 | 0.001 | 0.032 | |
5)灌溉排水
在农田灌溉输用水过程中,除了被土壤吸收、农作物带走等形式消耗掉以外,仍有部分回归到地表
径流的水量,这一部分水量带出的土壤重金属元素的年输出量按如下公式计算:
表10 2017年西乡塘区灌溉排水重金属平均输出通量
Table 10
| 端元 | As | Cd | Cr | Hg | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灌溉排水 | 0.450 | 0.006 | 0.428 | 0.005 | 0.006 |
3.3 土壤环境质量评价等级
表11 农用地土壤环境质量等级划分
Table 11
| 指数 | 污染物 | 分级类型 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pi=实测值/风险筛选值 Pj=实测值/风险管控值 | i=As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Hg、Pb、Ni、Zn; j =As、Cd、Cr、Hg、Pb | pi≤1 优先保护 | pi>1,pj≤1 安全利用 | pj>1 严格管控 |
4 结果与讨论
4.1 单时段增量模型预测土壤重金属元素含量情况
通过表4可以直观看出,WB3数据集的重金属元素含量普遍比WA数据集的重金属元素含量偏大,而pH指标则出现明显偏小。对一一配对的点位进行元素含量对比,发现重金属元素中,无一例外的,含量增大的点位个数均超过了含量减小的点位个数,As、Cd、Cr、Hg、Pb的含量增大点位个数分别占样点总数的62.96%、53.97%、91.53%、60.85%和68.25%。除Cd外,As、Cr、Hg、Pb中含量增大的样点元素含量增幅绝对值也均大于含量减小的样点元素含量降幅绝对值,其中Cr含量增大样点的增幅平均值为47.55×10-6,远大于含量减小样点的降幅平均值8.48×10-6。
假设每年的土壤元素含量不发生较大的变化,依据式(3)计算出每个点位预测的2027年土壤元素含量,计算平均值列于表12,各元素含量均有明显增幅,与2017年度相比,2027年预测的各元素含量增幅在1.88%(Cd)~27.74%(Cr)之间。
表12 单时段增量模型预测2027年土壤重金属元素含量
Table 12
| 指标 | w(As) | w(Cd) | w(Cr) | w(Hg) | w(Pb) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10-6 | 10-6 | 10-6 | 10-6 | 10-6 | ||
| 含量 | 40.23 | 0.465 | 197.12 | 0.243 | 40.38 | 5.67 |
4.2 通量模型预测土壤重金属元素含量情况
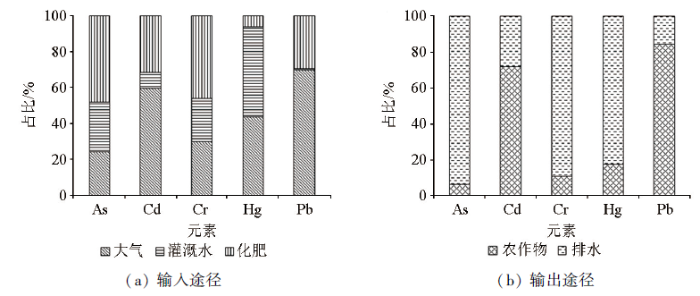
通过式(6)计算得到土壤中各重金属元素的年净输入通量列于表13。5个重金属元素年净输入通量均为正值,即输入通量是高于输出通量的,表明元素在土壤中呈积累趋势。
表13 通量模型土壤重金属年净输入通量
Table 13
| 净输入通量 | As | Cd | Cr | Hg | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | 2.466 | 0.115 | 2.769 | 0.014 | 2.342 |
以0~20 cm耕作层土壤作为研究土壤元素输入输出通量的主要目标层,单位面积土壤的重金属含量年变化率ΔW 为:
将式(12)代入式(1),得出:
式中:Wt为预测t年后的土壤重金属含量(10-6),WR为单位面积土壤质量,西乡塘区的土壤类型以赤红壤为主,根据《广西土壤》[37],赤红壤的容重1.18 g/cm3,本研究WR取2.36×108 kg/km2。
同样假设土壤元素含量每年的变化幅度不发生较大的变化,以2017年为预测基准年,通过计算预测2027年土壤重金属元素含量见表14。可以看出,重金属元素含量的年增幅并不大,较2017年度相比,增幅在0.08%(Cr)~1.06%(Cd)之间。
表14 通量模型预测2027年土壤重金属元素含量
Table 14
| 指标 | w(As) | w(Cd) | w(Cr) | w(Hg) | w(Pb) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10-6 | 10-6 | 10-6 | 10-6 | 10-6 | ||
| 含量 | 36.58 | 0.461 | 154.43 | 0.219 | 37.88 | 5.67 |
图3
图3
各元素不同输入途径对于输入输出通量的贡献比例
Fig.3
Contribution ratio of different input paths to input and output fluxes of each element
在输出途径中,As、Cr、Hg以地表径流为主要输出类型,分别占总输出通量的94%、89%、82%;而Cd和Pb则主要以农作物为主要输出类型,分别占总输出通量的72%和84%。这在广西全面开展的土地质量地球化学评价工作中也得到了佐证:在广泛采集农作物样品中,Cd和Pb是样品重金属元素含量超标的两个主要元素[50]。
4.3 土壤环境质量评价
表15 土壤环境质量分级点位数统计(n=189)
Table 15
| 评价类别 | 评价对象 | As | Cd | Cr | Hg | Pb | 综合分级 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 优先保护 | 2007年(1∶25万) | 126 | 133 | 152 | 189 | 186 | 99 |
| 2017年(1∶5万) | 118 | 121 | 103 | 188 | 185 | 75 | |
| 2027年(通量模型) | 115 | 121 | 106 | 188 | 181 | 70 | |
| 2027年(单时段增量) | 107 | 113 | 89 | 187 | 177 | 56 | |
| 安全利用 | 2007年(1∶25万) | 63 | 56 | 37 | 0 | 3 | 90 |
| 2017年(1∶5万) | 71 | 68 | 86 | 1 | 4 | 114 | |
| 2027年(通量模型) | 73 | 68 | 83 | 1 | 8 | 118 | |
| 2027年(单时段增量) | 81 | 76 | 100 | 2 | 12 | 132 | |
| 严格管控 | 2007年(1∶25万) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2017年(1∶5万) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2027年(通量模型) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| 2027年(单时段增量) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| 优先保护点位占比 | 2007年(1∶25万) | 66.67% | 70.37% | 80.42% | 100.00% | 98.41% | 52.38% |
| 2017年(1∶5万) | 62.43% | 64.02% | 54.50% | 99.47% | 97.88% | 39.68% | |
| 2027年(通量模型) | 60.85% | 64.02% | 56.08% | 99.47% | 95.77% | 37.04% | |
| 2027年(单时段增量) | 56.61% | 59.79% | 47.09% | 98.94% | 93.65% | 29.63% |
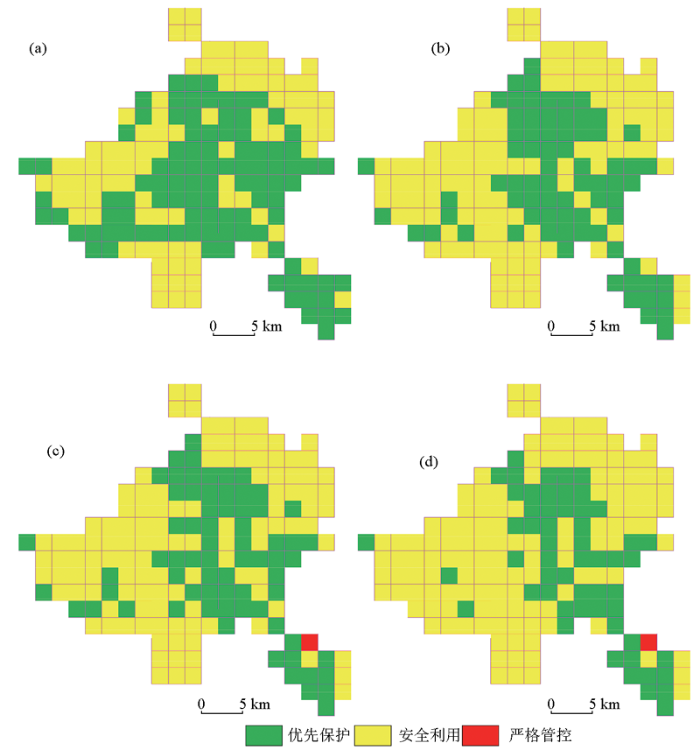
图4
图4
土壤环境质量综合等级
a—2007年调查数据;b—2017年调查数据;c—2027年通量模型预测数据;d—2027年单时段增量模型预测数据
Fig.4
Comprehensive grade map of soil environmental quality
a—2007 survey data;b—2017 survey data;c—2027 flux model forecast data;d—2027 single-period incremental model forecast data
从2007年、2017年的调查现状中就可以看出,土壤中的重金属含量超标点位比例还是比较高的,这与唐豆豆等[51]对广西的研究结果一致,其中As、Cd、Cr超标较为显著。2007年As、Cd、Cr单元素优先保护等级点位分别占比为66.67%、70.37%、80.42%,综合分级中优先保护等级点位占比52.38%;2017年As、Cd、Cr单元素优先保护等级点位占比分别为62.43%、64.02%、54.50%,综合分级占比为39.68%。通过通量模型、单时段增量模型预测的2027年土壤重金属含量超标点位较2007年、2017年调查的土壤重金属含量超标点位都有进一步的增加,综合分级中优先保护点位占样点总数下降至37.04%和29.63%。
不同预测模型得到的预测结果略有差异,通量模型依据单次调查结果,结合大量的统计数据对未来进行预测,其中调查数据中部分样品数量偏少、收集的统计数据资料则侧重区域平均值,加之部分输入输出途径并未考虑,有可能会人为放大或忽略影响土壤元素含量变化的因素。单时段增量模型是通过两次实际调查数据对未来进行推算,但可明显看出,因土壤元素含量的不均一性,不同调查精度(比例尺)的调查结果还是有所区别的,对大量数据进行平均处理,会使数据出现失真的情况。因此针对不同的工作目的,采取不同精度的调查工作是必要的,大比例尺的土壤调查工作更能展现土壤元素的空间变化细节。
两种模型所预测的研究区土壤中重金属元素含量基本都呈现增大的趋势,但单时段增量模型中两次实际调查数据中的单个对应点位数据有增有减。影响土壤元素含量变化的因素众多,包括地质背景、土壤类型、地形地貌、气候条件、生物等自然环境因素以及耕种、灌溉、施肥、污染等人为因素等。本研究中用于对比的2007年、2017年调查点位并不完全重合,即使间隔时间一定,采样点位固定,土壤元素的非均质性以及调查、分析测试等也不可避免会对结果产生一定的影响[52-53]。本研究中,十年甚至几十年相对于漫长的地质历史时期还是较为短暂的,自然条件对于土壤元素含量变化的影响相对有限,人为因素还是引起变化的主要影响因素。不同地块的耕作方式、种植结构、施肥和灌溉程度都能在短时间内改变土壤的pH值、氧化还原电位、有机质含量、CEC、湿度、黏度等理化性质,从而引起重金属元素含量的变化,区域上呈现出整体趋势一致,但单个点位有所不同情况。
单时段增量模型预测的土壤重金属含量年增加速率高于通量模型预测的土壤重金属含量年增加速率,因此单时段增量模型显示土壤环境质量等级下降趋势更为显著。因预测时间较短,通量模型预测结果与预测基准年(2017年)的差别不大,Cr还出现了负增长,表现为优先保护等级点位增加的现象,主要由于各点位的土壤pH值无法通过通量模型进行计算,采用的是单时段增量模型的对应点位的土壤pH值。总体来说本次研究选择的两种预测模型对研究区土壤重金属元素含量的变化趋势预测结果较为一致,即研究区土壤重金属元素含量呈逐年增加,土壤环境质量等级逐年下降。
按照目前施行的土壤环境质量标准(GB 5618—2018)给出的重金属元素风险筛选值、管控值进行土壤环境质量分类,研究区有一半以上的土壤样品都出现了重金属元素含量超过筛选值而未能达到优先保护级别,但在实际调查研究过程中,广西土壤的重金属含量总量虽然高,但生物有效性较低,在安全利用、严格管控区土壤中采集的农作物样品重金属含量却并不高。单纯按照土壤元素含量总量来对土壤环境进行等级划分并不贴合广西目前的实际,本研究暂不开展土壤元素的预警等相关讨论。
5 结论
通过不同的预测模型可以对土壤元素含量的未来变化情况进行定量预测,这是研究土壤环境质量的重要手段。本研究采用单时段增量和输入输出通量两种模型分别对研究区2027年土壤重金属含量进行预测,预测结果有所差异但趋势较为一致,研究区土壤的5种重金属元素的含量均为逐年增加,单时段增量模型的增幅要大于输入输出通量模型的增幅。输入输出通量模型中不同途径对于土壤重金属元素的净输入通量密度贡献度有所不同,总体上研究区大气干湿沉降是重金属元素进入土壤的主要途径类型。根据土壤环境质量标准(GB 15618—2018)对土壤点位的调查数据、预测数据进行土壤环境质量等级划分,发现优先保护等级的点位数量比例呈现下降趋势,说明土壤环境质量逐年下降。同时通过对比研究,不同精度(比例尺)的土壤调查结果有所差异,大比例尺调查更能展现土壤元素的空间变化细节。
本研究中的实际调查点位无法达到完全一一对应,输入输出通量模型中也未能考虑成土风化、土壤侵蚀、蒸腾作用等因素,由于土壤的非均质性以及调查资料、统计数据的局限性,致使模型还存在一定的不足。可以本研究为参考,在广西目前开展的1∶25万多目标区域地球化学调查、1∶5万土地质量地球化学评价重叠区域进行广泛深入的对比、预测研究,为广西土壤重金属源—汇研究以及重金属污染防控、预测预警等方面提供技术支撑。
参考文献
土壤质量评价研究进展
[J].
Research progress of soil quality evaluation
[J].
土壤健康与农业绿色发展:机遇与对策
[J].
Soil health and agriculture green development:Opportunities and challenges
[J].
可持续土壤管理:土壤学服务社会发展的挑战
[J].
Sustainable soil management:An emerging soil science challenge for global development
[J].
全球地球科学研究的可视化分析
[J].
DOI:10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2020.107
[本文引用: 1]

文献计量学可以对学科发展态势进行信息挖掘和分析,可视化是文献计量学发展的热点方向之一。基于文献计量方法和GIS的空间分析功能分析了 1994—2018年全球地球科学领域的发展态势,并将发文量、主要发文作者和研究机构的地理分布、研究重心时空迁移等研究结果可视化。结果表明,全球地球科学研究的科研产出明显增多。地球科学研究的发文重心逐渐往北半球的东南方向迁移。国际合作在逐年加强,越来越多的国家参与到地球科学领域的研究中,美国在地球科学领域的研究中处于核心地位,中国的科研论文实力显著提高。中国地质大学的Santosh发表的论文最多,赵国春的论文受关注度最高,国家科学院和高校为主要论文高产机构。研究结果可以为地球科学学科建设和相关研究提供参考。
A visual analysis of global geoscience research
[J].
DOI:10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2020.107
[本文引用: 1]

Bibliometrics is an important methodology to mine and analyze the information of the discipline development trend. Visualization is one of the hot topics in the development of bibliometrics. Based on the bibliometric methods and the spatial analysis function of GIS, the development trend of global geoscience research from 1994 to 2018 was comprehensively analyzed and the visual analysis mainly focused on the global geoscience articles, the geographical distribution of the main productive authors and main research institutions, and the spatiotemporal migration of the centroids of global geoscience research. The results showed that the global scientific output of geoscience increased significantly from 1994 to 2018. The centroids of geoscience articles gradually migrated to the southeast of the northern hemisphere, and the changing trend was mainly reflected in the longitude direction. The international collaboration was deepening year and year, more and more countries have participated in the geoscience research. The USA played an important role in global geoscience research and the scientific research ability of China has improved significantly. Santosh M of China University of Geosciences has published the most articles, while articles produced by Zhao Guochun have received the highest attention. The Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese universities and colleges were the main productive institutions. The results can provide beneficial reference for the discipline construction of geoscience and relative research.
2011—2020中国应用地球化学研究进展与展望之生态地球化学
[J].
Research progresses on applied geochemistry from 2011 to 2020 in China:Ecogeochemistry
[J].
全国土地质量地球化学调查二十年
[J].
DOI:10.13745/j.esf.sf.2019.8.25
[本文引用: 1]

土地质量地球化学调查计划是我国继区域化探全国扫面计划之后一个新的国家地球化学填图计划,该计划实施20年来,在支撑土壤环境污染防控、土地资源管理、国家重大立法、精准扶贫等方面做出了重大贡献,显著拓展了地质工作服务链。本文从计划的提出背景、项目的组织实施、主要进展、调查技术的进步和分析测试技术的提高与质量控制方案的完善等方面回顾了该计划的发展历程。从全国耕地地球化学状况、全国省会城市土壤环境质量状况、中国主要淡水湖泊沉积物环境质量状况、中国主要农耕区20年来土壤碳库变化4个方面对调查成果做了全面总结。全方位介绍了调查应用成果在土地管理、土壤污染防治、农业种植结构调整、脱贫攻坚、地方病防治、油气勘查、固体矿产勘查等7个领域中的应用。并在调查技术革新、评价方法创新和调查与研究融合三个方面对土地质量地球化学调查工作的未来发展趋势做了展望。
Vicennial implementation of geochemical survey of land quality in China
[J].
DOI:10.13745/j.esf.sf.2019.8.25
[本文引用: 1]

The geochemical survey of land quality project launched in 1999 is a new national geochemical mapping project, succeeding the regional geochemistry-national reconnaissance project in China. The project has since made significant contributions in supporting governmental actions in soil pollution prevention and control, land resource management, major agricultural legislation and precision poverty relief—expanding greatly its role of geological service. We provided here a historical review on the projects background, organization, main progress, survey methodology development, analysis and testing technology improvement and quality control scheme. We made a comprehensive summary of the projects achievements in the overview of the geochemical status of national cultivated land, environmental qualities of soils in provincial capital cities and sediments in nations main freshwater lakes, and changes of soil organic carbon pools in the main agricultural areas of China in the past 20 years. We then gave an all-around introduction of the applications of survey data in land management, soil pollution prevention and control, agricultural planting structural adjustment, poverty relief, endemic disease prevention and control, and explorations for oil & gas and metallic minerals. Finally, we offered a prospective view on the future developmental trend of geochemical survey of land quality regarding innovative survey technology, new evaluation methods and integration of survey and research.
西乡塘区概况
[N/OL]. http://www.xxtq.gov.cn/gk/xxtgk/,2019.
General situation of Xixiangtang District
[N/OL]. http://www.xxtq.gov.cn/gk/xxtgk/,2019.
广西南宁市西乡塘区土地质量地球化学评价成果报告
[R].
Land quality geochemical evaluation report of Xixiangtang District,Nanning,Guangxi
[R].
国务院关于印发土壤污染防治行动计划的通知
[N].
Circular of the State Council on the issuance of soil pollution prevention and control action plan
[N].
国务院关于重金属污染综合防治“十二五”规划的批复
[EB].
The State Council's reply on the comprehensive control of heavy metal pollution during the 12th Five-Year Plan
[EB].
衢州典型重金属污染农田镉、铅输入输出平衡分析
[J].
DOI:10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2020.05.1061
[本文引用: 1]

为定量评估区域农田土壤重金属输入输出平衡,以浙江省衢州市某典型镉(Cd)、铅(Pb)中、轻度复合污染农田为研究对象,对其主要输入源(大气沉降、灌溉、肥料和农药)的Cd、Pb输入通量以及输出通量(水稻秸秆与籽粒移出)开展了长期监测与定量平衡分析。结果表明,大气沉降通量无显著季节变化,由大气沉降导致的Cd、Pb年均输入量分别为3.18和54.46 g·hm<sup>-2</sup>,输入量占比分别达到34.98%和34.95%;而灌溉水Cd、Pb年均输入量分别为5.76和100.62 g·hm<sup>-2</sup>,占比分别达到63.37%和64.57%;由肥料带入的Cd、Pb年均输入量分别为0.15和0.74 g·hm<sup>-2</sup>,占比仅为1.65%和0.47%;而农药带入的Cd、Pb输入量可忽略不计。在该地区双季稻种植模式下,通过水稻秸秆和籽粒的收获和转移,Cd、Pb年输出量分别为10.69和41.74 g·hm<sup>-2</sup>。综上,调查区域农田土壤Cd的输入输出基本达到平衡,而土壤Pb仍为输入状态,建议对该地区灌溉水进行净化并开展长期监测,同时避免水稻秸秆直接还田。本研究强调了重金属污染区水稻秸秆移除的重要性,为农田土壤重金属污染风险管控提供了理论依据和数据支持。
Assessment of input-output patterns of Cd and Pb of typical heavy metal polluted agricultural land in Quzhou
[J].
中国农田重金属污染预警系统研究
[J].
The warning system of heavy metal pollution in the farmland of China
[J].
中国农田重金属污染趋势性预测和预报系统
[J].
The tendency prediction and forecast system for farmland heavy metal pollution in China
[J].
土壤环境质量预警体系构建与应用
[J].
Construction and application of early warning system for soil environmental quality
[J].
浙北嘉善县1990—2008 年土壤重金属元素及酸碱度变化和趋势预测
[J].
Content change and forecast of heavy metal and pH valuein soil for Jianshan Area:Northern Zhejiang Province from 1990 to 2008
[J].
湖北省钟祥市竹皮河污灌区土壤重金属Cd和As污染预测探讨
[J].
Discussion on soil heavy metal Cd and As pollution prediction of Zhupi River Sewage irrigation area of Zhongxiang City,Hubei Province
[J].
Effects of environmental governance in mining areas:The trend of arsenic concentration in the environmental media of a typical mining area in 25 years
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.07.010 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于环境容量的县域农用地土壤重金属风险概率预警研究
[J].
Risk prediction of heavy metals in farmland soil based on environmental capacity:Case study of the county scale in Northern Zhejiang Province
[J].
北京市土壤重金属潜在风险预警管理研究
[J].
Early warning of heavy metals potential risk governance in Beijing
[J].
Modelling cadmium contamination in paddy soils under long-term remediation measures:Model development and stochastic simulations
[J].
DOI:S0269-7491(16)30426-2
PMID:27257714
[本文引用: 1]

A pollutant accumulation model (PAM) based on the mass balance theory was developed to simulate long-term changes of heavy metal concentrations in soil. When combined with Monte Carlo simulation, the model can predict the probability distributions of heavy metals in a soil-water-plant system with fluctuating environmental parameters and inputs from multiple pathways. The model was used for evaluating different remediation measures to deal with Cd contamination of paddy soils in Youxian county (Hunan province), China, under five scenarios, namely the default scenario (A), not returning paddy straw to the soil (B), reducing the deposition of Cd (C), liming (D), and integrating several remediation measures (E). The model predicted that the Cd contents of soil can lowered significantly by (B) and those of the plants by (D). However, in the long run, (D) will increase soil Cd. The concentrations of Cd in both soils and rice grains can be effectively reduced by (E), although it will take decades of effort. The history of Cd pollution and the major causes of Cd accumulation in soil were studied by means of sensitivity analysis and retrospective simulation. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Assessing long-term environmental risks of trace elements in phosphate fertilizers
[J].The potential risks originating from arsenic and cadmium accumulations in cropland soils through the fertilizer applications have been public concern. A generalized trace element mass balance model was developed to evaluate the long-term fate and transport of arsenic and cadmium in cropland soils. Model simulation results showed that normal cropping practices do not have a significant effect on the total As content of the receiving soils, but the application of Cd-containing P fertilizers could, over time, cause Cd to accumulate in soil and therefore increases the risk of its transfer through the food chain. Regulations have been enacted in several states to set the maximum contaminant levels for arsenic and cadmium in fertilizers. The simulation outcomes indicated that some of the existing fertilizer regulations are not strict enough to prevent significant accumulation of Cd in cropland soils. Sensitivity analyses show the solid-solution partitioning coefficient, and the plant uptake factors are primary factors that affect the fate and transport of As and Cd in cropland soils. The uncertainty associated with assessing the fate of trace elements in cropland soils is due to the high variability of model parameters.
南方典型水稻土镉(Cd)累积规律模拟
[J].
Simulation cadmium (Cd) accumulation in typical paddy soils in South China
[J].
贵州草海沉积物汞的含量和分布特征初步研究
[J].
A preliminary study of the contents and distribution of mercury in the sediments of lake caohai in Guizhou
[J].
成都经济区农业生态系统土壤镉通量研究
[J].
Cadmium flux in soils of the agroecosystem in the Chengdueconomic region,Sichuan,China
[J].
湘乡市某地区土壤—水稻系统镉平衡源解析
[J].
Analysis of cadmium balance source in soil-rice system in a certain area of Xiangxiang City
[J].
2017年南宁市水资源公报
[EB/OL].
2017 Nanning water resources bulletin
[EB/OL].
2018年南宁市统计年鉴
[EB/OL].
Nanning statistical yearbook 2018
[EB/OL].
中国农田土壤重金属污染防治挑战与对策
[J].
Challenges and countermeasures for heavy metal pollution control in farmlands of China
[J].
我国南方红壤酸化问题及改良修复技术研究进展
[J].
Status of red soil acidification and its amelioration technologies in South China
[J].
遵义市植烟区灌溉水和有机肥料中重金属含量调查
[J].
Investigation of heavy metals in irrigation water and organic fertilizer in tobacco growing areas of Zunyi City,China
[J].
西安市农业产地环境农田灌溉水重金属污染评价
[J].
Evaluation of heavy metal pollution in farmland irrigation water of agricultural areas in Xian City
[J].
福建典型烟区土壤、灌溉水和肥料中重金属含量调查
[J].
Heavy metal contents in soil,irrigation water and fertilizersof typical tobacco-planting region of Fujian Province
[J].
Source and distribution of metals in urban soil of Bombay,India,using multivariate statistical techniques
[J].DOI:10.1007/BF00767413 URL [本文引用: 1]
An inventory of trace element inputs to agricultural soils in China
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.01.011
PMID:19246150
[本文引用: 1]

It is important to understand the status and extent of soil contamination with trace elements to make sustainable management strategies for agricultural soils. The inputs of trace elements to agricultural soils via atmospheric deposition, livestock manures, fertilizers and agrochemicals, sewage irrigation and sewage sludge in China were analyzed and an annual inventory of trace element inputs was developed. The results showed that atmospheric deposition was responsible for 43-85% of the total As, Cr, Hg, Ni and Pb inputs, while livestock manures accounted for approximately 55%, 69% and 51% of the total Cd, Cu and Zn inputs, respectively. Among the elements concerned, Cd was a top priority in agricultural soils in China, with an average input rate of 0.004 mg/kg/yr in the plough layer (0-20 cm). Due to the spatial and temporal heterogeneity of the sources, the inventory as well as the environmental risks of trace elements in soils varies on a regional scale. For example, sewage sludge and fertilizers (mainly organic and phosphate-based inorganic fertilizers) can also be the predominant sources of trace elements where these materials were excessively applied. This work provides baseline information to develop policies to control and reduce toxic element inputs to and accumulation in agricultural soils.
大气沉降及土壤扬尘对天津城郊蔬菜重金属含量的影响
[J].
Effects of atmospheric and dust deposition on content of heavy metals in vegetables in suburbs of Tianjin
[J].
Atmospheric deposition of heavy metals in the Pearl River Delta,China
[J].DOI:10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00929-9 URL [本文引用: 1]
鲁西南平原区大气干湿沉降元素输入通量及来源浅析:以巨野县为例
[J].
An analysis of the input flux and source of elements in dry and wet atmospheric deposition of southwest plain of Shandong:A case study of JuyeCounty
[J].
近十年中国土壤重金属污染源解析研究进展
[J].
Review on the last ten years of research on source identification of heavy metal pollution in soils
[J].
大气沉降对土壤和作物中重金属富集的影响及其研究进展
[J].
Advancement in researches on effect of atmospheric deposition on heavy metals accumulation in soils and crops
[J].
大气沉降重金属污染特征及生态风险研究进展
[J].
Progress in research on heavy metals in atmospheric deposition:Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment
[J].
南京市大气沉降中重金属特征及对土壤环境的影响
[J].
Atmospheric deposition of heavy metals and their impacts on soil environmentin in typical urban areas of Nanjing
[J].
广西土地质量地球化学调查研究报告
[R].
Report of land quality geochemical investigation in Guangxi
[R].
地质高背景农田土壤中水稻对重金属的富集特征及风险预测
[J].
Enrichment characteristics and risk prediction of heavy metals for rice grains growing in paddy soils with a high geological background
[J].
Soil acidification and factors controlling topsoil pH shift of cropland incentral China from 2008 to 2018
[J].
Predicting spatial and temporal variation of Cd concentration in rice grains in the Lower Changjiang Plain during 2004-2014 based on soil geochemical survey data with GIS
[J].