0 引言
土壤是岩石圈表面的疏松表层,是陆生植物生长的基质。土壤中的N、P、K是植物生长必备的大量养分元素,共同作用决定着土壤养分是否丰足。但现实中存在“木桶原理”,同一种养分元素在不同区域对植物生长发育的影响(权重)会不同,即不管该区域其他元素含量如何丰足,只要某元素含量低到一定的程度,就会严重影响植物生长发育,如缺氮影响蛋白质合成, 缺磷影响能量代谢, 缺钾影响膜脂透性[1],故在进行土壤养分地球化学综合评价时,应增大缺量元素权重,对其进行惩罚。而规范规定的方法为常权评价,权重始终不变,不随养分元素含量不同而变化,即以“不变”应“万变”,未能反映评价对土壤养分元素的水平组态均衡偏好,往往会出现某种元素含量较低,可能会被丰量元素评价等级“中和”,导致评价结果偏大[2]。因此,笔者依据汪培庄[3]、李洪兴[4,5]、李德清[2]等学者提出的变权思想,选择合适的状态变权向量,构造土壤养分地球化学变权综合评价模型,真实地反映土壤养分元素状态的变权规律,准确识别短板元素,从而更加科学地进行评价。
1 研究方法
土壤中各养分元素含量因地而异,均衡程度不同,在评价中的作用也不同。基于此,依据土壤养分元素含量状态间的均衡水平,利用变权思想,对《土地质量地球化学评价规范》DZ/T0295-2016规定的土壤养分地球化学综合评价方法进行改进,来调整各元素在具体样点综合评价中的权重,使其随含量而改变,既体现各元素的相对重要性,又体现含量值向量的水平组态[6]。
1.1 变权向量
变权向量综合反映了因素状态间的均衡性[6],直接反映权重随元素含量值的变化规律。设X=(x1,x2,…,xm)为土壤养分元素含量向量,W=(w1,w2,…,wm)为因素常权向量,S(X)=(S1(X),S2(X),…,Sm(X))为状态变权向量,则变权向量W(X)=(w1(X),w2(X),…,wm(X))可表示为W和S(X)的归一化的Hadamard乘积,即
1.2 状态变权向量
表1 常见的状态变权向量
Table 1
| 类别 | 均衡函数 | 状态变权向量 | 变权向量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 常权 | S1(X)=S2(X)=…=Sm(X) | wj(Xj)=wj | |
| 积型 | |||
| 和型 | Sj(x1,x2,…,xm)= | ||
| 指数型 | B(X)=e-αx(α≥0) | Sj(x1,x2,…,xm)= | wj(Xj)=wj/[wj+(1-wj)e-α] |
依据α值的不同,当α=0时,和型状态变权向量为积型状态变权向量,指数型状态变权向量为常权向量;当α=1时,和型状态变权向量为常权向量。
2 算例
2.1 研究区域概况
研究区域位于陕西延安市宝塔区(图1),处于东经109°13'17.40″~110°06'32.40″,北纬36°10'51.60″~37°05'42.00″之间,属半湿润半干旱大陆性季风气候,多年平均降水量为562.1 mm,最大为871.2 mm,最小为330 mm;年均气温10.3 ℃,地貌类型为黄土梁峁沟壑区,土壤类型主要为黄绵土,土壤质地以轻壤土和砂壤土为主。
图1
2.2 数据来源
采用生态地球化学调查(多目标区域地球化学调查或土地质量地球化学调查)2018年度取得的宝塔区域内1 260个表层组合样点中4项指标(N、P、K2O、Corg)含量数据。采样单点密度1个点/ 1 km2,组合样密度1个点/4 km2,单样点按梅花法分为3~5个点,遵从代表性、均匀性、合理性和多点混合的原则进行采样,采用常规采样法取0~20 cm土层的土样,每个样品1 000 g左右,同时,在采样时避开粪堆、新近堆积土等点状污染物。土壤样品去掉植物根系和岩石碎块,自然风干后,过20目尼龙筛,由自然资源部安徽地质测试实验室进行测试,其中K2O采用等离子体光谱法(ICP-AES)分析; P采用X荧光光谱法(XRF)分析;Corg采用硫酸亚铁铵容量法(VOL)分析;N采用凯氏丹蒸馏酸碱滴定(VOL)分析;分析质量符合地质矿产实验室测试质量管理规范(DZ0130.1-2006)的要求。本文对原始数据进行平均值、最大值、最小值和标准离差统计计算,用平均值±3倍离差替代原始数据中的异常数据,即小于平均值-3倍离差的数据用平均值-3倍离差数据替代,大于平均值+3倍离差的数据用平均值+3倍离差数据替代。
3 结果与讨论
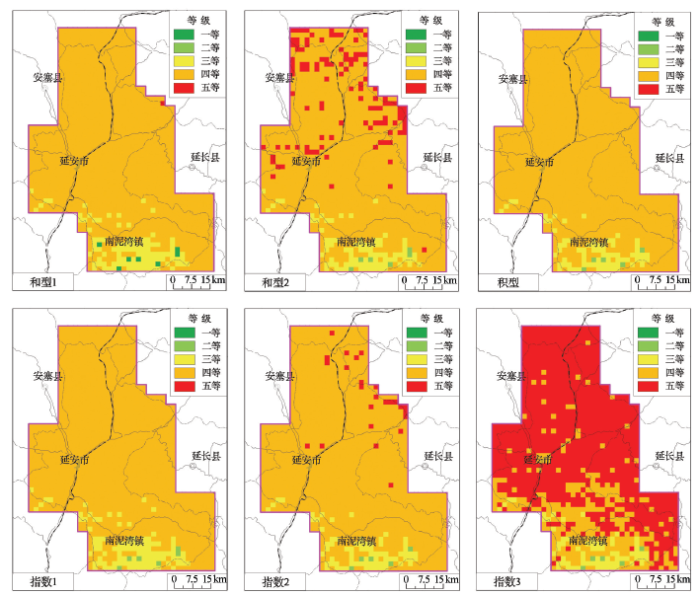
3.1 仿真方案
表2 不同仿真方案的状态变权向量和变权向量
Table 2
| 仿真方案 | 状态变权向量Sj(X) | 变权向量wj(Xj) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 类型 | 参数α值 | ||
| 常权 | 和型 | 1 | wj |
| 和型1 | 和型 | 0.6 | |
| 和型2 | 和型 | 0.2 | |
| 积型 | 和型 | 0 | |
| 指数3 | 指数型 | 3 | wj/[wj+(1-wj)e-3] |
| 指数2 | 指数型 | 2 | wj/[wj+(1-wj)e-2] |
| 指数1 | 指数型 | 1 | wj/[wj+(1-wj)e-1] |
注:1<j<4
图2
表3 不同仿真方案的土壤样品评价等级调权变化统计
Table 3
| 仿真方案 | 和型1 | 和型2 | 积型 | 指数3 | 指数2 | 指数1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 一等变二等 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 二等变三等 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 三等变四等 | 11 | 28 | 40 | 39 | 41 | 11 |
| 四等变五等 | 1 | 112 | 699 | 912 | 25 | 0 |
| 三等变五等 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| 合计 | 12 | 141 | 741 | 953 | 68 | 12 |
3.2 讨论
3.2.1 离散度
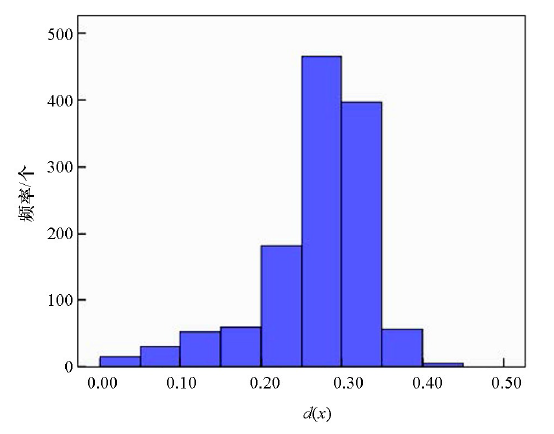
采用离散度[2]来衡量各样点的土壤养分元素含量间的均衡程度,以反映与绝对均衡时(各养分元素含量相同)的偏差程度,离散度越大,均衡程度越低,反之越高。利用各样点的N、P、K2O、Corg归一化后数据构成土壤养分元素含量状态因素向量X=(x1,x2,x3,x4),采用式(2)来计算离散度 d(x):
式中:1<j<4;xj为第j个土壤养分元素含量归一化后的数据。
宝塔区80%土壤样品养分元素含量数据离散度小于0.35(图3),100%样品离散度小于0.5,表明土壤养分元素含量数据的离散程度较低,均衡性较好。
图3
3.2.2 调节度
采用调节度[2]来衡量状态变权向量S(X)在土壤养分元素含量状态向量X下对常权向量wj的调节幅度,调节度越大,因素间权重的转移越多;反之,转移越少。利用各采样点的初始权重wj和变化的权重wj(xj),采用式(3)来计算其调节度D(X),定义如下:
式中,1<j<4;wj(X)为第j个指标的变权权重;wj 为第j个指标的常权权重。
研究区各状态变权向量的调节度较小,多集中在0.06以下(表4)。积型状态变权向量为α=1时的和型状态变权向量的特型,指数型与和型状态变权向量的调节度均随幂参数α的增大而增大,且权重向缺量元素转移越多,“惩罚”越重。
表4 不同仿真方案的调节度频率统计
Table 4
| 调节度 | 仿真方案 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常权 | 和型1 | 和型2 | 积型 | 指数3 | 指数2 | 指数1 | |
| 0~0.01 | 0 | 863 | 110 | 75 | 22 | 71 | 1245 |
| 0.01~0.02 | 0 | 397 | 125 | 61 | 52 | 174 | 15 |
| 0.02~0.03 | 0 | 0 | 351 | 108 | 60 | 955 | 0 |
| 0.03~0.04 | 0 | 0 | 538 | 221 | 157 | 54 | 0 |
| 0.04~0.05 | 0 | 0 | 115 | 446 | 748 | 4 | 0 |
| 0.05~0.06 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 274 | 188 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.06~0.07 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 50 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.07~0.08 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.08~0.09 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.09~0.10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
3.2.3 调权水平
式中,1<j<4;wj(xj)为第j个指标的变权权重。A关于α单增,当α→0时, A→1/4;当α→+∞时, A→1。
由定义可知,状态变权向量是调权水平唯一影响因素, wj(xj)的值越大,调权水平越大(表5)。
表5 不同仿真方案的调权水平
Table 5
| 仿真方案 | 常权 | 和型1 | 和型2 | 积型 | 指数3 | 指数2 | 指数1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 调权水平 | 0.2500 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.8649 | 0.7044 | 0.4714 |
3.3 变权评价结果分析
由前文可知,宝塔区土壤养分元素含量数据离散度值小,均衡程度高,为取得良好的变权效果需使用具有良好控制度的状态变权向量。而指数型状态变权向量能满足评价对调权水平的需求。因此,将其代入式(4),得到式(5),求取其幂参数α的值,以确定土壤养分各元素的权重变化规律,取得良好的变权效果。
表6 土壤样品评价等级调权变化统计
Table 6
| 类别 | 含量 | 规范规 定等级 | 得分 | 常权 | 指数3 | 指数2 | 指数1 | 综合确定 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A=0.8649 | A=0.7044 | A=0.4714 | A=0.8 | |||||
| N | 2.6174 | 1 | 5 | 0.3 | 0.1087 | 0.1614 | 0.2263 | 0.1321 |
| P | 0.9025 | 2 | 4 | 0.3 | 0.2472 | 0.2792 | 0.2976 | 0.2638 |
| K | 2.22 | 2 | 4 | 0.2 | 0.1409 | 0.1676 | 0.1883 | 0.1541 |
| Corg. | 1.09 | 4 | 2 | 0.2 | 0.5032 | 0.3918 | 0.2878 | 0.45 |
| 评价得分 | 3.9 | 3.1023 | 3.3778 | 3.6507 | 3.2321 | |||
| 评价等级 | 二等 | 三等 | 三等 | 二等 | 三等 |
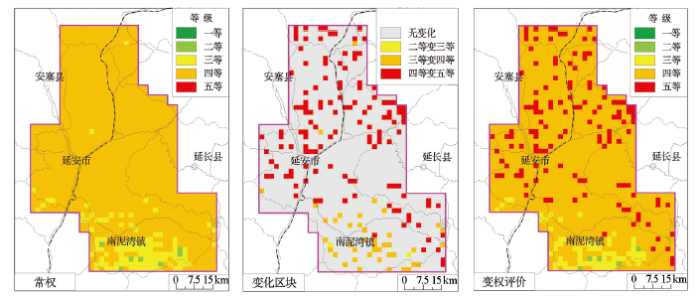
图4
图4
变权评价与常权评价结果对比
Fig.4
Comparison between variable weight evaluation and constant weight evaluation
选取YJ058样点来对比变权效果(表6),按照《土地质量地球化学评价规范》DZ/T0295-2016规定,N、P、K2O、Corg的单指标养分等级分别为1、2、2、4,得分分别为5、4、4、2,常权为0.3、0.3、0.2、0.2,其常权评价综合得分为3.9,等级为二等;变权为0.132 1,0.263 8,0.154 1,0.450 0,其变权评价综合得分为3.232 1,等级为三等,主要是由于崂山山脉的N、P、K2O养分元素含量丰富,等级较高,但是Corg的含量较低,影响植物生长发育,需要惩罚,权重由0.2增加到0.450 0,其他元素权重下降,综合得分降低,评价等级下降。经过统计,研究区内的评价等级无变化样点1 085个,发生变化175个,调整率为13.89%,具有良好的变权效果,其中,二等变三等有2个,三等变四等有42个,主要分布在南部;四等变五等有131个,主要分布在中北部(图4)。调查区的N、Corg的含量低,整体限制了土壤养分质量提升,且两者具有较强的正相关关系[17],需要保持水土流失,防止易溶性硝酸盐和有机质随流水迁移淋失,同时需要注重改良土壤,秸秆还田,有机、无机肥合理配合使用,以全面提高土壤养分质量。
4 结论
土壤养分地球化学变权综合评价综合反映了土壤各养分元素含量间的均衡性,克服了常权法在权重分配中的缺陷,确定了元素间权重的变化规律,更好地反映其在评价中的作用。
离散度、调节度能较好地度量状态变权向量的调节权重的能力,为分析变权效果提供了理论工具,且调权水平为科学评价而选择状态变权向量提供了一种可操作性的方法。和型与积型状态变权向量因其调节度难以控制而适用范围受限,且当因素状态允许存在明显缺陷,甚至为0时,易出现惩罚过度;而指数型状态变权向量的适用范围较大,其变权效果受幂参数控制,且可有效避免惩罚过度。
指数型状态变权向量较好地反映宝塔区土壤养分元素含量状态的变权规律,经过反复模拟,综合确定调权水平为0.8,幂参数α=2.524 8时,权重矩阵向N、Corg转移合理,惩罚有度,具有良好的变权效果,科学地调整了土壤养分综合评价等级。无论调查区南部的二等变为三等,三等变为四等,还是调查区中北部的四等变为五等,均是由于N、Corg含量低,严重地影响植物的生长发育,需要对其进行惩罚,权重矩阵向其转移,权重增加,评价等级下降。
参考文献
大量元素缺乏对小麦光合、呼吸作用和生理特性的影响
[J].
The effects of macronutrient deficiency on photosynthetic activity respiration and physiological parameters in wheat
[J].
变权决策中变权效果分析与状态变权向量的确定
[J].可量化的工具. 利用标准调节度讨论了选择状态变权向量的一些基本原则和理论依据, 并由调权水平给出了一种选择状态变权向量的可操作性方法.]]>
Analysis of variable weights effect and selection of appropriate state variable weights vector in decisionmaking
[J].
因素空间理论与知识表示的数学框架(VIII)
[J].
Factor spaces and mathematical frame of knowledge representation(VIII)
[J].
因素空间理论与知识表示的数学框架(IX)
[J].
Factor spaces and mathematical frame of knowledge representation(IX)
[J].
均衡函数及其在变权综合中的应用
[J].在这篇文章中,我们使用不同的非线性函数来对中国的广义货币M2(即,现金加企业机关的活期存款和定期存款加居民的各项储蓄存款)的需求来建立模型,特别地,我们将一个非常简单的人工神经网络(artificialneuralnetworks(ANNs))同协整与误差校正模型(cointegrationanderror-cor-rectionmodel)结合起来,给出一个非线性模型。这些模型是季度模型,采样区间为1980年的第一季度到1994年的第四季度。首先,我们利用给出的模型在区间1980年到1993年广义货币M2进行估计和分析,然后使用估计出的模型对1994年进行预测。无论是对M2的拟合值还是预测值都是令人满意的。结果表明在我国存在一个稳定的货币需求函数,我们可以用它对货币总量进行预测以及给出一些实施货币政策性的建议。
Balanced function and its application for variable weight synthesizing
[J].
等效均衡函数的性质及均衡函数的构造
[J].
Properties of equivalent balance function and construction approaches of balance function
[J].
基于集合均值的惩罚型状态变权向量的构造及应用
[J].
The structure of penalized state variable weight vector and its application based on the geomentric mean
[J].
基于GIS 的土壤质量模糊变权评价
[J].
GIS-based soil quality evaluation with fuzzy variable weight
[J].
基于变权的农村居民点用地空间适宜性模糊综合评价:以重庆市长寿区长寿湖镇为例
[J].
On suitability evaluation for rural residential land based on variable weights:A case study of changshou lake town of Changshou district in Chongqing
[J].
基于VW 模型的土地可持续利用评价及时空特征分析:以安徽省市域为例
[J].
Evaluation of regional sustainable land use and its spatial-temporal pattern based on the VW model:A case study of each city in Anhui Province
[J].
土地生态安全预警的惩罚型变权评价模型及应用:以淮安市为例
[J].日益严重的土地生态问题对人类的生存形成了很大威胁,并直接影响着人类社会的可持续发展。维护土地生态安全最有效办法就是及时发现土地生态安全危险事件的发展趋势并进行预警。针对以往常权评价难以体现土地生态安全预警中动态性要求的缺陷,本文将变权理论引入土地生态安全预警研究,结合层次分析法得到的基础权和预警指标值的动态发展趋势构建了土地生态安全预警的惩罚型变权模型,并用该模型对淮安市1996年-2010年土地生态安全警情变动趋势进行了综合评价和深入分析。结果表明惩罚型变权评价模型能够对基础权重做出局部调整以使评价结果更符合土地生态安全预警的动态性要求,1996年-2005年间淮安市土地生态安全的总体水平也由于自然、社会和经济因素三方面协同作用稳定处于轻警区间并有所提升,而且这一趋势将延续到2006年-2010年。
Application of an evaluation model based on punishing variable weight for early warning of land ecological security:A case study of Huai’an city
[J].Land ecosystems have been suffering increasingly serious degradation and destruction resulting from irrational development modes and intensifying human activities, which even threatens human’s survival. Early warning is generally considered one of the most effective ways to maintain land ecological security, which can eliminate land ecological crises at the early stage. Dynamic characteristics of early warning for land ecological security require an immediate review and foreseeing on land ecological crises. Aiming at overcoming the drawbacks of the model with constant weights that is not able to well reveal dangerous factors, the authors introduced the variable weight theory to early warning of land ecological security in the present paper. First, a warning index system of land ecological security can be established and the warning limit for each index can be determined. Second, Forecasting values of the warning indices can be estimated for further warning. Third, the ‘basic weight’ can be determined by certain methods, such as analytic hierarchy process (AHP). Fourth, the basic weight of each warning index in corresponding periods can be appropriately adjusted to a higher level in that actual values of the index were relatively lower than that at the denial level. At the last, a comprehensive evaluation value can be calculated using the specified index value and variable weight in conjunction with the punishing variable weight model. A lower comprehensive evaluation value would result in a lower actual value and a higher variable weight, which is the principle of the ‘punishing variable weight’. The authors applied the punishing variable weight model to Huai’an City, Jiangsu Province. Variation trends in land ecological security for the city during the period 1996-2010 were systematically evaluated and analyzed using the punishing variable weight model. Results showed that the variable weight value of the warning index was higher than its basic weight; however, its corresponding comprehensive evaluation value was found to be lower than that from the basic weight evaluation. Furthermore, the changing range of the weight was different in terms of basic weights. The general level of land ecological security of Huai’an City during 1996-2005 was shown to be relatively steady on the interval of high warning, which was caused by combined effects of natural factors, social factors and economic factors. However, some values with regard to human activity factors lay in the interval of moderate warning primarily owing to the increasing occupation of cultivated land through construction activities and to decreases in pollutant disposal levels as well. If relevant departments could take more positive and effective measures in protecting cultivated land, reducing emissions of pollutants, promoting social equality and balancing regional development, the land ecological security conditions would be continued and even increase during the period 2006-2010.
基于TOPSIS模型的京津冀城市群土地综合承载力评价
[J].
An evaluation of land comprehensive carrying capacity of Beijing-Tianjing-Hebei urban agglomeration based on TOPSIS model analysis
[J].
基于变权的城镇用地扩展生态适宜性空间模糊评价:以江苏省太仓市为例
[J].
DOI:10.11849/zrzyxb.2012.03.006
URL

城镇用地生态适宜性评价有助于引导城镇用地合理扩展。针对传统评价方法的不足及生态适宜性的模糊性,提出基于局部惩罚型变权的空间模糊综合评价方法,并选择7项生态适宜性影响因素,在GIS软件的支持下对江苏省太仓市城镇用地的生态适宜性进行综合评判。结果显示,变权模型可灵活而合理地处理各评价单元各因素的权重值;研究区内适宜、基本适宜、较不适宜和不适宜于城镇扩展的土地分别占土地面积的25.89%、8.35%、37.43%和28.33%,其生态敏感性评价结果及其空间分布与实际相符,通过生态敏感性综合分值的比较可为城镇用地扩展区位选择提供依据。研究表明,基于变权的空间模糊综合评价凸显了"瓶颈"因素的否决作用,更能精确、合理地反映城镇用地扩展的生态适宜性状况。
Spatial fuzzy assessment of ecological suitability for urban land expansion based on variable weights:A case study of Taicang
[J].
基于变权模型的唐山城市脆弱性演变预警分析
[J].
Early-warning of urban vulnerability in Tangshan city based on variable weight model
[J].
基于变权TOPSIS模型的三峡库区土地生态安全评估:以巫山县为例
[J].
Evaluation of land eco-security in the threegoeges reservoir region based on the variable weight TOPSIS model:A case study of Wushan
[J].
治沟造地新增耕地的土壤质量评价——延安宝塔区为例
[J].
The evaluation of soil nutrient status in newly reclaimed land from trench construction—Taking Baota district of Yan’an city as example
[J].