0 引言
微地震监测技术因其具有实时三维监测和动态灾害预警的优点,已广泛应用于采矿、隧道和水力压裂等领域[1,2,3]。微地震事件定位是一项基础工作,所有后续的微地震处理都受到位置精度的影响[4]。然而,微地震初至拾取的准确性对震源定位有着重要影响[5,6]。在过去的几十年中,学者们已经提出了各种可靠的算法来自动或半自动地确定初至,其中使用最广泛的方法是基于自回归模型的赤池信息准则(AR-AIC)方法和长短时窗比法(STA/LTA)[7]。作为一种通用的拾取算法,STA/LTA方法计算量很小,因此适用于分析非常大的数据集及实时拾取,并且对于含噪数据集,结合使用STA/LTA曲线的微分函数最大值的给定阈值,也可以实现可靠的到时识别。相似的,AR-AIC方法是估计P波到时的有力工具[8],已经广泛应用于各类商业软件中。然而,这类算法均受背景噪声和随机噪声的强烈影响,即数据质量是影响拾取算法有效性的重要因素,这使得强噪声微地震数据的到时拾取变得极为困难[9]。鉴于高质量数据有助于提高自动拾取技术的准确性,有效的措施是采用可靠的分解操作,来提取强噪声数据有效成分。
文中,考虑到各种噪声的随机性,首先采用小波多尺度分析(WMA)方法提取强噪声3C微地震数据的主成分,得到相应的重构近似数据和细节信息。然后在获得合理的数据集后,计算重构近似数据绝对值的最大值点,作为AIC计算数据段的时窗终点,进而利用AIC序列完成初至拾取操作。
1 M-AIC算法
式中,k遍历x序列中的所有样本,var(x[1,k])和var(x[k+1,N])是两个局部平稳区间的方差。考虑到AR系数计算的效率和复杂性,文中选用M-AIC拾取方法。
图1
图1
合成地震数据的不同AIC值
a—随机噪声占5%;b—随机噪声占60%;P波的主频为100 Hz,采样间隔为0.25 ms
Fig.1
Different AIC values for synthetic microseismic data
a—random noise account for 5%;b—random noise account for 60%;principal frequency of P-wave is 100 Hz,sample interval is 0.25 ms
2 小波多尺度分析(WMA)
2.1 小波变换及三分量微地震数据的参数选择
其中,φs,τ(t)是母小波函数,s被设定为尺度因子,τ是平移因子。因此,在低尺度下,高频信息被突出显示,而在大尺度下,低频特征被更好地处理,这意味着信号可以在不同频率下以不同分辨率(或尺度)进行分析。这也是处理包含各种频率成分信号的重点,如具有非线性和非平稳模式的信号的微地震信号。
利用小波多尺度分析处理微地震资料,主要集中在小波分解层次和小波基的选择,小波基的选取标准包括其支持度、对称性、规律性和消失矩数[14]。对于强噪声三分量微地震数据的到时拾取,其目的是凸显低频信息,而不是去噪,这避免了分解和重建时的相位失真。因此,消失矩越大,高频系数越小,通过抑制高频系数,有利于分解后的低频能量集中[15,16]。同时,它应具对称性,可以有效地防止相位失真。基于以上原理,文中选择Daubechies(db10,其消失矩数为10)小波基进行分解和重构,同时其也具有正交性、对称性、短支撑的特点。至于分解尺度,由于其目的在于提取低频近似成分,而不是通过用高频率逐渐分解细节信息来去噪,所以无需设置大尺度,文中分解尺度设置为3。
2.2 小波多尺度分析(WMA)的微地震数据分解和重构
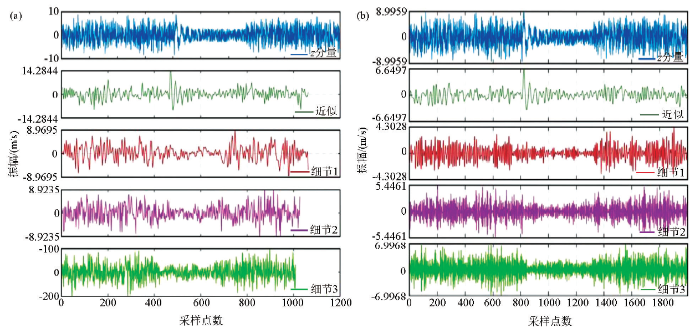
利用基于’db10’的母小波对强噪声合成微地震数据进行小波多尺度分解及重构,实现了可靠的信号分离。如图2所示,将相应的近似数据和细节信息分解,并且重构的近似数据代表低频成分,其代表了微地震数据中的有效信号。
图2
图2
使用合成微地震数据的小波多尺度分解和重构波形
a—原始数据和分解数据集;b—原始数据和重构数据集;随机噪声占80%,P波主频为100 Hz,采样间隔为0.25 ms,分解级别为3,母小波为db10
Fig.2
Wavelat multilevel decomposition and reconstruction waveforms using synthetic microseismic data
a—original data and decomposition datasets;b—original data and reconsruction datasets;random noise account for 80%,principal frequency of P-wave is 100 Hz,sample interval is 0.25 ms,decomposition level is 3,mother wavelet is the db10
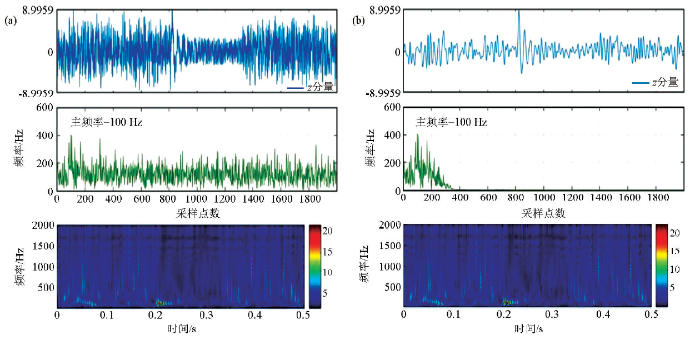
为进一步确认上述重构的有效性,进行了频谱分析和时频分析。分析图3的结果表明,信号主频在原始数据与重构近似数据之间能够保持一定的一致性,尤其是低频能量信息在时频谱上能够严格一致。因此,重构近似数据可以代替原始数据来执行初至拾取计算。
图3
图3
利用上述合成微地震数据对原始数据与重建近似数据进行时频分析比较
a—原始数据的时频分析;b—重构近似数据的时频分析
Fig.3
Time-frequency analysis comparison of original data and reconstructed approximation data using the above synthetic microseismic data
a—time-frequency analysis of the original data;b—time-frequency of the reconstructed approximation data
3 改进M-AIC拾取方法及实验结果
3.1 改进M-AIC拾取方法
文中,为提高M-AIC拾取方法的精度,首先利用小波多尺度分析(WMA)方法处理微地震数据,再对其进行初至拾取。步骤如下:
1)采用WMA方法分解和重建原始微地震记录。选择Daubechies(db10,其消失矩数为10)小波基来对微地震数据进行分解和重构,分解尺度为3。依据上述过程,相应的近似和详细信息是分开的,并提取表示主成分的相应近似信息。
2)选取M-AIC计算的数据段。
对纯信号而言,初至时刻应在信号的最大值之前。令x={x1,x2,…,xi,…,xN}表示重构后的微地震近似数据,其中i表示第i个采样点。通过式(4)很容易找到波形峰值的采样点
计算重构近似数据绝对值的最大值点作为实际计算数据段的截止点。
3)初至拾取。将M-AIC算法直接应用于所选取的微地震数据段,选择AIC序列的全局最小值为初至点。
3.2 合成三分量微地震数据的实验结果
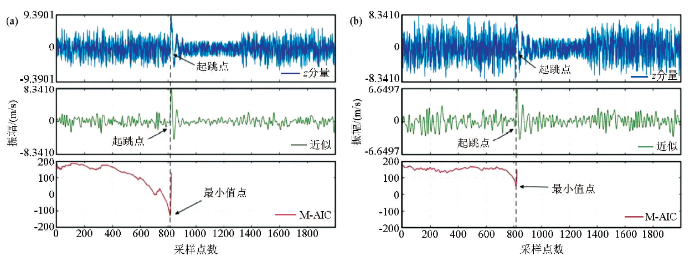
图4
图4
采用合成三分量微地震数据的改进算法的拾取实例
a—随机噪声为60%;b—随机噪声为80%;P波的主频为100 Hz,采样间隔为0.25 ms,db10小波基,分解级为3
Fig.4
Picking example of improved algorithm using synthetic 3C microseismic data
a—random noise account for 60%;b—random noise account for 80%;principal frequency of P-wave is 100 Hz,sample interval is 0.25 ms,mother wavelet is the db10,decomposition level is 3
表1 不同随机噪声下100次合成3C微地震数据的初至拾取误差统计
Table 1
| 随机噪声 | 最大误差/ms | 拾取数据误差占比/% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 误差小于等于0.25 ms | 误差小于等于0.5 ms | ||
| 60% | 0.25 | 97 | 100 |
| 80% | 0.25 | 95 | 100 |
| 90% | 0.50 | 92 | 97 |
| 100% | 0.75 | 90 | 95 |
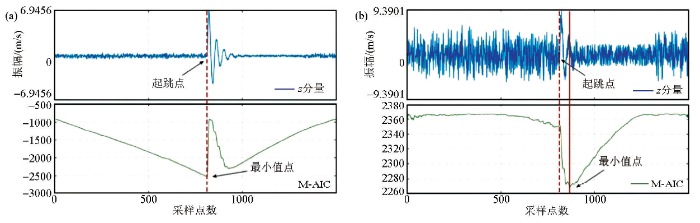
3.3 实际三分量微地震数据处理结果及对比
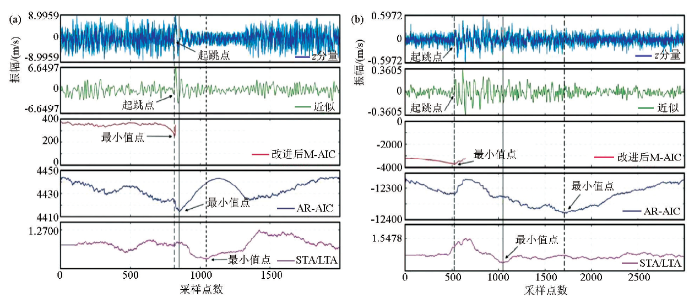
为更进一步测试改进算法的可靠性,文中采用白鹤滩水电站尾水1号隧洞岩爆监测数据,选取了其中一次信噪比较低的岩爆事件。下面将文中改进算法和其他两种算法(即STA/LTA方法和AR-AIC方法)分别应用于合成低信噪比三分量微地震数据和实际微地震监测数据,并将三种算法进行对比,其对比结果如图5所示。
图5
图5
改进M-AIC、STA/LTA和AR-AIC三种初至拾取方法的实验结果及对比
a—随机噪声为80%的合成三分量微地震数据;b—实际微地震监测数据
Fig.5
Pickup result and comparison among improved M-AIC、STA/LTA and AR-AIC algorithms
a—synthetic 3C microseismic data with 80% random noise;b—field microseismic data
从图5的结果分析可知,文中所提出的改进方法在低信噪比条件下能够准确拾取微地震事件的初至,然而,传统的STA/LTA和AR-AIC方法对强噪声微地震数据的拾取误差较大。因此,在强噪声条件下,文中改进算法具有更好的准确性和可靠性。
4 结论
文中提出了一种有效的强噪声三分量微地震数据初至拾取方法。首先,通过小波多尺度分析将微地震数据分解为近似信息(低频成分)和细节信息(高频成分)。然后,利用小波多尺度分析重构近似数据代替原始数据执行M-AIC计算,同时计算近似数据绝对值的最大值点,作为M-AIC计算时窗的约束终点。最后,选取所计算M-AIC序列的全局最小值点作为初至。文中将改进算法分别应用于合成低信噪比三分量微地震数据和实际微地震监测数据,并与STA/LTA方法和AR-AIC方法进行对比,进一步验证了所提出方法的有效性和可靠性。
参考文献
微地震信号到时自动拾取方法
[J].
DOI:10.6038/cjg20130523
URL
Magsci
[本文引用: 1]

<p>本文讨论了用于微地震信号到时自动拾取的几种方法的原理及特点,包括长短时均值比(STA/LTA)方法、AIC方法、基于高阶统计量偏斜度和峰度的PAI-S/K方法等,提出了移动时窗峰度的快速算法和改进的峰度拾取初至方法.对我国西部某地观测到的13359个微地震记录,采用两种时窗进行了初至到时拾取,并与人工拾取的结果进行了对比.为使所研究的方法达到最佳效果,采用DE全局搜索方法,以人工拾取的初至作为参照,以时差在0.3 s以内的记录所占百分比作为目标函数,自动搜索最佳的拾取参数.结果显示,在拾取时窗选为P波初至前3 s至S波初至位置时,AIC方法的结果最佳,时差在0.3 s以内的记录占比达到93.6%;在拾取时窗选为包含S波到时的时窗时,改进的峰度法效果最佳,时差在0.3 s以内的记录占比83.8%.</p>
On micro-seismic first arrival identification:A case study
[J].
Automatic Bayesian polarity determination
[J].
基于时窗能量比和AIC的两步法微震初至自动拾取
[J].
DOI:10.11720/j.issn.1000-8918.2013.2.17
URL
Magsci
[本文引用: 1]

传统的微地震数据震源定位算法依赖于波至时间的拾取。由于微地震数据量较大且信噪比较低,手动拾取纵波和横波的波至时间很耗时,且引入的人为误差不易控制。笔者在分析已有方法特点的基础上,给出一种较快捷、准确的两步法微地震初至自动拾取方法。该方法首先使用时窗能量比法识别微震事件并大致确定波至时间,然后使用局部AIC精确拾取波至时间。与常规时窗能量比法相比,该方法减弱了时窗大小对拾取精度的影响;与常规的AIC法相比,由于只在局部使用AIC,避免了在低信噪比情况下AIC会出现多个局部极小从而难以准确拾取的问题,同时也提高了拾取效率。最后通过野外实际微地震数据进行了测试,分析了该方法的性能,验证了该方法的有效性和实用性。
Automatic microseismic event detection and picking method
[J].
Accurate identification of P- and S-phase arrivals using the multi-step AIC algorithm
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.jappgeo.2018.01.007
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Identification of P- and S-phase arrivals is the primary work in Microseismic signal analysis. In this study, a new multi-step AIC algorithm is recommended. The algorithm consists of P- and S-phase arrival pickers (P-picker and S-picker). The P-picker has three steps: in step 1, a preliminary P-phase arrival window is determined by the waveform peak. Then a preliminary P-pick is identified using the AIC algorithm. Finally, the P-phase arrival window is narrowed based on the above P-pick. Thus the P-phase arrival can be identified accurately by using the AIC algorithm again. The S-picker has five steps: in step 1, a narrow S-phase arrival window is determined based on the P-pick and the AIC curve of amplitude biquadratic time-series. In step 2, the S-picker automatically judges whether the S-phase arrival is clear to identify. In step 3 and 4, the AIC extreme points are extracted, and the relationship between the local minimum and the S-phase arrival is researched. In step 5, the S-phase arrival is picked based on the maximum probability criterion. The field data tests show that the P- and S-pickers have a high picking accuracy in comparison with the manual P- and S-picks. Furthermore, the technique is independent of the kind of SNR. Even in the poor-quality signal group which the SNRs are below 5, the effective picking (the picking residual is <30 sample points) rates of P- and S-phase arrivals are still up to 81% and 84% respectively.
一种具有抗噪性的P波初至自动拾取方法
[J].The first-break picking accuracy greatly affects the seismic events discriminant and source localization.At present,none of the first-break picking algorithms proposed is ideal to collect the low SNR seismic data.In order to solve the noise problem (improve noise resistance performance),an improved first arrival picking method of micro-seismic event based on power ration and wavelet transform is proposed.Firstly,the characteristics function is introduced to the traditional energy ratio method wavelet transform method so as to search the range of the P-wave first break by adopting the improved energy ratio method.Then,the first break time of P-wave is positioned precisely by using wavelet transform.Finally,the seismic model data and actual measured seismic data are used to conduct experiment to analyze the performance of the method proposed in this paper.The results show that,the method based on energy ratio and wavelet transform is the first-break automatic picking method with the characteristics of noise resistance and stability.Besides that,it can identify the P-wave first arrival time from the data with a low signal to noise ratio accurately.
A first arrival automatic picking method of P-wave with noise resistence performance
[J].
微地震事件初至拾取SLPEA算法
[J].微地震事件初至拾取是微地震数据处理的关键步骤之一.实际微地震监测资料中存在大量低信噪比事件,而传统方法对这些事件的应用效果并不理想.为了克服传统方法抗噪性弱的缺点,本文通过综合地震信号与环境噪声在振幅、偏振以及统计特征等方面的存在的差异,设计了一种针对低信噪比微地震事件的初至拾取方法——SLPEA算法.为了检验本文方法的可行性和有效性,分别对模型数据和实际资料进行了处理,并将处理结果与传统方法及手工拾取的结果进行了对比.分析表明,利用本文方法得到的初至到时与手工拾取结果的绝对误差平均值仅为1.33×10^-3s,小于3个采样点;方差为3.21×10^-6s^2;初至到时在手工拾取结果±0.005s误差范围内的个数占总数的95.8%.这些参数值均优于传统方法的同类参数,证明了本文方法的可靠性.
Arrival picking of microseismic events using the SLPEA algorithm
[J].
基于时窗能量比与互信息量的微地震初至拾取方法
[J].
DOI:10.11720/wtyht.2016.2.23
URL
Magsci
[本文引用: 1]

<p>由于微地震事件本身能量弱、资料信噪比低的特点,初至快速精确的拾取成为其关键而又亟待解决的问题。针对微地震事件初至人工拾取效率低、时窗能量比方法拾取精度低的特点,从信息熵和互信息量的角度开始研究,根据互信息量是随机变量间统计依存性与关联程度的量度特点,研究了一种时窗能量比与互信息量准则的微地震初至拾取方法,首先以时窗能量比算法来粗略估计初至的到达时刻,然后再利用互信息量算法来准确的拾取初至,通过模型验证与实际数据的测试,并与常规方法对比分析,验证了方法的有效性与可行性,能够较为准确与快速地实现微地震初至的自动拾取。</p>
Automatic first arrival pickup method of microseismic event based on energy ratio and mutual information
[J].
低信噪比微地震P波震相初至自动拾取方法
[J].
Method of automatic detection on micro-seismic P-arrival time under low signal to noise ratio
[J].
A new first break picking for three-component VSP data using gesture sensor and polarization analysis
[J].
DOI:10.3390/s17092150
URL
PMID:5621385
[本文引用: 1]

A new first break picking for three-component (3C) vertical seismic profiling (VSP) data is proposed to improve the estimation accuracy of first arrivals, which adopts gesture detection calibration and polarization analysis based on the eigenvalue of the covariance matrix. This study aims at addressing the problem that calibration is required for VSP data using the azimuth and dip angle of geophones, due to the direction of geophones being random when applied in a borehole, which will further lead to the first break picking possibly being unreliable. Initially, a gesture-measuring module is integrated in the seismometer to rapidly obtain high-precision gesture data (including azimuth and dip angle information). Using re-rotating and re-projecting using earlier gesture data, the seismic dataset of each component will be calibrated to the direction that is consistent with the vibrator shot orientation. It will promote the reliability of the original data when making each component waveform calibrated to the same virtual reference component, and the corresponding first break will also be properly adjusted. After achieving 3C data calibration, an automatic first break picking algorithm based on the autoregressive-Akaike information criterion (AR-AIC) is adopted to evaluate the first break. Furthermore, in order to enhance the accuracy of the first break picking, the polarization attributes of 3C VSP recordings is applied to constrain the scanning segment of AR-AIC picker, which uses the maximum eigenvalue calculation of the covariance matrix. The contrast results between pre-calibration and post-calibration using field data show that it can further improve the quality of the 3C VSP waveform, which is favorable to subsequent picking. Compared to the obtained short-term average to long-term average (STA/LTA) and the AR-AIC algorithm, the proposed method, combined with polarization analysis, can significantly reduce the picking error. Applications of actual field experiments have also confirmed that the proposed method may be more suitable for the first break picking of 3C VSP. Test using synthesized 3C seismic data with low SNR indicates that the first break is picked with an error between 0.75 ms and 1.5 ms. Accordingly, the proposed method can reduce the picking error for 3C VSP data.
A method for reading and checking phase times in autoprocessing system of seismic data
[J].DOI:10.4294/zisin1948.38.3_365 URL [本文引用: 1]
利用偏振约束对最小信息准则方法自动拾取微地震初至的改进
[J].初至拾取是影响微震事件分析精度的重要因素之一。本文结合微震事件偏振特性和最小信息准则(akaike information criterion,AIC)函数特性,提出了一种利用偏振约束实现AIC初至拾取的改进方法:可以将偏振特征值拾取微震初至的应用扩展至单分量的微震数据,该方法将单分量微震数据视为三分量微震数据的一种特殊形式,利用三分量微震数据协方差矩阵的最大值序列对AIC方法进行约束,从而快速准确的拾取到微震数据的初至。文中应用该方法对不同信噪比的合成数据和实测数据进行了验证,同时与长短时平均(short time average/long time average,STA/LTA)、Maeda-AIC和偏振特征值方法进行了对比,结果显示该算法速度略低于上述3种方法,但精度和可靠性优于其他三种方法,同时与其他改进算法对比,不用设置阈值,并且选取时窗的长短对拾取结果几乎没有影响,可极大地提高算法的自动化程度。
An improved AIC method for automatic micro-seismic data arrival picking with the constraint by polarization
[J].
基于小波分解与Akaike信息准则的微地震初至拾取方法
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2011.01.002
URL
[本文引用: 1]

微地震震源的定位要求精确确定初至,人工拾取微地震有效事件需要很大的工作量。首先讨论了 Akaike信息准则(AIC)初至拾取方法;然后根据微地震信号在相邻小波尺度上连续的特点,将基于AIC的初至拾取方法与小波多尺度分析方法相结合, 对微地震资料进行多尺度分析;最后利用AIC拾取初至,并根据初至的分布特点确定地震记录中是否存在有效的微地震事件。克服了传统AIC法由于噪声影响使 初至点模糊而难以准确拾取的缺点。模型与实际资料的应用表明,基于小波分解与AIC相结合的初至拾取方法能够从信噪比低的资料中较准确地识别出有效微地震 事件。
Automatic detection method of microseismic event based on wavelet decomposition and Akaike information criteria
[J].
Hybrid seismic denoising using higher-order statistics and improved wavelet block thresholding,
重力资料多尺度分析最优小波基的选择
[J].
DOI:10.11720/wtyht.2015.5.22
URL
Magsci
[本文引用: 1]

<p>小波变换多尺度分析是重力资料处理中一种常用的方法,其分析的结果与最优小波基的选取有关。笔者结合重力数据特征,首先从理论层面上分析最优小波基的选取方法,再根据理论模型进行不同小波基的对比实验,最后对华北地区实测重力数据进行小波基对比试验,认为db11小波基为重力数据多尺度分析的最优小波基。</p>
The optimal choice of wavelet bases in gravity data multi-scale analysis
[J].
Simplified vanishing moment criteria for wavelets over general dilation groups, with applications to abelian and shearlet dilation groups
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.acha.2016.03.003
URL
[本文引用: 1]

We consider the coorbit theory associated to a square-integrable, irreducible quasi-regular representation of a semidirect product groupG=Rd . The existence of coorbit spaces for this very general setting has been recently established, together with concrete vanishing moment criteria for analyzing vectors and atoms that can be used in the coorbit scheme. These criteria depend on fairly technical assumptions on the dual action of the dilation group, and it is one of the chief purposes of this paper to considerably simplify these assumptions. We then proceed to verify the assumptions for large classes of dilation groups, in particular for all abelian dilation groups in arbitrary dimensions, as well as a class calledgeneralized shearlet dilation groups, containing and extending all known examples of shearlet dilation groups employed in dimensions two and higher. We explain how these groups can be systematically constructed from certain commutative associative algebras of the same dimension, and give a full list, up to conjugacy, of shearing groups in dimensions three and four. In the latter case, three previously unknown groups are found. As a result, the existence of Banach frames consisting of compactly supported wavelets, with simultaneous convergence in a whole range of coorbit spaces, is established for all groups involved.
Wavelet-based compressed sensing for SAR tomography of forested areas
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2012.2231081
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) tomography is a 3-D imaging modality that is commonly tackled by spectral estimation techniques. Thus, the backscattered power along the cross-range direction can be readily obtained by computing the Fourier spectrum of a stack of multibaseline measurements. In addition, recent work has addressed the tomographic inversion under the framework of compressed sensing, thereby recovering sparse cross-range profiles from a reduced set of measurements. This paper differs from previous publications, in that it focuses on sparse expansions in the wavelet domain while working with the second-order statistics of the corresponding multibaseline measurements. In this regard, we elaborate on the conditions under which this perspective is applicable to forested areas and discuss the possibility of optimizing the acquisition geometry. Finally, we compare this approach with traditional nonparametric ones and validate it by using fully polarimetric L-band data acquired by the Experimental SAR (E-SAR) sensor of the German Aerospace Center (DLR).