0 引言
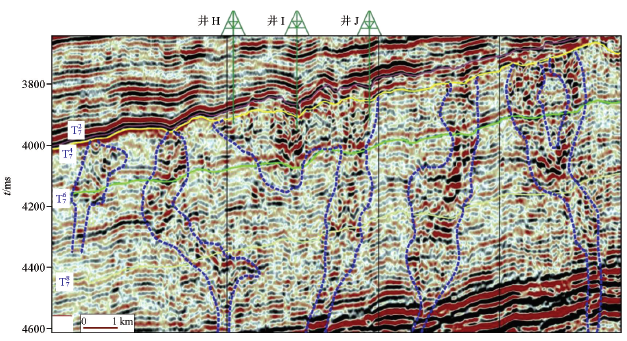
在断溶体油藏开发过程中,由于缝洞系统发育,钻井时常发生大量泥浆漏失与钻具放空的情形。在钻遇大型溶洞时往往封堵效果很差,这时无法继续钻进,而被迫完井。常规测井在漏失段和坍塌段都无法测量,导致生产时油源深度难以确定[5]。
计算流体力学(CFD)是研究流体流动和能量传递规律的一种实用方法,利用离散方程描述连续的流动场和温度场,通过数值方法求解整个计算区域的流体性质[14]。相应的CFD商业化软件可以实现模拟过程的可视化和参数精准检测,其中COMSOL软件具有强大的流体流动分析能力和多场耦合计算能力。
断溶体油藏是一种新型的石油富集圈闭,对该类油藏的温度分布规律尤其是生产时流温的评价方法还是空白。利用COMSOL软件,模拟断溶体油藏的石油生产过程中温度场的变化,进行流体流动场和温度场的耦合,分析不同井筒和溶洞关系时井中流温、静温曲线特征。为利用井中静温和流温差异研究储层与井筒的相对位置提供依据,为断溶体油藏的开发提供帮助。
1 数学物理模型及模拟方法
本文模拟的断溶体油藏生产过程为:①初始状态时,石油储存在溶洞中,温度分布就是地层原始温度;②钻井开发时,石油以一定的速度从溶洞进入井筒,井筒和周围地层的温度场发生改变,井中温度为瞬态温度;③稳定生产一段时间,井中温度分布达到稳态,不再变化,测得的井中温度为流温曲线;④关井一段时间后,井中温度逐渐恢复到与地层原始温度一致,流体静止,此时为静温。在热平衡建立的过程中,热量在井筒与地层中的传递存在5个典型阶段,分别为:原始温度分布被破坏、热量在井筒内做稳定径向导热、热量从井筒向地层传递、热量在地层内做径向导热以及达到热平衡[15]。本文模拟采取稳态方法,不考虑生产时间和关井时间的影响,直接得到流温、静温曲线。
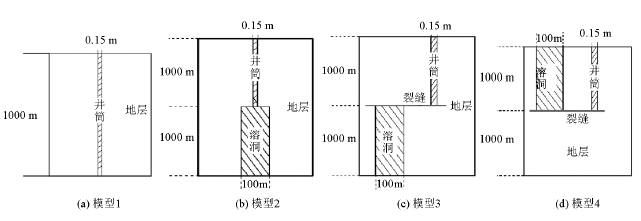
1.1 物理模型
图1
图2
1.2 计算方法
利用COMSOL软件的流体传热模块进行稳态模拟。假设井筒、裂缝和溶洞中的流动为层流,地层为固体无流体流动,地温梯度恒定,不考虑热辐射。
通过数值计算和图像显示,对包含有流体流动和热传导等相关物理系统进行分析。文中基于CFD采用的基本算法是:用有限个离散点上的温度和速度的集合表示速度场和温度场,通过守恒方程组建立这些离散点上两种场变量之间的代数关系,然后求解代数方程组获得各个离散点上的温度和速度的近似值。
1.2.1 控制方程
在断溶体油藏生产过程的数值模拟中,流体的流动和传热受质量守恒、动量守恒和能量守恒方程控制。
1)流体流动方程
动量守恒
质量守恒
2)传热方程
能量守恒
式中:ρ为流体密度,kg·cm-3;u为流动速度,m·s-1;μ流体粘度,Pa·s;p压力,Pa; Cρ为恒压热容,J·(kg·℃)-1;q热通量,W·m-2;k为导热系数,W·(m·℃)-1;T为温度,℃;F表示体积力,Q表示热源。文中不考虑重力等的影响,F=0;没有内部热源,Q=0。
1.2.2 边界条件
地层的外边界保持原始地温分布,TΩ=T0+gT·h;
流动入口在溶洞底部,Tin=T0+gT·h,
流动出口在井筒顶部pout=0;
表1 模拟参数
Table 1
| 名称 | 符号 | 单位 | 值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 石油密度 | ρ | kg·m-1 | 793.6 |
| 石油恒压热容 | Cρ | J·(kg·℃)-1 | 2200 |
| 石油粘度 | μ | Pa·s | 0.002 |
| 石油导热系数 | k | W·(m·℃)-1 | 1 |
| 地层密度 | ρf | kg·m-1 | 2715 |
| 地层恒压热容 | Cf | J·(kg·℃)-1 | 700 |
| 地层导热系数 | kf | W·(m·℃)-1 | 3.1 |
| 地温梯度 | gT | ℃·m-1 | 0.01818 |
| 地面温度 | T0 | ℃ | 23 |
| 石油流入速度 | ν | kg·s-1 | 1.39 |
图3
1.3 模拟方法
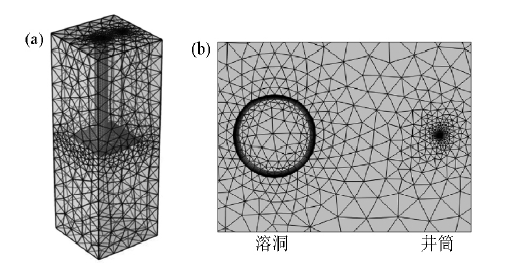
1.3.1 网格剖分
图4
图4
模型4的网格剖分
a—整体剖分网格;b—溶洞和井筒的局部网格
Fig.4
Grid generation of model 4
a—global;b—karst cave and wellbore
1.3.2 温度场求解方法
2 模拟结果分析
图5
图5
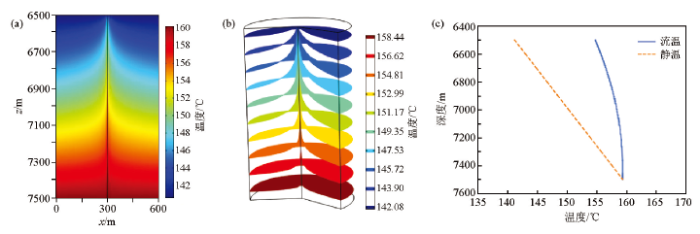
只有井筒时(模型1)的温度分布和井温曲线
a—温度分布切面;b—温度三维分布;c—井温曲线
Fig.5
The temperature distribution and well temperature curve of the wellbore(model 1)
a—section diagram of temperature distribution;b—three dimensional distribution of temperature;c—well temperature curve
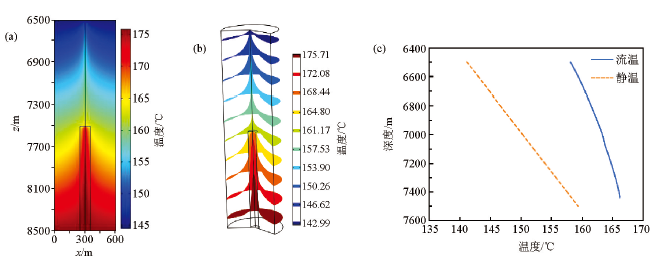
图6是溶洞在井筒下方时(模型2)的温度分布和井温曲线。模型参数为:井筒直径0.15 m,地层直径600 m,地层纵向厚度为2 000 m井筒长度1 000 m,溶洞直径100 m,长度1 000 m,井底位置在7 000 m,井底静温为159.35℃。石油在溶洞中流动时,由于与地层的接触面较小,且地层和石油的温差较小,溶洞中的石油冷却较慢,最终以较高的温度进入井筒,井底流温为 166.23℃。对比只有井筒时(模型1)的情况,存在溶洞时井底出现了较大的温度差异,且流温大于静温。
图6
图6
溶洞在井底下方(模型2)的温度分布和井温曲线
a—温度分布切面;b—温度三维分布;c—井温曲线
Fig.6
The temperature distribution and well temperature curve when the cave is below the well-bottom (model 2)
a—section diagram of temperature distribution;b—three dimensional distribution of temperature;c—well temperature curve
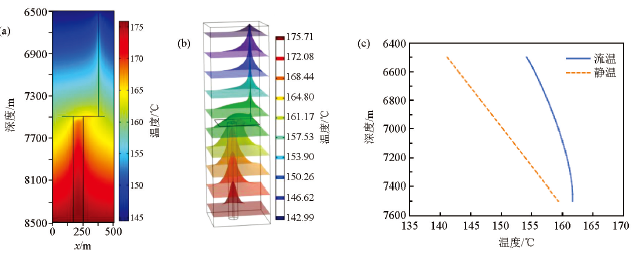
图7是溶洞在井底下方,通过裂缝与井筒相连时(模型3)的温度分布和井温曲线。模型参数为:井筒直径0.15 m,地层水平方向长宽均为500 m,地层纵向厚度为2 000 m,井筒长度1 000 m,溶洞直径100 m,长度1 000 m,裂缝宽度为0.05 m,井底位置在7 500 m,井底静温为159.35℃。石油通过裂缝进入井底时的流温为161.74℃。对比只有井筒时(模型1)的情况,井底温度差异较小,流温略大于静温。对比井筒直接与井筒相连的情况(模型2),模型3井筒中的流静温差较小。
图7
图7
溶洞在井底下方(模型3)的温度分布和井温曲线
a—温度分布切面;b—温度三维分布;c—井温曲线
Fig.7
The temperature distribution and well temperature curve when the cave is below the well-bottom (model 3)
a—section diagram of temperature distribution;b—three dimensional distribution of temperature;c—well temperature curve
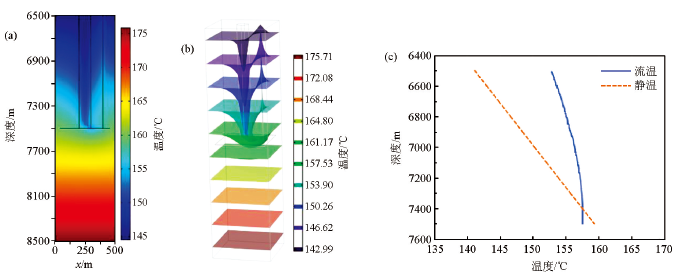
图8是溶洞在井底上方时(模型4)的温度分布和井温曲线。模型参数为:井筒直径0.15 m,地层水平方向长宽均为500 m,地层纵向厚度为1 600 m,井筒长度1 000 m,溶洞直径100 m,长度1 000 m,裂缝宽度为0.05 m井底位置在7 500 m,井底静温为159.35℃。由于溶洞在井底上方,温度较低的石油先向地层深部流动,逐渐被加热,但温度尚未上升到与地层温度一致即通过裂缝进入井筒。通过裂缝进入井筒时井底流温小于静温,井底流温为157.63℃。
图8
图8
溶洞在井底上方(模型4)的温度分布和井温曲线
a—温度分布切面;b—温度三维分布;c—井温曲线
Fig.8
The temperature distribution and well temperature curve when the cave is at the above of the well-bottom (model 4)
a—section diagram of temperature distribution;b—three dimensional distribution of temperature;c—well temperature curve
3 实际井温分析
图9
图9
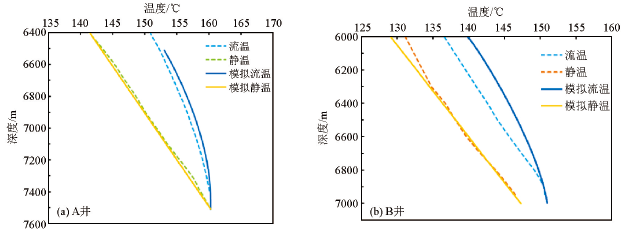
实测与模拟井温曲线对比
Fig.9
Comparison of measured and simulated well temperature curves
结果如下:A井井底在7 400 m,温度160.114℃,此深度的静温为158.733℃,温差1.381℃,该井的流温曲线形态与模型1相似,模拟结果显示该井的油源深度在7 510 m。B井井底在6 950 m,此深度的实测流温为150.947℃,静温为146.56℃,温差4.387℃,该井的井底流静温差较大,形态与模型2的模拟结果相似,推断溶洞在井孔下方,依据油源深度为7 500 m时的模拟结果(图9b的蓝色实线),推测该井的油源深度为7 500 m。
4 结论
断溶体油藏作为一种新型的石油富集圈闭,急需有效的测井评价方法,以确定储层深度。文中通过对不同井筒和溶洞相对位置设置不同的断溶体模型,模拟了受石油流动影响的温度场,发现利用井中流温、静温曲线可以确定断溶体油藏储层位置。当产油层位于井底时,井底的流温、静温一致;当石油产自井底上方时,井底流温小于静温;当石油产自井底下方时,井底流温大于静温。通过实测的流温与静温曲线的形态,可以推断合适的溶洞—井模型,结合油井的生产数据通过数值模拟计算出油源位置。在之后的研究中需要进一步确定流温曲线与油源位置的定量关系,以便更快捷地确定油源深度和溶洞大小等信息。
参考文献
塔河油田断溶体油藏地震反射特征类型及规律
[J].
Type and regularity of the seismic reflection characteristic of fault-karst carbonate reservoirs in the Tahe oilfield
[J].
塔里木盆地顺北特深碳酸盐岩断溶体油气藏发现意义与前景
[J].
Significance and prospect of ultra-deep carbonate fault-karst reservoirs in Shunbei area,Tarim Basin
[J].
塔河地区碳酸盐岩断溶体油藏特征与开发实践
[J].
Characteristics and development practice of fault-karst carbonate reservoirs in Tahe area,Tarim Basin
[J].
断溶体油藏高效井预测方法与应用效果——以HLHT油田奥陶系潜山区为例
[J].
Fault-karst carbonate reservoir prediction: a case study in Ordovician buried hills,HLHT Oilfield
[J].
利用测井资料评价钻井液漏失层
[J].
Evaluation of mud loss while drilling by using temperature logging and imaging logging data
[J].
Numerical simulation of wellbore and formation temperature fields in carbonate formations during drilling and shut-in in the presence of lost circulation
[J].
井温测井数值计算
[D].
Numerical computation of temperature logging
[D].
碳酸盐岩储层温度特征及温度测井资料应用研究
[D].
Research of temperature characteristics in carbonate reservoirs and temperature logging data applications
[D].
注聚合物井井下温度分布数值模拟研究
[J].
Numerical simulation of downhole temperature distribution in polymer injection well
[J].
缝洞型介质流体流动规律研究
[D].
Fluid flow law in fractured vuggy media
[D].
缝洞单元注水开发物理模拟
[J].
Physical simulation of water flooding in fractured-vuggy unit
[J].
缝洞型油藏注水驱油可视化物理模拟研究
[J].
Study on the visual modeling of water flooding in carbonate fracture-cavity reservoir
[J].
多井缝洞单元水驱见水模式宏观三维物理模拟
[J].
Macroscopic three-dimensional physical simulation of water flooding in multi-well fracture-cavity unit
[J].
基于数字岩心的致密砂岩微观渗流模拟
[D].
Microscopic flow simulation of tight sandstone based on digital core
[D].
气井井筒瞬态温度压力耦合模型研究
[D].
Study on transient temperature pressure coupling model of gas wellbore
[D].
塔河油田碳酸盐岩断溶体油藏分隔性描述方法研究
[J].
Description of the separation in fault-karst carbonate reservoirs in Tahe oilfield
[J].
New insights into the carbonate karstic fault system and reservoir formation in the Southern Tahe area of the Tarim Basin
[J].
塔河断溶体油藏典型断溶体注水驱替规律及剩余油分布特征
[J].
Study on water drive law and characteristics of remaining oil distribution of typical fault-karst in faul-tkarst reservoirs,Tahe Oilfield
[J].
基于COMSOL软件的非结构化网格下的二维大地电磁正演模拟
[J].
The simulation of unstructured grid two-dimensional magnetotelluric forward modeling based on COMSOL software
[J].