0 引言
利用重、磁异常识别地质体的边缘位置有很多类方法,其中有一类方法为比值类方法。如倾斜角方法(Ta)和Theta Map方法(cosθ)以及归一化标准差(NSTD)方法等。
Miller和Singh[1]首次提出了倾斜角法(Ta),该方法计算垂向导数(VDR)[2,3]与总水平导数(THDR)[4]比值的反正切值,并利用零值线位置识别地质体的边缘位置。Wijns等[5]首次提出了Theta Map(cosθ)方法,该方法利用总水平导数与解析信号振幅(ASM)[6]比值的极大值位置识别地质体的边缘位置。Cooper和Cowan[7]首次提出归一化标准差方法(NSTD),该方法计算滑动窗口内垂向一阶导数的标准差与水平方向和垂向方向一阶导数标准差总和的比值,并将该比值记为滑动窗口中心点的归一化标准差值,最后利用极大值位置识别地质体的边缘位置。王万银[8]研究认为倾斜角、Theta Map与VDR的识别结果完全相同,并且当总水平导数等于零时倾斜角存在“解析奇点”,解析信号振幅等于零时Theta Map存在“解析奇点”,这会使计算结果不稳定,但没有给出解决这一问题的方法。一些学者通过不同的导数组合构建了类似于倾斜角与Theta Map形式的比值类边缘识别方法[9,10,11,12,13,14,15],在模型试算和实际资料处理中取得了很好的识别效果,但是均没有考虑其在计算过程中分母为零或者接近零时计算的不稳定性问题。一些学者同样也构建了一些形如倾斜角和Theta Map的归一化边缘识别方法[12,14,16-17],通过在分母中引入一个常量,提高计算稳定性,该常量实质就是正则化因子,但是均没有系统的分析引入正则化因子对于原方法识别结果的影响。
边缘识别的比值类方法在分母为零或者接近零时,使计算结果不稳定,产生错误的识别边界,对于我们识别正确的边界造成干扰。本文依据正则化的思想,通过在分母加大于零的正则化因子来解决比值类方法在分母为零或者接近零时计算的不稳定性问题。正则化因子的引入同样可以提高以比值类方法为基础构建的二阶导数类边缘识别方法的计算稳定性,如倾斜角总水平导数(Ta-THDR)[27]。
1 基于正则化方法的比值类位场边缘识别方法
基于正则化方法的比值类位场边缘识别方法就是根据正则化方法的思想,在比值类边缘识别方法的分母上加入正则化因子。正则化因子取大于零的正则化调节因子α乘以相应分母的最大值,通过α来调节正则化因子的大小。
1.1 正则化倾斜角(R-Ta)
倾斜角(Ta)边缘识别方法的计算公式[1]为
其中:VDR=
其中,THDRmax是THDR的极大值。倾斜角利用零值位置识别地质体边缘,所以在分母上增加αTHDRmax不会改变倾斜角的零值点位置,即不会改变Ta的识别精度,但是能够有效的解决倾斜角边缘识别方法中分母为零或者接近零时的计算不稳定性问题。正则化因子的引入提高了Ta法的稳定性,相应也会提高以Ta为基础构建的二阶导数方法Ta-THDR法的稳定性。
1.2 正则化Theta Map(R-cosθ)
cosθ边缘识别方法的计算公式[5]为
其中,ASM=
其中,ASMmax是ASM的极大值。
由于cosθ方法是利用极大值位置识别地质体的边缘位置,加入正则化因子会改变其极值位置,因此我们需要研究cosθ和R-cosθ两种方法的极大值位置。根据求取极大值的必要条件,对cosθ求导,并令其为0得
当且仅当VDR=0时,(cosθ)'=0,即VDR的零值点位置对应cosθ的极值点位置,所以cosθ法和VDR法的识别结果相同。
同样对R-cosθ求导得
无法直接从上式判断出(R-cosθ)'=0的点,所以分两种情况对(R-cosθ)'进行讨论:
①当VDR=0时:
(R-cosθ)'=
②当THDR'=0时:
(R-cosθ)'=-
那么(R-cosθ)'=0的点位于VDR的零值点与THDR的极大值点之间,即R-cosθ的识别结果位于VDR法识别结果与THDR法识别结果之间,所以R-cosθ提高了cosθ的识别精度。
随着α增大,-
1.3 正则化归一化标准差(R-NSTD)
归一化标准差的公式为[7]:
其中:σ(fx),σ(fy),σ(fz)分别为位场数据f在x方向,y方向,z方向的一阶导数的标准差。当σ(fx)+σ(fy)+σ(fz)=0或者接近零时,
其中:(σ(fx)+σ(fy)+σ(fz))max是位场数据在x方向,y方向,z方向一阶导数的标准差和极大值。 NSTD法属于数理统计类方法,不能通过解析式来研究在分母增加正则化因子后极值位置的变化,只能通过模型试算研究其极值位置的变化。
2 模型测试
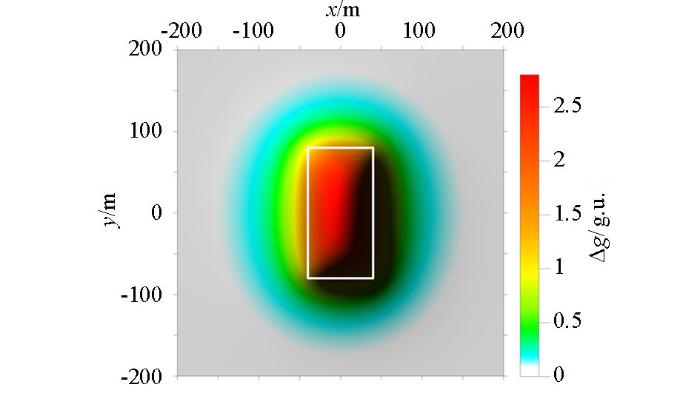
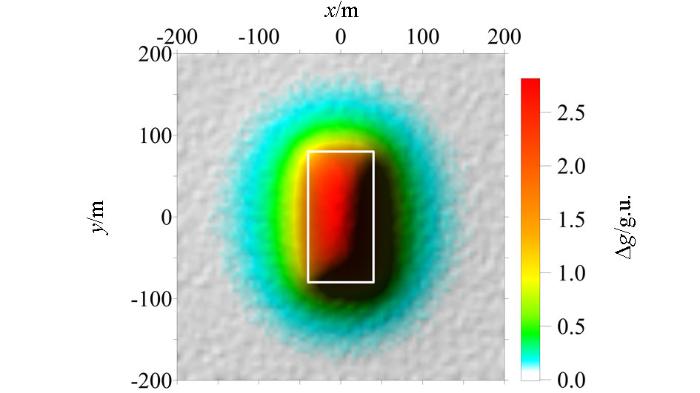
本次实验选用了4个重力异常模型和1个磁力异常模型进行模型测试,各个模型参数见表1。通过对比正则化方法识别结果与比值类方法识别结果,验证本文提出的正则化方法的有效性。所有图中白色线框均表示模型体边界投影到平面上的位置,Ta方法与R-Ta方法图中白色虚线表示识别的边界。
表1 使用模型参数说明
Table1
| 模型类别 | 形体个数 | 长/m | 宽/m | 埋深/m | 间隔/m | 模型设计目的 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模型A | 重力模型 | 1 | 160 | 80 | 10~50 | 测试比值类方法加入正则 化因子后的适用性 | |||||
| 模型B | 重力模型 | 2 | 160 | 90 | 10~50 | 20 | 测试比值类方法加入正则化 因子后,对于横向分辨率 的影响 | ||||
| 160 | 90 | 10~50 | |||||||||
| 模型C | 重力模型 | 3 | 160 | 40 | 10~50 | 90 | 测试比值类方法加入正则 化因子后,对于不同埋深地 质体边缘识别的影响 | ||||
| 160 | 40 | 25~65 | |||||||||
| 160 | 40 | 40~80 | |||||||||
| 模型D | 磁力模型 | 1 | 160 | 80 | 10~50 | 测试比值类方法加入正则化因子 后,对于磁力异常的适用性 | |||||
| 模型E | 加噪(1%) 重力模型 | 1 | 160 | 80 | 10~50 | 测试比值类方法加入正则 化因子后的稳定性 | |||||
2.1 模型A——单一直立六面体重力模型
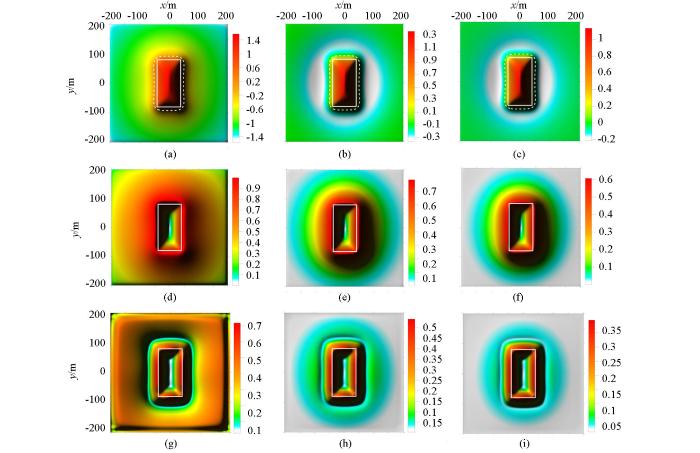
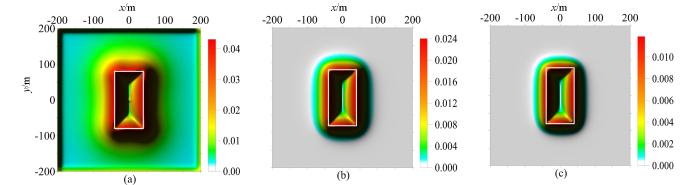
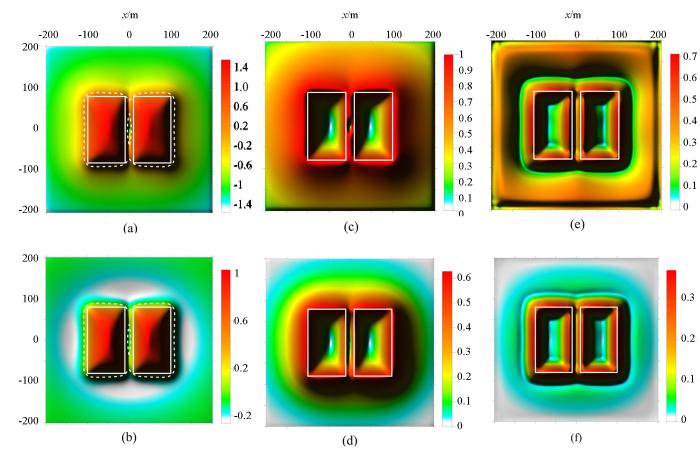
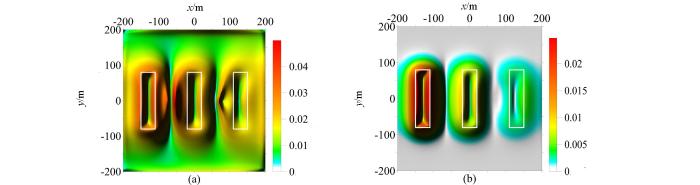
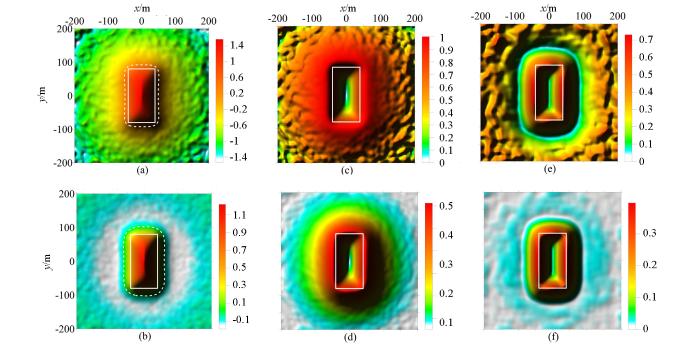
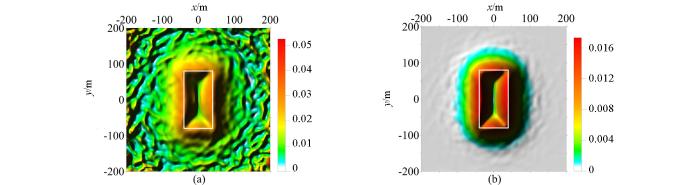
图1为模型A的重力异常图,图2为图1的比值类方法边缘识别结果图,图3为图1的倾斜角总水平导数边缘识别结果图。通过模型A的试算,可以看出常规方法(即α=0)中的Ta法(图2a)和cosθ法(图2d)识别出的边界大于真实形体的边界;NSTD法(图2g)和Ta-THDR法(图3a)识别出的边界与真实形体边界基本一致,两个方法均在测网边部产生了由假极值引起的虚假边界,NSTD法中的假极值的幅值接近形体边界对应的真实极值的幅值。加入正则化因子后,R-Ta法的零值线位置没有变化(图2b);R-cosθ法的极值位置向形体真实边界靠近(图2e);R-NSTD法(图2h)和R-Ta-THDR法(图3b)的极值位置也向形体真实边界靠近,由于NSTD法和Ta-THDR法自身识别精度很高,所以R-NSTD法和R-Ta-THDR法的极值位置的变化不是很明显;R-NSTD法中的假极值幅值变小,但假极值仍然存在,假极值位置向形体边界靠近(图2h);R-Ta-THDR法消除了Ta-THDR中的假极值(图3b)。由此可以看出,正则化因子的引入,提高了cosθ法、NSTD法、Ta-THDR法的识别精度;削弱了NSTD法产生的虚假边界;消除了Ta-THDR法中的虚假边界;没有改变Ta法的识别精度。对比α=0.2与α=0.5的识别结果可以看出,随着正则化调节因子α取值增大,R-Ta法(图2c)的识别结果不变,R-cosθ法(图2f)、R-NSTD法(2l)、R-Ta-THDR法(图3c)的识别结果越接近真实边界,R-NSTD法(图2l)的假极值的幅值会减小,但假极值不会被消除,假极值的位置也不发生变化。但是α取值过大,则会改变比值类方法的均衡特性,使深部形体对应的极值的幅值变得更小,较小的极值会使深部形体的识别边界变宽缓、模糊。因此在后续的模型试算与实际资料处理中,R-Ta法、R-cosθ法、R-NSTD法的正则化调节因子α均选择0.5;由于R-Ta-THDR属于二阶导数类方法,其计算的极值较小,所以其正则化调节因子α选择0.2。
图1
图2
图2
A模型比值类方法边缘识别结果对比
Fig.2
The ratio methods edge recognition results comparison map based on model A
a—Ta(α=0);b—R-Ta(α=0.2);c—R-Ta(α=0.5);d—cosθ(α=0);e—R-cosθ(α=0.2);f—R-cosθ(α=0.5);g—NSTD(α=0);h—R-NSTD(α=0.2);i—R-NSTD(α=0.5)
图3
图3
A模型倾斜角总水平导数边缘识别结果对比
Fig.3
The Ta-THDR method edge recognition results comparison map based on model A
a—Ta-THDR(α=0);b—R-Ta-THDR(α=0.2);c—R-Ta-THDR(α=0.5)
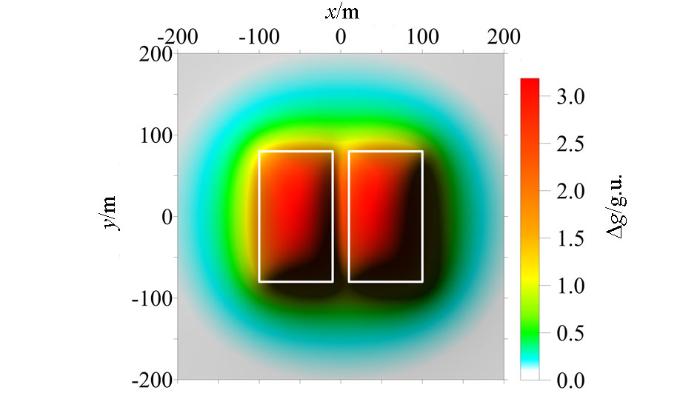
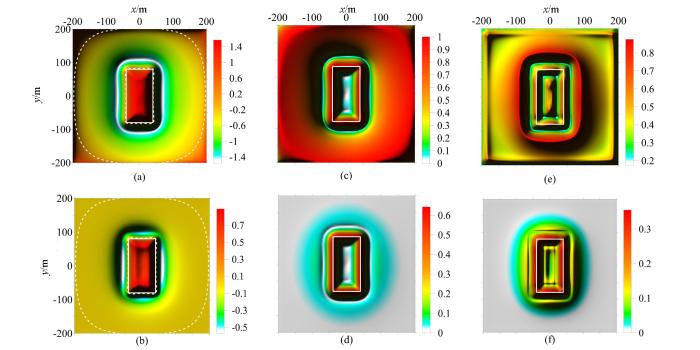
2.2 模型B——两个直立六面体组合重力模型
图4
图5
图5
B模型比值类方法边缘识别结果对比
Fig.5
The ratio methods edge recognition results comparison map based on model B
a—Ta;b—R-Ta;c—cosθ;d—R-cosθ;e—NSTD;f—R-NSTD
通过模型B的试算,可以看出Ta法(图5a)和cosθ法(图5c)识别出的相邻侧边界发生重叠,难以刻画两形体相邻边界;NSTD法(图5e)、Ta-THDR法(图6a)识别出的外侧边界均与真实形体外侧边界基本一致,识别出的内侧边界略微偏向形体内侧,两个方法都出现了由假极值引起的虚假边界,而且Ta-THDR法在相邻的形体之间产生了由计算不稳定性引起的局部突起(图6a)。加入正则化因子后,R-Ta法仍然识别不了内侧边界(图5b),R-cosθ法识别出的内侧边界与形体真实边界一致(图5d),R-NSTD法识别出的内侧边界更接近真实形体边界(图5f),R-Ta-THDR法消除了内侧边界之间的突起(图6b)。通过以上的对比研究发现,正则化因子的引入提高了R-cosθ法、NSTD法、Ta-THDR法的水平分辨率,但没有改变Ta法的水平分辨率。
图6
图6
B模型倾斜角总水平导数边缘识别结果对比
Fig.6
The Ta-THDR method edge recognition results comparison map based on model B
a—Ta-THDR;b—R-Ta-THDR
2.3 模型C——三个直立六面体组合重力模型
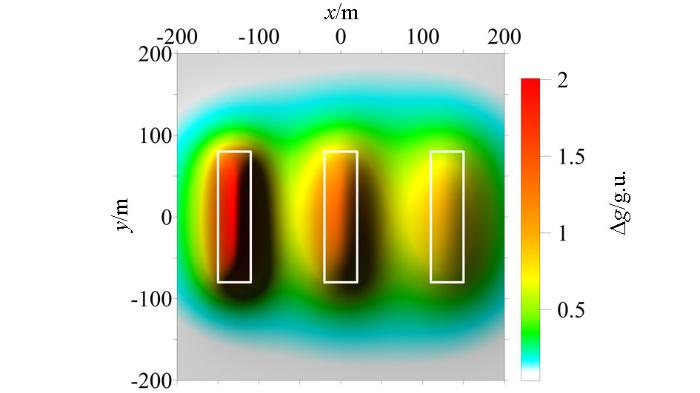
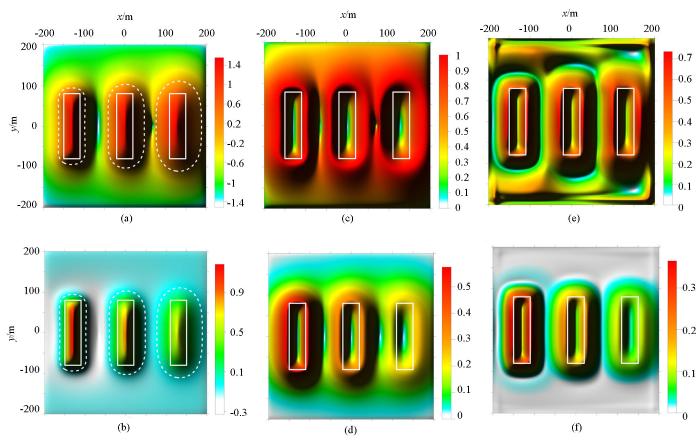
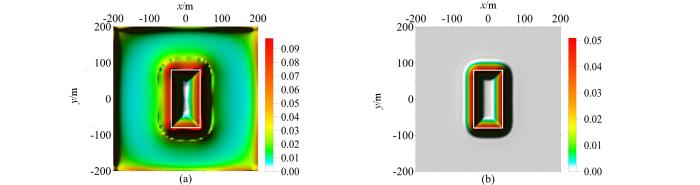
通过模型C的试算可以看出,随着形体埋深的增大,Ta法(图8a)、cosθ法(图8c)、NSTD法(图8e)、Ta-THDR法(9a)识别的边界逐渐外扩,距离真实形体的边界越来越远。NSTD法产生了假极值引起的虚假边界(图8e),Ta-THDR法在相邻的形体之间产生了由计算不稳定性引起的局部突起,并在测网边部存在虚假边界(图9a)。加入正则化因子后,没有改变R-Ta法对深部形体的识别能力;R-cosθ法(图8b)、R-NSTD法(图8f)、R-Ta-THDR法(图9b)识别出的深部形体边界与真实深部形体边界基本一致,但是识别的边界变得宽缓、模糊,这主要是因为正则化因子的引入改变了比值类方法的均衡特性,使深部形体对应极值的幅值变得更小。由此可以看出,正则化因子的引入,提高了cosθ法、NSTD法、Ta-THDR法对于深部形体的识别能力。
2.4 模型D——单一直立六面体磁力模型
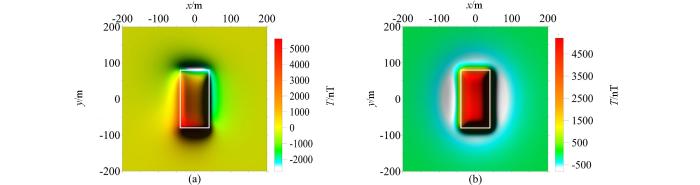
模型D 为磁力模型。所有比值类位场边缘识别方法均受到磁化方向和磁力异常分量方向影响,所以基于比值类方法改进的正则化边缘识别方法也受磁化方向和磁力异常分量方向的影响。使用磁力异常进行边缘识别时,需要将磁异常转换为伪重力异常或者化极磁异常。图10a和图10b分别是该模型体磁力异常和化极磁力异常。图11为模型D采用比值类方法对其化极磁力异常进行边缘识别的结果图。图12为模型D的倾斜角总水平导数边缘识别结果图。通过模型D的试算可以看出磁力异常的Ta法(图11a)、cosθ法(图11c)、NSTD法(图11e)、Ta-THDR法(图12a)的识别结果都存在严重的虚假边界的影响,这是因为磁力异常值有正有负。其中,cosθ法产生的假极值的幅值与真实极值基本接近(图11c),NSTD法产生的假极值的幅值大于真实极值的幅值(图11e)。加入正则化因子后,R-Ta法识别边界没有变化(图11b);R-cosθ法(图11d)、R-NSTD法(图11f)仍然存在假极值,但是假极值幅值变小,假极值位置向形体边界靠近;R-Ta-THDR法消除了假极值引起的虚假边界(图12b)。由此可以看出,正则化因子的引入,削弱了cosθ法、NSTD法产生的虚假边界,消除了Ta-THDR法的虚假边界,没有改变Ta法的识别结果。
图7
图8
图8
C模型比值类方法边缘识别结果对比
Fig.8
The ratio methods edge recognition results comparison map based on model C
a—Ta;b—R-Ta;c—cosθ;d—R-cosθ;e—NSTD;f—R-NSTD
图9
图9
C模型倾斜角总水平导数边缘识别结果对比
Fig.9
The Ta-THDR method edge recognition results comparison map based on model C
a—Ta-THDR;b—R-Ta-THDR
图10
图10
模型D磁力异常图与化极磁异常a—原始磁力异常;b—化极磁力异常
Fig.10
Magnetic anomaly and RTP magnetic anomaly map
a—magnetic anomaly map;b—RTP magnetic anomaly map
图11
图11
D模型比值类方法边缘识别结果对比
Fig.11
The ratio methods edge recognition results comparison map based on model D
a—Ta;b—R-Ta;c—cosθ;d—R-cosθ;e—NSTD;f—R-NSTD
图12
图12
D模型倾斜角总水平导数边缘识别结果对比
Fig.12
The Ta-THDR method edge recognition results comparison map based on model D
a—Ta-THDR;b—R-Ta-THDR
2.5 单一直立六面体加噪重力模型
图13
图14
图14
E模型比值类方法边缘识别结果对比
Fig.14
The ratio methods edge recognition results comparison map based on model E
a—Ta;b—R-Ta;c—cosθ;d—R-cosθ;e—NSTD;f—R-NSTD
图15
图15
E模型倾斜角总水平导数边缘识别结果对比
Fig.15
The Ta-THDR method edge recognition results comparison map based on model E
a—Ta-THDR;b—R-Ta-THDR
3 实际资料处理
图16
图17
图17
实测重力异常比值类方法边缘识别结果对比
Fig.17
The ratio methods edge recognition results comparison map based on real dataa—Ta;b—R-Ta;c—cosθ;d—R-cosθ;e—NSTD;f—R-NSTD
图18
图18
实测重力异常倾斜角总水平导数边缘识别结果对比
Fig.18
The Ta-THDR method edge recognition results comparison map based on real dataa—Ta-THDR;b—R-Ta-THDR
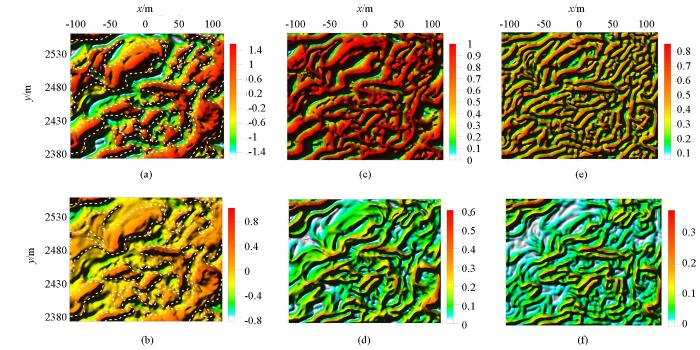
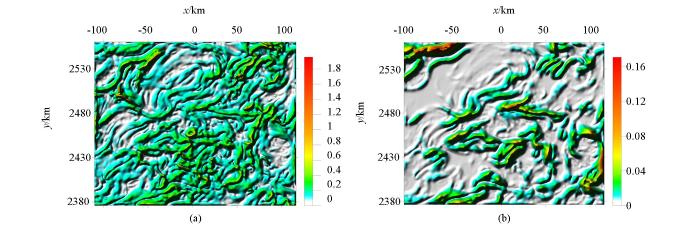
通过实际资料的处理可以看出,cosθ法(图17c)、NSTD法(图17e)和Ta-THDR法(图18a)产生由假极值引起的虚假边界,尤其NSTD法产生的虚假边界的影响最为严重,不能识别出地质体的真实边界(图17e)。加入正则化因子后,R-Ta法识别出的边界位置没有改变(图17b),R-cosθ法(图17d)、R-NSTD法(图17f)产生的虚假边界被削弱了,R-Ta-THDR消除了虚假边界,但同时也消除了一些细节信息(图18b)。实际资料的处理结果表明基于正则化方法的比值类位场边缘识别技术对于地质体边缘有较好的识别效果。水平分辨率从高到低依次是R-Ta-THDR、R-cosθ、R-NSTD、R-Ta。
4 结论
基于正则化的比值类位场边缘识别方法通过加入正则化因子,提高了比值类方法计算的稳定性,削弱了比值类方法受虚假边界的影响;同样提高了以比值类方法为基础构建的二阶导数方法的计算稳定性,如消除了Ta-THDR法虚假边界的影响。
本文通过理论推导证明了在比值类边缘识别方法中引入正则化因子没有改变Ta法的识别精度,但是提高了cosθ法的识别精度;通过模型试算发现在比值类边缘识别方法中引入正则化因子,提高了cosθ法、NSTD法、Ta-THDR法的识别精度、水平分辨率和对深部地质体的边界识别能力,降低了Ta法、cosθ法、NSTD法、Ta-THDR法受噪声干扰的影响;通过实际资料处理发现,正则化因子的引入,明显改善了cosθ、NSTD法、Ta-THDR的地质体边缘识别效果。
正则化边缘识别方法可以直接使用于重力异常,在使用于磁力异常时,由于受磁化方向和磁力异常分量方向影响,所以要将磁力异常转换为化极磁力异常或者伪重力异常,然后进行边缘识别。
参考文献
Potential field tilt-a new concept for location of potential field sources
[J].
DOI:10.1016/0926-9851(94)90022-1
URL
[本文引用: 2]

In this paper we expand on a new concept for potential field processing and interpretation, the potential field tilt, which we introduced in an earlier paper. The tilt angle is defined in terms of the ratio of the first vertical derivative of the potential field to the horizontal gradient of the field. This measure has the property of being positive over a source and negative elsewhere. The tilt angle is compared with other edge detection measures such as the horizontal gradient, the second vertical derivative and the analytic signal and found to have the added advantage of responding well to both shallow and deep sources. A map of the tilt angle is provided to illustrate its use in recognizing the horizontal location and extent of sources.
Gradient measures in ground magnetic prospecting
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.1439592
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Abstract The development of electronic magnetometers, i.e., the proton-precession and fluxgate instruments, for use in ground magnetic surveys has permitted the measurement of the first-vertical derivative of the total field, or of the vertical component of that field, with negligible addition to the total cost of the survey. The gain in information is, however, significant. Curves for the vertical gradient over a vertical contact, point pole, and finite dipole are presented. The vertical contact is outlined by the zero contour for the vertical gradient of the vertical component, and the depth of burial is half the horizontal distance between the positive and negative maxima. The depth of burial of the point pole and finite dipole is approximately equal to the horizontal distance between the negative half-maximum points on the vertical-gradient curves.
Two-dimensional harmonic analysis as a tool for magnetic interpretation
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.1439658
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Abstract The total magnetic field values over an area can be represented exactly by a double Fourier series expansion. In this analysis, such an expansion is used to evaluate very accurately the fields continued downward and upward from the plane of observation and the vertical derivatives of the total field. This harmonic expansion of the anomalous total field makes it possible to calculate, with exceptional accuracy, the field reduced to the magnetic pole and its second derivative. The results of the calculations are free from the effect of the inclination of the earth's main geomagnetic field and that of the polarization vector, at all magnetic latitudes and for all possible directions of polarization. In order to determine the influence of remanence on the above field, a number of anomalies caused by rectangular block-type bodies with known polarization are reduced to the magnetic pole, correcting only for the obliquity of the earth's normal field. It is concluded from a study of these anomalies that the interpretation of magnetic data based on the assumption of rock magnetization due solely to induction in the earth's field may yield erroneous results, particularly when remanence is important.
Gravimetric expression of graben faulting in Santa Fe Country and the Espanola Basin, New Mexico
[C]//
Theta map: Edge detection in magnetic data
[J].DOI:10.1190/1.1988184 URL [本文引用: 2]
The analytic signal of two-dimensional magnetic bodies with polygonal cross-section: its properties and use for automated anomaly interpretation
[J].DOI:10.1190/1.1440276 URL [本文引用: 1]
Edge enhancement of potential-field data using normalized statistics
[J].DOI:10.1190/1.2837309 URL [本文引用: 2]
位场边缘识别技术研究
[D].
The research on the edge recognition methods and techniques for potential field
[D].
Enhancing potential field data using filters based on the local phase
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.cageo.2006.02.016
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Measures of the local phase of potential fields can be a useful aid to their interpretation. There are several variations in use, such as the tilt angle, tilt derivative and the Theta map. This paper compares the results of these filters, and introduces some new phase-based filters which show improved performance as edge detectors in different ways. The filters are demonstrated on synthetic gravity data and on magnetic data from Australia. Source code in Matlab format is available from the server at: www.iamg.org.
改进的均衡滤波器在位场数据边界识别中的应用
[J].
DOI:10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.12.040
URL
Magsci
[本文引用: 1]

<p>边界识别是进行位场数据解释时一项必不可少的任务.现有的边界识别滤波器存在识别边界发散和深部地质体边界模糊的缺点.本文提出增强型均衡滤波器,可有效地改善上述缺点.该滤波器是利用不同阶导数之间的组合来进行地质体边界的识别,并在运算中引入一种计算高阶垂直导数的稳定算法.通过理论模型试验证明增强型均衡滤波器能使浅部与深部地质体的边界同时清晰地显示,且相对于其它边界识别滤波器能更加准确和清晰地识别出地质体的边界.最后将增强型均衡滤波器应用于实测位场数据的解释,根据其识别结果可容易地划分出断裂的水平位置及不同地层之间的界线,并能发现更多的细节信息.</p>
Application of improved balancing filters to edge identification of potential field data
[J].
扩展的倾斜角与倾斜角总水平导数
[J].
DOI:10.6038/pg20130340
Magsci
[本文引用: 1]

为了突出显示重磁场中地质体分布、断裂构造特征等信息,使图像显示错落有序、层次分明、清楚直观,有利于解释人员从不同角度认识重磁场异常特征.本文通过分析倾斜角概念,根据反余切函数特性,提出了扩展的倾斜角(iTdr)和倾斜角总水平导数(iTdr_Thdr)方法,来增强重磁异常信息,突出异常形状特点,以便于识别重磁异常中地质体边界和提取地质体分布、断裂构造平面展布特征等信息.理论模型和实际资料对比分析表明该方法简单、实用、具有较好的识别效果和较高的分辨能力,能够获取丰富的地质信息,对识别地质体边界、划分大地构造单元、确定断裂带和地质构造走向等具有实际意义.
Extended tilt angle and total horizontal derivatives
[J].
Reply to a discussion about the “Hyperbolic tilt angle method” by Zhou et al
[J]
DOI:10.1016/j.cageo.2012.11.007
URL
[本文引用: 2]

Abstract A two-dimensional mountainous mass flow dynamic procedure solver (Massflow-2D) using the MacCormack-TVD finite difference scheme is proposed. The solver is implemented in Matlab on structured meshes with variable computational domain. To verify the model, ...
位场边缘识别的新方法—增强型水平导数法
[J].
DOI:10.6038/pg20130145
URL
[本文引用: 1]

边界识别是位场数据解释的一项基本任务.现有边界识别方法大多是 基于水平与垂直导数的高通滤波器,但垂直导数的计算会明显地增大噪声的干扰.为了改善这一问题,本文提出了一种新的边界识别滤波器,该方法是利用不同阶水 平导数之间的线性组合来进行地质体边界的识别,由于该方法不需要垂直导数参与计算,因此其输出结果较稳定.理论模型试验表明,该方法能够更加清晰的识别地 质体的边界,且与其真实边界相吻合.最后将其应用于实际数据的处理中,其结果清晰地反映出断裂的位置及构造之间的界线,并能识别出更多的细节信息.
New edge detection method of potential field data-enhanced horizontal derivative method
[J].
Optimised edge detection filters in the interpretation of potential field data
[J].
DOI:10.1071/EG13059
URL
[本文引用: 2]

Many of the existing balanced edge detection filters of potential field data only use the feature that the vertical derivative is zero above the source edges to recognise the source edges. This will produce spurious edges in the interpretation of potential field data. In order to solve this disadvantage, a new format of the edge detection filter is presented, which produces maximum values only when the horizontal derivative is a maximum and the vertical derivative is zero, so the new filters will not produce spurious edges, and will provide more accurate results. The proposed filters are tested on synthetic potential field data. The recognised edges are shown to be consistent with the true edges, and do not produce additional edges. Moreover, the proposed filter suppresses the effect of noise, and displays the edges more clearly compared to previous edge detection filters. It is also applied to real magnetic data to obtain the horizontal locations of iron ore.
应用加强解析信号倾斜角进行位场数据的边界检测
[J].边界检测在地球物理位场数据解释中占有重要位置.现有的传统边界识别方法有的不能同时显示不同振幅的异常边界,有的虽然能均衡不同振幅的异常,但识别出来的边界信息中含有一些额外的错误的边界信息,尤其是当测量的异常中同时含有正异常和负异常时.目前已有的去除额外错误边界信息的方法存在着一定的人为主观性.为了解决这些问题,本文定义了加强解析信号倾斜角来进行地质体边界识别.通过模型试验证明了该方法不仅能同时清晰地识别深部和浅部地质体的边界,而且能有效地避免引入一些错误边界信息.最后将该方法应用到四川盆地的重力异常数据中,并取得了良好边界结果.
Edge detection of potential field data using an enhanced analytic signal tilt angle
[J].
Edge detection of potential field data with improved structure tensor methods
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.jappgeo.2014.06.013
[本文引用: 1]

61A newly technique was presented to balance the edges.61The new method can balance the amplitude well and get a higher resolution.61A parameter p can avoid bring false edges and reduce the noise effect.
利用加强水平方向总水平导数对位场全张量数据进行边界识别
[J].
DOI:10.6038/cjg20150730
URL
[本文引用: 1]

位场全张量梯度数据以其信息量大、含有更高频的信号成分,能更好地描述小的异常特征等优点在地球物理领域中得到广泛应用.边界检测是位场解释中不可缺少的任务,需要新的边界探测器来处理位场梯度张量数据.为了充分利用位场梯度张量数据的多信息成分,本文定义了方向总水平导数和加强方向总水平导数,并利用其定义新的边界检测器.为了能同时显示不同振幅大小异常的边界,本文对其进行了归一化处理.通过模型试验,证明了归一化方法能更加清晰准确地显示浅部和深部的地质体边界信息.最后将该边界检测方法用于加拿大圣乔治湾实际测得全张量重力梯度数据和中国朱日和地区的磁异常数据中,并得到了较好的边界检测结果.
Using of the regularization method in non-linear problems
[J].
DOI:10.1016/0041-5553(65)90150-3
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Abstract — Rinsing experiments with mouthwashes containing zinc ions, hexetidine and a combination of hexetidine and zinc ions were performed with a group of 10 vohmtcers. The amount of plaque was assessed after rinsing with the test solutions for 4 days during which mechanical toothcleaning was discontinued. Significantly improved inhibition was observed by the combination of hexetidine and zinc ions compared with the two agents used separately. In vitro bacteriaal tests showed that hexetidine and zinc ions had a synergistic inhibitory effect on the growth of Streptococcus mutans.
Regularized derivatives of potential and their role in semi-automated interpretation methods
[J].
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2478.2008.00780.x
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Evaluation of higher derivatives (gradients) of potential fields plays an important role in geophysical interpretation (qualitative and/or quantitative), as has been demonstrated in many approaches and methods. On the other hand, numerical evaluation of higher derivatives is an unstable process it has the tendency to enlarge the noise content in the original data (to degrade the signal-to-noise ratio). One way to stabilize higher derivative evaluation is the utilization of the Tikhonov regularization. In the submitted contribution we present the derivation of the regularized derivative filter in the Fourier domain as a minimization task by means of using the classical calculus of variations. A very important part of the presented approach is the selection of the optimum regularization parameter we are using the analysis of the C-norm function (constructed from the difference between two adjacent solutions, obtained for different values of regularization parameter). We show the influence of regularized derivatives on the properties of the classical 3D Euler deconvolution algorithm and apply it to high-sensitivity magnetometry data obtained from an unexploded ordnance detection survey. The solution obtained with regularized derivatives gives better focused depth-estimates, which are closer to the real position of sources (verified by excavation of unexploded projectiles).
位场各阶垂向导数换算的新正则化方法
[J].
DOI:10.6038/cjg20150426
URL
Magsci
[本文引用: 1]

<p>位场垂向导数大量应用于位场数据处理与解释中.当前广泛采用的位场各阶垂向导数换算方法为基于Laplace方程并结合波数域和空间域方法的具有递推特性的ISVD(integrated second vertical derivative)算法.本文在位场垂向导数换算的正则化方法和径向平均功率谱的基础上,提出一种位场各阶垂向导数换算的新正则化方法.新正则化方法仅需通过分析位场径向平均功率谱来确定一个截止波数,即可稳定换算位场各阶垂向导数.理论模型和实测数据实验结果表明:(1)新正则化方法物理意义明确、计算简单,且各阶垂向导数换算的稳定性和精度明显优于ISVD算法;(2)在用新正则化方法求得各阶垂向导数的基础上,利用泰勒级数法可以获得大深度、高精度的位场向下延拓结果.</p>
An adaptive iteration method for downward continuation of potential-field data from a horizontal plane:
场位解析延拓的稳定化算法
[J].本文讨论场位解析延拓的稳定化算法。首先叙述问题的古典提法,并且为以后作准备,将它化成另一类不适定问题。接着建立问题解的连续依赖性估计。然后根据这个估计式,将问题化成求解一个条件变分问题。最后利用正则化方法解这个变分问题,得到问题解的一个稳定化的计算公式。
Stabilization algorithm for analytical continuation of potential field
[J].
位场向下延拓的正则化方法
[J].The four frequency response formulas of rcgularization methods for downward continuation of potential fields are discussed and their characteristics are analyzed. These methods can effectively restrict the oscillations due to the measuring errors or the high frequency disturbances. The trend of downward continuation is stable. The results of various trials are given.
Regularization method for downward continuation of potential field
[J].
A stable downward continuation of airborne magnetic data: A case study for mineral prospectivity mapping in Central Iran
[J].
Enhancemant of magnetic data by stable downward continuation for UXO application
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2012.2220146
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The magnetic method has been proven to be a successful geophysical tool for the detection of unexploded ordnance (UXO). Aeromagnetic surveys are advantageous since they can acquire data over large areas. The downside is that magnetic anomalies due to multiple metallic targets can overlap significantly due to flight height restrictions. Such overlap combined with the acquisition noise may significantly decrease the signal-to-noise ratio of data. These adverse effects can mask the true level of contamination at a site during the initial assessment based on the magnetic method as well as decrease the overall effectiveness of discrimination during the active clearance stage. We propose a method to ameliorate these difficulties using stable downward continuation, which reconstructs the field at a lower observation height from the observed data. The stable algorithm formulates the downward continuation as an inverse problem and incorporates the expected power spectrum of UXO anomalies. The power spectrum preserves the spectral properties and subdues the amplification of high-frequency noise. Synthetic and field examples show that the algorithm can reliably reconstruct the magnetic anomaly at the ground surface within the limitation imposed by the noise. The reconstructed field exhibits significant enhancement compared to the original data.
迭代Tikhonov正则化位场向下延拓方法及其在尕林铁矿的应用
[J].
DOI:10.11720/wtyht.2015.4.14
URL
Magsci
[本文引用: 1]

<p>解析延拓是一种广泛应用的位场处理方法,向下延拓可以压制深部地质体的影响,突出浅部异常。但是,向下延拓滤波因子是一个高通滤波器,会造成下延结果震荡,从而限制了该方法在实际资料中的应用。文中详细介绍并实现了迭代Tikhonov正则化向下延拓方法,在理论模型上将该方法与传统频率域延拓方法进行对比,表明迭代Tikhonov正则化向下延拓方法的有效性;并将该方法应用于青海尕林格铁矿区磁测资料的处理解释中,下延结果与钻探情况相符,说明在厚覆盖层的勘查区中,运用迭代Tikhonov正则化向下延拓方法能够有效地提高资料处理解释的效果。</p>
The iterative regularization method for downward continuation of potential fields and its application to the Galinge iron deposit
[J].
The meter reader-New insights into magnetic derivatives for structural mapping
[J].DOI:10.1190/1.1651454 URL [本文引用: 1]
位场边缘识别方法研究进展
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.01.027
URL
Magsci

<FONT face=Verdana>研究地质体的边缘位置是重、磁位场数据解释永恒的主题,也是其优势.最近几年,国内外利用重、磁位场进行地质体边缘识别研究的文章明显增多,但没有作者系统整理和对比各方法的优点和缺点,给使用者带来诸多不便.本文首先将现有重、磁位场边缘识别方法分为数理统计、数值计算和其他三大类,并概述了各类方法的研究现状;之后较详细总结了数值计算类中垂向导数、总水平导数、解析信号振幅、倾斜角、<EM>θ</EM>图这5种基本的边缘识别方法以及在这些基本方法之上发展起来的诸如倾斜角总水平导数、增强解析信号振幅等方法的研究历史和应用效果;并用理论模型对比了几种主要边缘识别方法的识别效果.通过以上总结、对比和分析,指出了重、磁位场边缘识别方法使用中需要注意的问题以及将来的研究重点及发展方向.</FONT>
Some advances in the edge recognition of the potential field
[J].
Step-edge detection filters for the Interpretation of potential field data
[J].
DOI:10.1007/s00024-015-1053-6
URL

Edge detection is a useful tool in the interpretation of potential field data, and the existing edge detection filters are almost functions of first-order horizontal and vertical derivatives. We propose step-edge detection filters to improve the resolution of edge detection results, which use the functions of different-order derivatives to accomplish the edge detection task. We demonstrate the proposed filters on synthetic potential field data, and the results show that the new methods can recognize the edges of the sources more precisely and clearly. We also discuss the application effect of different step-edge detection filters. Lastly, we apply the proposed filters to real potential field data, and the recognized edges of the stratigraphic markers are more precise and clear.
Edge detection of potential field data using improved local phase filter
[J].
DOI:10.1071/EG12022
URL

Edge detection is a requisite task in the interpretation of potential field data. There are many high-pass filters based on horizontal and vertical derivatives in use, such as total horizontal derivative, tilt angle, theta map, et al. In this paper, we present a new edge detection filter, which uses the combination of the different order horizontal derivatives to delineate the edges of the sources, called improved local phase (ILP) filter. The new filter is computationally stable, as it does not need the computation of the vertical derivatives of potential field data. The new filter is tested on synthetic and real potential field data. The resolving power of the ILP filter is tested by comparing the results with those obtained by the other filters. The advantage of the ILP filter in the edge detection of potential field data is due to the fact that it can display the edges of the causative sources more precisely and clearly, and can bring out more subtle details.
基于三维构造张量的位场边界识别滤波器
[J].地质体构造边界位置的确定是位场数据解释中的一项重要工作,现有很多基于位场梯度张量数据的边界检测滤波器,但存在识别边界位置模糊且无法均衡深浅地质体异常的缺点.本文定义了位场数据的三维构造张量,并提出基于位场构造张量的边界滤波器.为了同时显示不同振幅异常的边界位置,对新定义的滤波器进行归一化处理.在高阶均衡滤波器的计算中需要计算位场的垂向高阶导数,本文引入一种计算的稳定算法,基于拉普拉斯方程利用位场水平导数求解垂向导数,可减小垂向导数计算中产生的误差.将定义的滤波器应用到合成的重磁数据中证明了新方法相比传统的滤波器能更加清晰、准确地圈定边界位置,而且针对同时含有正负异常的地质情况,可避免产生额外的错误边界.最后将新的滤波器应用到实测的重磁数据的解释中,结果显示基于构造张量的滤波器可更准确清晰地划分出断裂的边界位置,发现更多的构造细节.
Construction of potential Field Boundary recognition filter based on three-dimensional Construction of Zhang Liang
[J].
应用加强解析信号倾斜角进行位场数据的边界检测
[J].边界检测在地球物理位场数据解释中占有重要位置.现有的传统边界识别方法有的不能同时显示不同振幅的异常边界,有的虽然能均衡不同振幅的异常,但识别出来的边界信息中含有一些额外的错误的边界信息,尤其是当测量的异常中同时含有正异常和负异常时.目前已有的去除额外错误边界信息的方法存在着一定的人为主观性.为了解决这些问题,本文定义了加强解析信号倾斜角来进行地质体边界识别.通过模型试验证明了该方法不仅能同时清晰地识别深部和浅部地质体的边界,而且能有效地避免引入一些错误边界信息.最后将该方法应用到四川盆地的重力异常数据中,并取得了良好边界结果.
Boundary Detection of potential Field data by strengthening the inclination Angle of Analytic signal
[J].
位场数据解释的Theta-Depth法
[J].Theta图是利用位场(重磁)数据识别边界的常用方法,其表达式为重磁异常水平变化与垂直变化的比值函数.该方法计算浅源地质体边界的效果较好,而由于深源位场数据在换算过程中会产生趋同效应,在深源地质体识别应用中计算结果不准确,为此,本文提出Theta-Depth法并进行地质体埋深的计算.首先给出直接利用Theta图像进行场源体深度估算的方法,然后推导出基于Theta导数的线性方程来自动估算场源位置参数,本文方法可有效地利用Theta图像的特征为约束条件来提高反演结果的精度.理论模型试验证明本文提出的Theta-Depth法能有效地计算出场源体位置和深度.将该方法应用于满都拉地区实测磁数据的解释,帮助圈定了矿脉的分布.
Theta-Depth method for potential Field data interpretation
[J].