0 引言
随着页岩油气勘探在四川盆地取得重大突破,近两年页岩作为储层成为国内非常规勘探领域研究的热点。作为一种典型的具有垂向对称轴的横向同性介质(vertically transverse isotropy,简称VTI介质),焦石坝地区五峰组—龙马溪组底部富含有机质页岩具有较强的各向异性,如果将页岩储层岩石当作各向同性体来对待是显然不符合实际情况的[5]。对于存在明显层理的页岩,在进行页岩储层评价时只有考虑其各向异性的影响,才能准确地评价页岩岩石力学性质,提高页岩储层预测精度,为有利勘探目标的优选提供更可靠的依据。本次研究首先利用JY1井岩石力学三轴压缩试验数据计算得到富含有机质页岩的各向异性参数,并将其与常用的几个各向异性经验公式计算结果进行了对比;在获得页岩的各向异性参数后,分别探讨了各向异性对页岩地层速度、力学性质以及AVO响应的影响。
1 研究区概况
图1
2 各向异性参数的计算
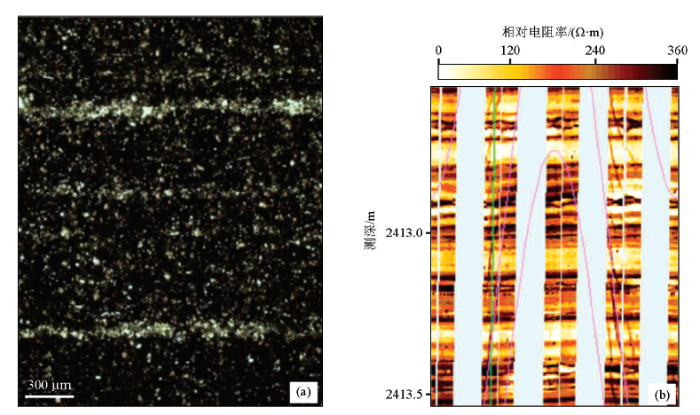
对于焦石坝地区页岩来讲,在岩心薄片照片及地层微电阻率扫描成像测井结果上可见灰黑色硅质泥岩内部发育大量水平层理,这种特质使页岩成为典型的VTI介质(图2),具有较强的各向异性,造成弹性波在垂直水平层理方向和平行层理方向传播时通常会有较大的速度差异。目前通常采用Thomsen三参数(如式(1)所示,ε表示纵波各向异性大小、γ表示横波各向异性大小、δ表示纵向与横向之间的各向异性变化快慢程度)来表现岩石各向异性的大小[7],获得VTI介质Thomsen三参数的方法主要包括两种:①静态测试法,即采用应力—应变方法测得柔度张量矩阵S,计算S矩阵的逆得到刚度矩阵C,然后利用式(1)计算各向异性参数[8];②动态测试法,即测试与对称轴夹角为0°、90°两个方向上岩样的纵、横波速度VP(0°)、VP(90°)、VSV(0°)、VSV(90°)、VSH(0°)、VSH(90°),以及与对称轴夹角为45°方向上的纵波速度VP(45°),并进一步计算样品的刚度矩阵C,再利用式(1)计算各向异性参数[9]:
图2
图2
JY1井页岩岩心薄片(a)及地层微电阻率扫描成像结果(b)
Fig.2
Thin section (a) and FMI image (b) of shale reservoir for JY1
式中,Cij为弹性刚度张量;i,j=1,2,3,4,5,6。
在利用静态测试法和动态测试法获得大量的页岩各向异性参数数据后,一些学者在有关页岩各向异性研究中总结出各向异性参数与石英含量、黏土含量、有机质含量之间的经验公式。例如Ryan-Grigor在1997年利用71个页岩样品统计出Thomsen参数与纵横波速度比之间的关系[10]。Li等2006年通过对Toasya、Han、Castagna等人的测试数据进行分析发现可以利用黏土矿物含量、地层水纵波速度、黏土纵波速度、黏土横波速度、石英纵波速度和石英横波速度来计算各向异性参数ε、δ;其中,由于地层水纵波速度、黏土和石英矿物的纵、横波速度基本保持不变,因此各向异性参数主要受黏土矿物含量影响;此外,他们还进一步给出δ与ε的线性统计关系式(式2a)[11]。2012年,Sone在其博士论文中针对Li的研究成果进行了简化,直接给出了ε、γ与黏土矿物含量的线性公式,并进一步给出了基于速度的各向异性参数拟合公式[12]。2012年,Sayers利用Abousleiman和Ortega等的页岩测试数据总结发现了ε、γ、δ与黏土含量、石英含量、有机质含量的关系式[13]。2014年,Deng等利用长宁、习水、黔江地区五峰—龙马溪组页岩数据统计得出ε、γ与黏土含量(X衍射分析获得,介于6.5%~51.9%,平均值为28.5%)的指数关系式[14]:
式中:Vclay为黏土含量,单位为%。
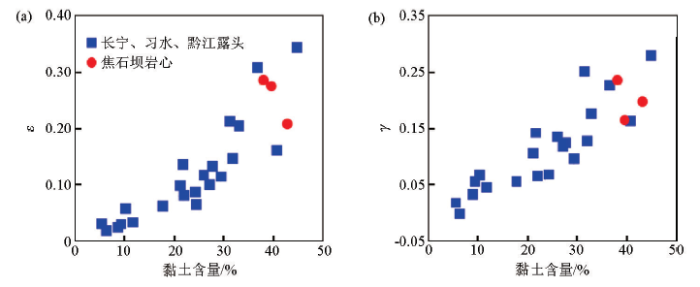
这类经验关系式尽管因为页岩样品源自不同区域而呈现出一定差异(表1),但是各向异性受黏土含量影响大这一现象是类似的;即使Ryan-Grigor等人所建立的是各向异性参数与纵横波速度的关系式,但是背后所隐含的是黏土矿物纵横波速度比与石英矿物纵横波速度比差异明显,因此各向异性参数的影响还是要归结于黏土含量的大小。
图3
图3
各向异性参数ε(a)、γ(b)与黏土含量交会
Fig.3
Crossplot of anisotropic parameters ε(a)、γ(b)versus clay content
表1 不同各向异性参数计算方法计算结果
Table 1
| 计算方法 | ε | γ | δ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 焦石坝三轴压缩实验 | 0.209 | 0.191 | 0.067 |
| Deng经验公式 | 0.215 | 0.209 | 0.069 |
| Sone经验公式 | 0.245 | 0.274 | 0.078 |
| Syaers经验公式 | 0.293 | 0.515 | 0.006 |
3 各向异性对页岩储层响应特征的影响
3.1 各向异性对页岩速度的影响
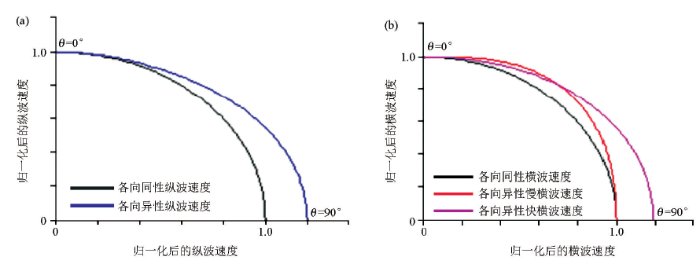
对于页岩这类典型的VTI介质来讲,地震波在这类介质传播时垂直页岩层理方向的速度将低于平行于层理方向的速度, Thomsen于1986年给出速度与各向异性参数以及角度之间的关系式为[7]:
式中:VP为纵波速度;VSV为慢横波速度;VSH为快横波速度;θ为波前的垂直方向与对称轴夹角;VP0、VS0分别是θ为0°时的纵波速度和横波速度。
图4
图4
归一化后的纵波速度(a)、横波速度(b)随地层角度变化关系
Fig.4
Normalized P-(a) and S-wave (b) velocity variation with dip angle of shale layers
表2 不同小层速度、密度及各向异性参数
Table 2
| 序号 | 层段 | 纵波速度/(m·s-1) | 横波速度/(m·s-1) | 密度/(g·cm-3) | ε | γ | δ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ① | 龙一段页岩 | 4036 | 2373 | 2.60 | 0.234 | 0.228 | 0.075 |
| ② | 龙一段二亚段页岩 | 4220 | 2516 | 2.63 | 0.237 | 0.231 | 0.076 |
| ③ | 龙一段一亚段页岩 | 4000 | 2344 | 2.53 | 0.174 | 0.169 | 0.056 |
| ④ | 涧草沟组灰岩 | 6007 | 3101 | 2.72 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
3.2 各向异性对页岩储层AVO特征的影响
式中,Ran(θ)为各向异性反射系数;Ris(θ)为各向同性反射系数;Δδ=δ2-δ1;Δε=ε2-ε1;ε1和δ1、ε2和δ2分别为上下介质的各向异性参数;θ为入射角。
图5
图5
各向同性与各向异性方法计算AVA曲线对比
Fig.5
Comparison of AVA curve between isotropic and anisotropic methods
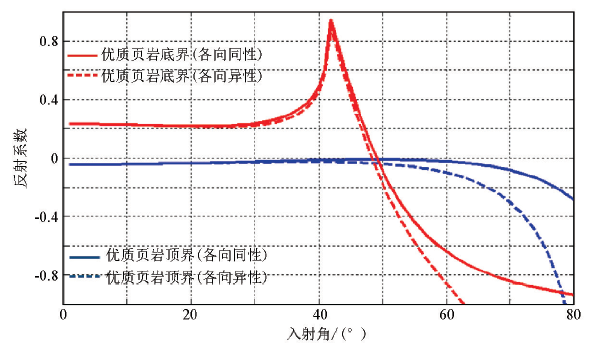
对比各向同性方法和各向异性方法计算结果可知,两者在入射角在小于40°时较为接近;当入射角大于50°时,各向异性计算结果略小,两种方法计算结果开始出现一定差异。由于焦石坝地区地震资料入射角在40°左右,因此页岩各向异性对于这一入射角范围的影响较小,利用各向同性反演方法代替各向异性反演方法在页岩储层预测方面是可行的。
图6
图6
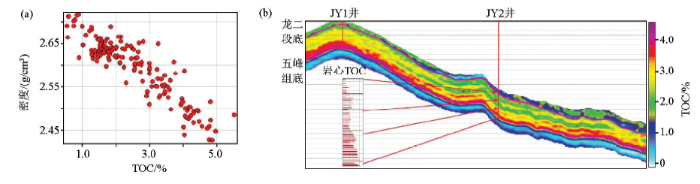
密度与TOC交会图(a)及各向同性反演方法得到的TOC反演剖面(b)
Fig.6
Crossplot of density and TOC (a) and inverted TOC section using isotropic method (b)
3.3 各向异性对岩石力学参数计算的影响
式中,EH为水平方向杨氏模量、νH为水平方向泊松比、Ea为视杨氏模量、νa为视泊松比、Ma为视纵波模量、μa为视剪切模量。
由于页岩水平井方向与页岩层理方向近似平行,而射孔方向与层理方向近似垂直,压裂时受力面与层理方向近似垂直,因此平行层理方向的岩石力学参数才是真正反映页岩可压性的参数。
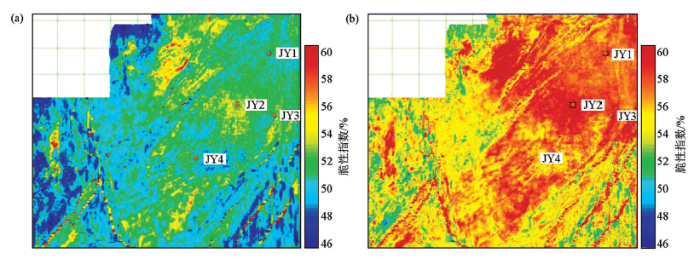
为获得基于各向异性的脆性指数数据体:①利用多属性反演获得黏土含量数据体,②将黏土含量数据体代入式(2)计算各向异性参数数据体,③利用叠前地震反演获得杨氏模量、泊松比、剪切模量、纵波模量数据体;④将②和③计算结果代入式(5)计算得到水平方向的杨氏模量和泊松比;⑤最终利用Rickman脆性指数公式得到水平方向脆性指数。与视脆性指数相比(图7a),水平方向脆性指数数值明显增高(图7b)。造成这一差异的主要原因是视脆性指数类似于等应力平均模型,即Reuss下限,这种介质的杨氏模量低、泊松比高;水平方向脆性指数则类似于等应变平均模型,即Voight上限,这种介质的杨氏模量高、泊松比低。但是页岩作为有机质、黏土、石英、黄铁矿等多种组分的混合物,其矿物几何分布特征比于上述两种理论模型复杂的多,因此视脆性指数与水平方向脆性指数的差异小于Voight上限与Reuss下限之差。视脆性指数平均值为 50.9%;水平脆性指数数值约高11%,平均值为 56.5%。对比可知各向异性参数对脆性指数的计算存在较大影响,是岩石可压性预测中不可忽略的影响因素。
图7
图7
视脆性指数(a)与水平方向脆性指数(b)平面图
Fig.7
Slices of shale apparent brittleness index (a) and horizontal brittleness index (b)
4 结论
通过对焦石坝地区页岩进行各向异性分析共获得以下几点认识:
1)各向异性对速度影响较大,垂直页岩层理方向(θ=0°)与平行页岩层理方向(θ=90°)之间的纵波速度、快横波速度差异可达约20%,当地层倾角较大时各向异性对页岩储层的横向评价及钻井时深关系对比产生较大的影响。
2)各向异性方法计算的AVA曲线在入射角大于50°时与各向同性算法出现较大差异,小于40°时两种方法计算结果较为接近;鉴于焦石坝地区地震资料入射角小于40°,各向同性反演方法在页岩储层预测方面是可行的,利用研究区密度与TOC之间较高的相关性以及各向同性叠前反演方法获得的TOC反演剖面与岩心TOC测试结果具有较高的一致性。
3)各向异性对岩石脆性指数影响较大,水平方向页岩脆性指数比视脆性指数数值高约11%。
参考文献
四川盆地焦石坝地区龙马溪组页岩微观孔隙结构特征及其控制因素
[J].
DOI:10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.06.002
URL
[本文引用: 1]

页岩储层岩石的孔隙结构是影响页岩气藏储集能力和页岩气开采效果的主要因素。为此以四川盆地焦石坝地区下志留统龙马溪组页岩为研究对象,运用氩离子抛光扫描电镜技术、低温氮气吸附脱附法和高压压汞实验对该区页岩储层的微观孔隙结构进行了系统研究。结果表明:①焦石坝地区龙马溪组页岩孔径主要为纳米级,孔隙类型可分为有机质孔、无机孔(粒间孔、粒内孔、晶间孔、溶蚀孔)、微裂缝(矿物颗粒内构造缝、层间滑动缝、成岩收缩缝、有机质演化异常压力缝),以有机质孔和黏土矿物粒间孔为主,其中有机质孔分布最为广泛;②TOC与有机质孔含量存在着明显的正相关性,在底部优质泥页岩段(TOC2%)有机质孔最为发育,含量高达50%;③微观孔隙结构复杂,多呈开放形态,以两端开口的圆筒状孔及四边开放的平行板状孔为主,孔径大小主要分布在2~30nm,以中孔为主。在此基础上,分析了该区页岩储层微观孔隙结构的控制因素,结论认为,有机质丰度和热演化程度为其主控因素,黏土矿物含量对其影响相对不明显。
Characteristics and controlling factors of micro-pore structures of Longmaxi Shale Play in the Jiaoshiba area,Sichuan Basin
[J].
Velocity anisotropy in shales:A petrophyscial study
[J].DOI:10.1190/1.1444162 URL [本文引用: 1]
Rock physics of organic shales
[J].
The effect of kerogen on the elastic anisotropy of organic-rich shales
[J].
DOI:10.1190/GEO2012-0309.1
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The elastic properties of reservoir rocks are important for geomechanics applications; the most important of which are: analysis of stress changes due to production, analysis of rock deformation and failure, wellbore trajectory optimization, and the design of hydraulic fractures. Organic-rich shales are often observed to be strongly anisotropic due to the partial alignment of anisotropic clay minerals and the bedding-parallel lamination of organic material within the shale. Neglecting shale anisotropy may lead to incorrect estimates of the in situ stress or stress changes resulting from production. As a result, isotropic models may fail to describe geomechanical behavior correctly. The distribution of the organic phase plays an important role in determining the elastic properties of organic-rich shales, and this has a significant effect on production-induced stress changes. The presence of kerogen leads to a decrease in all of the elastic moduli, and has a significant effect on the geomechanical behavior of shales. The change in horizontal effective stress for a given change in pore pressure resulting from production is greater for kerogen-rich shales, and the neglect of anisotropy in predicting such stress changes may lead to significant errors.
复杂构造区高演化程度海相页岩气勘探突破的启示——以四川盆地东部盆缘JY1井为例
[J].<p>四川盆地东部盆缘JY1井龙马溪组页岩测试获得高产工业气流,经过长时间试采,压力、产量稳定,实现了南方复杂构造、高演化程度海相页岩气的战略突破。通过对JY1井构造、岩性与龙马溪组TOC、热演化程度及矿物含量特征的分析,结合区域地质资料,得到如下启示:①与北美地区不同,在多期构造演化和抬升剥蚀背景下,构造与保存条件是页岩气富集成藏的首要条件;②龙马溪组只有下部优质烃源岩才起到滑脱作用,多期层滑和构造作用形成的网状裂缝是页岩气富集高产的关键;③上奥陶统灰岩为龙马溪组页岩气的形成起到了良好的封隔作用;④与常规气藏不同,断裂和抬升的破坏作用对优质页岩层系的影响相对较弱,对南方广大地区页岩气的勘探具有示范意义。</br></p>
Implications from marine shale gas exploration breakthrough in complicated structural area at high thermal stage:Taking Longmaxi Formation in well JY1 as an example
[J].
Weak elastic anisotropy
[J].DOI:10.1190/1.1442051 URL [本文引用: 2]
各向异性岩石的静态模量与动态模量实验研究
[J].Shales are important source rocks and sealing rocks with intrinsic anisotropy. The character of stress-strain response and ultrasonic speed response for shales are obtained by experimental measurement,and the features of static and dynamic moduli on anisotropic rock are studied. The dynamic modulus of anisotropic rock is gained by measuring vertical and horizontal wave velocities of core under different directions,and the static modulus is obtained through the measurement of stress-strain characteristics in loading process. Characteristics of wave velocity and elasticity modulus of anisotropic rock under quasi-static and dynamic conditions are analyzed. Except the difference of loading frequency,the strain amplitude difference are obtained respectively under static and dynamic measurements. Study of geophysical response characteristics for anisotropic rocks is of great significance.
Experimental study of static and dynamic moduli for anisotropic rock
[J].
Laboratory measurements of brittleness anisotropy in synthetic shale with different cementation
[C]//
Empirical relationships between transverse isotropy parameters and VP/VS: Implications for AVO
[J].DOI:10.1190/1.1444239 URL [本文引用: 1]
An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks
[J].DOI:10.1190/1.2210052 URL [本文引用: 1]
Mechanical properties of shale gas reservoir rocks and its relation to the insi-tu stress variation observed in shale gas reservoir
[D].
The effect of anisotropy on the Young’s moduli and Poisson’s ratios of shales
[J].
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2478.2012.01130.x
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio are required for geomechanics applications such as hydraulic fracture design, analysis of wellbore stability and rock failure, determination of in situ stress and assessment of the response of reservoirs and surrounding rocks to changes in pore pressure and stress. Shales are usually anisotropic and models that neglect shale anisotropy may fail to describe geomechanical behaviour correctly. Anisotropy in shales results from a partial alignment of anisotropic clay particles, kerogen inclusions, microcracks, low-aspect ratio pores and layering. For shales, the Young's modulus measured parallel to bedding E1 is usually greater than the Young's modulus measured perpendicular to bedding E3. However, the Poisson's ratio 31 corresponding to stress applied perpendicular to bedding and strain measured parallel to bedding can be greater than, equal to, or less than the Poisson's ratio 12 for stress applied parallel to bedding and strain measured parallel to bedding.For transverse isotropy, the elastic anisotropy resulting from a partial alignment of clay particles can be written in terms of the coefficients W200 and W400, which describe the impact of clay particle orientation on the anisotropy of shales. Disorder in the orientation of clay particles acts to reduce W400 faster than W200, since W400 is a higher order moment of the clay particle orientation distribution function than W200. This is confirmed by analysis of measured anisotropy parameters for shales. A partial alignment of clay particles is consistent with the measured Young's moduli for shales and with values of Poisson's ratio 31 > 12 but not with values 31 < 12. These values can be explained if there exist kerogen inclusions, microcracks, or low-aspect ratio pores aligned parallel to the bedding plane.
Dynamic elastic properties of the Wufeng-Longmaxi formation shale in the southeast margin of the Sichuan Basin
[J].
海相页岩TOC地震定量预测技术及应用——以四川盆地焦石坝地区为例
[J].
DOI:10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.06.004
URL
[本文引用: 1]

总有机碳含量(TOC)是评价 页岩生烃能力和页岩油气藏的一个重要指标,目前国内外利用地震资料直接定量预测TOC的报道很少,因此,有必要对地震预测TOC的方法作进一步的研究。为 此,以四川盆地焦石坝地区为例,从岩心实测TOC出发,通过TOC与地球物理参数交会分析,寻找到TOC敏感地球物理参数——密度,并建立密度与TOC之 间的最佳拟合方程,得到计算总有机碳含量的经验公式;结合叠前地震反演获得的密度体便可计算出TOC数据体,从而达到定量预测页岩TOC的目的。将改进的 预测方法应用于四川盆地焦石坝地区海相页岩气勘探,结果表明:①利用叠前同时反演直接求得的密度体避免了累计误差,稳定性好,多解性少,结果可靠,为精细 定量预测TOC提供了基础保证;②预测的TOC与实测结果吻合程度高,相对误差较小。结论认为,该技术在四川盆地海相页岩气勘探中具有广阔的应用前景。
Quantitative seismic prediction technique of marine shale TOC and its application:A case from the Longmaxi Shale Play in the Jiaoshiba area,SichuanBasin
[J].
Seismic reservoir characterization in resource shale plays:Stress analysis and sweet spot discrimination
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.3609090
URL
[本文引用: 1]

http://library.seg.org/doi/abs/10.1190/1.3609090
The effects of transverse isotropy on reflection amplitude versus offset
[J].DOI:10.1190/1.1442325 URL [本文引用: 1]
Weak anisotropic reflections,Offset Dependent Reflectivity:Theory and Practice of AVO analysis
[C]//
Reflection coefficients and azimuthal AVO Analysis in anisotropic media
[C]//
A practical use of shale petrophysics for stimulation design optimization:All shale plays are not clones of the Barnett Shale
[C]//
On the use of isotropic parameters λ,E,ν,K to understand anisotropic shale behavior
[C]//