0 引言
1 工作区简介
区内进行1∶20万化探异常查证时,在陈贾村一带发现一处铅矿化线索,因此在该地区部署了地气剖面进行验证,测量结果显示除了已发现矿化线索的地方出现低缓地气异常外,覆盖区其余地方出现了多处强异常。在对这些异常进行查证时,发现强异常区为全覆盖区,而在发现铅矿点的相邻沟谷中岩石较破碎,覆盖较浅,通过剥土施工,发现一条金、铜、铅、锌多金属矿体。
2 地气工作方法简介
2.1 地气野外采样方法
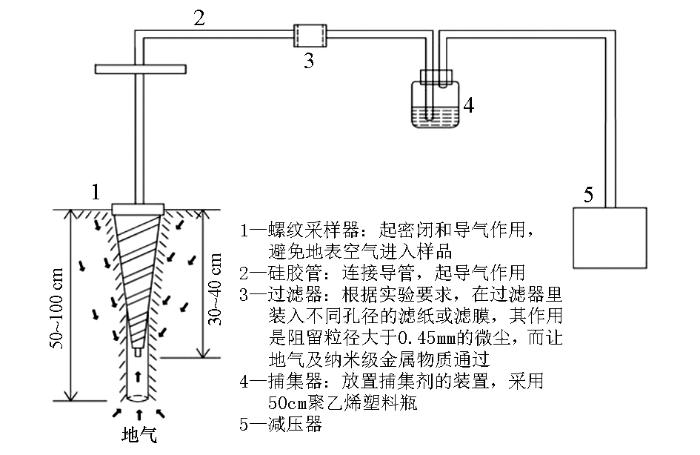
采样装置主要由螺纹采样器、硅胶管、过滤器、捕集器和减压器组成(图1)。
图1
2.2 地气样品分析方法
地气测量样品分析测量工作由中国地质科学院地球物理地球化学勘查研究所分析实验室完成。使用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS),工作条件采用跳峰模式,进样时间10 s,测量的目标元素包括Na、Mg、Al、P、K、Ca、Sc、Ti、V、Cr、Mn、Fe、Co、Ni、Cu、Zn、Ga、Rb、Sr、Y、Zr、Nb、Mo、Ag、Cd、In、Sn、Sb、Cs、Ba、La、Ce、Pr、Nd、Sm、Eu、Gd、Tb、Dy、Ho、Er、Tm、Yb、Lu、W、Au、Tl、Pb、Bi、Th、U等51种元素。鉴于篇幅有限,笔者只对其中所涉及的Cu、Pb、Zn、Ni、Sn、Sb、W、Bi、Cd等元素数据进行讨论。
2.3 地气样品重复性分析
由于缺乏标准物质监控分析质量,为评价高分辨率质谱(HR-ICP-MS)对地气样品金属元素分析数据的稳定性和再现性,监控分析质量,在所有样品分析完成后,按10%比例每10件抽取1件样品,在相同测试条件下进行重复测定,共分析重复样品123件,并计算两次测定结果的相对误差(Er/%),结果见表1。
表1 重复样品分析结果(n=50)
Table 1
| 元素 | Er/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | |
| Cu | 0.09 | 33.38 | 2.76 |
| Pb | 0.11 | 50.63 | 4.80 |
| Zn | 0 | 53.23 | 3.76 |
| Ni | 0.01 | 44.30 | 5.88 |
| Sn | 0.11 | 32.90 | 8.97 |
| Sb | 0.19 | 69.17 | 17.04 |
| W | 0.15 | 120.95 | 12.42 |
| Bi | 0.09 | 47.30 | 9.22 |
| Cd | 0.24 | 200.00 | 44.96 |
| Au | 0.07 | 200.00 | 73.16 |
由表1可以看出,地气样品中成矿元素Cu、Pb、Zn、Ni、W平均相对误差分别为2.76%、4.8%、3.76%、5.88%、12.42%,表明这些元素分析质量较好,完全满足地气测量精度要求。
通过以上分析可以看出,本次地气测量由于采用了最新型的高分辨率质谱(HR-ICP-MS)作为测定方法,总体分析质量较高,基本满足地气测量要求。
2.4 地气样品空白控制
捕集材料空白控制是地气测量能否成功的关键技术。本次采用Mos级高纯酸,再采用特殊工艺再提纯并活化,作为地气测量捕集剂。为了解其空白含量,按实际测量采用的捕集剂浓度,选择20件空白样品放入测量样品中一同分析,结果见表2。
表2 地气测量捕集剂空白元素分析
Table 2
| 元素 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | 0.8173 | 1.6986 | 1.1415 |
| Pb | 0.1519 | 0.2581 | 0.1764 |
| Zn | 0.9914 | 10.3634 | 3.6235 |
| Ni | 0.3793 | 0.5383 | 0.4275 |
| Sn | 0.0568 | 0.4262 | 0.1058 |
| Sb | 0.0120 | 0.0478 | 0.0206 |
| W | 0.0126 | 0.0483 | 0.0211 |
| Bi | 0.0050 | 0.0094 | 0.0070 |
| Cd | 0.00001 | 0.0103 | 0.0025 |
| Au | 0.0003 | 0.0046 | 0.0016 |
注:各元素含量单位为ng/L
由表2可以看出,空白样品大多数元素不仅平均含量非常低(微量元素平均值都低于1 ng/L),且比较均匀。金属成矿元素只有Zn空白样相对较高,最高值大于10ng/L,而地气测量样品中Zn一般大于20 ng/L,故本次的捕集剂空白完全能够满足本区地气测量要求。
3 地气异常重现性问题
异常重现性是勘查地球化学方法技术成熟的重要标志。由于地气测量受到多种因素的影响,因此在实际生产过程中,地气异常重现性表现较差。长期以来,重现性差成为限制地气方法在实际找矿中推广的主要障碍。 由于地气测量的特殊性,地气测量不能按常规化探方法来评价其重现性,而应参照测汞规范来评价,只要两次测量结果异常趋势基本一致即可,不能要求绝对含量一致。
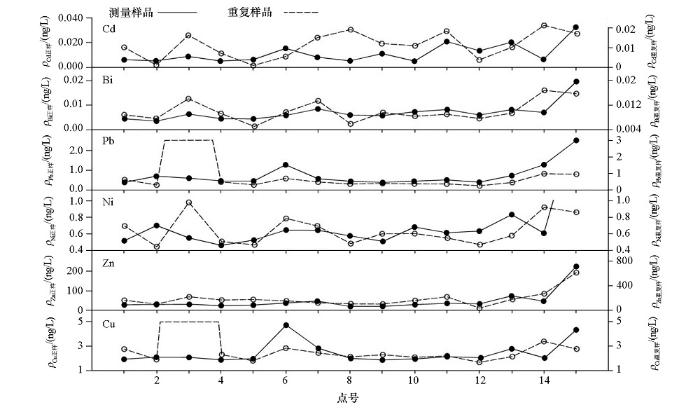
本次地气测量重共采集重复样37件,由于篇幅所限,笔者只对工作区19线的15件重复样中Cd、Bi、Pb、Ni、Zn、Cu 5种亲硫元素的重现性结果进行了对比分析。从图2可以看出,虽然气体流通性强,但本次地气测量和重复样的主要金属成矿元素Cu、Pb、Zn、Ni、Bi、Cd分布趋势比较一致,特别是Zn,趋势完全一致。但在3号点,重复样Cu、Ni、Pb含量显著增高,分布趋势与第一次采样结果不一致。从元素含量看,除重复样Zn含量系统性高于测量样品近3倍,原因不明外,其他元素两次采样结果总体比较相差不大(除3号点)。
图2
图2
19线地气重复样Cd-Bi-Pb-Ni-Zn-Cu结果对比
Fig.2
Comparison of the results of Cd-Bi-Pb-Ni-Zn-Cu on the line 19 of the geogas repeats
4 地气测量有效性
工作区内地气测量试验测量剖面23条,采集样品1 196件,重复样37件,分析51种元素,但为了节省篇幅,只对陈贾村地区的部分元素成图。通过数据处理及对比分析研究,地气测量有效性主要表现在以下几个方面。
4.1 地气异常与区内断裂位置对应
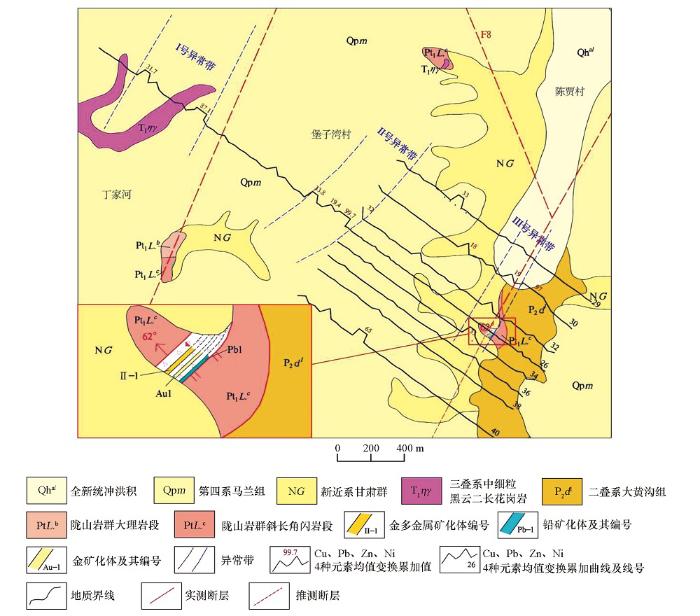
图3
图3
陈贾村一带地气试验Cu、Pb、Zn、Ni均值变换累加值平面剖面
Fig.3
The plane profile of the cumulative transformation of the mean values of Cu, Pb, Zn and Ni in the area of Chenjiacun area
4.2 地气异常与矿化体位置吻合
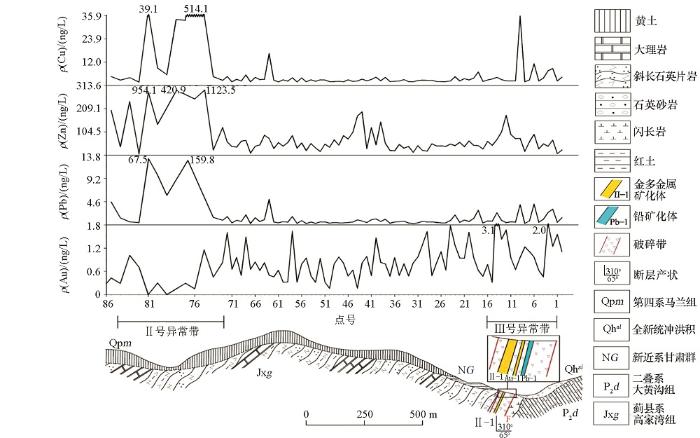
陈贾村26线地气测量显示(图4),在已知小型金及多金属矿化体正上方,捕获到了地气异常,且异常幅度显著,不仅有矿体主要元素形成的地气异常,还有V、Mn、Co、Sb、U、Bi等元素的地气异常,为指示深部矿体的存在提供了更多依据。异常与矿体在平面投影上的位置是基本一致的,证实了在该区地气资料对于隐伏金属矿产指示的有效性与准确性,且各异常区的元素组合特征相似。
图4
图4
陈贾村26线地气试验结果
Fig.4
Ground gas measurement test results of Chenjiacun line 26
4.3 地气异常与物探异常高度对应
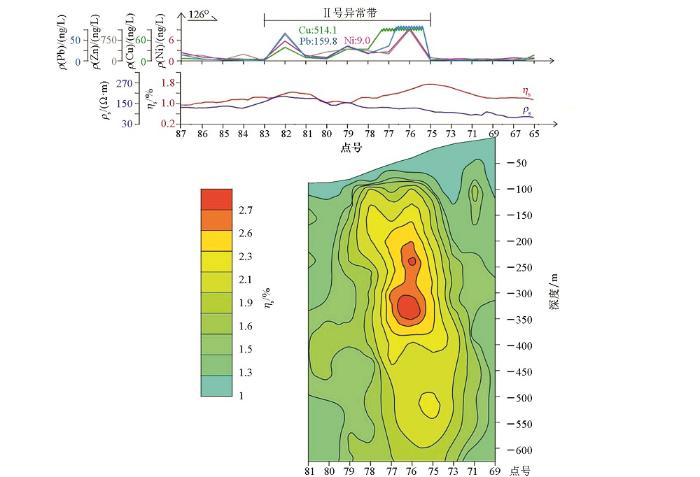
此次地气测量获得了多处异常,笔者选取部分异常部署了激电中梯测量、激电测深及可控源测深进行验证,均发现了较好的物探异常。尤其是陈贾村地区26线中II号异常带,该异常带被黄土全覆盖,但地气异常强度高、连续性好,对该处布设激电中梯剖面及激电测深,发现在地气异常处深部存在低阻高极化异常(图5)。
图5
图5
陈贾村地区地气、激电中梯、激电测深极化率等值线断面综合剖面
Fig.5
Comprehensive profiles of geogas, induced polarization mid-ladder and induced polarization sounding in Chenjiacun area
5 结论
1) 在黄土覆盖区利用地气测量能够清晰反映金属元素异常,异常元素组合与亲硫元素组合基本一致。
2) 异常强度高且与矿(化)体空间位置吻合,这表明地气异常样品所捕集的地气物质主要来自于矿(化)体。
3) 地气异常与区内断层展布方向基本一致。
综上所述,在陈贾村地区,地气测量找矿成果显著,方法有效。
参考文献
地气测量在湖南锡田地区深部找矿中的应用与意义
[J].
The application and significance of deep prospecting by using geogas survey in Xitian area,Hunan province
[J].
金窝子矿带戈壁覆盖区化探深穿透找矿方法研究
[J].
Structure and genesis of Gobi-overburden and gold surface migration in the eastern Tianshan area
[J].
地气测量在隐伏铀矿找矿中的应用与现状
[J].
Application and current status of geogas prospecting in concealed uranium deposits exploratio
[J].
地球化学勘查的新技术及发展趋势
[J].
DOI:10.11720/wtyht.2015.4.05
URL

近几年,地球化学勘查无论从技术层面还是思想层面都得到迅速发展,主要包括:解决了几种特殊景观区普遍存在的有机质和风成砂等因素对异常的干扰问题;电地球化学、地气溶胶地球化学、金属元素活动态地球化学等深穿透地球化学勘查技术在寻找隐伏矿的理论和应用上逐渐趋于成熟;构造地球化学勘查技术成为隐伏矿定位预测评价中的关键技术之一,并形成一套完整的勘查技术流程;人工神经网络分析等地球化学数据处理新方法不断发展;建立了多目标区域地球化学调查体系,实现了资源调查与环境调查并举。未来,地球化学勘查将在农业、土地利用规划、坏境预警和保护等领域得到越来越多的应用。
The new technology and development trend of geochemical survey
[J].
DOI:10.11720/wtyht.2015.4.05
URL

In recent years, geochemical survey has seen a high-speed development not only at the technical level but also at the ideological level. The disturbances of organic material and eolian sands on anomalies over some special landscape areas have been solved. Deep-penetrating geochemical survey techniques such as electrogeochemical survey techniques, aerosol geochemical survey techniques, active metallic element geochemical survey techniques in search for concealed ore deposits have gradually matured in theory and application. Exploration technique of tectono-geochemistry has been one of key technology in the locating, predicting and evaluating of buried ore deposits, and has formed a complete technical process. Artificial neural network and other new methods for analysis of geochemical data have been steadily improved. The system of muti-purpose regional geochemical survey has been established, which helps concurrent development of resource survey and environmental survey. In the future, geochemical survey will get more and more applications in such fields as agriculture, land use and plan, environmental early warning and protection.
冲积平原区隐伏金属矿地气法试验研究
[J].
Results of geogas test in exploring blind metallic deposits in alluvial plain
[J].
DOI:10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2011.3. 019
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Distribution characteristics of geogas elements over metallic deposits concealed by alluvial plain are sumarized on basis of geogas test and research on Wangjiazhuang Cu deposit in Shandong province and comparison between the geogas survey and conventional soil geochemical survey.The results show that: ① the geogas survey displays clear metal element anomalies that are not displayed by conventional soil gochemical survey under various cover conditions and the geogas anomaly is strong and well coincided spatially with the ore bodies thus geogas survey is unique to discover concealed metallic deposit;② the liquid trapping agent and ICP-MS technique improves trapping efficiency and reliability of geogas data and provides technical support of standarization and engineering apllication for the geogas technique and the geogas technique provides a geochemical tool for concealed metallic deposits.
地电化学法在豫西崤山黄土覆盖区找矿中的应用——以洛宁县石龙山预查区为例
[J].
The application of geo-electrochemical methods to prospecting in the loess-covered Xiaoshan Mountain,western Henan Province:A case study of the Shi long shan gold polymetallic ore prospecting area in Luoning County
[J].
地电化学在隐伏铜镍矿勘查中的应用及异常形成机理探讨
[J].
Mechanism of geoelectrochemistry anomalies and application to prospecting of buried Cu-Ni deposits
[J].
深穿透地球化学对比研究两例
[J].
Deep-penetrating geochemistry comparison studies of two concealed deposits
[J].
新疆金窝子矿区深穿透地球化学对比研究
[J].
Deep penetrating geochemistry: A comparative study in the Jinwozi gold ore district, Xinjiang
[J].
纳米地球化学:穿透覆盖层的地球化学勘查
[J].
Nanogeochemistry:Deep penetrating geochemical exploration through cover
[J].
地气动态提取技术的研制及在寻找隐伏矿上的初步试验
[J].
Dynamic collection of geogas and its preliminary application in search for concealed deposits
[J].
纳米科学与隐伏矿藏——一种寻找隐伏矿的新方法、新技术
[J].
Nanoscience and concealed minerals — A new method and new technology for searching concealed minerals
[J].
地气测量寻找深部隐伏金矿及其机理研究
[J].
Geogas prospecting and its mechanismin the search for deep-seated or concealed gold deposits
[J].
地气测量在北祁连盆地区找矿突破及其意义
[J].
Breakthrough in mineral exploration using geogas survey in the basin area of northern Qilian region and its significance
[J].
戈壁覆盖区金窝子矿带深穿透地球化学方法研究
[J].
Deep penetration geochemistry methods in gobi-overburden terrain of the Jinwozi metallogenic belt
[J].
盆地金属矿穿透性地球化学勘查模型与案例
[J].
Models and case history studies of deep-penetrating geochemical exploration for concealed deposits in basins
[J].
申家窑金矿床地气测量异常特征
[J].
Anomalous characteristics of geo-gas measurements in Shenjiayao Gold Deposits
[J].
深穿透地球化学方法在十红滩砂岩型铀矿中的试验研究
[J].
An experimental study of deep penetration geochemical technology in the Shihongtan uranium deposit
[J].
综合气体地球化学测量
[J].
Integrated geochemical gas survey
[J].
黄土覆盖区金属矿床地气元素特征及示踪研究
[J].
Tracing the source of metals in geogas from metal deposits in a loess-covered region
[J].
纳米物质测量的液态捕集剂研究
[J].
The liquid collecting media for nanoscal material geochemical survey
[J].