0 引言
目前已有一些针对低幅度构造的识别方法及成图技术,如均值滤波法和变速成图法等,但是他们都有些不足,要么无法准确地建立速度变化大的三维速度场,导致畸变、计算量大、成本高,要么过分依赖于构造背景数据,从而出现低幅构造“假象”,影响低幅构造识别效果。传统方法低幅度构造识别难度大,主要是构造背景频段多,影响复杂低幅度构造的判断。本文采用去低频化的方法,提出利用趋势分解法和小波变换法对构造走时数据进行细节与趋势(或低频背景)分解,使斜坡背景或复杂构造背景趋于水平化。从而可以弱化区域构造形态的影响,消除不同构造背景对低幅构造解释的干扰,突出局部构造的细节变化,使局部构造的形态更为直观、清晰[6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]。
1 基本原理
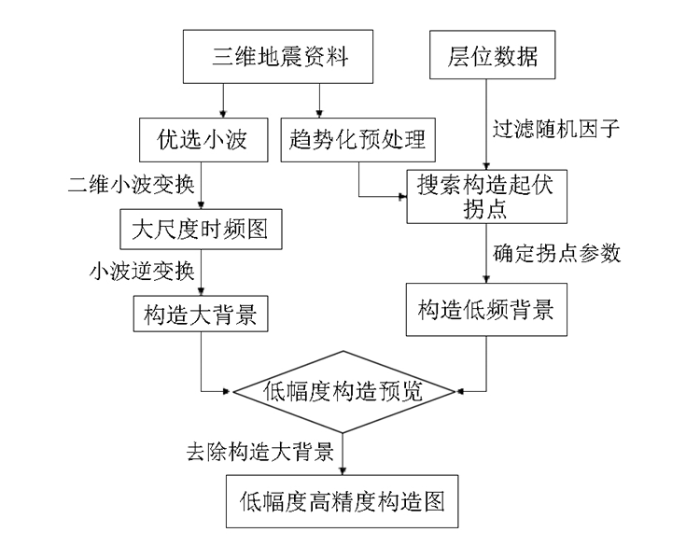
本文利用两类技术从不同的角度对构造解释数据进行分解,进而将构造解释数据分为构造大背景和低幅构造细节,最终削弱构造大背景影响,增强局部微构造特征,使低幅构造得以彰显。这两种技术手段分别是对三维地震构造解释数据进行处理的趋势分解构造成图技术和对二维构造平面数据进行处理的小波分解构造成图技术,图1为技术路线图。
图1
图1
低幅度构造识别技术路线
Fig.1
Roadmap of low-amplitude structure recognition technology
1.1 趋势分解法原理
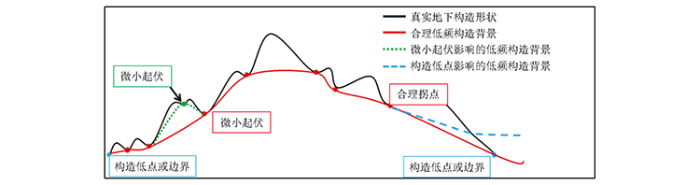
趋势分解法是在三维地震解释构造走时数据体上,根据构造上下起伏及走势搜索拐点位置,再根据拐点位置的构造走时信息插值得到构造趋势面,最后用原来的构造数据减去构造趋势面,即可获得低幅度构造的细节。趋势分解构造成图技术主要包括4个步骤:①趋势化预处理,即对构造层位数据预处理,滤掉随机因子对趋势面的影响,有效控制构造趋势面;②构造起伏拐点搜索,构造起伏拐点是指构造由逐渐下降转为逐渐上升的转折点,往往对应于低幅构造的圈闭溢出点,是勾勒低频构造背景的关键控制点,在成图过程中可以根据构造的幅度自适应调整搜索拐点半径寻找局部极值点来确定拐点;③构造低频背景勾勒,针对构造起伏拐点,利用反距离加权法得到低频背景;④去低频化构造成图,将构造解释与低频背景叠合,提取低幅构造数据,形成低幅度构造平面图。
图2
图3
图3
构造起伏拐点及搜索半径示意
Fig.3
Construction of undulation inflection point and search radius map
通过趋势分解法进行构造成图,最大的优势就在于不用构造速度场,通过拐点的有效搜索和确定,使得构造解释既包含低幅度构造趋势又突出局部微小起伏。
1.2 小波分解法原理
在本文中,我们用到的二维小波正变换公式为:
式中:a为尺度参数,b、c分别为沿x、y方向平面位置参数,f (x,y)代表构造走时解释平面数据,gx
二维构造走时解释平面数据经过二维小波多尺度分析后,选取大尺度数据进行二维小波逆变换即得到构造大背景。其二维小波逆变换的公式为:
其中:Cg为小波函数的傅里叶变换,Gg为g的傅里叶变换。
1.3 去低频化构造成图
利用去低频化思路,采用趋势分解法和小波分频法进行低幅度构造成图。值得注意的是,在趋势分解法实现过程中,先进行趋势化预处理,滤掉随机因子干扰趋势面的影响。然后进行构造低频背景勾勒,通过搜索构造起伏拐点,利用反距离加权法得到低频背景。随后在构造大背景预测图中,重新调整成图参数,进一步提高构造的大尺度连续性。为了提高构造成图的细节变化,可利用小波分频的原理。优选出小波基函数,对构造数据进行二维小波变换,得到二维尺度时频图。再通过小波逆变换,得到基于小波分解的低幅度构造平面图。
图4为两种方法的局部对比,从图中可知,两种方法体现构造宏观趋势一致,只是局部有差异,因此在实现过程中,将二者有效结合,利用这两种方法,可以消除大构造背景影响,展现低幅构造细节。
图4
图4
两种构造成图法对比
a—趋势分解低频背景;b—小波分解低频背景;c—趋势分解低幅构造细节;d—小波分解低幅构造细节
Fig.4
Comparison map of two construction methods
a—low frequency background of trend decomposition;b—low frequency background of wavelet decomposition;c—low amplitude strunctural details of trend decomposition;d—low amplitude strunctural details of wavelet decomposition
2 实例应用及效果分析
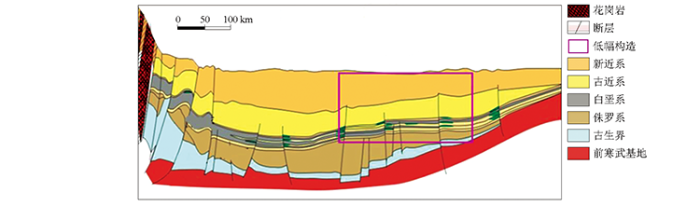
本次选取的研究区位于E盆地,目的层为白垩系M组砂岩油层,主要发育低幅度构造和构造—岩性复合圈闭,如图5所示,其构造幅度不超过10~15 m,由于构造幅度小于地质构造解释精度,加上储层薄的特点,常规构造方法难以精细刻画低幅度构造圈闭中的油气分布。
图5
图6
图7
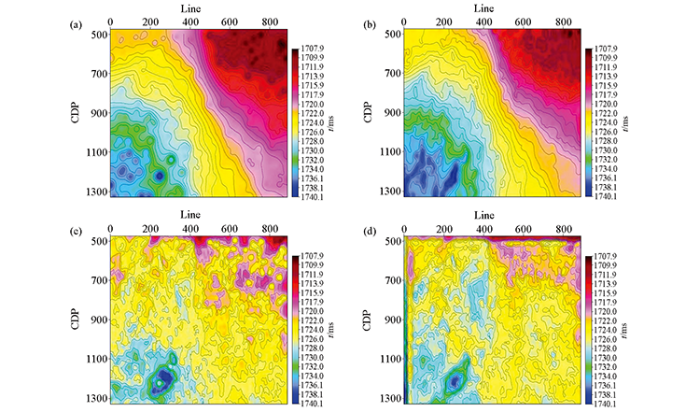
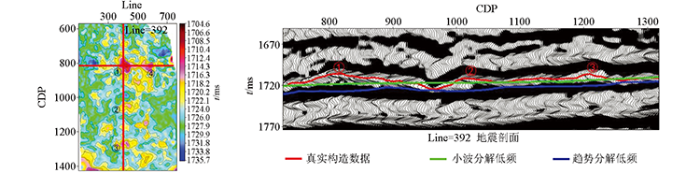
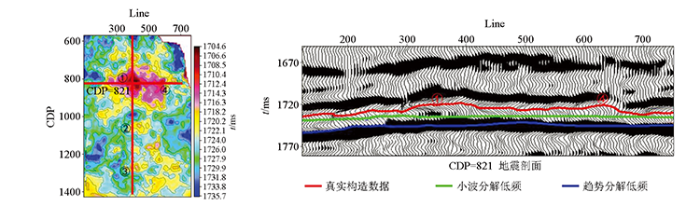
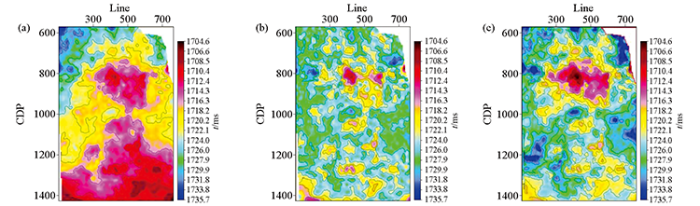
图8为研究区M1层低幅构造平面对比,从图中不难看出:两种方法预测结果相似性较大,趋势分解法在工区西部,幅度较小的低幅构造识别上效果更精细,小波分解法可以辅助低幅构造的解释。但趋势分解法成图效果依赖搜索半径,使得构造特征不连续,稍逊色于尺度连续的小波变换。经过小波变换后的大尺度时频分析,保持住构造低频背景,从而保证构造连续性。既有构造背景趋势,又具有局部聚焦性。整体上看,利用小波分解法消除了大构造背景影响,展现了低幅构造细节。将两者有机结合,通过与单一方法对比,结合后得到的构造图不仅消除了大构造背景的影响,而且可以展现低幅构造细节。可以有效实现对研究区低幅度构造的识别和构造成图分析。
图8
图8
研究区M1层低幅度局部构造平面对比
a—M1层原始局部构造平面;b—基于趋势分解法M1层局部构造平面;c—基于小波分解法M1层局部构造平面
Fig.8
Contrast map of low-amplitude structural plane of M1 layer in the study area
a—original local tectonic plane of M1 layer;b—local tectonic plane of M1 layer based on trend decomposition method;c—local tectonic plane of M1 layer based on wavelet decomposition method
3 结论
本文利用趋势分解法和小波分解法联合的低幅度构造识别及成图方法,既增强了局部微构造特征,又兼顾了低幅度构造宏观背景。在E盆地北部中的应用中效果明显,给后续的地质解释和储层描述提供了依据。通过分析研究,得出以下结论:
1)由于低幅构造尺度大小不一,本文充分利用二维小波变换尺度的冗余特性,实现了对构造解释成果的二维图像多尺度分解;
2)为避免小波变换在构造解释数据缺失的情况下,边缘效应严重的问题,本文使用趋势分解法,实现了去低频化的多尺度处理,并在较大程度上克服了因数据点缺失带来的边缘效应;
3)针对目前低幅构造成图技术的不足,本文从不同角度采用趋势分解法与二维小波分解法分别对低幅构造进行成图,实现区域背景与局部低幅度构造的有效分离,增强局部微构造特征,使其在构造平面图上得以凸显。
参考文献
低幅度构造地震解释探讨
[J].
Discussion on the interpretation of low-amplitude structural Seismic
[J].
二维小波变换在地震勘探面波消除中的应用
[J].
Application of two-dimensional wavelet transform in eliminating surface waves in seismic exploration
[J].
Application of two dimensional trend surface analysis in the process of recognizing the tiny structure
[J].
Multi-parameter analysis of identifying micro amplitude structures by moving trend surface method
[J].
低幅度构造识别技术在南美奥连特盆地油气勘探中的应用
[J].
Application of low-amplitude structural identification technology in oil and gas exploration in Orient Basin,South America
[J].
A bandwidth enhancement workflow through wavelet analysis
[C]//
Applications of time-domain high-resolution Radon demultiple
[J].
基于广义S变换的地震资料高效时频谱分解
[J].
Efficient time-frequency spectrum decomposition of seismic data based on generalized S transform
[J].
三肇凹陷微幅度构造群与油气聚集规律
[J].
Micro-amplitude structural groups and oil and gas accumulation rules in Sanzhao Sag
[J].
地层倾角测井资料在低幅度构造解释中的应用
[J].
Application of formation dip log data in low-amplitude structural interpretation
[J].
沙漠覆盖区的低幅度构造研究
[J].
Research on low amplitude structure in desert covered area
[J].
准噶尔盆地近地表结构复杂条件下低幅度和岩性、地层圈闭的勘探
[J].
Exploration of low amplitude,lithology and stratigraphic traps under complex conditions of near surface structure in Junggar Basin
[J].
二维地震资料落实低幅度圈闭方法探讨
[J].
Discussion on the method of implementing low amplitude traps in 2D seismic data
[J].
南海低幅度构造解释中Paradigm软件的应用
[J].
Application of paradigm software in the interpretation of low amplitude structure in the South China Sea
[J].
低幅度构造成图技术
[J].
Low-amplitude construction mapping technology
[J].
利用叠前Kirchhoff积分偏移识别小断裂与低幅度构造
[J].
Identification of small faults and low-amplitude structures using pre-stack Kirchhoff integral migration
[J].
低幅度构造油藏研究方法
[J].
Low-amplitude structural reservoir research method
[J].
南美前陆盆地斜坡带低幅度构造的识别方法
[J].
Recognition method of low-amplitude structures in slope zone of South American foreland basin
[J].
S变换在低幅度构造识别中的应用——以准噶尔盆地腹部陆10—陆6井区为例
[J].
Application of S-transform in the identification of low-amplitude structures:A case study from Well No.10 to No.6 in the hinterland of Junggar Basin
[J].