0 引言
近年来鄂尔多斯盆地超低渗透储层中的天然裂缝对注水开发的影响愈来愈引起了油田开发工作者的重视[1,2,3,4,5]。据公开发表的文献显示,鄂尔多斯盆地众多区域已开展了裂缝研究工作,包括姬塬—元城、麻黄山、庆城—合水、沿河湾、五谷城、白豹、华庆、定边、镇原—泾川、侯市—杏河、胡尖山、陇东、宁县、靖安—安塞、吴旗、盆地中东部、盆地中西部、鄂南(延长油矿)等地区[6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30]。这些研究成果表明,除仅在盆地西南缘天环坳陷内红河油田发现了与断层伴生的裂缝系统[31]外,其他成果均认为盆地内三叠系延长组裂缝主要为区域性水平构造应力场作用下形成的区域构造裂缝,其研究对象主要为岩心中钻遇的天然小尺度裂缝。
长期以来,鄂尔多斯盆地被认为是稳定的、弱构造活动的构造单元, 盆地内延长组地层是不发育断层的[32]。然而,越来越多的资料和证据表明盆地伊陕斜坡内延长组地层发育有不同规模的断层,对于超低渗透储层仅研究小尺度裂缝是不全面的,裂缝与断层之间的关系以及裂缝研究和预测方法需要重新审视。本文以合水地区延长组为例,探讨断层存在的证据、裂缝发育特征及控制因素。
1 断层、破碎带及小尺度裂缝组成复杂的断裂系统
合水地区位于鄂尔多斯盆地伊陕斜坡西南部(图1),近期综合利用地震、钻井、测井、岩心等资料在该区延长组地层中发现了典型的断层、破碎带以及小尺度裂缝。
图1
1.1 断层
图2
图2
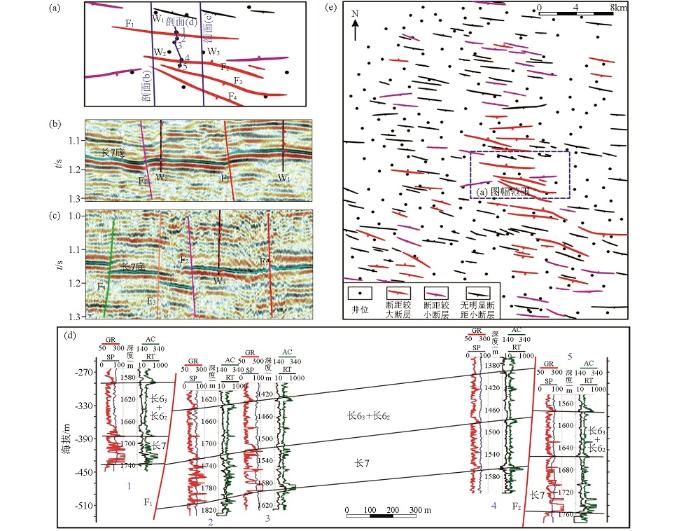
断层证据及断层分布
a—开发区断层分布图;b—过W1井二维地震剖面;c—过W3井二维地震剖面;d—1~5井长6地层对比剖面;e—合水地区长7底断层分布
Fig.2
The faults development evidence and distribution map
a—fault distribution in development zone;b—2D seismic profile through the W1 well;c—2D seismic profile through the W3 well;d—Chang 6 formation correlation section from well 1 to well 5;e—fault distribution map at Chang 7 formation bottom in Heshui area
1.2 断层破碎带
图3
图3
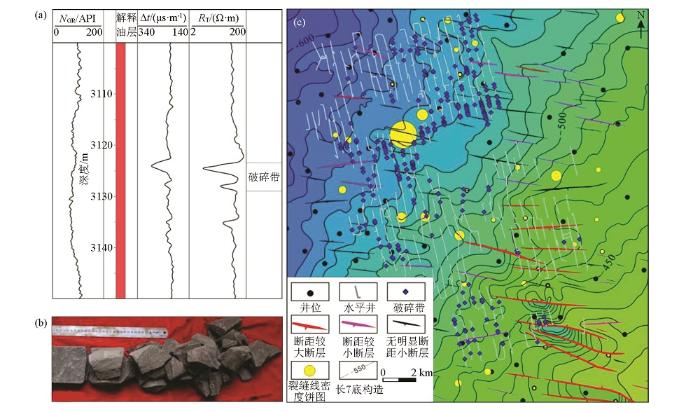
断层破碎带特征及其在水平井开发区的平面分布
a—断层破碎带电测曲线特征;b—断层破碎带岩心;c—水平井开发区钻遇的破碎带与构造叠合分布
Fig.3
The characteristics of fault damage zone and its distribution in horizontal wells development area
a—log curve characteristics of fault damage zone;b—the cores of fault damage zone;c—the overlap map of the drilled fault damage zone in horizontal well development area and the structure map
研究区水平井钻遇的破碎带主要分布在研究区西北部及南部断层末端延伸处,中部及东南部大断层发育区破碎带不发育(图3c)。
1.3 天然小尺度裂缝
总之,合水地区延长组发育由断层—破碎带—小尺度裂缝组成的复杂断裂系统,它们共同作用影响地下储层的非均质性、渗流能力,从而对油气生产产生重要影响。
图4
图4
两种类型的小尺度裂缝
a—受岩性界面控制的小尺度裂缝;b—与断层伴生的小尺度裂缝
Fig.4
Two types of small-scale fractures
a—small-scale fractures controlled by lithologic interface;b—small-scale fractures associated with faults
2 影响裂缝发育程度的主控因素
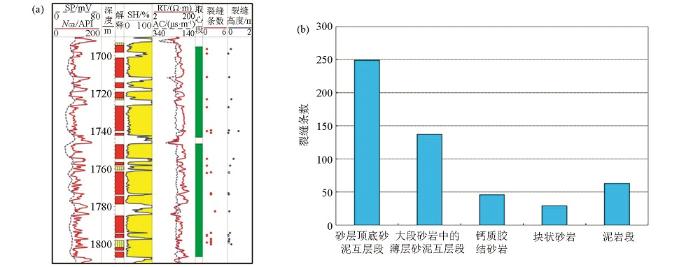
2.1 小尺度裂缝发育程度与岩性及地层厚度的关系
图5
图5
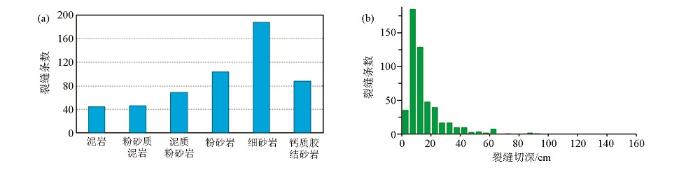
裂缝发育程度与岩性及层厚的关系
a—发育程度与岩性的关系;b—裂缝切深分布直方图
Fig.5
The relationship between fracture development degree and lithology and bed thickness
a—the relationship between fracture development and lithology;b—the histogram of fracture height
2.2 小尺度天然裂缝纵向分布特征
对50口井3 200 m岩心中发现的500余条天然小尺度裂缝统计分析表明,纵向上天然裂缝主要发育在砂体顶部、底部的砂泥互层层段中,其次为砂体内部的薄层以及钙质胶结砂岩中;大段块状砂岩内总体裂缝不发育(图6)。众多吸水剖面资料也表明,注水井尖峰状吸水段也主要分布在砂体顶部、底部的砂泥互层层段中。这一特征表明天然裂缝在纵向上的分布具有一定的优势层位,这为天然小尺度裂缝发育段的横向预测提供了依据。
图6
图6
天然裂缝纵向发育特征及不同位置分布频率统计
a—某井天然裂缝纵向分布;b—纵向不同位置小尺度裂缝分布频率统计
Fig.6
The longitudinal development characteristics of small-scale fractures and its distribution frequency in different zones
a—longitudinal distribution of natural fractures in a well;b—statistics on the distribution frequency of small scale fractures at different longitudinal position
2.3 破碎带与小尺度裂缝平面分布特征
岩心裂缝线密度饼图与破碎带及断层分布的叠合图(图3c)表明,平面上岩心中裂缝发育密度与破碎带分布具有很好的一致性。在水平井钻遇的破碎带较发育区,总体裂缝线密度和裂缝发育段比例相对较高。在研究区中部、东南部大断层发育区,破碎带总体不发育,岩心裂缝线密度和裂缝发育段总体比例较低;在这一区带内,其中有一口井的岩心中未发现裂缝,另一口井中发现3条裂缝,而其他两口井中仅各见1条裂缝。
由此可见,小断层末端延伸方向往往破碎带密集发育,大断距断层附近破碎带和裂缝相对不发育,破碎带发育区小尺度天然裂缝较发育。
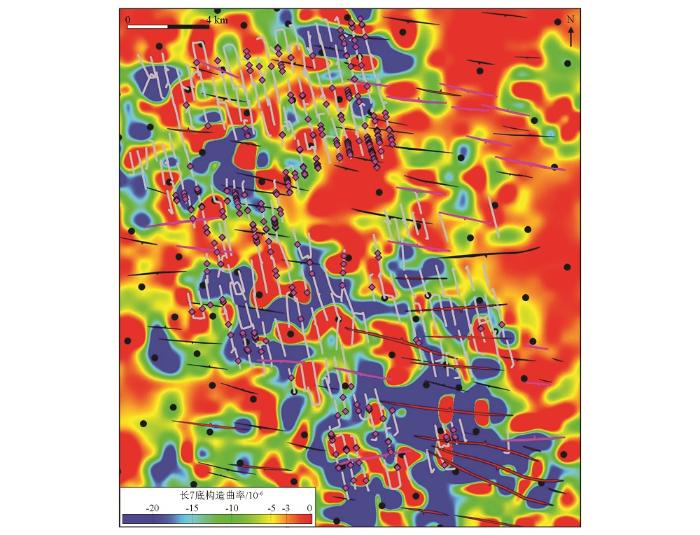
2.4 破碎带、小尺度裂缝发育程度与构造曲率的关系
破碎带和裂缝较发育处,构造起伏大、曲率高;破碎带和裂缝不发育处,构造较平缓,曲率低。另外,生产中裂缝型见水的水平井主要分布在鼻状隆起两翼的低洼部位,这说明构造曲率对裂缝发育具有一定的控制作用。
图7
图7
水平井开发区钻遇破碎带与长7底构造曲率叠合图(图例同
Fig.7
Overlapped map of the fault damage zones distribution and Chang7 bottom structure map in horizontal wells development area(legends are the same as figure3)
表1 不同曲率区裂缝发育程度统计
Table 1
| 曲率区域 | 水平井 | 直井岩心 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水平 井数 | 钻遇破 碎带井数 | 破碎带钻遇 井比例/% | 平均破碎 带段数 | 平均破碎 带宽度/m | 裂缝 条数 | 裂缝段岩心 长度/m | 平均每米 裂缝数 | 裂缝段 比例/% | |
| 低曲率区(趋负高值) | 54 | 14 | 25.9 | 2.2 | 2.8 | 107 | 17.45 | 3.82 | 62.321 |
| 中等曲率区 | 103 | 31 | 30.1 | 3.7 | 4.3 | 230 | 37.07 | 5.35 | 86.209 |
| 高曲率区(趋正高值) | 102 | 67 | 65.7 | 4.2 | 5.2 | 218 | 31.59 | 4.19 | 60.750 |
综上所述,天然小尺度裂缝的发育明显受机械层控制,断层、破碎带、小尺度裂缝之间存在着成因联系;构造曲率可以很好地预测破碎带和小尺度裂缝的发育程度;具有明显断距的走滑逆断层发育带总体裂缝发育程度低,其外围裂缝总体较发育。这一认识为研究区裂缝定量预测提供了思路和依据。
3 几点启示
本次研究表明,合水地区延长组地层发育由断层、断层破碎带和天然小尺度裂缝组成的复杂断裂系统;断层破碎带受断层控制、裂缝特别发育,纵向和横向均能延伸一定的距离,对油井生产有一定的影响;相对于断层破碎带,普遍发育的天然小尺度裂缝切深小,受岩性界面控制,主要发育在砂层顶底薄层砂泥互层中,其密度较低、难以提供有效的等效渗透率,对油水井生产的直接影响是有限的。此前公开发表的有关鄂尔多斯盆地伊陕斜坡内延长组的裂缝研究,主要围绕的是天然小尺度裂缝,没有认识到断层和断层破碎带的存在。因此,在今后合水地区乃至整个鄂尔多斯盆地伊陕斜坡内研究超低渗透储层的裂缝时,应充分重视断层和破碎带的各种响应特征,重点研究断层破碎带对油水井生产的影响,将断层、破碎带和天然小尺度裂缝当作一个系统来研究,而不应仅研究天然小尺度裂缝。
在断层—破碎带—小尺度裂缝这一复杂系统中,断层可以利用二维地震、钻井资料来确定,其分布是确定的;破碎带受断层控制,而对于小尺度天然裂缝而言,能够直接用于描述其分布特征的资料是十分有限的,其分布具有很大的不确定性。分析三者之间的关系,有助于较准确地预测这一复杂断裂系统的分布特征,提高裂缝预测精度,减小裂缝分布的不确定性。
目前在超低渗透油藏开发过程中储层均要经过大规模水力压裂改造,如何更好地利用超低渗透储层中发育的天然复杂断裂系统,应是今后类似油藏高效开发的一个重要课题。因此,本区的裂缝研究给了我们以下几点启示,也具有一定的指导意义。
1)水平井是开发此类储层的最优方式。天然构造裂缝、破碎带均以高角度为主,因此直井钻遇裂缝的概率是非常低的;而水平井的水平段与天然构造裂缝、破碎带近于垂直,因此钻遇的概率非常高;而且可以钻遇多段破碎带或天然裂缝,沟通更多的储层。所以,水平井是开发这类储层的最优井型。本次研究发现的破碎带,除了50口直井岩芯观察井中有3口井发现4段破碎带外,其余的均为水平井钻遇。如果研究区内没有这些水平井,仅利用斜井或直井资料,则难以认识到破碎带的普遍存在。
2)选择最优化的完井方式。目前合水地区套管水泥固井的完井方式导致大多天然裂缝和破碎带未能直接与井底沟通,其对油水井生产的影响可能有限。建议今后针对类似储层开展水平井完井方式优化研究并现场试验,如裸眼筛管完井方式等。
3)水平段方位优化。目前完钻水平井水平段方位均垂直于现今最大主应力方向,没有考虑其它的因素。发育的断层破碎带延伸方位与邻近断层方位一致,其与现今最大主应力方向NE75°有一定夹角。因此,建议今后开展水平井水平段方位优化工作,考虑利用断层破碎带。
4)采用合理的压裂改造规模。对不同裂缝发育程度区,超低渗透储层应采用不同的压裂改造规模。破碎带及天然小尺度裂缝不发育区,应加大储层的压裂改造规模;破碎带及天然小尺度裂缝发育区,应减小储层的压裂改造规模。
4 结论
1)研究表明,合水地区延长组地层发育由断层—破碎带—小尺度裂缝组成的复杂断裂系统,因此,鄂尔多斯盆地伊陕斜坡内延长组地层的天然裂缝研究应将断层、破碎带和天然小尺度裂缝作为一个系统来考虑分析,而不应仅针对天然小尺度裂缝进行研究。
2)小尺度裂缝的发育明显受机械层控制,断层、破碎带、小尺度裂缝之间存在着成因联系,而构造曲率可以很好地预测破碎带和小尺度裂缝的发育程度。
3)如何更好地利用超低渗透储层中发育的天然复杂断裂系统,应是今后类似油藏高效开发的一个重要课题。
参考文献
鄂尔多斯盆地特低渗透砂岩储层裂缝压力敏感性及其开发意义
[J].
The pressure sensitivity of fractures and its development significance for extra low-permeability sandstone reservoirs in Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地长8、长6天然裂缝差异性研究及其对开发的影响
[J].
Study on the difference between the natural fractures in Chang 8 and Chang 6 reservorirs in Ordos Basin and its influence on the development of the reservoirs
[J].
开发井网与裂缝系统适应性对特低渗油藏注水开发的影响——以鄂尔多斯盆地安塞油田沿25井区长6油藏开发为例
[J].
Influence of well pattern and fracture system adaptability on water injection development in ultra-low permeability reservoirs—Taking Chang 6 reservoir development of Yan 25 area in Ansai oilfield of Ordos Basin as an example
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区天然裂缝有效性分析
[J].
Analysis of the natural fracture effectiveness in Longdong area of Ordos Basin
[J].
裂缝性低渗透砂岩油藏合理注水压力——以鄂尔多斯盆地安塞油田王窑区为例
[J].
Discussion on optimal injection pressure of fractured low-permeability sandstone reservoirs——A case sudy from Wangyao Block in Ansai Oilfield,Ordos Basin
[J].
陕甘宁盆地延长统区域裂缝的形成及其油气地质意义
[J].
Origin of the regional fracturing in Yanchang epoch,Shanganning basin,significance for geology of oil and gas
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地镇原—泾川地区三叠系延长组构造裂缝分布定量预测
[J].
Quantitative prediction of distribution of tectonic fractures in the Yanchang formation in the Zhenyuan-Jingchuan area,Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地上三叠统延长组特低渗透砂岩储层裂缝特征及成因
[J].
Characteristics and origin of fractures in the extra low permeability sandstone reservoris of the Upper Triassic Yanchang formation in the Ordos basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区延长组长6—8特低渗透储层微裂缝研究
[J].
Micro-fractures in extra-low permeability reservoir of Yanchang formation in Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区特低渗透砂岩储层裂缝分布规律及其渗流作用
[J].
Fracture distribution and seepage of ultra-low permeability sandstone reservoirs in Longdong area of Ordos Basin
[J].
吴旗探区长61 储层构造裂缝特征及分布规律
[J].
Characteristics and distribution of tectonic fractures in Chang 61 low-permeable reservoir in Wuqi area in Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地沿河湾探区低渗储层长61 构造裂缝主要形成期应力环境判识
[J].
Palaeo stress judgement of tectonic fractures in Chang 61 low permeable reservoir in Yanhewan area,Ordos Basin in main forming period
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬油田上三叠统延长组超低渗透砂岩储层微裂缝研究
[J].
A study on micro cracks in super-low permeability sandstone reservoir of the Upper Triassic Yanchang formation in the Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬地区上三叠统延长组裂缝特征及其地质意义
[J].
Fracture characteristics and geological significance of Upper Triassic Yangchang formation in Jiyuan area,Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地东南缘延长组砂岩储集层裂缝特征研究
[J].
Characteristics of fractures in the sandstone reservoirs of Yanchagn formation in Southeastern Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地麻黄山西区块延长、延安组裂缝成因及期次
[J].
Genetic mechanism and development periods of fracture in Yanchang and Yan'an formatin of Western Mahuangshan block in Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地胡尖山地区长4+5~长6油层组裂缝发育特征及对原油运聚的控制作用
[J].
Fracture development characteristics of Chang 4+5~ Chang 6 oil formation and its control on crude oil migration and accumulation in Hujianshan area of Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬地区延长组裂缝特征及成因
[J].
Feature and genesis of the reservoir fractures of Upper Triassic Yanchang formation in Jiyuan area,Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地南泥湾地区古构造应力场模拟与裂缝储层有利区分析
[J].
Paleotectonic stress field simulation and analysis of favorable zones of fractured reservoirs in Nanniwan area of Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯陕北斜坡中部志丹地区砂岩储层裂缝研究
[J].
Study on Fracture of sandstone reservoir in Zhidan area of central north Shaanxi Slope in Ordos
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地富黄探区西部长6裂缝特征及控制因素
[J].
Characteristics and control factors for the Chang 6 fractured-type reservoir in the west Fuhuang prospecting District,Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地下寺湾地区长8储层裂缝特征研究
[J].
Fracture characteristics of Chang 8 reservoir of Yanchang formation in Xiasiwan area,Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地中西部三叠系延长组裂缝特征研究
[J].
Fracture characteristics of the Triassic Yanchang Formation in the midwest of Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地吴起地区长6储层裂缝系统研究及意义
[J].
The study of fracture system and significance of Wuqi Chang 6 super-low permeability oil reservoir in Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地合水地区长8段裂缝发育特征及其对产油量的影响
[J].
The study of relationship between fracture characteristics and yield of Chang 8 section in Heshui area,Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地宁县一合水地区长6 、长7 、长8 储层裂缝差异性及开发意义
[J].
Differences of natural fracture characteristics and their development significance in Chang 6,Chang 7 and Chang 8 reservoir,Ningxian-Heshui area,Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地东南部黄陵地区延长组裂缝特征及形成期次探讨
[J].
Fracture characteristics and stages of Yanchang Formation in Huangling area of southeastern Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地南部延长组中段剪裂缝方向分析
[J].
Shear fracture direction and mechanical characteristics of the middle Yanchang Formation,southern Ordos Basin,China
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地定边地区延长组长71储层构造裂缝分布预测
[J].
Quantitative prediction of tectonic fracture distribution in the Chang 71 reservoirs of the Yanchagn Formation in the Dingbian area,Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯南部正宁地区长6致密储集层裂缝识别
[J].
Fracture identification of Tight Reservoir in Chang 6,south of Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地红河油田长9段裂缝分布定量评价
[J].
Quantitative evaluation of fracture distribution of Chang 9 member in Honghe oilfield,Ordos Basin
[J].
鄂尔多斯盆地北部断裂分析
[J].
Analysis of the faults in the northern Ordos BaSIN,Northwest China
[J].
Fault damage zones
[J].