0 前言
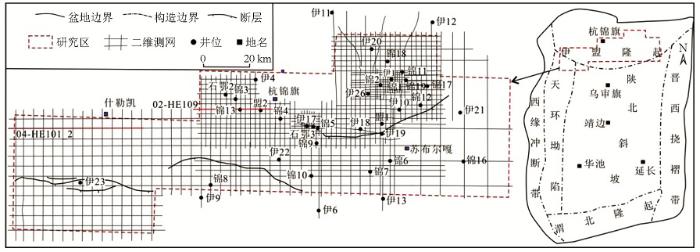
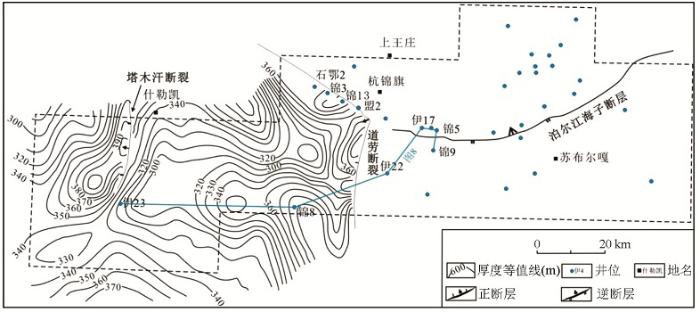
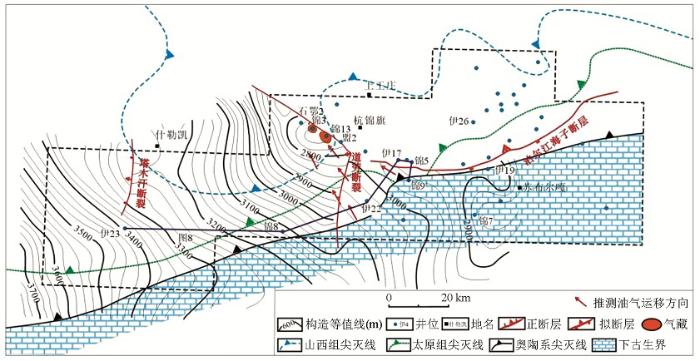
鄂尔多斯盆地是中三叠世—早白垩世形成的沉积盆地[12,13],其构造演化大致经历了太古宙—古元古代的基底形成、中元古代—新元古代的大陆裂谷发育、早古生代隆起剥蚀、石炭纪—晚三叠世的稳定发育和中—新生代的不均衡发育几个阶段[13,14]。盆地北部杭锦旗的二维地震资料较清楚地揭示了一套介于太古宇基底与上古生界之间的断陷层序,可分为下部断陷层和上部坳陷层两个次级层序,而且在锦13井对应层位的石英砂岩中测试日产天然气3 816~23 970 m3,甲烷含量达93.85%~95.3%。本文根据地震和钻井资料将这两套次级层序与露头进行了对比,从上覆在太古宇片麻岩之上和未变质—轻微变质程度初步认定它们为元古宇,并分析了它们的沉积学和油气地质特征。杭锦旗区块总面积约9 790.36 km2,现有4 km×4 km和2 km×2 km测网二维地震测线共5 000余千米(图1),油气勘探研究主要集中在古生界[15],研究区36口探井中只有锦13、17、5、9、伊22井等钻至太古宇片麻岩,锦13井钻遇断陷层和坳陷层,锦3井钻至坳陷层。杭锦旗地区沉积盖层较薄,厚度小于3 000 m,古生界不同层位超覆在下伏太古宇—中元古界之上。
图1
1 地层格架
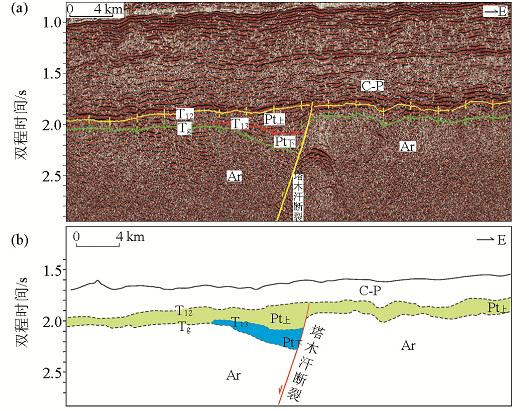
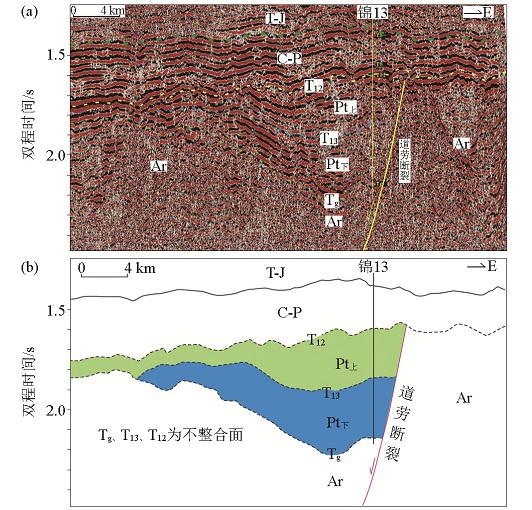
二维地震剖面揭示杭锦旗地区西部和中部存在两个位于古生界之下的半地堑断陷,分别受两条近SN向的正断层塔木汗断层和道劳断层控制(图2~图5)。它们与上覆古生界和下伏太古宇(Ar)呈角度不整合接触,两个不整合对应的地震反射界面分别为T12和Tg。根据断陷层序内部不整合面(T13)和地层厚度受断层控制来看,可将其分为下部断陷层Pt下与上部坳陷层Pt上两个次级层序。Pt上为坳陷层,与其上覆石炭—二叠系(C-P)地层和下伏Pt下或Ar均为不整合接触,Pt下为断陷层,与下伏Ar地层为角度不整合接触。坳陷层在地震剖面上表现为中—强振幅,呈缓倾—水平平行—前积反射结构,断续至连续反射,具丘状外形。断陷层具有楔状反射形态,中—强振幅,分布局限,朝断裂附近加厚明显(图2~图3)。
图2
图2
杭锦旗地区04-HE101_2二维测线地震剖面(a)及地质解释剖面(b)
Fig.2
The 2D-seismic profile 04-HE101_2 of the fault (a) and geological interpretation profile (b)
图3
图3
杭锦旗地区过锦13井02-HE109二维测线地震剖面(a)及地质解释剖面(b)
Fig.3
The 2D-seismic profile 02-HE109 of the fault(a) and geological interpretation profile(b)
图4
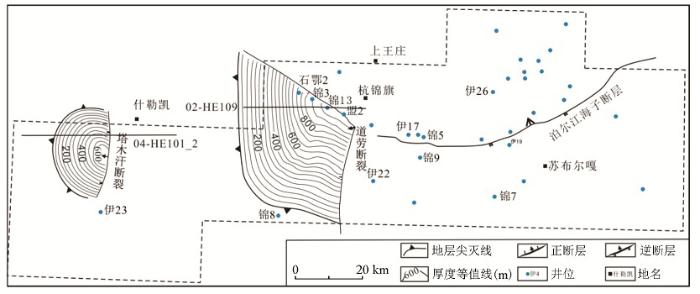
图4
杭锦旗地区中元古界断陷层厚度
Fig.4
Thickness map of fault strata of Mesoproterozoic in Hangjinqi area
图5
图5
杭锦旗地区中元古界坳陷层厚度
Fig.5
Thickness map of depression strata of Mesoproterozoic in Hangjinqi area
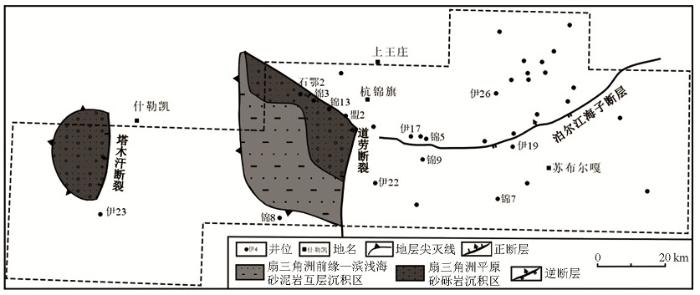
根据锦13井的时深关系和地震解释,分别制作断陷层Pt下和坳陷层Pt上两个层序的地层厚度图。该区作为阴山造山带和克拉通分界线的泊尔江海子逆断层,形成于加里东期—早海西期的近EW向区域大断裂,断开白垩系志丹群组之下的所有层位[16]。控制断陷层且形成于中—新元古代的塔木汗断层和道劳断层却与该区域性断裂近于垂直(图4~图5)。断陷层孤立分布于塔木汗断层和道劳断层下降盘(图4、图5),东断西超,地层厚度自断层处向西逐渐减薄至尖灭。研究区西部塔木汗断层控制的断陷层规模较小,长约30 km,宽约20 km,平面上呈近半圆形SN展布,断层处厚约600 m(图4)。中部道劳断裂附近的断陷形状呈扇形,NW向展布,北部和东部均为陡坡断裂边界,最大厚度达到950 m,长约70 km,宽约50 km。坳陷层厚约300~400 m,连续分布于道劳断层以西区域,断层处厚度最大约400 m(图5)。
2 地层学与岩石学特征
在前人研究的基础上[17],结合杭锦旗地区和盆地内其他钻井资料和二维地震资料,对比野外露头测量和分析资料,探讨地震资料上断陷层Pt下和坳陷层Pt上的时代和岩石特征。根据露头区元古宇长城系为未变质—微变质的陆源碎屑岩层序,大致推断钻井所钻到这套由砂砾岩组成的断陷—坳陷层序可能属于元宇长城系。理由如下:
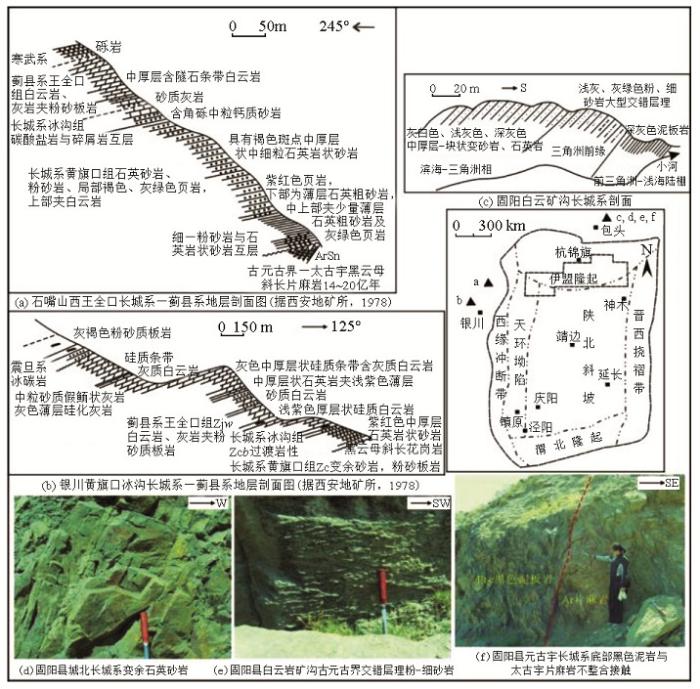
贺兰山地区的元古宇研究程度较高,主要有4个剖面出露元古宇,其中王全口和黄旗口剖面出露了较完整的长城系和蓟县系。贺兰山地区蓟县系为泥板岩、细晶白云岩、灰岩、少量硅质岩等;长城系为变余砂岩、变余砾岩,上部夹碳酸盐岩、褐铁矿,底部含海绿石砂岩;古元古界—太古宇为混合岩化片岩、片麻岩、花岗片麻岩(图6a、6b)[17,18]。固阳地区中元古界长城系顶部为变余砂岩和石英砂岩,底部为厚约40 m的深灰色泥板岩(图6c~6e);古元古界为千枚岩、石英岩(图6e);太古宇为混合岩化片岩、片麻岩、与花岗片麻岩,有些地区古元古界地层缺失,中元古界底部灰黑色泥板岩直接与太古宇千枚岩呈不整合接触[17,20](图6f)。
图6
图7
图7
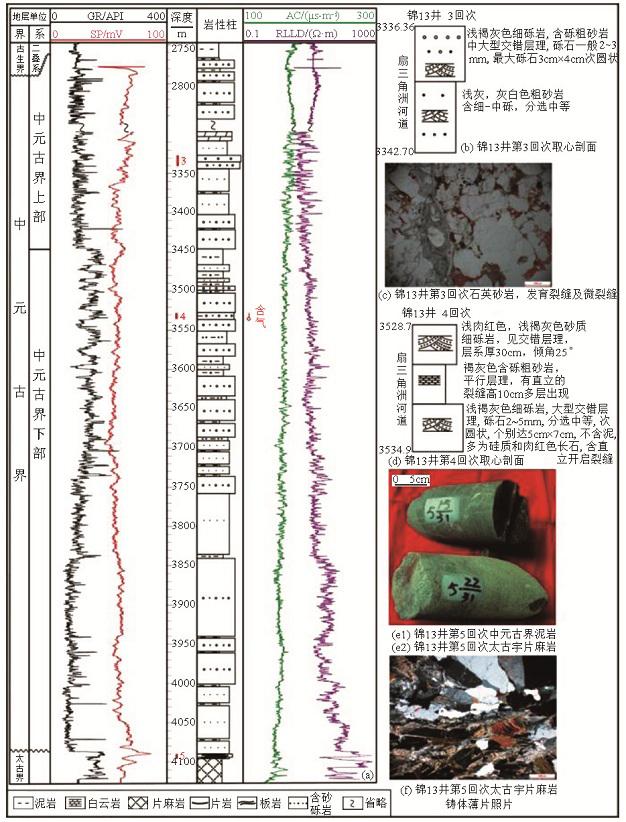
杭锦旗地区锦13井单井综合柱状剖面图
Fig.7
Comprehensive geological histogram of well Jin13 of Mesoproterozoic in Hangjinqi area
图8
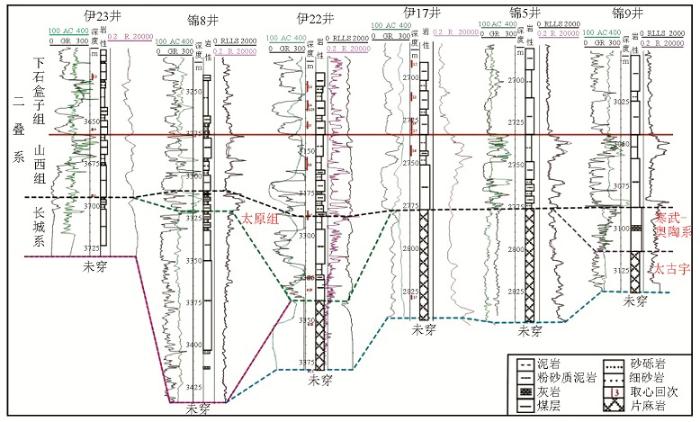
图8
杭锦旗地区过伊23井—锦8井—伊22井—伊17井—锦5井—锦9井连井剖面(剖面位置见
Fig.8
A cross-well profile of wells Yi23,Jin37,Yi22,Yi17,Jin5,and Jin9 of Mesoproterozoic-Lower Paleozoic in Hangjinqi area
图9
3 沉积特征
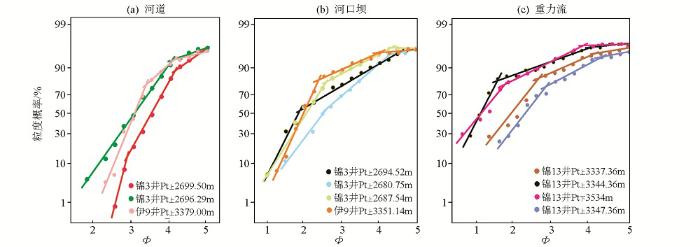
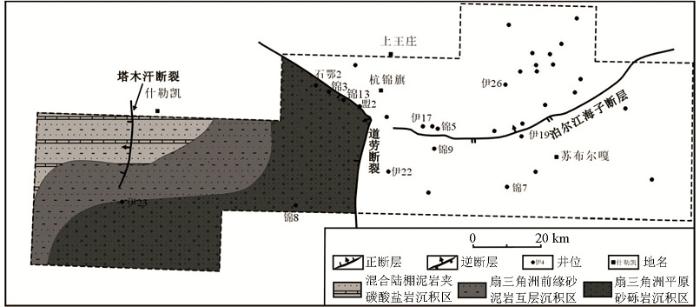
通过地震、测井、取心、薄片等资料综合分析认为伊盟地区元古宇坳陷层为扇三角洲—混合陆棚沉积。扇三角洲岩性主要为块状砂砾岩,并且普遍含有细砾、局部含中砾,剖面上90%以上为石英粗砂和细砾,属于近源碎屑物(图7c、10a)。中等—次圆状结构、差—中等分选和部分泥质和泥晶白云质杂基支撑颗粒排除了其滨海沉积(图7c铸体薄片照片),砂岩具有正粒序和底部冲刷切割等分流河道的特征(图10b、10c),粒度概率曲线(图11)表现为三角洲平原分流河道、河口砂坝和扇三角洲重力流的特征。坳陷层的混合陆棚沉积岩性主要为灰色、灰褐色泥岩以及粉砂岩,岩心上可见波状层理、脉状层理、透镜状层理、交错层理、波痕以及潮道砂岩的底部冲刷等。根据锦13井的井壁取心资料,在坳陷层砂岩、泥岩中局部夹有白云岩(图7a),显示了白云质潮坪的沉积特征。因此,研究区内坳陷层为既有云坪沉积又有陆源碎屑潮坪沉积的混合陆棚,自研究区西北部混合陆棚至道劳断层处过渡为扇三角洲平原(图12)。
图10
图10
杭锦旗地区中元古界岩心照片
Fig.10
Crop and drilled core observations of Mesoproterozoic in wells Jin13 and Jin3
图11
图11
杭锦旗地区中元古界粒度概率曲线
Fig.11
The cumulative probability curves of Mesoproterozoic core grain sizes in Hangjinqi area
图12
图12
杭锦旗地区中元古界坳陷层沉积体系分布
Fig.12
Sedimentary facies map of depression strata of Mesoproterozoic in Hangjinqi area
图13
图13
杭锦旗地区中元古界断陷层沉积体系分布
Fig.13
Sedimentary facies map of fault strata of Mesoproterozoic in Hangjinqi area
4 结论
1)杭锦旗地区元古宇地层受近SN向塔木汗正断层和道劳正断层控制,分别在研究区西部和中部形成两个半地堑断陷。中元古界由断陷层和坳陷层两个层序组成,二者之间为角度不整合。
2)断陷—坳陷层序可能为长城系。露头区中新元古界为未变质到轻微变质,杭锦旗地区中新元古界总体上未变质,其中坳陷层主要为砂泥岩、砾岩;断陷层主要为砂岩、砾岩夹薄层泥岩;古元古界—太古宇主要为混合岩化片岩、片麻岩、花岗片麻岩等。
3)断陷层为扇三角洲—滨浅海陆源碎屑沉积,分布局限;坳陷层为扇三角洲—混合陆棚沉积,分布广泛,将两个断陷区连成一片。
4)固阳露头元古宇20 m黑色泥岩有机碳含量较高,但处于过成熟演化阶段。锦13井和锦3井中元古界地层的天然气主要由上古生界煤成气沿上古生界与中元古界之间的不整合面和道劳断层以及泊尔江海子断层运移聚集而成的。
参考文献
Precambrian geology of China:Preface
[J].
The boring billion-Lid tectonics,continental growth and environmental change associated with the Columbia supercontinent
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.gsf.2013.05.004 URL [本文引用: 1]
Meso-Neoproterozoic petroleum systems of the Eastern Siberian sedimentary basins
[J].
扬子陆核与神农架地块中元古代相互关系:来自锆石U-Pb年代学和Hf同位素的约束
[J].
Correlation between the Mesoproterozoic Yangtze Continental Nucleus and the Shennongjia Area:Constraints from Zircon Geochronological and Hf Isotope
[J].
论中—新元古界的原生油气资源
[J].
On Meso-Neoproterozoic primary petroleum resources
[J].
Composition of biomarker-hydrocarbons in genetic families of Precambrian and Cambrian oils of the Siberian platform
[J].
Fractures in continental shale reservoirs:a case study of the Upper Triassic strata in the SE Ordos Basin,Central China
[J].
Riphean hydrocarbon reservoirs of the Yurubchen-Tokhom Zone,Lena-Tunguska Province,NE Russia
[J].DOI:10.1111/jpg.1997.20.issue-4 URL [本文引用: 1]
Indigenous Precambrian petroleum revisited
[J].
燕山地区震旦亚界油苗的原生性及其石油地质意义
[J].
Prototype of oil seedlings in Aurora Subboundary in Yanshan area and its petroleum geological significance
[J].
四川盆地威远气田和资阳含气区震旦系油气成藏差异性研究
[J].本文通过对四川盆地元古宇-下古生界勘探最成功的两个地区--威远震旦系气田和资阳震旦系含气区天然气成藏要素和成藏过程的详细比较,得出 ①资阳含气区和威远气田的原始烃源相同,均是下寒武统生成的油裂解的天然气,不同的是资阳为残留的气顶气,威远是水溶气脱溶气.②资阳含气区和威远气田震旦系碳酸盐岩基质孔隙度相近,资阳地区溶蚀洞穴发育,但裂缝不发育,储层渗透性较差,非均质性强;威远地区储层洞穴不发育,但裂缝发育,形成统一的裂缝-孔洞系统.③威远地区具有统一的圈闭,闭合度高(800 m),闭合面积大(895 km2).资阳含气区不具有统一的圈闭,多为局部的小高点.④喜马拉雅期隆升作用使资阳统一含气区分散化和气藏变小,形成多压力系统的含气区;威远地区快速大幅度隆升, 溶于水中的天然气脱溶, 形成具同一压力系统的整装气田.⑤资阳含气区的成藏过程为 (资阳-威远)古油藏→原油裂解→气顶天然气→隆升调整→现今(残留)含气区,其天然气藏是隆升调整成藏,是在原古气藏的基础上改造残留而成;威远地区的成藏过程则是(资阳-威远)古油藏→原油裂解→天然气大量溶于水中→隆升使得带有大量天然气的水向威远运移和天然气脱溶→现今(新生)气藏,属天然气的脱溶成藏.资阳含气区受古构造的控制明显;威远气田则主要受今构造的制约.因此, 在四川盆地震旦系和下古生界的油气勘探中, 既要研究其古构造的特征和演化, 也要研究今构造的特征和分布规律, 才能发现不同类型的天然气藏.
Studying on the differences of Sinian natural gas pools between Weiyuan gas field and Ziyang gas-brone area,Sichuan Basin
[J].
Mesozoic structural evolution of the Hangjinqi area in the northern Ordos Basin,North China
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.07.014 URL [本文引用: 1]
鄂尔多斯盆地西北部早—中侏罗世延安期沉积边界恢复
[J].
Restoration of the Sedimentary Boundary of the Yan'an Period of Early-Middle Jurassic,the Northwest of Ordos Basin
[J].
Sedimentation during the transgression period in Late Triassic Yanchang Formation,Ordos Basin
[J].DOI:10.1016/S1876-3804(10)60025-0 URL [本文引用: 1]
鄂尔多斯盆地北部杭锦旗地区上古生界气源岩分析
[J].8 m3/km2之间,具备形成大气田的气源条件。因此,研究区天然气来源具有原地性的特征,泊尔江海子断裂南部烃源岩优于北部烃源岩。]]>
Research on the Upper Paleozoic gas source of the Hangjinqi Block in the Northern Ordos basin
[J].8m3/km2,having the conditions of gas source for developing large gas field.In conclusion,the gas accumulation in study area is characteristic of generating in situ,and the quality of gas source rocks in the south of Boerjianghaizi fault is better than rocks in the north.]]>
鄂尔多斯盆地北部泊尔江海子断裂对上古生界天然气成藏的控制
[J].为了揭示泊尔江海子断裂对鄂尔多斯盆地北部杭锦旗地区上古生界天然气成藏的控制作用,应用地震和钻井资料,在断裂活动性分析的基础上,根据断层泥比率和断层连通概率法对泊尔江海子断裂的侧向和垂向封闭性进行半定量评价,探讨断裂和天然气富集区的关系。结果表明:泊尔江海子断裂呈现3次明显的活动高峰期,分别为加里东期—早海西期的断裂形成期、印支期—早燕山期的挤压逆断裂活动期、中晚燕山期的走滑撕裂活动期,而中晚燕山期的走滑撕裂控制了上古生界天然气主要成藏期。断裂的封闭性具有“横向分段、纵向分层”的特点;横向上,以断层泥比率(SGR)等于0.3为界将泊尔江海子断裂分为侧向优势输导区和侧向封闭区;纵向上,在石千峰组和上石盒子组断裂启闭系数基本都小于1.0,断裂垂向封闭,在下石盒子组和山西组断裂启闭系数主要集中在4.0~10.0,断裂垂向开启。在断裂侧向优势输导区,断裂南部主力烃源区生成的天然气,经断裂发生垂向和侧向运移,易在断裂北部地区富集成藏;在侧向封闭区,则易在断裂南部地区富集成藏。
Control of Boerjianghaizi fault on gas accumulation of Upper Paleozoic in Northern Ordos Basin
[J].In order to reveal the control functions of Boerjianghaizi fault on natural gas accumulation of Upper Paleozoic in Hangjinqi block of the northern Ordos Basin, the history of the fault activity, the lateral and vertical sealing ability of the fault were studied by using fault growth index evolution, fault shale gouge ratio method and fault connectivity probability method through seismic and drilling data of this area. Then Boerjianghaizi fault effects on the natural gas enrichment zones were discussed. The results showed that Boerjianghaizi fault had three obvious peaks of activity in the history of evolution, which were Caledonian to Early Hercynian fracture period, Indosinian to Early Yanshanian squeezing thrust fault activity period, and Mid-late-Yanshanian strike-slip tearing activity period. Mid-late-Yanshanian strike-slip tearing activity period matched well with the main stage of gas accumulation of Upper Paleozoic. It was pointed out that sealing ability of Boerjianghaizi fault had the characteristics of “horizontal sectioning, vertical layering”. In the horizontal direction, Boerjianghaizi faults were divided into lateral migration fault areas and lateral sealed fault areas according to the shale gouge ratio (SGR) which equals to 0.3 as the dividing line. In the vertical direction , the fault plane was vertically sealed in Upper Shihezi and Shiqianfeng formations because the fault sealing coefficients were almost less than 1.0 in the section, while the fault plane was vertically open in Lower Shihezi and Shanxi formations because the fault sealing coefficients mostly range from 4.0 to 10.0 in the section. Meanwhile, in the lateral migration fault areas, natural gas generated from the main source areas which were in the south side of Boerjianghaizi fault was transmitted in the vertical and lateral direction through the fault, then natural gas accumulated in large amount in the north side of the fault easily, but in the lateral sealed fault areas, it is easy to find the natural gas pools in the south side of the fault.
宁夏贺兰山区震旦亚界
[J].
Aurora sub-boundary in Helan Mountain, Ningxia
[J].
杭锦旗地区中晚元古界油气地质特征与勘探潜力分析
[D].
Analysis of petroleum geological characteristics and exploration potential of Mesoproterozoic strata in Hanggin Banner area
[D].
鄂尔多斯盆地北部奥陶系碳酸盐岩层序地层研究
[J].
Carbonate sequence stratigraphy of Ordovician in the Northern Ordos Basin
[J].
Lower Paleozoic source rocks and natural gas origins in Ordos Basin,NW China
[J].DOI:10.1016/S1876-3804(16)30069-6 URL [本文引用: 1]
鄂尔多斯地块中元古代长城纪盆地属性研究
[J].中元古代长城纪华北克拉通南缘的大地构造背景一直备受关注。学者们主要依据该时期火成岩地球化学性质推断其构造背景,提出了B型俯冲、安第斯型俯冲、非造山环境以及与Columbia超大陆裂解有关的伸展环境。本次研究应用地球物理方法来剖析鄂尔多斯盆地中南部长城系构造格架和地层分布,以探索研究区大地构造背景及盆地属性。二维地震资料显示长城纪构造旋回包含裂陷期和裂后期。裂陷期半地堑主控边界断层活动强度大,下降盘发生旋转掀斜,发育次级地堑、半地堑,同时发育扇三角洲、水下扇沉积,楔状体沉积中心地层厚度大。裂后期断层活动减弱,水体范围扩大,地层超覆在早期楔状地层之上,地层厚度变化小。重力异常反演表明,研究区存在同期的凹陷和凸起,它们可能受控于边界断裂。结合地块周缘长城系沉积特征,我们认为鄂尔多斯地块中元古代长城纪盆地属性为陆内裂陷。
Researches on basin property of Ordos block during Mesoproterozoic Changcheng Period
[J].The tectonic setting of southern margin of North China Craton has drawn much attention during Mesoproterozoic Changcheng Period. Researchers have proposed several plausible models of geological settings mostly based on geochemical properties of volcanic rocks. The main views about the geological background are B-type subduction, Andean type subduction, non-orogenic extension and stretching which is related to the breakup of Supercontinent Columbia. This paper focus on tectonic features and stratum distribution of Changcheng Group in the south central Ordos block with geophysical methods meanwhile makes some study on its tectonic setting and basin property. The 2D seismic data indicates tectonic cycle in Changcheng Period with syn-rift and post-rift phase included. In syn-rift phase, the boundary faults act intensely, and the hanging wall rotated, leading to the development of sub-grabens and half-grabens. In the meantime fan delta and subaqueous fans filled in. The formations thicknesses are huge in depocenter of wedges. In post rift phase, the activity of faults was weak, resulting in the formation with consistent thickness, which overlapped on the wedges. Besides, the consequence of gravity anomaly inversion suggests several depressions and salients developed during the same period which were probably controlled by the boundary faults. Combined with the sedimentary characteristics of block margin, we deem the study area to be a rift basin during the Changcheng Period.
Precambrian tectonic evolution of the North China Craton
[C]//
华北克拉通中元古代裂解事件:以渣尔泰—白云鄂博—化德裂谷带岩浆与沉积作用研究为例
[J].华北克拉通存在三个主要的中元古代裂谷带,从南到北分别为熊耳裂谷带、燕辽裂谷带以及渣尔泰-白云鄂博-化德裂谷带。其中熊耳群中火山岩的峰期年龄为1780~1750Ma,其上还有形成于被动大陆边缘的五佛山群、汝阳群以及官道口群。中北部的燕辽裂谷带包括长城系、蓟县系和青白口系,其中长城系团山子组和大红峪组火山岩的年龄分别为~1640Ma和1626~1622Ma,蓟县系高于庄组、雾迷山组和铁岭组凝灰岩的年龄分别为1560Ma、1485Ma和1437Ma,而下马岭组凝灰岩年龄为1366~1380Ma。北缘渣尔泰-白云鄂博-化德裂谷带中渣尔泰群书记沟组玄武岩年龄为1743Ma,阿古鲁沟组酸性火山岩年龄为~810Ma,白云鄂博群尖山组中基性火山岩年龄为1728Ma,化德群比鲁特组火山碎屑岩年龄为1515Ma。中元古代岩浆事件除了裂谷带中的火山作用外,还包括三期基性岩墙群(~1780Ma 太行-吕梁岩墙群、~1730Ma密云岩墙群和~1620Ma泰山岩墙群)以及1.76Ga到1.65Ga非造山岩浆组合(斜长岩-环斑花岗岩体-A型花岗岩)。中元古代中期,华北克拉通北缘发育了基性岩席(墙)、A型花岗岩以及碳酸岩脉,双峰式岩浆作用说明华北北缘在中元古代中期经历了裂谷作用,与哥伦比亚超大陆的最终裂解有关,并且与白云鄂博巨型REE-Nb-Fe矿床的形成具有成因上的联系。华北克拉通北部两个裂谷带中的地层具有可以对比的层序以及时代,而中元古代中期辉绿岩墙、A型花岗岩以及碳酸岩脉可以与其它克拉通同时期的非造山岩浆作用对比,证明华北克拉通经历了哥伦比亚超大陆的最终裂解。古地磁数据已经证明在哥伦比亚超大陆时期Siberia、Laurentia、Baltica、Amazion以及华北克拉通是连接在一起的,而北缘中元古代中期大陆裂谷相关岩浆岩的发现也说明它是与另一个古大陆相连的。华北克拉通南缘熊耳火山岩的构造背景到底是大陆裂谷还是大陆边缘弧则关系着其是与另一个克拉通相连还是面向大海,这需要我们进一步深入研究。
The Mesoproterozoic rifting in the North China Craton:A case study for magmatism and sedimentation of the Zhaertai-Bayan Obo-Huade rift zone
[J].The Mesoproterozoic rift zones in the North China Craton include the Xiong'er, Yanliao and Zhaertai-Bayan Obo-Huade rift zones from south to north. The Xiong'er Group is featured by the major volcanism at 1780~1750Ma, above which the Wufoshan, Ruyang and Guandaokou groups were formed in a passive continental margin. The Yanliao rift zone includes the Changcheng, Jixian and Qingbaikou systems. The Tuanshanzi and Dahongyu formations of the Changcheng system have volcanic rocks at ca.1640Ma and 1626~1622Ma, respectively. The tuffs in the Gaoyuzhuang, Wumishan and Tieling formations of the Jixian system were formed at 1560Ma, 1485Ma and 1437Ma respectively, whereas the Xiamaling tuffs in the unnamed system have ages of 1366~1380Ma. In the Zhaertai-Bayan Obo-Huade rift zone, the Shujigou basalts and Agulugou felsic volcanics of the Zhaertai Group have ages of 1743Ma and ~810Ma, respectively. The Jianshan Formation of the Bayan Obo Group has mafic volcanics of 1728Ma and the Bilute tuffs of the Huade Group formed at 1515Ma. Besides the volcanisms in the rift zones, the Mesoproterozoic magmatism include three episodes of mafic dyke swarms (ca.1780Ma Taihang-Lüliang dyke swarm, ca.1730Ma Miyun dyke swarm and ca.1620Ma Taishan dyke swarm) and 1.76~1.65Ga anorogenic magmatism (anorthosite-rapakivi granite-A-type granite). In the Middle Mesoproterozoic, mafic sills (dykes), A-type granites and carbonate dykes develop in the northern margin of the North China Craton. The bimodal magmatism suggests that the northern margin of North China Craton has experienced rifting in the Middle Mesoproterozoic, which are related with final breakup of the Columbia Supercontinent and formation of the giant Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit. The two rift zones in the northern North China Craton have similar stratigraphic sequences and formation ages. The Middle Mesoproterozoic anorogenic magmatism can be compared with those in other cratons and suggests that the North China Craton is involved in the final breakup of the Columbia Supercontinent. Paleomagnetic data indicate that the Siberia, Laurentia, Baltica, Amazion and North China cratons are connected together in the Columbia Supercontinent, and the rift-related magmatic rocks in the northern margin suggest that it connected with another craton. However, whether the Xiong'er volcanics in the southern margin of the North China Craton formed in a continental rift or active continental margin is important about whether it was connected with another craton or faced an ocean, which need further studies.