0 引言
1 含水采空区正演模拟响应
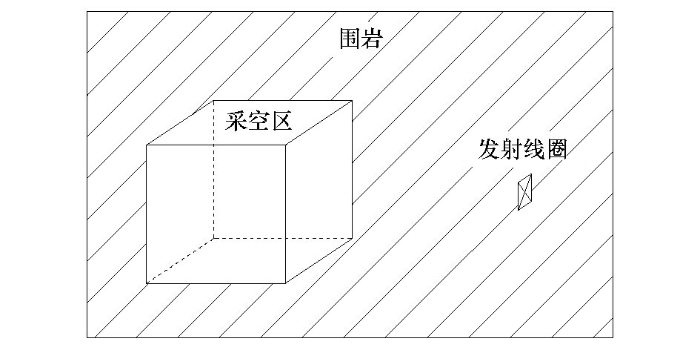
建立全充水采空区有限元模型,如图1所示。综合考虑煤层采后形成的顶板导水裂缝带,设置低阻体为棱长50 m正方形,几何中心距离线圈75 m,电阻率为0.25 Ω·m。均质围岩背景场电阻率设置为1 000 Ω·m,线圈发射电流频率设置为25 Hz。按照15°间隔,由右帮0°~左帮180°沿扇面均匀布置13个测点,其中90°测点方向指向含水采空区模型。
图1
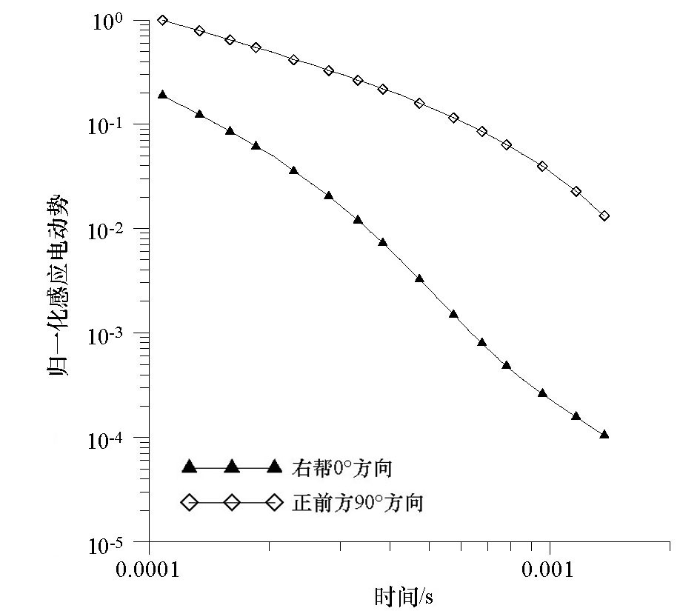
图2所示为电性响应差异最大的右帮0°及正前方90°测点方向的感应电动势衰减曲线,可以看出在观测初期二者处于同一量级水平,随观测时间的增加,含水采空区方向电动势值下降2个量级,为初期值的1/50左右,背景场方向电动势下降达4个量级,为初期值的1/2 000左右。在观测阶段内,含水采空区感应电动势值域水平整体显著高于背景场。
图2
图2
含水采空区测点电动势模拟成果
Fig.2
EMF simulation results of measuring points in water bearing goaf
根据时间域电磁法特点,模拟所得数据体反映的是二次场电动势—时间关系,需通过
计算转化为视电阻率—时间关系[12],再进行相应时间—深度转换关系得出电阻率—深度关系。式中:ρs为视电阻率;B、C分别为装置、空间响应系数;S、N和s、n分别表示发射和接收线圈的面积、匝数;
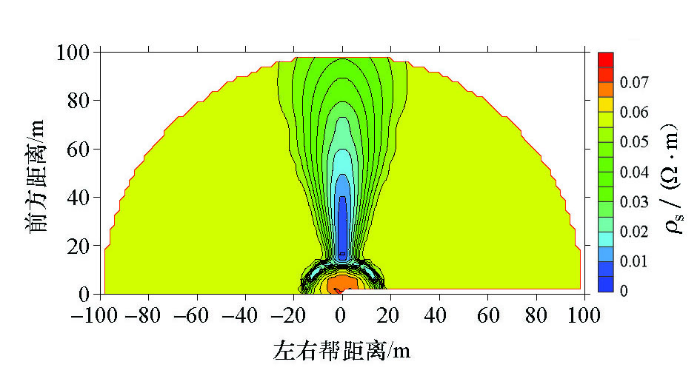
图3
图3
含水采空区空间电性模拟结果
Fig.3
Spatial electrical simulation results of water bearing goaf
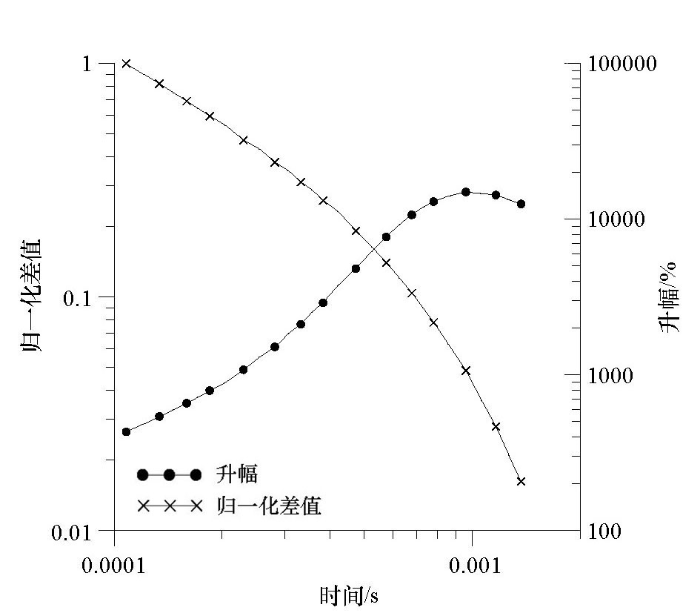
图4
图4
模拟含水采空区二次场电动势变化
Fig.4
Simulation of EMF change of secondary field in water bearing goaf
由图4中升幅曲线可以得出,观测初期正前方90°含水采空区影响下的二次场感应电动势相比右帮0°相对正常围岩背景场下的感应电动势数值增大4倍左右,但由于对低阻体敏感,二者间的电位升幅呈现急剧增大而后稳中有降特征,在0.001 s内总体升幅可达100倍以上。
进一步对两个方向的感应电动势差值进行归一化分析,可以发现与图2双对数坐标系中电动势差值逐步增大的表象不同的是,观测阶段异常体及背景场的二次场感应电动势差值随时间实际为单调递减关系,与升幅曲线变化趋势大体上相反。
2 应用实例
2.1 物探成果
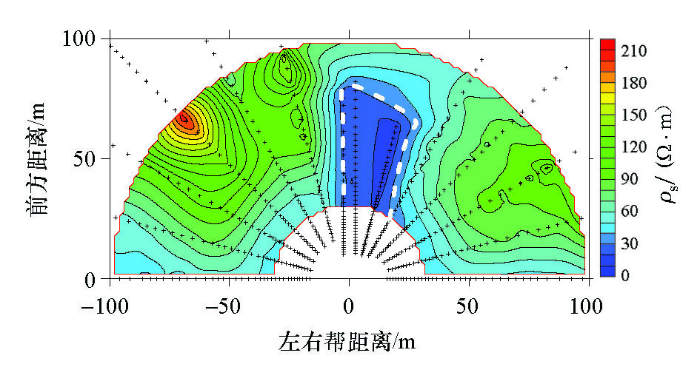
探测地点位于晋煤集团9号煤层,现场物探施工条件较好,布置扇形观测系统。根据矿方地质资料,本次探测范围内存在资源整合矿井遗留空巷,具体赋存情况未知,水平横向探测成果如图5所示。
图5
图5
含水采空区空间电性实测成果
Fig.5
Measured results of spatial electrical properties of water bearing goaf
图5中,右帮75°至正前方90°范围内存在1处低阻区域,如虚线部分所示,深度范围为沿探测方向80 m以内。该区域内的数据散点距离密度高于其他方向,反映出相同观测时窗下的对应测点二次场传播距离小,衰减速度慢。
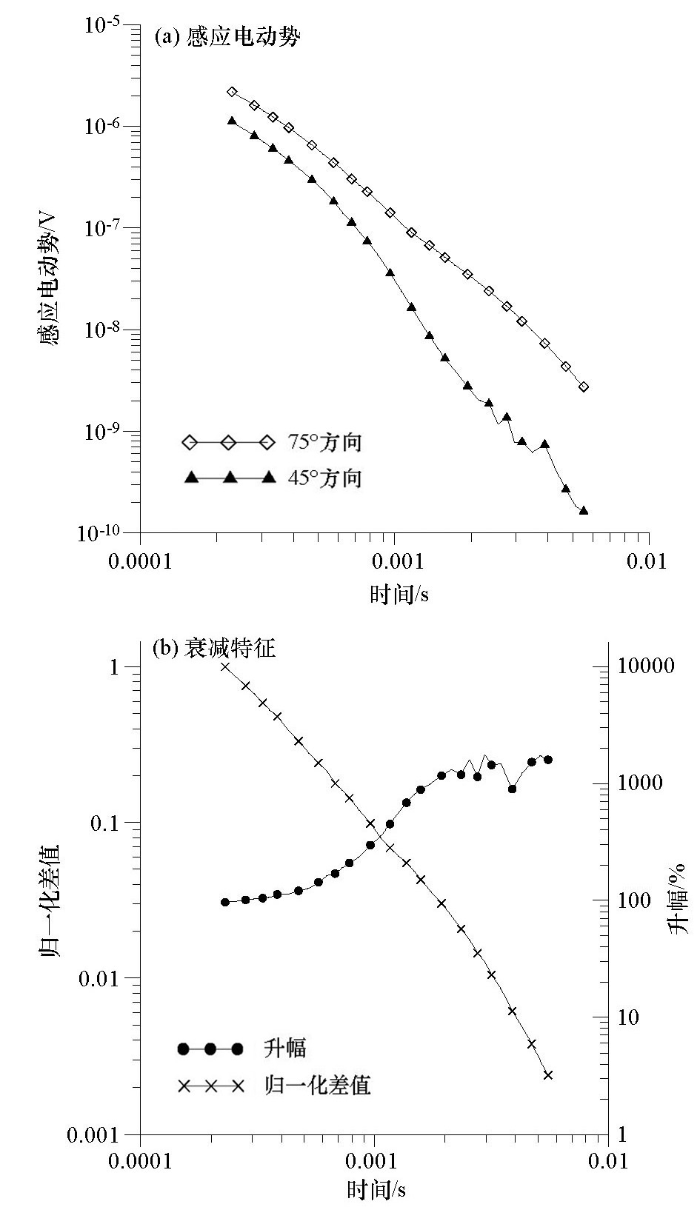
提取右帮45°方向相对正常背景场及75°方向低阻响应测点电动势曲线进行分析,探测过程中测点角度逆时针旋转对应的感应电动势变化情况如图6所示。
图6
图6
实测含水采空区二次场电动势及其衰减特征
Fig.6
Measured EMF of secondary field and its attenuation characteristics in water bearing goaf
从图6a的电动势衰减曲线对比可以得出,观测初期二者值域水平位于同一量级,为n×10-6 V。随时间推移,二者数值均跨量级衰减,观测后期分别降至n×10-9、n×10-10 V,分别下降3个量级和4个量级。
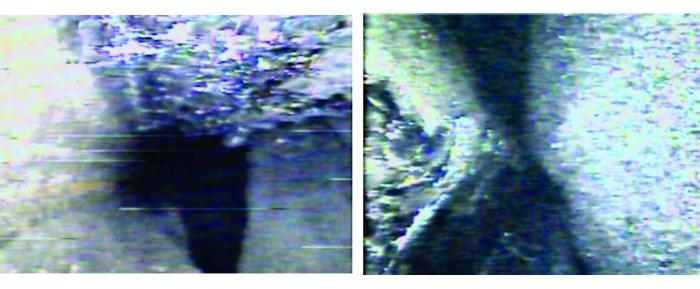
2.2 钻孔窥视
图7
图8
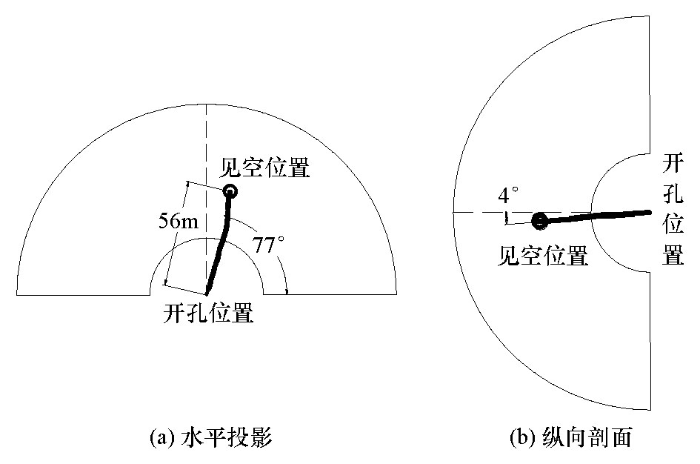
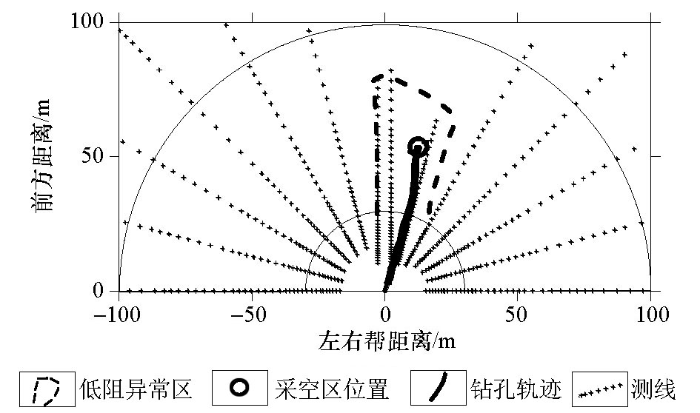
将钻孔窥视轨迹与物探异常区范围叠加,如图9所示。图中,实线表示钻孔轨迹,末端为见空出水位置;闭合虚线为划定的低阻异常区范围,放射状散点为各探测方向相应距离深度的视电阻率数据。
图9
2.3 化探分析
表1 水样离子浓度
Table 1
| 离子 | 浓度/(mg·L-1) | 占比/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| K+ | 8.71 | 0.67 | |
| Na+ | 216 | 28.29 | |
| 阳离子 | Ca2+ | 112 | 16.87 |
| Mg2+ | 217.6 | 53.96 | |
| Fe3+ | 1.27 | 0.21 | |
| Cl- | 50.35 | 7.79 | |
| 420 | 37.83 | ||
| 阴离子 | 0 | 0 | |
| 473.9 | 54.24 | ||
| 1.19 | 0.14 |
3 结论
1) 模拟及实测成果共同显示,含水采空区瞬变电磁响应的横向角度对应一致性比纵向深度对应性更好,现场探测前需做好深度参数试验工作。
2) 含水采空区感应电动势升幅呈现出在二次场观测初期急剧增大而后趋缓的特征,整体可达10倍以上。感应电动势差值在观测时间内整体单调递减,与升幅曲线变化趋势总体上相反。
3) 钻孔窥视及化探水质分析进一步验证了物探成果,为后续防治工作奠定基础。
参考文献
地面与井下瞬变电磁法联合探测煤矿富水区域
[J].
The application of combined ground and underground coal mine transient electromagnetic methods to the exploration of water-rich area
[J].
小煤窑采空积水区的探查方法
[J].
Method for finding out water accumulation area in small coal mine
[J].
瞬变电磁法在探查工作面上覆煤层采空区富水性中的应用
[J].
Application of transient electromagnetic method in detecting water richness in goaf of overburden coal seam at working face
[J].
地—井瞬变电磁响应特征研究
[J].
Research on response of ground-borehole TEM
[J].
瞬变电磁法探测超高水材料注浆治理采空区效果
[J].
TEM inspecting of goaf treatment effect with grouting super high water material
[J].
积水采空区地面-钻孔瞬变电磁探测技术
[J].
Technology of detecting water-filled goaf beside borehole using downhole transient electromagnetic method
[J].
老空水全空间瞬变电磁法探测三维数值模拟研究
[J].
Study on whole space transient electromagnetic method prospect three dimensional numerical modeling of gob water
[J].
典型地质异常体电磁法响应特征研究
[J].
Study of electromagnetic response characteristics of typical geological anomalous body
[J].
矿井瞬变电磁法参数优化试验及超前探测应用
[J].
Parameters optimization test of mine transient electromagnetic method and application of advanced detection
[J].
井下富水区瞬变电磁响应特征分析
[J].
Transient electromagnetic response characteristics of mine water-rich area
[J].
煤矿采空区瞬变电磁超前探测波场成像研究
[J].
Wave field imaging system in advance detection of watery goaf using mine transient electromagnetic method
[J].
矿井瞬变电磁探测技术的应用
[J].
The application of mine transient electro-magnetic detection technology
[J].