0 引言
噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作。为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类。首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] 。
与预测滤波方法和降秩滤波方法不同的是,NLM方法并不基于线性假设,因此在处理弯曲同相轴时,该方法可以有效地保护有效信号,压制随机噪声。传统NLM方法起源于图像的随机噪声压制处理[28 ] ,随后Bonar成功地将该方法引入到地震数据噪声压制处理中[13 ] 。然而,传统NLM方法在应用上也存在一定局限性。相比于矩阵降秩或预测滤波等方法,该方法计算时间较长,在处理大型地震数据时效率低下。为了解决这一问题,前人提出了分块NLM法[28 ] 、并行分块NLM法[29 ] 、基于随机投影算法的NLM法[30 ] 、下采样的快速NLM法[31 ] 、变窗口的快速NLM法[32 ] 等。但由于前述方法为了提高计算效率,在计算过程中并没有完全遍历每个数据点,因此可能会牺牲计算精度。而基于数据积分算法的快速NLM法[33 ] ,原理上等价于在计算过程中遍历所有数据点,因此在提高计算速度的同时避免了牺牲精度的可能。传统NLM方法在处理实际地震数据时,所选择的滤波参数值通常为一常数,为了进一步提高去噪效果,前人利用结构张量算法[34 -35 ] 、矩阵本征特性算法[36 ] 、灰色关联分析算法[37 ] 等方法,针对不同区域可选择不同的滤波参数来提高去噪效果,但会明显增加计算量。NLM方法的去噪效果很大程度上受滤波器参数的选择影响,如果参数太大,就会丢失细节信息,使图像模糊,如果参数过小,则噪声不能被完全抑制。因此,一些学者通过局部数据的随机噪声估计来自适应的计算滤波参数,例如高通滤波法[38 ] 和最小方差估计法[15 -16 ] 。上述这些方法在提高传统NLM方法去噪效果的同时,可以减少滤波参数对计算速度的影响,但该方法在计算效率上仍有提升空间。
本文提出了一种基于快速自适应非局部均值滤波的地震随机噪声压制方法,可快速且有效地压制地震随机噪声。首先,为了提高NLM方法的计算效率,本文给出了一种中心对称数据积分算法,有效地降低了计算成本。其次,通过计算两个邻域窗口的相似度,本文给出了利用均匀度来自适应调整滤波参数分布的方法。最后,通过模型数据和实际数据验证了该方法的有效性、实用性。
1 方法
1.1 非局部均值滤波方法
(1) Dnoise (t ,x )=Dtrue (t ,x )+n ,
式中:Dtrue (t ,x )表示无噪声数据;n 表示随机噪声。假设(Ds ,Ds )表示搜索窗口半径,(ds ,ds )表示邻域窗口半径,Ddenoise (t ,x )表示去噪后的数据,通过对Dtrue (t ,x )进行加权平均计算即可得到每个点处的Ddenoise (t ,x )数据[13 ,28 ] 。因此,Ddenoise (t ,x )可以表示为:
(2) Ddenoise (t,x)= 1 Z ( t , x ) ∑ i , j ∈ Ω e x p ( - V ( t , x ) - V ( i , j ) ‖ 2 2 h 2 ) D n o i s e ( i , j )
式中,滤波参数h 为常数,是控制去噪水平的主要参数。V ( t , x ) - V ( i , j ) ‖ 2 2
(3) V ( t , x ) - V ( i , j ) ‖ 2 2 1 ( 2 d s + 1 ) 2 ∑ z 1 , z 2 ∈ Z noise (t+z1 ,x+z2 )- D n o i s e ( i + z 1 , j + z 2 ) ‖ 2 2
式中,ℤ=z 1 , z 2 ∈ Z : | z 1 | ≤ d s , | z 2 | ≤ d s 1 Z ( t , x ) V ( t , x ) - V ( i , j ) ‖ 2 2 h 2 ) 之和等于1。因此,Z (t ,x )可表示为:
(4) Z(t,x)= ∑ i , j ∈ Ω V ( t , x ) - V ( i , j ) ‖ 2 2 h 2 i , j ∈ Ω : i - t ≤ D s , j - x ≤ D s
NLM方法可以有效地处理弯曲同相轴,但计算成本较高。假设D noise (t ,x )总点数为N =Nt Nx ,两个正方形邻域窗口之间的相似度计算量为d 2 =(2 d s + 1 ) 2 D noise (t ,x )中的每个数据点,必须在搜索窗内计算D 2 =( 2 D s + 1 ) 2 O (ND 2 d 2 ),计算量巨大。因此,传统NLM方法在处理大型实际地震数据时,会明显受到计算效率的制约。
1.2 中心对称数据积分算法
为了提高NLM方法的计算效率,前人提出了一种用数据积分算法来加速NLM方法[33 ,39 ] 。常规算法在计算‖V (t ,x )-V (i ,j )‖ 2 2 St (t 1 ,x 1 ),可以通过对差分矩阵s (t ,x )积分来表示:
(5) s(t,x)= ‖ D n o i s e ( t , x ) - D n o i s e ( t + r 1 , x + r 2 ) ‖ 2 2 r 1 , r 2 ∈ R ; r 1 ≤ D s , r 2 ≤ D s t (t1 ,x1 )= ∑ t , x ∈ N
(6) ℕ= t , x ∈ N ; 1 ≤ t ≤ t 1 , 1 ≤ x ≤ x 1
(7) V ( t , x ) - V ( i , j ) ‖ 2 2 1 ( 2 d s + 1 ) 2 t (t+ds ,x+ds )+St (t-ds -1,x-ds -1)-St (t+ds ,x-ds -1)-St (t-ds -1,x+ds )],
由式(5)~ 式(7),V ( t , x ) - V ( i , j ) ‖ 2 2 NLM 方法的计算复杂度降低至O (ND 2 )。
通过观察式(5),发现建立的差分矩阵s(t ,x )为中心对称的,因此本文给出了一种中心对称数据积分算法,利用数据积分的数学对称性来提高NLM 方法的计算效率。假设
(8) s ( t , x ) [ + r ] = ‖ D n o i s e ( t , x ) - D n o i s e ( t + r 1 , x + r 2 ) ‖ 2 2 , s ( t , x ) [ - r ] = ‖ D n o i s e ( t , x ) - D n o i s e ( t - r 1 , x - r 2 ) ‖ 2 2 , R = r 1 , r 2 ∈ R : r 1 ≤ D s , r 2 ≤ D s 。
(9) s ( t - r 1 , x - r 2 ) [ + r ] ‖ D n o i s e ( t - r 1 , x - r 2 ) - D n o i s e ( t , x ) ‖ 2 2 [- r ] ,
据此s (t ,x )[- r ] 的值可被表示为s (t ,x )[+ r ] 的中心对称值,在计算过程中,即可避免构建s (t ,x )[- r ] 矩阵,进而减少了一半的计算量,将式(9)代入式(6)中,
(10) St ( t 1 - r 1 , x 1 - r 2 ) [ + r ] t ( t 1 , x 1 ) [ - r ]
(11) V ( t , x ) - V ( i , j ) ‖ 2 [ - r ] 2 1 ( 2 d s + 1 ) 2 S t ( t + d s - r 1 , x + d s - r 2 ) [ + r ] + S t ( t - d s - r 1 - 1 , x - d s - r 2 - 1 ) [ + r ] S t ( t + d s - r 1 , x - d s - r 2 - 1 ) [ + r ] - S t ( t - d s - r 1 - 1 , x + d s - r 2 ) [ + r ]
通过利用式(8)~ 式(11),可以避免建立差分矩阵s (t ,x )[- r ] 和积分矩阵St ( t 1 , x 1 ) [ - r ] V ( t , x ) - V ( i , j ) ‖ 2 2 NLM 的计算复杂度降低至O (ND 2 / 2)。
1.3 均匀性估计
式(2)中的滤波参数h的选择,对于NLM 方法的去噪效果是至关重要的。大量地震资料表明,不同地层的有效信号能量差异较大,甚至随机噪声的分布也不是完全随机的,因此滤波参数h的取值通常难以确定。相比于整个区域的地震数据取相同的滤波参数h, 利用一个参数矩阵h 来控制不同区域数据的去噪水平可以提高噪声压制效果。基于最小方差估计的自适应算法可以自适应选择滤波参数h [15 - 16] ,该方法认为参数h 的估计是噪声σ 的标准差,满足下式
(12) E V ( t , x ) - V ( i , j ) ‖ 2 2 ‖ V 0 ( t , x ) - V 0 ( i , j ) ‖ 2 2 2 ,
其中,V 0 代表无噪声数据。自适应滤波参数矩阵h 2 的估计即可表示为
(13) h2 (t,x)≈σ2 =min(E V ( t , x ) - V ( i , j ) ‖ 2 2
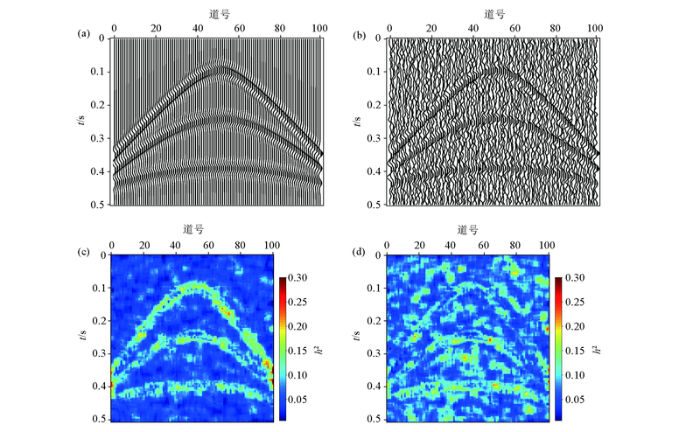
通过利用最小方差估计的方法即可调整整个数据区域内部的滤波参数值。图1 给出了一个含噪声数据估计的滤波参数h 2 的分布情况,如图1 c所示,利用最小方差估计方法得到的滤波参数h 2 在有效信号结构边缘处相对较大,而背景均匀区域的滤波参数值相对较小。
图1
图1
滤波参数h 2 分布
a—无噪声的数据;b—加噪数据;c—最小方差估计的参数分布情况;d—相似度标准差的参数分布情况
Fig.1
Distribution of the filtering parameter h 2
a—noise-free data;b—noisy data;c—parameter distribution of minimum variance estimation;d—parameter distribution of standard deviation of similarity
为了进一步提高随机噪声的压制效果,在均匀区域的滤波参数h 应相对较大,而在结构边缘区域则应相对较小[35 ] 。因此本文给出了一种利用相似度标准差算法来自适应估计均匀性和调整滤波参数分布的方法。通过利用自然指数函数来调节滤波参数h a d p 2 h a d p 2
(14) h a d p 2 h 2 1 - 2 S T D s m a x ( S T D s )
(15) STDs (t,x)= s t d i , j ∈ Ω V ( t , x ) - V ( i , j ) ‖ 2 2 i , j ∈ Ω ; i - t ≤ D s , j - x ≤ D s
相似度标准差值STDs (t ,x )较大时,表示搜索区域内的数据变化较大,即位于数据结构的边缘;相似度标准差值较小时,表示搜索区域内数据变化不明显,即数据位于均匀区域。此外,在本文中相似度标准差的计算是通过利用NLM方法中已计算的相邻窗口间距离项V ( t , x ) - V ( i , j ) ‖ 2 2
本文给出的基于快速自适应非局部均值滤波方法,通过引入中心对称数据积分算法进一步提高了传统NLM方法的计算效率,同时利用相似度标准差来估计均匀性,实现了自适应滤波参数调整,有效地提高了去噪效果和计算效率。
2 模型数据试验
在地震数据噪声压制处理中,通常采用信噪比(SNR )[40 ] 、峰值信噪比(PSNR )和均方误差(MSE )[41 ] 来定量分析方法的地震数据去噪效果,其定义如下:
(16) SNR=20lg ‖ D t r u e ‖ 2 ‖ D d e n o i s e - D t r u e ‖ 2
(17) PSNR=20lg 255 M S E
(18) MSE= ‖ D d e n o i s e - D t r u e ‖ 2 N x N t
式中:Dtrue 和Ddenoise 分别代表原始无噪声数据和噪声压制后数据;N =Nt Nx 表示噪声数据Dnoise (t ,x )的总点数。结合传统NLM方法[13 ] 和基于最小方差估计的NLM方法[15 ] 与本文快速自适应NLM方法进行对比,利用2个模型地震数据,从计算效率和精度两方面分别验证本文方法的有效性。
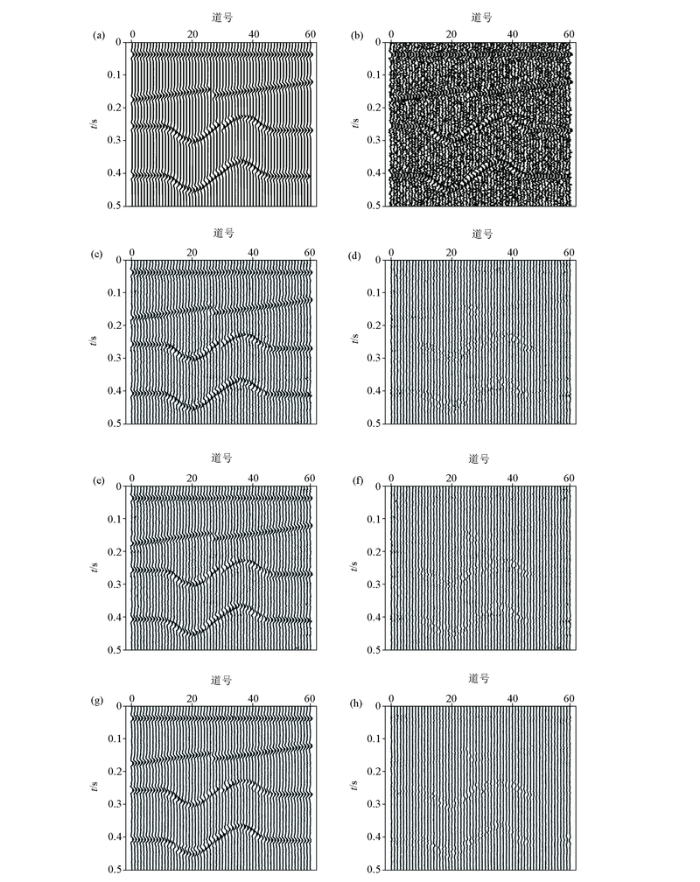
模型数据试验1为简单合成地震剖面,包括两个线性同相轴和两个弯曲同相轴。图2 a为60道无噪声模型数据,图2 b为加噪数据,信噪比为-4.55 dB,图2 c~h分别为传统NLM法、基于最小方差估计的NLM法和本文方法的去噪结果及相应的残差剖面。由于F-X 预测滤波方法[10 ] 和降秩方法[18 ] 算法本身基于线性假设,因此对于弯曲同相轴的处理存在误差,而NLM方法对于弯曲同相轴的计算精度就要明显高于上述两种方法(图2 c~h)。由于从图中很难看出3种NLM方法的不同之处,因此分别计算上述方法去噪结果的SNR 、PSNR 和MSE ,如表1 。可以看出,利用本文方法得到的SNR 和PSNR 都高于其他方法,且MSE 明显低于其他方法,该方法对于随机噪声的压制效果要优于上述其他方法。
图2
图2
模型试验1的合成模型数据噪声压制结果
a—无噪声的数据;b—噪声数据(SNR =-4.55 dB);c—传统NLM方法去噪结果;d—a与c的差剖面;e—基于最小方差估计的NLM方法去噪结果;f—a与e的差剖面;g—本文方法去噪的结果;h—a与g的差剖面
Fig.2
Noise attenuation results of synthetic model data from model data test 1
a—noise-free data;b—noisy data(SNR =-4.55 dB);c—denoised result by using conventional NLM method;d—difference between a and c;e—denoised result by using NLM based on minimum variance estimation;f—difference between a and e;g—denoised result by using proposed method;h—difference between a and g
模型数据试验2为正演偏移剖面。图3 a为100道无噪声模型数据,图3 b为噪声数据,其信噪比为-3.01 dB,图3 c~h分别展示了传统NLM方法、基于最小方差估计的NLM方法和本文方法去噪后的结果及相应的残差剖面。上述方法去噪后的SNR分别为17.254 5 dB、20.727 4 dB、22.557 9 dB,利用本文方法去噪结果的SNR最高。结果表明,本文方法除在合成数据的残差剖面中泄漏少量能量外,在压制随机噪声和保留有效信号方面具有较好的效果。
图3
图3
模型试验2的合成模型数据噪声压制结果
a—无噪声的数据;b—噪声数据(SNR =-3.01 dB);c—传统NLM方法去噪结果;d—a与c的差剖面;e—基于最小方差估计的NLM方法去噪结果;f—a与e的差剖面;g—本文方法去噪的结果;h—a与g的差剖面
Fig.3
Noise attenuation results of synthetic model data from model data test 2
a—noise-free data;b—noisy data (SNR =-3.01 dB);c—denoised result by using conventional NLM method;d—difference between a and c;e—denoised result by using NLM based on minimum variance estimation;f—difference between a and e;g—denoised result by using proposed method;h—difference between a and g
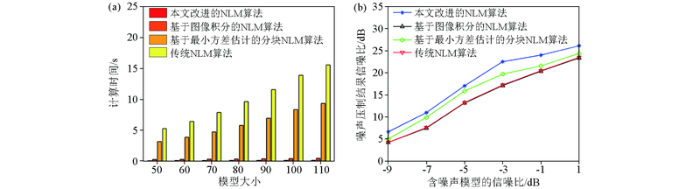
最后,利用一系列不同大小的地震数据对比不同方法的计算时间。图4 a显示了本文快速自适应NLM方法、基于数据积分方法的NLM方法、基于最小方差估计的分块NLM方法和传统NLM方法的计算时间对比。图4 b显示了不同信噪比的噪声地震模型数据下,这些方法的去噪质量。与其他方法相比,本文方法计算效率明显高于其他方法,且当利用不同信噪比的模型进行去噪处理后,本文方法也具有更好的去噪质量。
图4
图4
基于模型数据2不同方法去噪计算时间及效果对比
a—计算时间对比;b—去噪质量对比
Fig.4
Comparison of calculation time and effect of different denoising methods based on model data test 2
a—computational time comparison;b—denoising quality comparison
3 实际数据试验
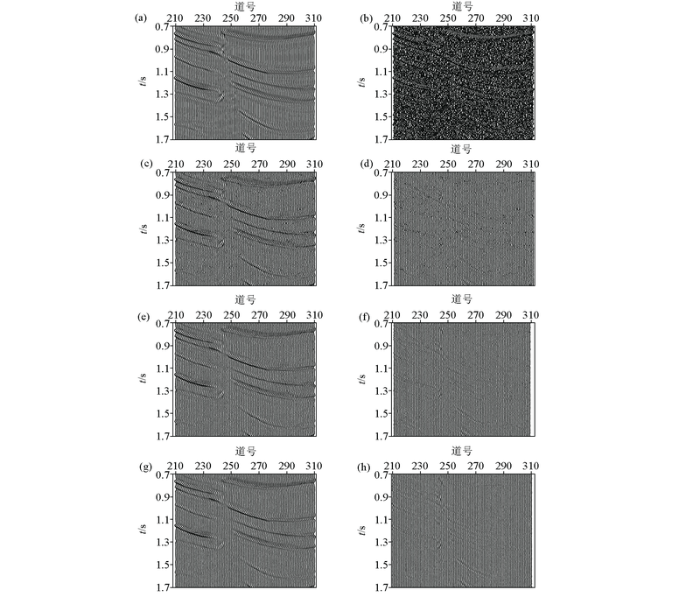
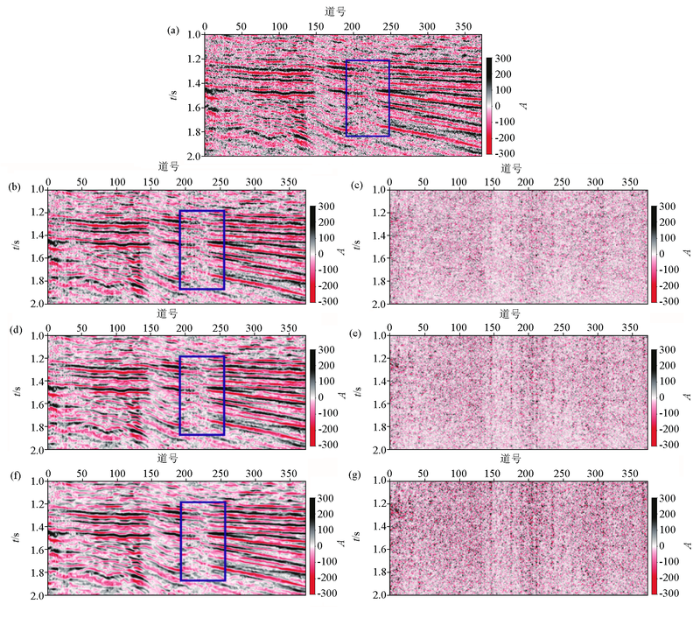
为了验证本文快速自适应非局部均值滤波方法的实用性,将该方法应用于实际地震数据的随机噪声压制处理中,结果如图5 所示。从图5 a中方框区域可以看出,随机噪声污染了实际地震资料,使得地层模糊,断层构造不清晰,难以进行后续地震资料解释工作。图5 b~d分别展示了传统NLM方法、基于最小方差估计的NLM方法以及本文方法的去噪结果。图5 e~g显示了这些方法的差剖面。从图5 b~g可以看出,传统的NLM方法、基于最小方差估计的NLM方法以及本文提出的方法都可以有效压制随机噪声。但从图5 b、5c和5d中的方框区域可以看出,本文方法处理结果中的断层结构相比于另外两种方法更加清晰,有效信号的信息得到了很好的保存,有效地压制了随机噪声。在实际地震数据的噪声压制处理中,本文快速自适应NLM方法、基于数据积分方法的NLM方法、基于最小方差估计的分块NLM方法和传统NLM方法的计算时间分别为:0.63 s、1.14 s、58.42 s和94.22 s。本文提出方法的计算时间也有明显的提高。因此,在处理大型地震数据资料时,本文快速自适应非局部均值滤波方法具有更好的实用性。
图5
图5
实际地震数据去噪结果
a—实际地震数据;b—传统NLM方法去噪结果;c—基于最小方差估计的NLM去噪结果;d—本文方法去噪结果;e—a与b的差剖面;f—a与c的差剖面;g—a与e的差剖面
Fig.5
Noise attenuation results of field data
a—field data;b—denoised result by using conventional NLM method;c—denoised result by using NLM based on minimum variance estimation;d—denoised result by using proposed method;e—difference between a and b;f—difference between a and c;g—difference between a and e
4 结论
本文给出了一种用于地震资料随机噪声压制的快速自适应非局部均值滤波方法。首先,基于数据积分算法的数学对称性,利用中心对称数据积分算法来加速传统NLM滤波方法。其次,利用相似度标准差来估计均匀性,自适应地计算NLM滤波参数,进一步提高噪声压制效果。因此,本文方法在有效提高计算效率的同时,又提高了噪声压制的效果。最后,通过对模型数据和实际数据的处理,验证了该方法的有效性、实用性。
参考文献
View Option
[1]
Naghizadeh M . Seismic data interpolation and denoising in the frequency-wavenumber domain
[J]. Geophysics , 2012 , 77 (2 ): V71 -V80.
DOI:10.1190/geo2011-0172.1
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[2]
Latif A Mousa W A . An efficient undersampled high-resolution radon transform for exploration seismic data processing
[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2016 , 55 (2 ): 1010 -1024 .
DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2016.2618848
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[3]
鲁娥 , 李庆春 . 混合Radon变换地震噪声压制的应用
[J]. 物探与化探 , 2013 , 37 (4 ):706 -710 .
[本文引用: 1]
Lu E Li Q C . The application of seismic noise attenuation based on hybrid radon transform
[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration , 2013 , 37 (4 ): 706 -710 .
[本文引用: 1]
[4]
Oliveira M S Henriques M V C Leite F E A , et al . Seismic denoising using curvelet analysis
[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications , 2012 , 391 (5 ): 2106 -2110 .
DOI:10.1016/j.physa.2011.04.009
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[5]
Yang H Y Long Y Lin J , et al . A seismic interpolation and denoising method with curvelet transform matching filter
[J]. Acta Geophysica , 2017 , 65 : 1029 -1042 .
DOI:10.1007/s11600-017-0078-x
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[6]
袁艳华 , 王一博 , 刘伊克 , 等 . 非二次幂Curvelet变换及其在地震噪声压制中的应用
[J]. 地球物理学报 , 2013 , 56 (3 ):1023 -1032 .
[本文引用: 1]
Yuan Y H Wang Y B Liu Y K , et al . Non-dyadic Curvelet transform and its application in seismic noise elimination
[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics , 2013 , 56 (3 ): 1023 -1032 .
[本文引用: 1]
[7]
Huang W L Wu R S Wang R Q . Damped dreamlet representation for exploration seismic data interpolation and denoising
[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2018 , 56 (6 ), 3159 -3172 .
DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2018.2793856
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[8]
Goudarzi A Riahi M A . Seismic coherent and random noise attenuation using the undecimated discrete wavelet transform method with WDGA technique
[J]. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering , 2012 , 9 (6 ): 619 -631 .
DOI:10.1088/1742-2132/9/6/619
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[9]
Liu N H Yang Y Li Z , et al . Seismic signal de-noising using time-frequency peak filtering based on empirical wavelet transform
[J]. Acta Geophysica , 2020 , 68 : 425 -434 .
DOI:10.1007/s11600-020-00413-4
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[10]
Canales Luis L . Random noise reduction
[J]. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts , 1984 :329 .
[本文引用: 2]
[11]
梁传坤 . 频波谱在地震噪声分析与衰减中的应用
[J]. 物探与化探 , 1995 , 19 (1 ):34 -40 .
[本文引用: 1]
Liang C K . The application of frequency wave spectra to the analysis and attenuation of seismic noise
[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration , 1995 , 19 (1 ): 34 -40 .
[本文引用: 1]
[12]
Liu Y Liu N Liu C . Adaptive prediction filtering in t-x-y domain for random noise attenuation using regularized nonstationary autoregression
[J]. Geophysics , 2015 , 80 (1 ): V13 -V21
DOI:10.1190/geo2014-0011.1
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[14]
黄英 , 文晓涛 , 贺振华 . 地震图像随机噪声的非局部均值去噪法
[J]. 断块油气田 , 2013 , 20 (6 ):730 -732 .
[本文引用: 1]
Huang Y Wen X T He Z H . Denoising algorithm of random noise with seismic image based on nonlocal means
[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field , 2013 , 20 (6 ): 730 -732 .
[本文引用: 1]
[15]
Shang S Han L G Lyu Q T , et al . Seismic random noise suppression using an adaptive nonlocal means algorithm
[J]. Applied Geophysics , 2013 , 10 (1 ): 33 -40 .
DOI:10.1007/s11770-013-0362-8
URL
[本文引用: 3]
[16]
Manjón V J Pierrick C Luis M , et al . Adaptive non-local means denoising of mr images with spatially varying noise levels
[J]. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging , 2010 , 31 (1 ): 192 -203 .
DOI:10.1002/jmri.22003
PMID:20027588
[本文引用: 2]
To adapt the so-called nonlocal means filter to deal with magnetic resonance (MR) images with spatially varying noise levels (for both Gaussian and Rician distributed noise).Most filtering techniques assume an equal noise distribution across the image. When this assumption is not met, the resulting filtering becomes suboptimal. This is the case of MR images with spatially varying noise levels, such as those obtained by parallel imaging (sensitivity-encoded), intensity inhomogeneity-corrected images, or surface coil-based acquisitions. We propose a new method where information regarding the local image noise level is used to adjust the amount of denoising strength of the filter. Such information is automatically obtained from the images using a new local noise estimation method.The proposed method was validated and compared with the standard nonlocal means filter on simulated and real MRI data showing an improved performance in all cases.The new noise-adaptive method was demonstrated to outperform the standard filter when spatially varying noise is present in the images.(c) 2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
[17]
Gao J J Sacchi M D Chen X H . A fast reduced-rank interpolation method for prestack seismic volumes that depend on four spatial dimensions
[J]. Geophysics , 2013 , 78 (1 ): V21 -V30.
DOI:10.1190/geo2012-0038.1
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[18]
Wang S H Gao J J Li J Y . A fast uncoiled randomized QR decomposition method for 5D seismic data reconstruction
[J]. Journal of Seismic Exploration , 2018 , 27 (3 ): 255 -276 .
[本文引用: 2]
[19]
Xu Y K Cao S Y Pan X , et al . Random noise attenuation using a structure-oriented adaptive singular value decomposition
[J]. Acta Geophysica , 2019 , 67 : 1091 -106 .
DOI:10.1007/s11600-019-00301-6
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[20]
Gao J J Stanton A Sacchi M D . Parallel matrix factorization algorithm and its application to 5D seismic reconstruction and denoising
[J]. Geophysics , 2015 , 80 (6 ): V173 -V187.
DOI:10.1190/geo2014-0594.1
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[21]
Kreimer N Sacchi M D . A tensor higher-order singular value decomposition for prestack seismic data noise reduction and interpolation
[J]. Geophysics , 2012 , 77 (3 ): V113 -V122.
DOI:10.1190/geo2011-0399.1
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[22]
Liu L Plonka G Ma J W . Seismic data interpolation and denoising by learning a tensor tight frame
[J]. Inverse Problems , 2017 , 33 (10 ): 105011 .
DOI:10.1088/1361-6420/aa7773
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[23]
Si X Yuan Y J Si T H , et al . Attenuation of random noise using denoising convolutional neural networks
[J]. Interpretation , 2019 , 7 (3 ): SE269 -SE280.
DOI:10.1190/INT-2018-0220.1
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[24]
Wang S N Li Y Zhao Y X . Desert seismic noise suppression based on multimodal residual convolutional neural network
[J]. Acta Geophysica , 2020 , 68 : 389 -401 .
DOI:10.1007/s11600-020-00405-4
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[25]
Zhao Y Li Y Dong X , et al . Low-frequency noise suppression method based on improved DnCNN in desert seismic data
[J]. Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters,IEEE , 2018 , 16 (5 ): 811 -815 .
DOI:10.1109/LGRS.2018.2882058
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[26]
郭奇 , 曾昭发 , 于晨霞 , 等 . 基于高精度字典学习算法的地震随机噪声压制
[J]. 物探与化探 , 2017 , 41 (5 ):907 -913 .
[本文引用: 1]
Guo Q Zeng Z F Yu C X , et al . Seismic random noise suppression based on the high-preicision dictionary learning algorithm
[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration , 2017 , 41 (5 ): 907 -913 .
[本文引用: 1]
[27]
李勇 , 张益明 , 雷钦 , 等 . 模型约束下的在线字典学习地震弱信号去噪方法
[J]. 地球物理学报 , 2019 , 62 (1 ):411 -420 .
[本文引用: 1]
Li Y Zhang Y M Lei Q , et al . Online dictionary learning seismic weak signal denoising method under model constraints
[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics , 2019 , 62 (1 ): 411 -420 .
[本文引用: 1]
[28]
Buades A Coll B Morel J M . Image denoising methods. A new nonlocal principle
[J]. SIAM Review , 2010 , 52 (1 ): 113 -147 .
DOI:10.1137/090773908
URL
[本文引用: 3]
[29]
Coupe P, Yger, P Prima S , et al . An optimized blockwise nonlocal means denoising filter for 3-d magnetic resonance images
[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging , 2008 , 27 (4 ): 425 -441 .
DOI:10.1109/TMI.2007.906087
PMID:18390341
[本文引用: 1]
A critical issue in image restoration is the problem of noise removal while keeping the integrity of relevant image information. Denoising is a crucial step to increase image quality and to improve the performance of all the tasks needed for quantitative imaging analysis. The method proposed in this paper is based on a 3-D optimized blockwise version of the nonlocal (NL)-means filter (Buades, et al., 2005). The NL-means filter uses the redundancy of information in the image under study to remove the noise. The performance of the NL-means filter has been already demonstrated for 2-D images, but reducing the computational burden is a critical aspect to extend the method to 3-D images. To overcome this problem, we propose improvements to reduce the computational complexity. These different improvements allow to drastically divide the computational time while preserving the performances of the NL-means filter. A fully automated and optimized version of the NL-means filter is then presented. Our contributions to the NL-means filter are: 1) an automatic tuning of the smoothing parameter; 2) a selection of the most relevant voxels; 3) a blockwise implementation; and 4) a parallelized computation. Quantitative validation was carried out on synthetic datasets generated with BrainWeb (Collins, et al., 1998). The results show that our optimized NL-means filter outperforms the classical implementation of the NL-means filter, as well as two other classical denoising methods [anisotropic diffusion (Perona and Malik, 1990)] and total variation minimization process (Rudin, et al., 1992) in terms of accuracy (measured by the peak signal-to-noise ratio) with low computation time. Finally, qualitative results on real data are presented.
[30]
Lai R Yang Y T . Accelerating non-local means algorithm with random project
[J]. Electronics Letters , 2011 , 47 (3 ): 182 -183 .
DOI:10.1049/el.2010.2618
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[31]
周兵 , 韩媛媛 , 徐明亮 , 等 . 快速非局部均值图像去噪算法
计算机辅助设计与图形学学报 , 2016 , 28 (8 ):1260 -1268 .
[本文引用: 1]
Zhou B Han Y Y Xu M L . A fast non-local means image denoising algorithm
[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics , 2016 , 28 (8 ): 1260 -1268 .
[本文引用: 1]
[32]
Maraschini M Turton N . Random noise attenuation preserving geological detail - A fast and effective Non-Local-Means filter
[C]// London : European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers , 2013 .
[本文引用: 1]
[33]
Froment J . Parameter-free fast pixel wise non-local means denoising
[J]. Image Processing on Line 4 , 2014 : 300 -326 .
[本文引用: 2]
[34]
Yang S Chen A Q Chen H D . Seismic data filtering using non-local means algorithm based on structure tensor
[J]. Open Geosciences , 2017 , 9 (1 ): 151 -160 .
[本文引用: 1]
[35]
Zeng W L Du Y J Hu C H . Noise suppression by discontinuity indicator controlled non-local means method
[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications , 2017 , 76 : 13239 -13253 .
DOI:10.1007/s11042-016-3753-z
URL
[本文引用: 2]
[36]
Chen P Wu S Q Fang H P , et al . Gaussian noise detection and adaptive non-local means filter
[J]. China: Pacificrim Symposium on Image and Video Technology , 2017 : 396 -405 .
[本文引用: 1]
[37]
Verma R Pandey R . Grey relational analysis based adaptive smoothing parameter for non-local means image denoising
[J]. Multimedia tools and applications , 2018 , 77 : 25919 -25940 .
DOI:10.1007/s11042-018-5828-5
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[38]
Colom M Buades A . Analysis and extension of the percentile method, estimating a noise curve from a single image
[J]. Image Processing on Line 5, 2013 , 365 -390 .
[本文引用: 1]
[39]
Wang J Guo Y W Ying Y T , et al . Fast non-local algorithm for image denoising
[C]// Atlanta: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing , 2007 :1429 -1432 .
[本文引用: 1]
[40]
Yu S Sun J G Meng X F , et al . Seismic random noise attenuation based on PCC classification in transform domain
[J]. IEEE Access , 2019 , 8 :30368 -30377 .
DOI:10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2959024
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[41]
Yusra A N Chen S D . Comparison of image quality assessment: PSNR, HVS, SSIM, UIQI
[J]. International Journal of scientific and Engineering Research , 2012 , 3 (8 ): 1 -5 .
[本文引用: 1]
Seismic data interpolation and denoising in the frequency-wavenumber domain
1
2012
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
An efficient undersampled high-resolution radon transform for exploration seismic data processing
1
2016
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
混合Radon变换地震噪声压制的应用
1
2013
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
混合Radon变换地震噪声压制的应用
1
2013
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
Seismic denoising using curvelet analysis
1
2012
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
A seismic interpolation and denoising method with curvelet transform matching filter
1
2017
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
非二次幂Curvelet变换及其在地震噪声压制中的应用
1
2013
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
非二次幂Curvelet变换及其在地震噪声压制中的应用
1
2013
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
Damped dreamlet representation for exploration seismic data interpolation and denoising
1
2018
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
Seismic coherent and random noise attenuation using the undecimated discrete wavelet transform method with WDGA technique
1
2012
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
Seismic signal de-noising using time-frequency peak filtering based on empirical wavelet transform
1
2020
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
Random noise reduction
2
1984
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
... 模型数据试验1为简单合成地震剖面,包括两个线性同相轴和两个弯曲同相轴.图2 a为60道无噪声模型数据,图2 b为加噪数据,信噪比为-4.55 dB,图2 c~h分别为传统NLM法、基于最小方差估计的NLM法和本文方法的去噪结果及相应的残差剖面.由于F-X 预测滤波方法[10 ] 和降秩方法[18 ] 算法本身基于线性假设,因此对于弯曲同相轴的处理存在误差,而NLM方法对于弯曲同相轴的计算精度就要明显高于上述两种方法(图2 c~h).由于从图中很难看出3种NLM方法的不同之处,因此分别计算上述方法去噪结果的SNR 、PSNR 和MSE ,如表1 .可以看出,利用本文方法得到的SNR 和PSNR 都高于其他方法,且MSE 明显低于其他方法,该方法对于随机噪声的压制效果要优于上述其他方法. ...
频波谱在地震噪声分析与衰减中的应用
1
1995
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
频波谱在地震噪声分析与衰减中的应用
1
1995
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
Adaptive prediction filtering in t-x-y domain for random noise attenuation using regularized nonstationary autoregression
1
2015
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
Denoising seismic data using the nonlocal means algorithm
4
2012
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
... 与预测滤波方法和降秩滤波方法不同的是,NLM方法并不基于线性假设,因此在处理弯曲同相轴时,该方法可以有效地保护有效信号,压制随机噪声.传统NLM方法起源于图像的随机噪声压制处理[28 ] ,随后Bonar成功地将该方法引入到地震数据噪声压制处理中[13 ] .然而,传统NLM方法在应用上也存在一定局限性.相比于矩阵降秩或预测滤波等方法,该方法计算时间较长,在处理大型地震数据时效率低下.为了解决这一问题,前人提出了分块NLM法[28 ] 、并行分块NLM法[29 ] 、基于随机投影算法的NLM法[30 ] 、下采样的快速NLM法[31 ] 、变窗口的快速NLM法[32 ] 等.但由于前述方法为了提高计算效率,在计算过程中并没有完全遍历每个数据点,因此可能会牺牲计算精度.而基于数据积分算法的快速NLM法[33 ] ,原理上等价于在计算过程中遍历所有数据点,因此在提高计算速度的同时避免了牺牲精度的可能.传统NLM方法在处理实际地震数据时,所选择的滤波参数值通常为一常数,为了进一步提高去噪效果,前人利用结构张量算法[34 -35 ] 、矩阵本征特性算法[36 ] 、灰色关联分析算法[37 ] 等方法,针对不同区域可选择不同的滤波参数来提高去噪效果,但会明显增加计算量.NLM方法的去噪效果很大程度上受滤波器参数的选择影响,如果参数太大,就会丢失细节信息,使图像模糊,如果参数过小,则噪声不能被完全抑制.因此,一些学者通过局部数据的随机噪声估计来自适应的计算滤波参数,例如高通滤波法[38 ] 和最小方差估计法[15 -16 ] .上述这些方法在提高传统NLM方法去噪效果的同时,可以减少滤波参数对计算速度的影响,但该方法在计算效率上仍有提升空间. ...
... 式中:Dtrue (t ,x )表示无噪声数据;n 表示随机噪声.假设(Ds ,Ds )表示搜索窗口半径,(ds ,ds )表示邻域窗口半径,Ddenoise (t ,x )表示去噪后的数据,通过对Dtrue (t ,x )进行加权平均计算即可得到每个点处的Ddenoise (t ,x )数据[13 ,28 ] .因此,Ddenoise (t ,x )可以表示为: ...
... 式中:Dtrue 和Ddenoise 分别代表原始无噪声数据和噪声压制后数据;N =Nt Nx 表示噪声数据Dnoise (t ,x )的总点数.结合传统NLM方法[13 ] 和基于最小方差估计的NLM方法[15 ] 与本文快速自适应NLM方法进行对比,利用2个模型地震数据,从计算效率和精度两方面分别验证本文方法的有效性. ...
地震图像随机噪声的非局部均值去噪法
1
2013
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
地震图像随机噪声的非局部均值去噪法
1
2013
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
Seismic random noise suppression using an adaptive nonlocal means algorithm
3
2013
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
... 与预测滤波方法和降秩滤波方法不同的是,NLM方法并不基于线性假设,因此在处理弯曲同相轴时,该方法可以有效地保护有效信号,压制随机噪声.传统NLM方法起源于图像的随机噪声压制处理[28 ] ,随后Bonar成功地将该方法引入到地震数据噪声压制处理中[13 ] .然而,传统NLM方法在应用上也存在一定局限性.相比于矩阵降秩或预测滤波等方法,该方法计算时间较长,在处理大型地震数据时效率低下.为了解决这一问题,前人提出了分块NLM法[28 ] 、并行分块NLM法[29 ] 、基于随机投影算法的NLM法[30 ] 、下采样的快速NLM法[31 ] 、变窗口的快速NLM法[32 ] 等.但由于前述方法为了提高计算效率,在计算过程中并没有完全遍历每个数据点,因此可能会牺牲计算精度.而基于数据积分算法的快速NLM法[33 ] ,原理上等价于在计算过程中遍历所有数据点,因此在提高计算速度的同时避免了牺牲精度的可能.传统NLM方法在处理实际地震数据时,所选择的滤波参数值通常为一常数,为了进一步提高去噪效果,前人利用结构张量算法[34 -35 ] 、矩阵本征特性算法[36 ] 、灰色关联分析算法[37 ] 等方法,针对不同区域可选择不同的滤波参数来提高去噪效果,但会明显增加计算量.NLM方法的去噪效果很大程度上受滤波器参数的选择影响,如果参数太大,就会丢失细节信息,使图像模糊,如果参数过小,则噪声不能被完全抑制.因此,一些学者通过局部数据的随机噪声估计来自适应的计算滤波参数,例如高通滤波法[38 ] 和最小方差估计法[15 -16 ] .上述这些方法在提高传统NLM方法去噪效果的同时,可以减少滤波参数对计算速度的影响,但该方法在计算效率上仍有提升空间. ...
... 式中:Dtrue 和Ddenoise 分别代表原始无噪声数据和噪声压制后数据;N =Nt Nx 表示噪声数据Dnoise (t ,x )的总点数.结合传统NLM方法[13 ] 和基于最小方差估计的NLM方法[15 ] 与本文快速自适应NLM方法进行对比,利用2个模型地震数据,从计算效率和精度两方面分别验证本文方法的有效性. ...
Adaptive non-local means denoising of mr images with spatially varying noise levels
2
2010
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
... 与预测滤波方法和降秩滤波方法不同的是,NLM方法并不基于线性假设,因此在处理弯曲同相轴时,该方法可以有效地保护有效信号,压制随机噪声.传统NLM方法起源于图像的随机噪声压制处理[28 ] ,随后Bonar成功地将该方法引入到地震数据噪声压制处理中[13 ] .然而,传统NLM方法在应用上也存在一定局限性.相比于矩阵降秩或预测滤波等方法,该方法计算时间较长,在处理大型地震数据时效率低下.为了解决这一问题,前人提出了分块NLM法[28 ] 、并行分块NLM法[29 ] 、基于随机投影算法的NLM法[30 ] 、下采样的快速NLM法[31 ] 、变窗口的快速NLM法[32 ] 等.但由于前述方法为了提高计算效率,在计算过程中并没有完全遍历每个数据点,因此可能会牺牲计算精度.而基于数据积分算法的快速NLM法[33 ] ,原理上等价于在计算过程中遍历所有数据点,因此在提高计算速度的同时避免了牺牲精度的可能.传统NLM方法在处理实际地震数据时,所选择的滤波参数值通常为一常数,为了进一步提高去噪效果,前人利用结构张量算法[34 -35 ] 、矩阵本征特性算法[36 ] 、灰色关联分析算法[37 ] 等方法,针对不同区域可选择不同的滤波参数来提高去噪效果,但会明显增加计算量.NLM方法的去噪效果很大程度上受滤波器参数的选择影响,如果参数太大,就会丢失细节信息,使图像模糊,如果参数过小,则噪声不能被完全抑制.因此,一些学者通过局部数据的随机噪声估计来自适应的计算滤波参数,例如高通滤波法[38 ] 和最小方差估计法[15 -16 ] .上述这些方法在提高传统NLM方法去噪效果的同时,可以减少滤波参数对计算速度的影响,但该方法在计算效率上仍有提升空间. ...
A fast reduced-rank interpolation method for prestack seismic volumes that depend on four spatial dimensions
1
2013
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
A fast uncoiled randomized QR decomposition method for 5D seismic data reconstruction
2
2018
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
... 模型数据试验1为简单合成地震剖面,包括两个线性同相轴和两个弯曲同相轴.图2 a为60道无噪声模型数据,图2 b为加噪数据,信噪比为-4.55 dB,图2 c~h分别为传统NLM法、基于最小方差估计的NLM法和本文方法的去噪结果及相应的残差剖面.由于F-X 预测滤波方法[10 ] 和降秩方法[18 ] 算法本身基于线性假设,因此对于弯曲同相轴的处理存在误差,而NLM方法对于弯曲同相轴的计算精度就要明显高于上述两种方法(图2 c~h).由于从图中很难看出3种NLM方法的不同之处,因此分别计算上述方法去噪结果的SNR 、PSNR 和MSE ,如表1 .可以看出,利用本文方法得到的SNR 和PSNR 都高于其他方法,且MSE 明显低于其他方法,该方法对于随机噪声的压制效果要优于上述其他方法. ...
Random noise attenuation using a structure-oriented adaptive singular value decomposition
1
2019
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
Parallel matrix factorization algorithm and its application to 5D seismic reconstruction and denoising
1
2015
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
A tensor higher-order singular value decomposition for prestack seismic data noise reduction and interpolation
1
2012
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
Seismic data interpolation and denoising by learning a tensor tight frame
1
2017
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
Attenuation of random noise using denoising convolutional neural networks
1
2019
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
Desert seismic noise suppression based on multimodal residual convolutional neural network
1
2020
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
Low-frequency noise suppression method based on improved DnCNN in desert seismic data
1
2018
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
基于高精度字典学习算法的地震随机噪声压制
1
2017
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
基于高精度字典学习算法的地震随机噪声压制
1
2017
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
模型约束下的在线字典学习地震弱信号去噪方法
1
2019
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
模型约束下的在线字典学习地震弱信号去噪方法
1
2019
... 噪声压制在地震数据处理中起着至关重要的作用,去噪效果将直接影响地震资料解释工作.为了有效压制地震资料随机噪声,提高地震资料的信噪比,国内外许多学者提出了不同的方法,本文将这些方法大致分为5类.首先是基于数学变换的方法,如Fourier变换[1 ] 、Radon变换[2 -3 ] 、Curvelet变换[4 ⇓ -6 ] 、Dreamlet变换[7 ] 和Wavelet变换[8 -9 ] ;第二种是基于预测滤波的方法,如F-X预测滤波[10 -11 ] 和自适应预测方法[12 ] ;第三种是基于非局部均值(NLM)滤波的方法,如传统NLM方法[13 -14 ] 和自适应NLM滤波[15 -16 ] ;第四种是基于降秩的方法,如矩阵降秩法[17 ⇓ -19 ] 和张量降秩法[20 -21 ] ;第五种是基于人工智能的方法,如数据驱动紧密框架[22 ] 和机器学习[23 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -27 ] . ...
Image denoising methods. A new nonlocal principle
3
2010
... 与预测滤波方法和降秩滤波方法不同的是,NLM方法并不基于线性假设,因此在处理弯曲同相轴时,该方法可以有效地保护有效信号,压制随机噪声.传统NLM方法起源于图像的随机噪声压制处理[28 ] ,随后Bonar成功地将该方法引入到地震数据噪声压制处理中[13 ] .然而,传统NLM方法在应用上也存在一定局限性.相比于矩阵降秩或预测滤波等方法,该方法计算时间较长,在处理大型地震数据时效率低下.为了解决这一问题,前人提出了分块NLM法[28 ] 、并行分块NLM法[29 ] 、基于随机投影算法的NLM法[30 ] 、下采样的快速NLM法[31 ] 、变窗口的快速NLM法[32 ] 等.但由于前述方法为了提高计算效率,在计算过程中并没有完全遍历每个数据点,因此可能会牺牲计算精度.而基于数据积分算法的快速NLM法[33 ] ,原理上等价于在计算过程中遍历所有数据点,因此在提高计算速度的同时避免了牺牲精度的可能.传统NLM方法在处理实际地震数据时,所选择的滤波参数值通常为一常数,为了进一步提高去噪效果,前人利用结构张量算法[34 -35 ] 、矩阵本征特性算法[36 ] 、灰色关联分析算法[37 ] 等方法,针对不同区域可选择不同的滤波参数来提高去噪效果,但会明显增加计算量.NLM方法的去噪效果很大程度上受滤波器参数的选择影响,如果参数太大,就会丢失细节信息,使图像模糊,如果参数过小,则噪声不能被完全抑制.因此,一些学者通过局部数据的随机噪声估计来自适应的计算滤波参数,例如高通滤波法[38 ] 和最小方差估计法[15 -16 ] .上述这些方法在提高传统NLM方法去噪效果的同时,可以减少滤波参数对计算速度的影响,但该方法在计算效率上仍有提升空间. ...
... [28 ]、并行分块NLM法[29 ] 、基于随机投影算法的NLM法[30 ] 、下采样的快速NLM法[31 ] 、变窗口的快速NLM法[32 ] 等.但由于前述方法为了提高计算效率,在计算过程中并没有完全遍历每个数据点,因此可能会牺牲计算精度.而基于数据积分算法的快速NLM法[33 ] ,原理上等价于在计算过程中遍历所有数据点,因此在提高计算速度的同时避免了牺牲精度的可能.传统NLM方法在处理实际地震数据时,所选择的滤波参数值通常为一常数,为了进一步提高去噪效果,前人利用结构张量算法[34 -35 ] 、矩阵本征特性算法[36 ] 、灰色关联分析算法[37 ] 等方法,针对不同区域可选择不同的滤波参数来提高去噪效果,但会明显增加计算量.NLM方法的去噪效果很大程度上受滤波器参数的选择影响,如果参数太大,就会丢失细节信息,使图像模糊,如果参数过小,则噪声不能被完全抑制.因此,一些学者通过局部数据的随机噪声估计来自适应的计算滤波参数,例如高通滤波法[38 ] 和最小方差估计法[15 -16 ] .上述这些方法在提高传统NLM方法去噪效果的同时,可以减少滤波参数对计算速度的影响,但该方法在计算效率上仍有提升空间. ...
... 式中:Dtrue (t ,x )表示无噪声数据;n 表示随机噪声.假设(Ds ,Ds )表示搜索窗口半径,(ds ,ds )表示邻域窗口半径,Ddenoise (t ,x )表示去噪后的数据,通过对Dtrue (t ,x )进行加权平均计算即可得到每个点处的Ddenoise (t ,x )数据[13 ,28 ] .因此,Ddenoise (t ,x )可以表示为: ...
An optimized blockwise nonlocal means denoising filter for 3-d magnetic resonance images
1
2008
... 与预测滤波方法和降秩滤波方法不同的是,NLM方法并不基于线性假设,因此在处理弯曲同相轴时,该方法可以有效地保护有效信号,压制随机噪声.传统NLM方法起源于图像的随机噪声压制处理[28 ] ,随后Bonar成功地将该方法引入到地震数据噪声压制处理中[13 ] .然而,传统NLM方法在应用上也存在一定局限性.相比于矩阵降秩或预测滤波等方法,该方法计算时间较长,在处理大型地震数据时效率低下.为了解决这一问题,前人提出了分块NLM法[28 ] 、并行分块NLM法[29 ] 、基于随机投影算法的NLM法[30 ] 、下采样的快速NLM法[31 ] 、变窗口的快速NLM法[32 ] 等.但由于前述方法为了提高计算效率,在计算过程中并没有完全遍历每个数据点,因此可能会牺牲计算精度.而基于数据积分算法的快速NLM法[33 ] ,原理上等价于在计算过程中遍历所有数据点,因此在提高计算速度的同时避免了牺牲精度的可能.传统NLM方法在处理实际地震数据时,所选择的滤波参数值通常为一常数,为了进一步提高去噪效果,前人利用结构张量算法[34 -35 ] 、矩阵本征特性算法[36 ] 、灰色关联分析算法[37 ] 等方法,针对不同区域可选择不同的滤波参数来提高去噪效果,但会明显增加计算量.NLM方法的去噪效果很大程度上受滤波器参数的选择影响,如果参数太大,就会丢失细节信息,使图像模糊,如果参数过小,则噪声不能被完全抑制.因此,一些学者通过局部数据的随机噪声估计来自适应的计算滤波参数,例如高通滤波法[38 ] 和最小方差估计法[15 -16 ] .上述这些方法在提高传统NLM方法去噪效果的同时,可以减少滤波参数对计算速度的影响,但该方法在计算效率上仍有提升空间. ...
Accelerating non-local means algorithm with random project
1
2011
... 与预测滤波方法和降秩滤波方法不同的是,NLM方法并不基于线性假设,因此在处理弯曲同相轴时,该方法可以有效地保护有效信号,压制随机噪声.传统NLM方法起源于图像的随机噪声压制处理[28 ] ,随后Bonar成功地将该方法引入到地震数据噪声压制处理中[13 ] .然而,传统NLM方法在应用上也存在一定局限性.相比于矩阵降秩或预测滤波等方法,该方法计算时间较长,在处理大型地震数据时效率低下.为了解决这一问题,前人提出了分块NLM法[28 ] 、并行分块NLM法[29 ] 、基于随机投影算法的NLM法[30 ] 、下采样的快速NLM法[31 ] 、变窗口的快速NLM法[32 ] 等.但由于前述方法为了提高计算效率,在计算过程中并没有完全遍历每个数据点,因此可能会牺牲计算精度.而基于数据积分算法的快速NLM法[33 ] ,原理上等价于在计算过程中遍历所有数据点,因此在提高计算速度的同时避免了牺牲精度的可能.传统NLM方法在处理实际地震数据时,所选择的滤波参数值通常为一常数,为了进一步提高去噪效果,前人利用结构张量算法[34 -35 ] 、矩阵本征特性算法[36 ] 、灰色关联分析算法[37 ] 等方法,针对不同区域可选择不同的滤波参数来提高去噪效果,但会明显增加计算量.NLM方法的去噪效果很大程度上受滤波器参数的选择影响,如果参数太大,就会丢失细节信息,使图像模糊,如果参数过小,则噪声不能被完全抑制.因此,一些学者通过局部数据的随机噪声估计来自适应的计算滤波参数,例如高通滤波法[38 ] 和最小方差估计法[15 -16 ] .上述这些方法在提高传统NLM方法去噪效果的同时,可以减少滤波参数对计算速度的影响,但该方法在计算效率上仍有提升空间. ...
快速非局部均值图像去噪算法
1
2016
... 与预测滤波方法和降秩滤波方法不同的是,NLM方法并不基于线性假设,因此在处理弯曲同相轴时,该方法可以有效地保护有效信号,压制随机噪声.传统NLM方法起源于图像的随机噪声压制处理[28 ] ,随后Bonar成功地将该方法引入到地震数据噪声压制处理中[13 ] .然而,传统NLM方法在应用上也存在一定局限性.相比于矩阵降秩或预测滤波等方法,该方法计算时间较长,在处理大型地震数据时效率低下.为了解决这一问题,前人提出了分块NLM法[28 ] 、并行分块NLM法[29 ] 、基于随机投影算法的NLM法[30 ] 、下采样的快速NLM法[31 ] 、变窗口的快速NLM法[32 ] 等.但由于前述方法为了提高计算效率,在计算过程中并没有完全遍历每个数据点,因此可能会牺牲计算精度.而基于数据积分算法的快速NLM法[33 ] ,原理上等价于在计算过程中遍历所有数据点,因此在提高计算速度的同时避免了牺牲精度的可能.传统NLM方法在处理实际地震数据时,所选择的滤波参数值通常为一常数,为了进一步提高去噪效果,前人利用结构张量算法[34 -35 ] 、矩阵本征特性算法[36 ] 、灰色关联分析算法[37 ] 等方法,针对不同区域可选择不同的滤波参数来提高去噪效果,但会明显增加计算量.NLM方法的去噪效果很大程度上受滤波器参数的选择影响,如果参数太大,就会丢失细节信息,使图像模糊,如果参数过小,则噪声不能被完全抑制.因此,一些学者通过局部数据的随机噪声估计来自适应的计算滤波参数,例如高通滤波法[38 ] 和最小方差估计法[15 -16 ] .上述这些方法在提高传统NLM方法去噪效果的同时,可以减少滤波参数对计算速度的影响,但该方法在计算效率上仍有提升空间. ...
快速非局部均值图像去噪算法
1
2016
... 与预测滤波方法和降秩滤波方法不同的是,NLM方法并不基于线性假设,因此在处理弯曲同相轴时,该方法可以有效地保护有效信号,压制随机噪声.传统NLM方法起源于图像的随机噪声压制处理[28 ] ,随后Bonar成功地将该方法引入到地震数据噪声压制处理中[13 ] .然而,传统NLM方法在应用上也存在一定局限性.相比于矩阵降秩或预测滤波等方法,该方法计算时间较长,在处理大型地震数据时效率低下.为了解决这一问题,前人提出了分块NLM法[28 ] 、并行分块NLM法[29 ] 、基于随机投影算法的NLM法[30 ] 、下采样的快速NLM法[31 ] 、变窗口的快速NLM法[32 ] 等.但由于前述方法为了提高计算效率,在计算过程中并没有完全遍历每个数据点,因此可能会牺牲计算精度.而基于数据积分算法的快速NLM法[33 ] ,原理上等价于在计算过程中遍历所有数据点,因此在提高计算速度的同时避免了牺牲精度的可能.传统NLM方法在处理实际地震数据时,所选择的滤波参数值通常为一常数,为了进一步提高去噪效果,前人利用结构张量算法[34 -35 ] 、矩阵本征特性算法[36 ] 、灰色关联分析算法[37 ] 等方法,针对不同区域可选择不同的滤波参数来提高去噪效果,但会明显增加计算量.NLM方法的去噪效果很大程度上受滤波器参数的选择影响,如果参数太大,就会丢失细节信息,使图像模糊,如果参数过小,则噪声不能被完全抑制.因此,一些学者通过局部数据的随机噪声估计来自适应的计算滤波参数,例如高通滤波法[38 ] 和最小方差估计法[15 -16 ] .上述这些方法在提高传统NLM方法去噪效果的同时,可以减少滤波参数对计算速度的影响,但该方法在计算效率上仍有提升空间. ...
Random noise attenuation preserving geological detail - A fast and effective Non-Local-Means filter
1
2013
... 与预测滤波方法和降秩滤波方法不同的是,NLM方法并不基于线性假设,因此在处理弯曲同相轴时,该方法可以有效地保护有效信号,压制随机噪声.传统NLM方法起源于图像的随机噪声压制处理[28 ] ,随后Bonar成功地将该方法引入到地震数据噪声压制处理中[13 ] .然而,传统NLM方法在应用上也存在一定局限性.相比于矩阵降秩或预测滤波等方法,该方法计算时间较长,在处理大型地震数据时效率低下.为了解决这一问题,前人提出了分块NLM法[28 ] 、并行分块NLM法[29 ] 、基于随机投影算法的NLM法[30 ] 、下采样的快速NLM法[31 ] 、变窗口的快速NLM法[32 ] 等.但由于前述方法为了提高计算效率,在计算过程中并没有完全遍历每个数据点,因此可能会牺牲计算精度.而基于数据积分算法的快速NLM法[33 ] ,原理上等价于在计算过程中遍历所有数据点,因此在提高计算速度的同时避免了牺牲精度的可能.传统NLM方法在处理实际地震数据时,所选择的滤波参数值通常为一常数,为了进一步提高去噪效果,前人利用结构张量算法[34 -35 ] 、矩阵本征特性算法[36 ] 、灰色关联分析算法[37 ] 等方法,针对不同区域可选择不同的滤波参数来提高去噪效果,但会明显增加计算量.NLM方法的去噪效果很大程度上受滤波器参数的选择影响,如果参数太大,就会丢失细节信息,使图像模糊,如果参数过小,则噪声不能被完全抑制.因此,一些学者通过局部数据的随机噪声估计来自适应的计算滤波参数,例如高通滤波法[38 ] 和最小方差估计法[15 -16 ] .上述这些方法在提高传统NLM方法去噪效果的同时,可以减少滤波参数对计算速度的影响,但该方法在计算效率上仍有提升空间. ...
Parameter-free fast pixel wise non-local means denoising
2
2014
... 与预测滤波方法和降秩滤波方法不同的是,NLM方法并不基于线性假设,因此在处理弯曲同相轴时,该方法可以有效地保护有效信号,压制随机噪声.传统NLM方法起源于图像的随机噪声压制处理[28 ] ,随后Bonar成功地将该方法引入到地震数据噪声压制处理中[13 ] .然而,传统NLM方法在应用上也存在一定局限性.相比于矩阵降秩或预测滤波等方法,该方法计算时间较长,在处理大型地震数据时效率低下.为了解决这一问题,前人提出了分块NLM法[28 ] 、并行分块NLM法[29 ] 、基于随机投影算法的NLM法[30 ] 、下采样的快速NLM法[31 ] 、变窗口的快速NLM法[32 ] 等.但由于前述方法为了提高计算效率,在计算过程中并没有完全遍历每个数据点,因此可能会牺牲计算精度.而基于数据积分算法的快速NLM法[33 ] ,原理上等价于在计算过程中遍历所有数据点,因此在提高计算速度的同时避免了牺牲精度的可能.传统NLM方法在处理实际地震数据时,所选择的滤波参数值通常为一常数,为了进一步提高去噪效果,前人利用结构张量算法[34 -35 ] 、矩阵本征特性算法[36 ] 、灰色关联分析算法[37 ] 等方法,针对不同区域可选择不同的滤波参数来提高去噪效果,但会明显增加计算量.NLM方法的去噪效果很大程度上受滤波器参数的选择影响,如果参数太大,就会丢失细节信息,使图像模糊,如果参数过小,则噪声不能被完全抑制.因此,一些学者通过局部数据的随机噪声估计来自适应的计算滤波参数,例如高通滤波法[38 ] 和最小方差估计法[15 -16 ] .上述这些方法在提高传统NLM方法去噪效果的同时,可以减少滤波参数对计算速度的影响,但该方法在计算效率上仍有提升空间. ...
... 为了提高NLM方法的计算效率,前人提出了一种用数据积分算法来加速NLM方法[33 ,39 ] .常规算法在计算‖V (t ,x )-V (i ,j ) ‖ 2 2 St (t 1 ,x 1 ),可以通过对差分矩阵s (t ,x )积分来表示: ...
Seismic data filtering using non-local means algorithm based on structure tensor
1
2017
... 与预测滤波方法和降秩滤波方法不同的是,NLM方法并不基于线性假设,因此在处理弯曲同相轴时,该方法可以有效地保护有效信号,压制随机噪声.传统NLM方法起源于图像的随机噪声压制处理[28 ] ,随后Bonar成功地将该方法引入到地震数据噪声压制处理中[13 ] .然而,传统NLM方法在应用上也存在一定局限性.相比于矩阵降秩或预测滤波等方法,该方法计算时间较长,在处理大型地震数据时效率低下.为了解决这一问题,前人提出了分块NLM法[28 ] 、并行分块NLM法[29 ] 、基于随机投影算法的NLM法[30 ] 、下采样的快速NLM法[31 ] 、变窗口的快速NLM法[32 ] 等.但由于前述方法为了提高计算效率,在计算过程中并没有完全遍历每个数据点,因此可能会牺牲计算精度.而基于数据积分算法的快速NLM法[33 ] ,原理上等价于在计算过程中遍历所有数据点,因此在提高计算速度的同时避免了牺牲精度的可能.传统NLM方法在处理实际地震数据时,所选择的滤波参数值通常为一常数,为了进一步提高去噪效果,前人利用结构张量算法[34 -35 ] 、矩阵本征特性算法[36 ] 、灰色关联分析算法[37 ] 等方法,针对不同区域可选择不同的滤波参数来提高去噪效果,但会明显增加计算量.NLM方法的去噪效果很大程度上受滤波器参数的选择影响,如果参数太大,就会丢失细节信息,使图像模糊,如果参数过小,则噪声不能被完全抑制.因此,一些学者通过局部数据的随机噪声估计来自适应的计算滤波参数,例如高通滤波法[38 ] 和最小方差估计法[15 -16 ] .上述这些方法在提高传统NLM方法去噪效果的同时,可以减少滤波参数对计算速度的影响,但该方法在计算效率上仍有提升空间. ...
Noise suppression by discontinuity indicator controlled non-local means method
2
2017
... 与预测滤波方法和降秩滤波方法不同的是,NLM方法并不基于线性假设,因此在处理弯曲同相轴时,该方法可以有效地保护有效信号,压制随机噪声.传统NLM方法起源于图像的随机噪声压制处理[28 ] ,随后Bonar成功地将该方法引入到地震数据噪声压制处理中[13 ] .然而,传统NLM方法在应用上也存在一定局限性.相比于矩阵降秩或预测滤波等方法,该方法计算时间较长,在处理大型地震数据时效率低下.为了解决这一问题,前人提出了分块NLM法[28 ] 、并行分块NLM法[29 ] 、基于随机投影算法的NLM法[30 ] 、下采样的快速NLM法[31 ] 、变窗口的快速NLM法[32 ] 等.但由于前述方法为了提高计算效率,在计算过程中并没有完全遍历每个数据点,因此可能会牺牲计算精度.而基于数据积分算法的快速NLM法[33 ] ,原理上等价于在计算过程中遍历所有数据点,因此在提高计算速度的同时避免了牺牲精度的可能.传统NLM方法在处理实际地震数据时,所选择的滤波参数值通常为一常数,为了进一步提高去噪效果,前人利用结构张量算法[34 -35 ] 、矩阵本征特性算法[36 ] 、灰色关联分析算法[37 ] 等方法,针对不同区域可选择不同的滤波参数来提高去噪效果,但会明显增加计算量.NLM方法的去噪效果很大程度上受滤波器参数的选择影响,如果参数太大,就会丢失细节信息,使图像模糊,如果参数过小,则噪声不能被完全抑制.因此,一些学者通过局部数据的随机噪声估计来自适应的计算滤波参数,例如高通滤波法[38 ] 和最小方差估计法[15 -16 ] .上述这些方法在提高传统NLM方法去噪效果的同时,可以减少滤波参数对计算速度的影响,但该方法在计算效率上仍有提升空间. ...
... 为了进一步提高随机噪声的压制效果,在均匀区域的滤波参数h 应相对较大,而在结构边缘区域则应相对较小[35 ] .因此本文给出了一种利用相似度标准差算法来自适应估计均匀性和调整滤波参数分布的方法.通过利用自然指数函数来调节滤波参数 h a d p 2 h a d p 2
Gaussian noise detection and adaptive non-local means filter
1
2017
... 与预测滤波方法和降秩滤波方法不同的是,NLM方法并不基于线性假设,因此在处理弯曲同相轴时,该方法可以有效地保护有效信号,压制随机噪声.传统NLM方法起源于图像的随机噪声压制处理[28 ] ,随后Bonar成功地将该方法引入到地震数据噪声压制处理中[13 ] .然而,传统NLM方法在应用上也存在一定局限性.相比于矩阵降秩或预测滤波等方法,该方法计算时间较长,在处理大型地震数据时效率低下.为了解决这一问题,前人提出了分块NLM法[28 ] 、并行分块NLM法[29 ] 、基于随机投影算法的NLM法[30 ] 、下采样的快速NLM法[31 ] 、变窗口的快速NLM法[32 ] 等.但由于前述方法为了提高计算效率,在计算过程中并没有完全遍历每个数据点,因此可能会牺牲计算精度.而基于数据积分算法的快速NLM法[33 ] ,原理上等价于在计算过程中遍历所有数据点,因此在提高计算速度的同时避免了牺牲精度的可能.传统NLM方法在处理实际地震数据时,所选择的滤波参数值通常为一常数,为了进一步提高去噪效果,前人利用结构张量算法[34 -35 ] 、矩阵本征特性算法[36 ] 、灰色关联分析算法[37 ] 等方法,针对不同区域可选择不同的滤波参数来提高去噪效果,但会明显增加计算量.NLM方法的去噪效果很大程度上受滤波器参数的选择影响,如果参数太大,就会丢失细节信息,使图像模糊,如果参数过小,则噪声不能被完全抑制.因此,一些学者通过局部数据的随机噪声估计来自适应的计算滤波参数,例如高通滤波法[38 ] 和最小方差估计法[15 -16 ] .上述这些方法在提高传统NLM方法去噪效果的同时,可以减少滤波参数对计算速度的影响,但该方法在计算效率上仍有提升空间. ...
Grey relational analysis based adaptive smoothing parameter for non-local means image denoising
1
2018
... 与预测滤波方法和降秩滤波方法不同的是,NLM方法并不基于线性假设,因此在处理弯曲同相轴时,该方法可以有效地保护有效信号,压制随机噪声.传统NLM方法起源于图像的随机噪声压制处理[28 ] ,随后Bonar成功地将该方法引入到地震数据噪声压制处理中[13 ] .然而,传统NLM方法在应用上也存在一定局限性.相比于矩阵降秩或预测滤波等方法,该方法计算时间较长,在处理大型地震数据时效率低下.为了解决这一问题,前人提出了分块NLM法[28 ] 、并行分块NLM法[29 ] 、基于随机投影算法的NLM法[30 ] 、下采样的快速NLM法[31 ] 、变窗口的快速NLM法[32 ] 等.但由于前述方法为了提高计算效率,在计算过程中并没有完全遍历每个数据点,因此可能会牺牲计算精度.而基于数据积分算法的快速NLM法[33 ] ,原理上等价于在计算过程中遍历所有数据点,因此在提高计算速度的同时避免了牺牲精度的可能.传统NLM方法在处理实际地震数据时,所选择的滤波参数值通常为一常数,为了进一步提高去噪效果,前人利用结构张量算法[34 -35 ] 、矩阵本征特性算法[36 ] 、灰色关联分析算法[37 ] 等方法,针对不同区域可选择不同的滤波参数来提高去噪效果,但会明显增加计算量.NLM方法的去噪效果很大程度上受滤波器参数的选择影响,如果参数太大,就会丢失细节信息,使图像模糊,如果参数过小,则噪声不能被完全抑制.因此,一些学者通过局部数据的随机噪声估计来自适应的计算滤波参数,例如高通滤波法[38 ] 和最小方差估计法[15 -16 ] .上述这些方法在提高传统NLM方法去噪效果的同时,可以减少滤波参数对计算速度的影响,但该方法在计算效率上仍有提升空间. ...
Analysis and extension of the percentile method, estimating a noise curve from a single image
1
... 与预测滤波方法和降秩滤波方法不同的是,NLM方法并不基于线性假设,因此在处理弯曲同相轴时,该方法可以有效地保护有效信号,压制随机噪声.传统NLM方法起源于图像的随机噪声压制处理[28 ] ,随后Bonar成功地将该方法引入到地震数据噪声压制处理中[13 ] .然而,传统NLM方法在应用上也存在一定局限性.相比于矩阵降秩或预测滤波等方法,该方法计算时间较长,在处理大型地震数据时效率低下.为了解决这一问题,前人提出了分块NLM法[28 ] 、并行分块NLM法[29 ] 、基于随机投影算法的NLM法[30 ] 、下采样的快速NLM法[31 ] 、变窗口的快速NLM法[32 ] 等.但由于前述方法为了提高计算效率,在计算过程中并没有完全遍历每个数据点,因此可能会牺牲计算精度.而基于数据积分算法的快速NLM法[33 ] ,原理上等价于在计算过程中遍历所有数据点,因此在提高计算速度的同时避免了牺牲精度的可能.传统NLM方法在处理实际地震数据时,所选择的滤波参数值通常为一常数,为了进一步提高去噪效果,前人利用结构张量算法[34 -35 ] 、矩阵本征特性算法[36 ] 、灰色关联分析算法[37 ] 等方法,针对不同区域可选择不同的滤波参数来提高去噪效果,但会明显增加计算量.NLM方法的去噪效果很大程度上受滤波器参数的选择影响,如果参数太大,就会丢失细节信息,使图像模糊,如果参数过小,则噪声不能被完全抑制.因此,一些学者通过局部数据的随机噪声估计来自适应的计算滤波参数,例如高通滤波法[38 ] 和最小方差估计法[15 -16 ] .上述这些方法在提高传统NLM方法去噪效果的同时,可以减少滤波参数对计算速度的影响,但该方法在计算效率上仍有提升空间. ...
Fast non-local algorithm for image denoising
1
2007
... 为了提高NLM方法的计算效率,前人提出了一种用数据积分算法来加速NLM方法[33 ,39 ] .常规算法在计算‖V (t ,x )-V (i ,j ) ‖ 2 2 St (t 1 ,x 1 ),可以通过对差分矩阵s (t ,x )积分来表示: ...
Seismic random noise attenuation based on PCC classification in transform domain
1
2019
... 在地震数据噪声压制处理中,通常采用信噪比(SNR )[40 ] 、峰值信噪比(PSNR )和均方误差(MSE )[41 ] 来定量分析方法的地震数据去噪效果,其定义如下: ...
Comparison of image quality assessment: PSNR, HVS, SSIM, UIQI
1
2012
... 在地震数据噪声压制处理中,通常采用信噪比(SNR )[40 ] 、峰值信噪比(PSNR )和均方误差(MSE )[41 ] 来定量分析方法的地震数据去噪效果,其定义如下: ...