0 引言
20世纪60年代,地面伽马能谱测量已被前苏联等国提出并应用在铀矿找矿中。之后,美国将航空伽马能谱测量的应用拓展到油气田、金属矿等能源矿产的勘查中[1,2,3,4]。1954年我国首次在辽宁省海城利用伽马能谱测量寻找铀矿。20世纪70~80年代,随着我国航空和地面伽马能谱仪的技术的发展[5,6,7],伽马能谱测量成为开展区域铀矿资源勘查的重要手段。在这期间,我国大多数铀矿床是由航空伽马能谱发现的[8,9]。然而,在可地浸砂岩型铀矿勘查中,地面伽马能谱测量因受地面覆盖层等的影响,找矿示踪效果不明显。因此,文章以松辽盆地开鲁坳陷大林地区铀矿产地为研究对象,对区内地面伽马能谱测量数据进行钍归一化法处理,据此分析区内铀元素的分布特征,探讨铀元素的迁移富集与铀成矿之间的关系。
1 区域地质概况及地球物理特征
1.1 地质概况
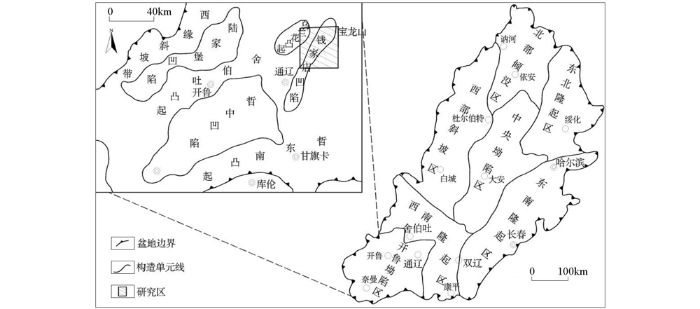
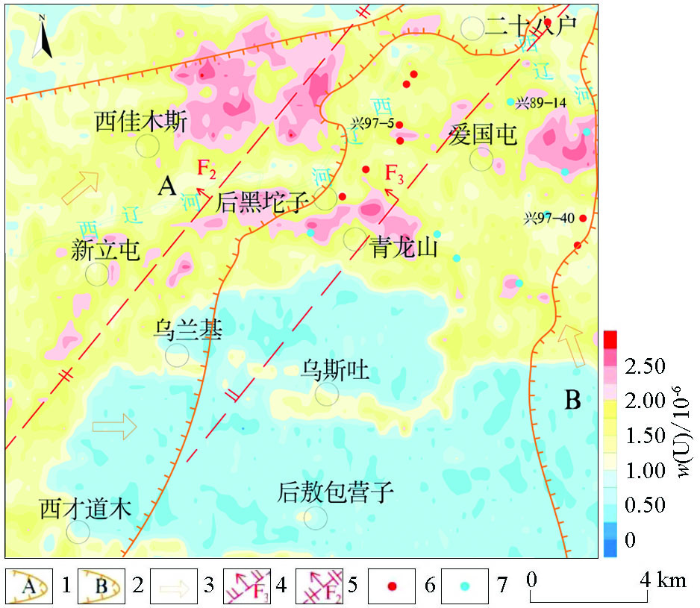
图1
图1
研究区位置及构造单元划分
Fig.1
Location of study area and interior tectonic units of the Basin
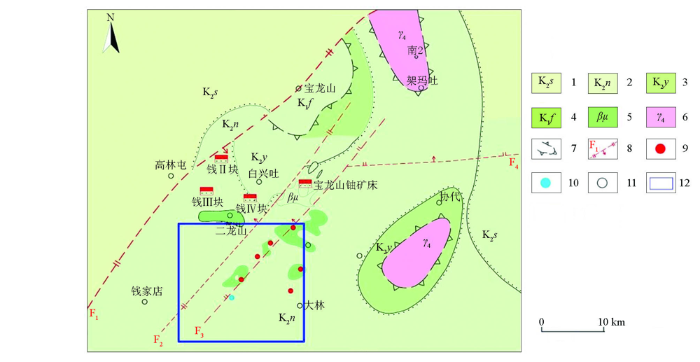
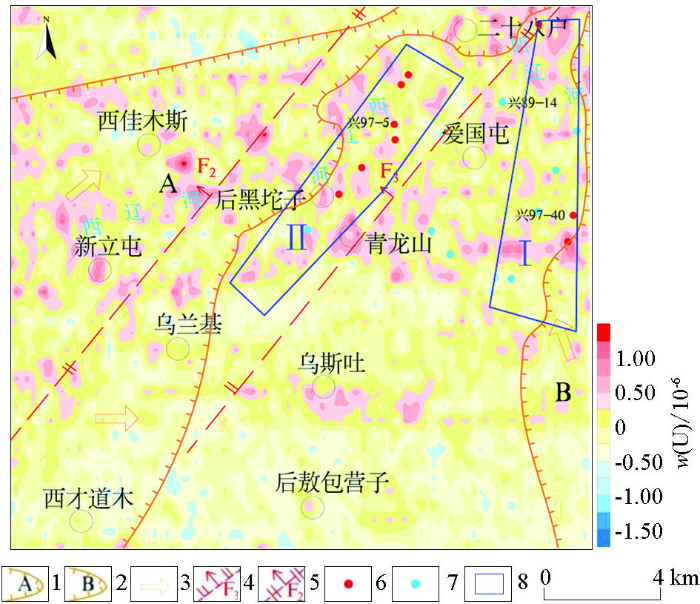
图2
图2
大林地区构造纲要
1—上白垩统四方台组;2—上白垩统嫩江组;3—上白垩统姚家组;4—下白垩统阜新组;5—辉绿岩;6—海西期花岗岩;7—花岗岩古隆起边界;8—断层;9—铀工业矿孔;10—铀矿化孔;11—无矿孔;12—工作区范围
Fig.2
Structural outline map of Dalin area
1—Sifangtai formation of upper Cretaceous;2—Nenjiang formation of upper Cretaceous;3—Yaojia formation of upper Cretaceous;4—Fuxin formation of lower Cretaceous;5—diabase; 6—Hercynian granite;7—boundary of granite palaeo-uplift; 8—fault;9—uranium industrial hole;10—uranium mineralization hole;11—non mineralized hole;12—workspace area
1.2 地球物理特征
表1 大林地区铀、钍、钾含量及特征参数统计
Table 1
| 类别 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数/% | X+δ | X+2δ | X+3δ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U/10-6 | 0.10 | 3.70 | 1.25 | 0.62 | 49.16 | 1.87 | 2.49 | 3.10 |
| Th/10-6 | 0.20 | 14.00 | 5.18 | 2.60 | 50.07 | 7.78 | 10.37 | 12.97 |
| K/% | 0.70 | 2.80 | 1.66 | 0.22 | 13.29 | 1.88 | 2.11 | 2.33 |
| Th/U | 0.25 | 9.29 | 4.21 | 1.67 | 2.69 | 5.88 | 7.55 | 9.22 |
| (U /K)/10-4 | 0.04 | 1.87 | 0.76 | 0.37 | 2.14 | 1.13 | 1.50 | 1.87 |
| (Th / K)/10-4 | 0.14 | 7.93 | 3.13 | 1.61 | 1.77 | 4.74 | 6.35 | 7.96 |
2 方法理论依据
在自然界中,放射性元素铀、钍、钾的分布受地球化学条件的影响较大,它们的基本特性是:铀的化学性质相对较活泼,属于典型的亲氧元素。在不同的地球化学环境下,6价铀和4价铀可以相互转化。当在氧化环境中可形成6价易溶于水的铀盐,以溶液的形式运移;但在还原环境中,6价铀通过还原作用转化为4价铀而沉淀下来;钍元素形成的化合物性质稳定,主要以机械迁移为主,一般不受其他因素干扰;钾的化学性质与钠相似,不同环境形成的盐类均易迁移。据铀、钍、钾化学特性的差异可以看出,钍元素可以真实反映出地层原始状态下的元素分布特点。对于砂岩型铀矿化,钾是无效的,而深部的铀元素或钍元素经衰变产生的氡及其子体,可以通过断裂构造提供的向上运移的通道,从而使得地表测量出来的铀元素和钍元素含量增高[17,18],因此可利用铀或钍作为指示元素[19],圈定铀成矿有利地段。
已有研究表明,铀、钍、钾3种天然放射性元素是按一定的比例赋存于地层之中,且各元素之间呈正相关[24],各地层U、Th之间遵循以下回归方程:
式中:QUy为据钍含量计算得到的预测铀含量值;A、B为方程的回归系数;QUd为已消除非矿化因素干扰,可作为砂岩型铀矿找矿有用信息的铀剩差。这种将钍元素含量作为控制因素来确定预测铀元素“理想”原始含量,称之为钍归一化法。
3 钍归一化法在大林地区的应用
3.1 方法的实施
在已有预处理的大林地区地面伽马能谱数据的基础上,依据全区铀、钍含量变化的特点,对全区所有测量结果进行统计分析,建立大林地区U-Th拟合曲线并得到回归方程,其拟合方程为:
利用式(3)可求得大林地区各测点预测铀含量值。结合式(2),可得各测点归一化铀剩差值。
3.2 区域场分析
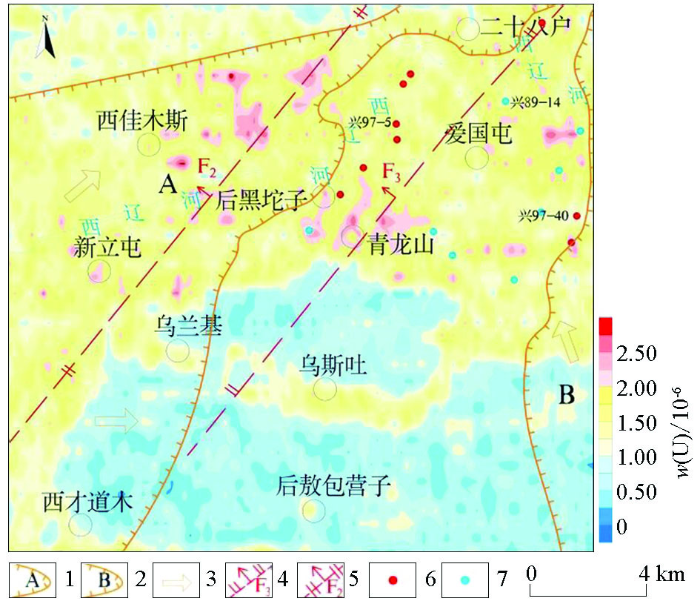
区内地表均为第四系覆盖,实测铀的含量最低为0.10×10-6,最高含量为3.70×10-6,背景值为1.25×10-6,标准偏差为0.62,变异系数为49.16%,铀含量背景值相对较低,异常晕较多,但规模较小,多呈椭圆状、不规则面状分布;空间上多集中在研究区中北部,异常晕分布在西佳木斯以东、后黑坨子—青龙山及爱国屯东侧,异常晕(带)整体上受NE向构造控制,呈NE向展布,位于氧化带附近(图3),反映出区内实测铀含量的变化与NE向构造及氧化带存在着较为密切的联系。
图3
图3
大林地区实测铀含量等值线
1—A号氧化带;2—B号氧化带;3—氧化水流向;4—正断层;5—反转断层;6—铀工业矿孔;7—铀矿化孔
Fig.3
Contour map of measured uranium content in the Dalin area
1—oxidation zone A; 2—oxidation zone B; 3—flow direction of oxidation water; 4—normal fault; 5—inverted fault; 6—uranium mineralization hole; 7—non mineralized hole
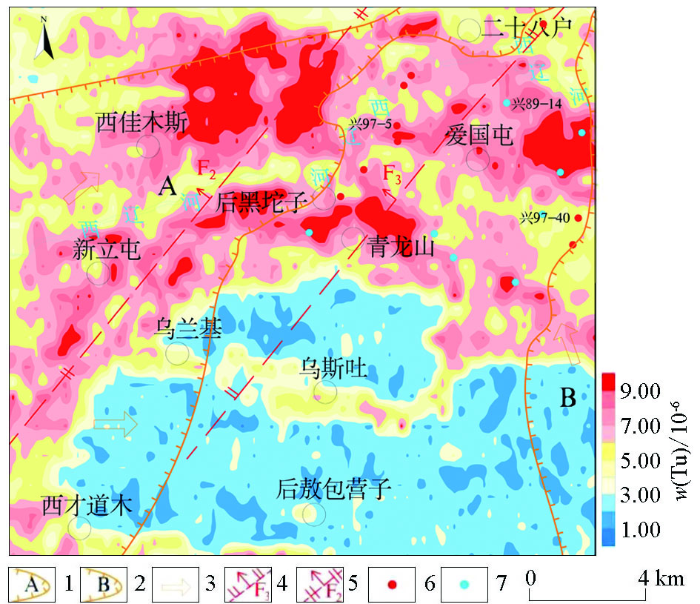
区内实测钍的含量最低为0.20×10-6,最高为14.00×10-6,背景值为5.18×10-6,标准偏差为2.60,变异系数为50.07%,总体较为平稳。图4表明,钍元素分布特征与铀元素分布特征相似,具有北高南低的特征,异常晕主要分布在研究区的北部,连续性较好且面积较大,主要位于NE向构造F2和F3两侧,整体呈近NNE向分布。
图4
图4
大林地区实测钍含量等值线
1—A号氧化带;2—B号氧化带;3—氧化水流向;4—正断层;5—反转断层;6—铀工业矿孔;7—铀矿化孔
Fig.4
Contour map of measured thorium content in the Dalin area
1—oxidation zone A; 2—oxidation zone B; 3—flow direction of oxidation water; 4—normal fault; 5—inverted fault; 6—uranium mineralization hole; 7—non mineralized hole
3.3 钍归一化处理
利用式(3),将研究区内地面伽马能谱数据进行钍归一化处理,求得各测点预测铀含量值,预测铀含量值最低为0.50×10-6,最高为2.30×10-6,背景值为1.26×10-6,标准偏差为0.37,变异系数为21.74%。预测铀含量空间分布(图5)表明,预测铀含量与实测铀含量整体分布相似,也具有北高南低的特征,呈NE向展布,异常晕面积增大,整体呈面状分布于构造及氧化带两侧。通过预测铀含量与实测铀含量异常晕分布情况的对比,可知区内铀元素存在迁移富集现象。
图5
图5
大林地区预测铀含量等值线
1—A号氧化带;2—B号氧化带;3—氧化水流向;4—正断层;5—反转断层;6—铀工业矿孔;7—铀矿化孔
Fig.5
Contour map of predicted uranium content in the Dalin area
1—oxidation zone A;2—oxidation zone B;3—flow direction of oxidation water;4—normal fault;5—inverted fault;6—uranium mineralization hole;7—non mineralized hole
为进一步了解大林地区铀矿化与铀元素分布的关系,通过式(2)可求得区内各测点钍归一化铀剩差值。区内铀剩差值最低为-1.97×10-6,最高为2.09×10-6,标准偏差为0.50,变异系数为-135.86%,铀剩差变化相对较大。由图6可知,铀剩差异常晕大多分布在工作区北部的F2和F3断裂两侧,受区内氧化带控制较为明显。结合大林地区目前钻探查证及地质因素等综合分析,大林地区铀矿化主要受控于区内的构造及层间氧化作用,大致可推测出有利地段2处(即有利地段Ⅰ和Ⅱ)。其中有利地段Ⅰ位于断裂F3及爱国屯的东侧,主要受氧化带B控制。该区异常晕集主要位于北段,中段有零星异常晕分布,该区目前已发现多个铀工业矿孔;有利地段Ⅱ位于断裂F2和F3之间的青龙山附近,异常晕呈NE向串珠状展布,局部呈带状。该区为目前大林主矿体所处部位,位于氧化带A的前锋线附近,受氧化带A控制较明显。通过对大林地区铀剩差异常与大林地区控矿因素的综合分析可知,位于氧化带前锋线的铀剩差异常晕区域极有可能为铀矿富集区。
图6
图6
大林地区铀剩差等值线
1—A号氧化带;2—B号氧化带;3—氧化水流向;4—正断层;5—反转断层;6—铀工业矿孔;7—铀矿化孔;8—有利地段及编号
Fig.6
Contour map of residual uranium content in the Dalin area
1—oxidation zone A; 2—oxidation zone B; 3—flow direction of oxidation water; 4—normal fault; 5—inverted fault; 6—uranium mineralization hole; 7—non mineralized hole; 8—favorable areas and number
4 铀找矿有利地段
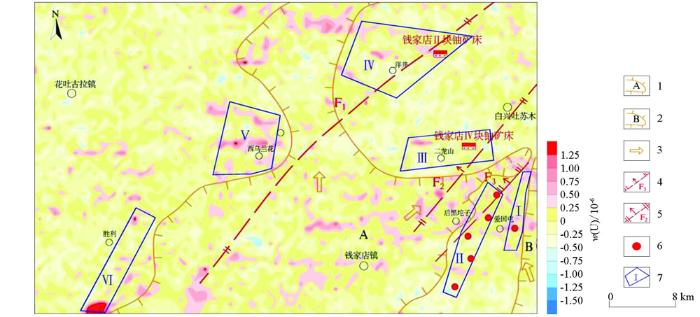
为了进一步研究钍归一化铀剩差与深部铀矿化之间的关系,通过对开鲁坳陷地面伽马能谱数据进行钍归一化处理,提取了铀剩差信息(图7)。从图7可知,开鲁坳陷铀剩差异常晕大多呈片状、串珠状,异常晕分布较为零散,皆位于区内断裂及氧化带附近。异常晕整体呈NE向展布,与区内断裂及氧化带走向一致,进一步说明铀异常晕受构造及氧化带控制较为明显。依据大林地区铀剩差异常晕与断裂、氧化带之间的关系,结合开鲁坳陷已知构造及钻孔控制的推测氧化带位置,可划分出有利地段6处。其中已确定的大林地区有利地段2处,其余4处分别位于二龙山、洋井、西乌兰花及胜利,均分布于氧化带前锋线。其中钱家店Ⅳ块铀矿床位于有利地段Ⅲ附近,与断裂F2毗邻;钱家店Ⅱ块铀矿床位于有利地段Ⅳ附近,与断裂F1关系密切。有利地段Ⅴ及Ⅵ均位于断裂F1西侧,受氧化带A控制较为明显。由此可见,铀剩差异常晕对铀矿化信息具有一定的指示作用。
图7
图7
开鲁坳陷铀剩差
1—A号氧化带;2—B号氧化带;3—氧化水流向;4—正断层;5—反转断层;6—铀工业矿孔;7—有利地段及编号
Fig.7
Contour map of residual uranium content in Kailu Sub-basin
1—oxidation zone A; 2—oxidation zone B; 3—flow direction of oxidation water; 4—normal fault; 5—inverted fault; 6—uranium mineralization hole; 7—favorable areas and number
5 结论
1) 通过对大林地区地面伽马能谱实测铀含量、预测铀含量及铀剩差分布特征可知,异常晕与区内深大断裂关系密切。因该区断裂对铀成矿控制作用明显,故钍归一化法对该区铀矿勘探具有一定指示作用。
2) 铀元素在氧化环境中易溶解迁移,还原环境中沉淀富集。对比铀剩差异常晕与氧化带的空间位置关系,表明铀剩差异常晕可能位于氧化还原过渡带。
3) 将铀剩差异常晕与区内断裂和氧化带的空间位置相对比,圈定有利地段6处。经钻探查证,有利地段Ⅰ和Ⅱ异常晕展布情况与大林地区主矿体分布相吻合;有利地段Ⅲ、Ⅳ内已分别探明了钱家店Ⅳ、Ⅱ块铀矿床。
4) 利用地面伽马能谱经钍归一化法,分析铀剩差分布特征,结合区域控矿因素,在可地浸砂岩型铀矿找矿中具有一定的指导作用。
参考文献
地面高精度磁测与γ能谱测量一体化研究
[D].
The integration studies of ground high-accuracy magnetic prospecting and gamma-ray spectrometry measurement
[D].
步行式γ能谱测量在航磁异常查证中的应用研究
[D].
Application study of the walking gamma spectrometer measurement method in the aeromagnetic anomalies
[D].
基于PDA和蓝牙的数字化γ能谱仪的研制
[D].
The development of digital γ spectrometer based on PDA and bluetooth
[D].
伽玛能谱低能谱段地质填图方法研究
[D].
The Research on geological mapping method for low energy spectrum of gamma-ray spectrometry
[D].
应用航空伽玛能谱全谱信息预测铀成矿远景区
[C]
Prognoses of prospective areas for uranium metallogenesis with full-spectrum information of airborne gammy-ray survey
[C]
航空伽玛探测器能谱响应规律研究
[D].
The study of γ energy spectrum response law in airborne gamma-ray spectrometry
[D].
用航空γ能谱法普查铀矿
[J].
Uranium prospectingby airborne gamma spectrometry
[J].
相山铀矿田航空能谱数据图像处理与分析
[J].
Image processing and analysis of airborne gamma spectrum in Xiangshan uranium ore-field
[J].
开鲁盆地晚中生代地层
[J].
Late mesozoic strata of the Kailu basin
[J].
CSAMT法在松辽盆地伊胡塔地区嫩江组中的定位应用
[J].上白垩统嫩江组不仅是松辽盆地南部重要的生油层系,而且在本区砂岩型铀成矿中也起着非常重要的作用。从ZK4孔的方法过井测深试验以及地电结构的对比分析入手,对探区内嫩江组的空间分布范围进行了分析研究,通过钻探施工,证实了CSAMT法应用的有效性。
The orienting application of the CSAMT method in Nenjiang formation, Yihuta area, southwest Songliao basin
[J].Upper Cretaceous Nenjiang Formation not only is an important oil formation in south Songliao Basin, but also plays an important role in the formation of the sandstone type uranium deposit. This paper made orientation for spatial distribution characteristics of regional Nenjiang Formation through the measurement of the depth in ZK4 and a geoelectric structural contrast analysis. The results have proved the validity of the application of this method and attained the expected purpose.
中国北方中新生代盆地砂岩型铀超常富集的驱动力
[J].
Driving forces for sandstone-type uranium super-enrichment in Meso-Cenozoic basins, north China
[J].
Global miocene tectonics and regionalsandstone-style uranium mineralization
[J].
相山河元背铀矿床近外围物化探异常特征及找矿效果
[J].
Geophysical and geochemical abnormal characteristics and ore-prospecting effect in the near perimeter area of Heyuanbei uranium deposit, Xiangshan ore-field
[J].
伽玛能谱测量的应用及资料处理的探讨
[J].
Application of gamma spectrometry survey and discussion on data processing
[J].
青海查查香卡地区地面伽马能谱特征与铀成矿关系研究
[J].
Characteristics of ground gamma spectrum and its relationship with uranium mineralization in Chachaxiangka area, Qinghai
[J].
地面氡及其子体测量在新疆汉水泉地区砂岩型铀矿找矿中的应用
[J].
The application of Fadon and its doughters survey to exploration of sandstone-type uranium deposits in Hanshuiquan area
[J].
应用特征参数GU、FU、B处理区域伽玛能批资料的效果初探
[J].
The primary results of using the characteristic parameters GU,FU,B to process the regional data of gamma-ray spectrometry
[J].
中国铀、钍、钾元素地球化学场特征及与铀矿化关系
[J].
DOI:10.11720/j.issn.1000-8918.2014.2.03
URL
[本文引用: 1]

一直以来,利用铀、钍、钾同位素的γ能谱寻找铀矿是铀矿地质重要的放射性物探手段。同样,水系沉积物化探中铀、钍、钾元素作为铀矿化探重要指示元素,在铀矿资源潜力预测评价中亦发挥了重要作用。笔者论述了水系沉积物铀、钍、钾元素在铀矿预测评价中的指示作用和异常特点,以及中国铀、钍、钾元素地球化学场分布特点和规律,将铀、钍、钾异常按累频占比划分为特高异常(异常内带)、高异常(异常中带)、异常(异常外带)和高背景,同时,论证了铀、钍、钾异常分布与铀成矿关系。可以看出,铀、钍、钾异常分布有明显的区域特征,现有的异常分布区与我国四大类型铀矿产区高度一致,其异常分布对我国铀、钍矿资源预测评价具有重要意义。
Geochemical characteristics of uranium, thorium and potassium anomalies in China in relation to uranium mineralization
[J].
DOI:10.11720/j.issn.1000-8918.2014.2.03
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The utilization of uranium, thorium, potassium isotope gamma spectra for uranium prospecting is an important means of radioactive exploration. Similarly, uranium, thorium, potassium elements in stream sediments can serve as important indicator elements for uranium geochemical prospecting and have played important roles in the evaluation of China's uranium resource potential. This paper discusses the effect and anomaly characteristics of uranium, thorium, potassium elements in stream sediments, and expounds geochemical distribution characteristics and regularity of China's uranium, thorium, potassium elements. According to percentages of strokes, the anomalies of these elements can be divided into ultra-high anomaly (abnormal inner zone), high anomaly (abnormal mesozone), anomaly (abnormal outer zone) and high background. the relationship between the distribution of uranium, thorium, potassium anomalies and uranium mineralization is also demonstrated in this paper. As can be seen, the distribution of uranium, thorium, potassium anomalies has obvious regional characteristics, the existing anomaly area are highly consistent with four major types of uranium mineral areas in China, and hence the anomaly distribution has great significance for the prediction and evaluation of uranium and thorium mineral resources.
地面和航空放射性钍归一化数据与地下油藏的关系
[J].
Relationship between surface and airborne radioactive thorium normalization and underground oil reservoirs
[J].
利用钍归一化法判断古地下水的迁移
[J].
Judgment of movement of ancient underground water with normalization method of thorium data
[J].
钍归一化在盆地γ能谱资料处理中的应用
[J].
Application on Th normalization for basin gamma spectrometry data processing
[J].
全国铀矿资源潜力评价航放数据处理与研究
[J].
Airborne radioactivity data processing and application in the potential evaluation of uranium resource in China
[J].