0 引言
探地雷达(ground penetrating radar,GPR)的最终目的是反演地下介质的几何参数、介电常数和电导率等参数[1,2,3],目前探地雷达反演的方法有多种,其中以波形拟合为基础的全波形反演是当前反演效果较好的方法。然而探地雷达全波形反演属于非线性问题,用传统的线性反演法反演非线性问题,容易陷入局部极小,因此很有必要采用寻优能力强的非线性反演方法来进行探地雷达全波形反演[4]。文中研究的粒子群反演方法,是近年来应用比较广泛的一种非线性反演方法[5,6],粒子群优化算法(particle swarm optimization,PSO)是由Kennedy和Eberhart通过对鸟群、鱼群和人类社会某些行为的观察研究,于1995年提出的一种进化算法[7]。该算法在诸如信号与图像处理[8,9]、自动控制[10]、机械工程[11,12]、电气工程[13]、通信工程[14]、岩土力学[15]以及经济管理[16]等很多科研领域取得了成功应用。近年来,粒子群优化算法在地球物理领域的应用研究也越来越多[17,18,19,20],但是在GPR反演领域,PSO反演却没有过多的相关研究[21,22]。
此外,虽然PSO被广泛应用到诸多领域解决了许多问题,但经典PSO存在早熟收敛、易陷于局部最优、种群多样性丢失等问题,为了有效提高PSO的搜索效率和精度,文献[23]提出了一种社会学习型的PSO算法(social learning particle swarm optimization,SLPSO)。该方法将社会学习机制引入PSO来开发社会学习。与基于历史信息更新粒子的经典PSO不同,该算法的粒子不仅根据历史信息进行更新,而且每个粒子都向当前群中比其更好的粒子(称为示范者)学习,并不局限于只向全局最优的粒子进行学习。文中采用该改进型算法对GPR波形进行反演分析,将层状介质的厚度、介电常数以及电导率作为反演的参数,充分验证了该算法在GPR一维反演中的有效性和准确性。
1 PSO算法描述
1.1 经典PSO算法
PSO是通过模拟鸟群觅食过程中的迁徙和群聚行为而提出的一种基于群体智能的全局随机搜索算法,与其他进化算法一样,它也是基于“种群”和“进化”的概念,通过个体间的协作与竞争,实现复杂空间最优解的搜索。同时,PSO不像其他进化算法那样对个体进行交叉、变异、选择等进化算子操作,而是将群体中的个体看作是在n维搜索空间中没有质量和体积的粒子,每个粒子以一定的速度在解的区间内搜索,并向自身历史最佳位置和邻域历史最佳位置聚集,实现对候选解的进化[24]。
假设t时刻,在一个n维搜索空间S∈Rn和由m个粒子组成的种群中,第i个粒子的位置是用一个n维向量表示的,即Xi=[Xi1,Xi2,…,Xin]。每个粒子都代表所求问题的一个候选解,将Xi代入到适应度函数中计算得到适应值,每个解的好坏由其对应的适应值所决定,适应值越好,表明其关联的解就越接近真实解。粒子的移动速度也是一个n维向量,即Vi=[Vi1,Vi2,…,Vin]。第i个粒子迄今为止在S空间搜索到的最优位置称为个体极值,记为Pi=[Pi1,Pi2,…,Pin]。整个粒子群迄今为止搜索到的最优位置为全局极值,记为gbest=[Pg1,Pg2,…,Pgn]表示种群最好粒子的位置。在寻优的过程中,每个粒子根据式(1)和式(2)来更新自己的速度和位置:
其中,粒子序号i=1,2,…,m,t为当前迭代次数,ω为惯性权重,表示上一次速度对粒子的影响系数。c1、c2是学习因子,c1表示粒子自身经验的认知能力,用来调节粒子飞向自身最好位置方向的前进步长;c2表示粒子学习社会经验的认知能力,调节粒子向全局最优位置前进的步长。r1、r2是均匀分布在区间[0,1]的随机数,其目的是让粒子能够以等概率的加速度飞向粒子本身最好位置和粒子全局最好的位置[25]。
1.2 改进型PSO算法
该算法将社会学习机制引入到PSO,粒子的学习行为在排序后的群体上执行。不同于经典PSO,该算法中粒子向当前群体中的任何更好的粒子学习,而不是向历史上最好的粒子学习。并且,为了减轻参数设置的负担,该算法中使用了一种依赖于维度n的参数控制策略,以增强其对要优化的问题的搜索维度的能力。
在算法执行前首先要定义一个适应性函数,用该函数解决最小化问题:
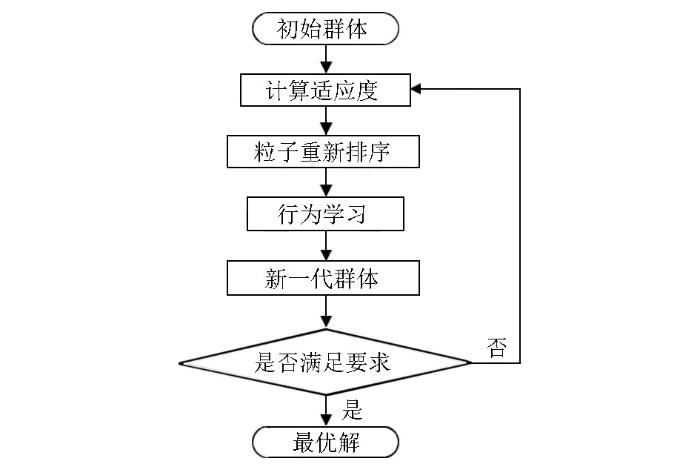
在寻优过程中,先随机生成一个包含了m个粒子的初始群体X,m=100+[n/10]。群体中第i个粒子Xi ,i∈{1,2,…,m}代表了满足适应性函数的一个解,解的好坏程度由适应值fitness(i)决定,适应值越小,适应度越高,解越接近真实解。在计算完所有粒子的适应值后,将粒子按照适应度递增的顺序排列,此后,每个粒子(适应度最高的除外)将向适应度更高的粒子(示范者)学习。具体的算法流程如图1。
图1
图2
图2
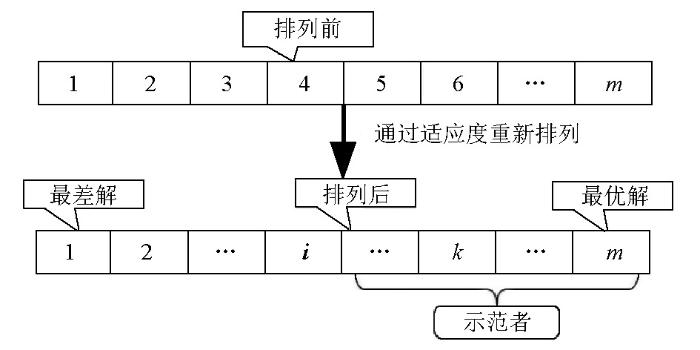
粒子重排和行为学习示意
Fig.2
Schematic diagram of particle rearrangement and behavioral learning
粒子1的示范者可以是粒子2到粒子m,而对于粒子(m-1),只有粒子m可以是它的示范者。因此,粒子1 (最差的一个)永远不能成为示范者,而粒子m(最好的)永远不会成为模仿者。也就是说,当前群中最好的粒子不会被更新。
算法规定了粒子的学习行为主要由式(4)的方式进行操作:
式中,
其中:
式(5)中的矫正量Δ
前面提到的每个粒子学习概率
正如前面提到的,在群体中一个粒子适应度越高,粒子向其他粒子学习的可能性越小。一般而言,大多数启发式算法的性能随着优化问题的搜索维度增加而降低,因此定义学习概率和问题维度之间成反比关系。式中
2 基于SLPSO的GPR全波形反演
2.1 GPR时域有限差分法(FDTD)正演
利用SLPSO进行全波形反演,必须对每一个粒子(模型参数)进行正演,文中采用时域有限差分法(FDTD)[26,27]进行GPR数值模拟,由于GPR的高频电磁波在介质中传播的过程服从Maxwell方程组,所以FDTD能将此类问题当作初值问题来处理,采用电场和磁场在空间和时间上的交替抽样的离散方式,在每一个电场(或者磁场)分量周围有4个磁场(或电场)分量环绕,应用这种离散方式将含有时间变量的Maxwell旋度方程化为一组差分方程,并在时间轴上逐步推进地求解空间电磁场[28-29]。本文的GPR正演部分以Maxwell两个旋度方程为基本出发点,运用K.S.Yee[30] 的空间网格模型理论和时域有限差分法的基本原理,推导出二维空间的探地雷达正演方程组,并采用了Mur一阶吸收边界条件,取得了较好的模拟效果[31]。
2.2 SLPSO反演步骤
其中,
具体的算法的实施步骤为:
1)在包含了层状介质厚度、介电常数和电导率的n维参数空间内随机的初始化粒子群,并计算粒子个数和社会影响因子;
2)将反演模型和粒子群内所有粒子进行有限差分正演模拟,在正演过程中,用雷克子波作为激励源,采用自激自收的模式;
3)GPR信号振幅补偿,相对于直达波,反射波的振幅较少,利用式(8)定义优度函数直接进行计算,反映的往往是直达波的拟合程度,而忽略我们更关心的反射波的拟合,因此必须对GPR波形进行振幅补偿,削弱直达波,增强反射波,使得直达波和反射波的振幅相当。这是保证反演质量的关键;
4)将正演信号和实测信号代入式(8)计算每个粒子的适应值;
5)将粒子按照适应值进行重排,计算每个粒子的学习概率,并按照式(5)计算每个粒子的矫正量;
6)通过式(4)更新每个粒子,形成新的粒子群;
7)由最大迭代次数或者迭代精度判断迭代是否结束,若结束,则将步骤(4)中粒子重排后得到的全局最优解输出,作为整个算法的输出,否则,进入步骤(2)开始下一次迭代。
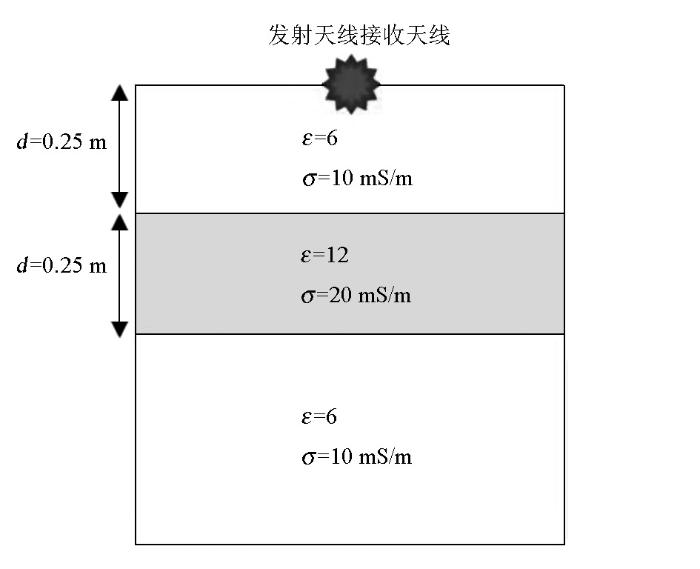
以层状介质为例进行正演,如图3所示,背景地层的相对介电常数ε=6,电导率为σ=10 mS·m-1。目标地层的相对介电常数ε=12,电导率为σ=20 mS·m-1。目标地层的上顶面深度为0.25 m,目标层下底面深度为0.5 m。根据所探测的深度,激励源采用主频为900 MHz的雷克子波,且采取自激自收的方式,时窗长度为20 ns。
图3
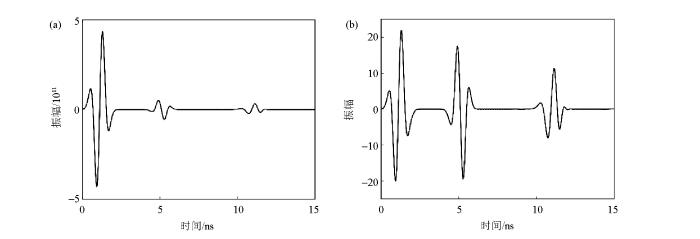
图4a为所得的记录,从图中可以看出反射波和直达波信号强度有数量级的差距,所以可以采取对原波形乘上增益函数的措施来削弱直达波同时增强反射波。增益方式如式(9)所示:
式中,A0(t)是原始记录,A(t)是增益后的记录,λ和η可以按照补偿的不同需求进行调节,文中取λ=210、η=1.95为宜,经过振幅补偿后的记录如图4b。
图4
图4
一维层状模型正演波形
a—增益前正演波形;b—增益后正演波形
Fig. 4
Forward waveform of a one-dimensional layered model
a—forward waveform before gain;b—forward waveform after gain
3 基于SLPSO的GPR全波形反演算例
为验证反演方法的有效性,对于一个给定的模型,利用FDTD进行正演,作为实测信号。从简单起见,采用层状模型参数正演出来的波形参数作为拟合目标,以反演模型的厚度、介电常数以及电导率。对比经典PSO算法、改进型PSO算法和加噪20%后的改进型PSO算法。模型假设了一个3层的层状结构,具体参数如表1所示。
表1 理论模型参数
Table 1
| 模型 | 层序号 | 层厚度/m | 相对介电常数 | 电导率/(mS·m-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.25 | 6 | 0.01 | |
| 模型1 | 2 | 0.25 | 12 | 0.02 |
| 3 | 无限 | 6 | 0.05 | |
| 1 | 0.25 | 17 | 0.01 | |
| 模型2 | 2 | 0.25 | 12 | 0.02 |
| 3 | 无限 | 7 | 0.05 | |
| 1 | 0.25 | 6 | 0.01 | |
| 模型3 | 2 | 0.25 | 11 | 0.02 |
| 3 | 无限 | 16 | 0.05 |
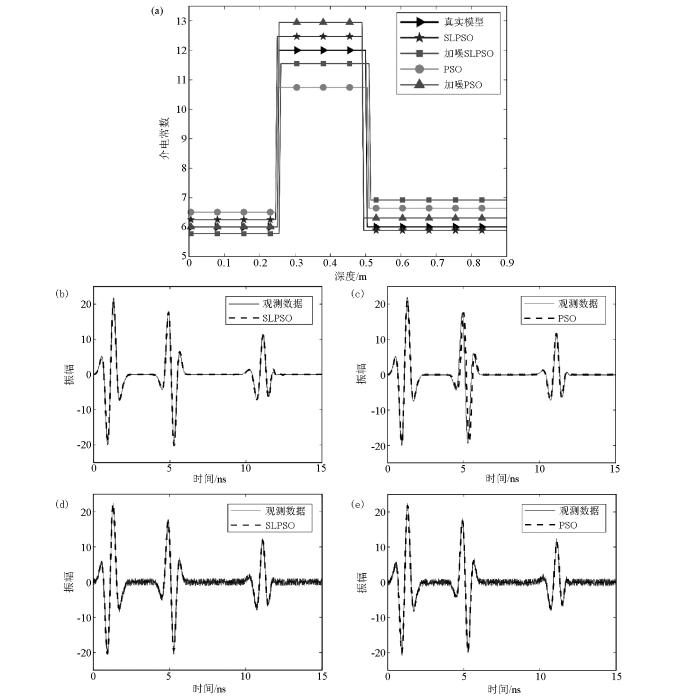
图5
图5
模型1反演结果对比
a—深度及介电常数反演结果综合对比;b—SLPSO理想数据反演结果;c—PSO理想数据反演结果;d—SLPSO加躁数据反演结果;e—PSO加躁数据反演结果
Fig. 5
Comparison of the inversion results Model 1
a—comprehensive comparison of depth and dielectric constant inversion results;b—SLPSO ideal data inversion results;c—PSO ideal data inversion results;d—SLPSO add noise data inversion results;e—PSO add noise data inversion results
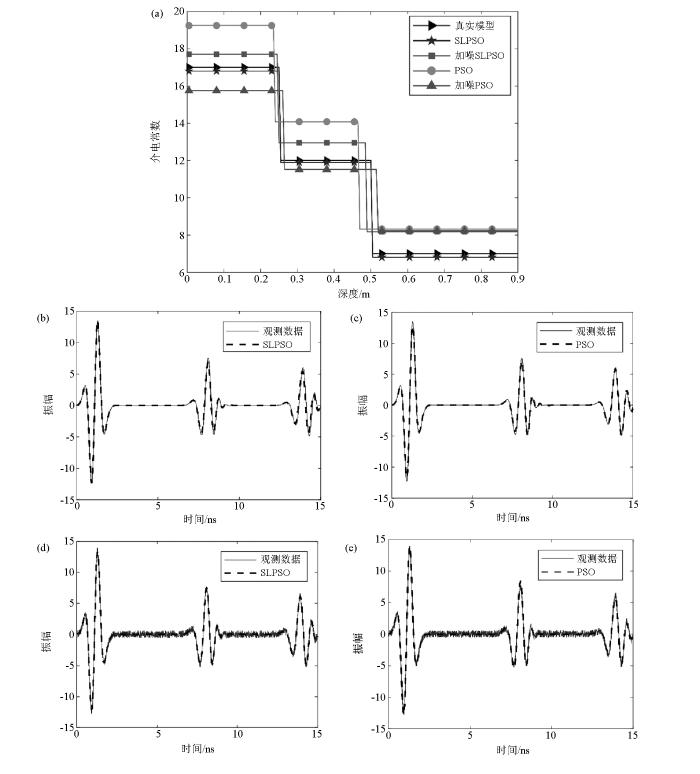
图6
图6
模型2反演结果对比
a—深度及介电常数反演结果综合对比;b—SLPSO理想数据反演结果;c—PSO理想数据反演结果;d—SLPSO加躁数据反演结果;e—PSO加躁数据反演结果
Fig. 6
Comparison of the inversion results Model 2
a—comprehensive comparison of depth and dielectric constant inversion results;b—SLPSO ideal data inversion results;c—PSO ideal data inversion results;d—SLPSO add noise data inversion results;e—PSO add noise data inversion results
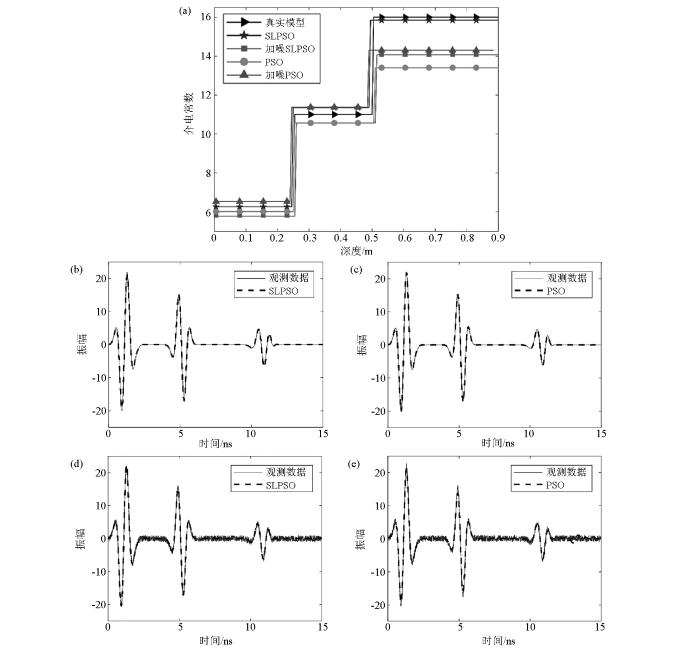
图7
图7
模型3反演结果对比
a—深度及介电常数反演结果综合对比;b—SLPSO理想数据反演结果;c—PSO理想数据反演结果;d—SLPSO加躁数据反演结果;e—PSO加躁数据反演结果
Fig. 7
Comparison of the inversion results Model 3
a—comprehensive comparison of depth and dielectric constant inversion results;b—SLPSO ideal data inversion results;c—PSO ideal data inversion results;d—SLPSO add noise data inversion results;e—PSO add noise data inversion results
表2 模型1反演迭代效率对比
Table 2
| 迭代步数 | SLPSO适应值 | 时间/s | PSO适应值 | 时间/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 5385 | 11.25 | 4983 | 11.30 |
| 20 | 4700 | 22.50 | 3371 | 22.60 |
| 30 | 2741 | 33.75 | 3054 | 33.90 |
| 40 | 2741 | 45.00 | 2892 | 45.20 |
| 50 | 256 | 56.25 | 2784 | 56.50 |
| 60 | 256 | 67.50 | 2762 | 67.80 |
| 70 | 77 | 78.75 | 2580 | 79.10 |
| 80 | 32 | 90.00 | 77 | 90.40 |
| 90 | 10 | 101.25 | 63 | 101.70 |
对比3种模型参数两种方法的反演结果可见:相比于传统PSO算法,SLPSO在反演的精度和迭代收敛速度上有较大的提高,更容易搜索出最优值。此外,在加入20%噪声后依然有良好的反演效果,说明该方法有较好的抗噪能力。
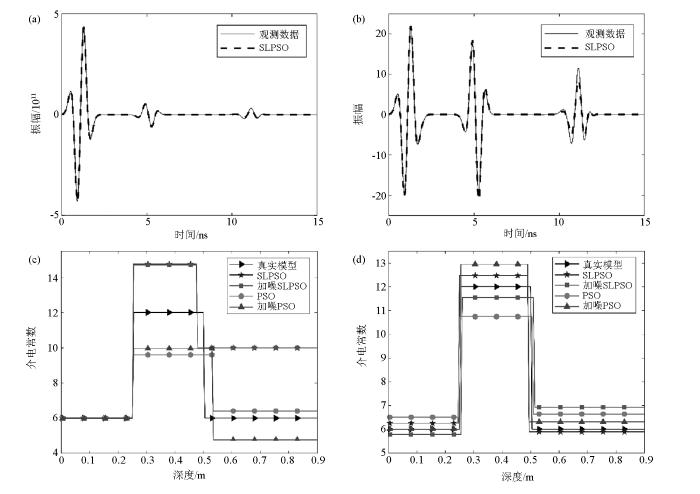
此外,为了验证振幅补偿对反演效果的影响,对模型1未做振幅补偿的反演和做了振幅补偿的反演结果进行对比,结果如图8所示。
图8
图8
模型1反演振幅补偿效果对比
a—未增益数据反演结果;b—增益数据反演结果;c—未增益数据反演参数综合对比;d—增益数据反演参数综合对比
Fig. 8
Comparison of amplitude compensation effects in model 1 inversion
a—no gain data inversion results;b—gain data inversion results;c—inversion parameters comprehensive comparison of no gain data;d—inversion parameters comprehensive comparison of gain data
对比的效果表明:未使用振幅补偿进行反射波形增益的反演效果较差,反演数据的精度差,而使用了振幅补偿对反射波形进行增益的反演效果则远好于未做增益的效果,反演的精度有了较大的提高。
4 结论
通过采用时域有限差分法正演的SLPSO算法进行层状介质参数的反演,与理论模型的对比,改进的粒子群算法较传统的粒子群算法,反演精度有较大的提升,计算的收敛速度也更快。对比传统的线性反演方法,该方法不需要设定初始值,不易陷进局部最小值,对高精度反演具有重要实际意义。此外,借鉴地震勘探中地震波形振幅补偿的原理,使用振幅补偿的方式对GPR反射波形采取合理的增益,同样有助于提高反演的精度,增强反演的能力。文中采用二维的FDTD进行正演,可把基于SLPSO的GPR全波形反演推广到二维复杂模型。
参考文献
Ground-penetrating radar and its use in sedimentology: principles,problems and progress
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2004.01.004
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Ground-penetrating radar (GPR, also referred to as ground-probing radar, surface-penetrating radar, subsurface radar, georadar or impulse radar) is a noninvasive geophysical technique that detects electrical discontinuities in the shallow subsurface (<50 m). It does this by generation, transmission, propagation, reflection and reception of discrete pulses of high-frequency (MHz) electromagnetic energy. During the 1980s radar systems became commercially available, but it was not until the mid-1990s that sedimentary geologists and others began to widely exploit the technique. During the last decade numerous sedimentological studies have used GPR to reconstruct past depositional environments and the nature of sedimentary processes in a variety of environmental settings; to aid hydrogeological investigations, including groundwater reservoir characterisation, and to assist in hydrocarbon reservoir analogue studies. This is because in correctly processed radar profiles, and at the resolution of a survey, primary reflections usually parallel primary depositional structure. Despite the wide use of GPR, a number of fundamental problems remain in its application to sedimentary research. In particular, there are a wide range of approaches to the processing of radar data and interpretation techniques used on the final subsurface images vary widely, with little consensus over a common methodology. This review attempts to illustrate that methods for the collection, processing and interpretation of radar data are intimately linked and that thorough understanding of the nature, limitations and implications of each step is required if realistic sedimentological data are to be generated. In order to extract the maximum amount of meaningful information, the user must understand the scientific principles that underlie the technique, the effects of the data collection regime employed, the implications of the technique's finite resolution and depth of penetration, the nature and causes of reflections unrelated to primary sedimentary structure, and the appropriateness of each processing step with respect to the overall aim of the study. Following suitable processing, a radar stratigraphy approach to reflection profile interpretation should be adopted. New or modified terminologies and techniques to define a radar stratigraphy are also recommended, in order to make the interpretation process more transparent and to avoid confusion with related methodologies such as seismic stratigraphy and sequence stratigraphy. The full potential of GPR in sedimentary research will only be realised if more thorough and systematic approaches to data collection, processing and interpretation are adopted.
地球物理资料非线性反演方法讲座(十)——粒子群反演方法
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2009.04.001
URL
[本文引用: 1]

绝大多数地球物理反演问题是非线性问题。近年来,非线性反演方法的研究和应用,都有了一定的 进展,涌现了许多新的反演方法,引起了人们的重视。本讲座类比遗传算法和模拟退火等智能随机非线性反演方法寻优思想之后,在前人工作的基础上,详细地介绍 了我们首次在地球物理资料反演中付诸实现的一种新的非线性反演方法——粒子群反演算法。文中以地震波阻抗数值模拟和实际资料为例,说明了该方法的可行性及 有效性。
Lecture on nonlinear inversion methods of geophysical data(10):particle swarm inversion method
[J].
Particle swarm optimization
[J].
A quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization with diversity-guided mutation for the design of two-dimensional IIR digital filters
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TCSII.2009.2038514
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This brief proposes quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization with diversity-guided mutation (QPSO-DGM) to solve the problem of designing the optimal 2-D zero-phase IIR digital filters. The new method integrates a diversity control strategy into QPSO to guide the particle's search and thus improve the capabilities of exploration. Numerical results demonstrate that the design approach based on QPSO-DGM can obtain better digital IIR filters than the existing methods.
Multilevel thresholding for image segmentation through an improved quantum-behaved particle swarm algorithm
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TIM.2009.2030931
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Multilevel thresholding is one of the most popular image segmentation techniques. Some of these are time-consuming algorithms. In this paper, by preserving the fast convergence rate of particle swarm optimization (PSO), the quantum-behaved PSO employing the cooperative method (CQPSO) is proposed to save computation time and to conquer the curse of dimensionality. Maximization of the measure of separability on the basis of between-classes variance method (often called the OTSU method), which is a popular thresholding technique, is employed to evaluate the performance of the proposed method. The experimental results show that, compared with the existing population-based thresholding methods, the proposed PSO algorithm gets more effective and efficient results. It also shortens the computation time of the traditional OTSU method. Therefore, it can be applied in complex image processing such as automatic target recognition.
基于合作粒子群算法的PID神经网络非线性控制系统
[J].
DOI:10.7641/j.issn.1000-8152.2009.12.ccta080998
URL
[本文引用: 1]

PID神经元网络(PIDNN)模型为一种新型的神经网络模型,兼有PID与神经网络的共同优点,应用于复杂的控制系统,取得优良控制性能,但其后向传播算法(BP)限制了该模型的应用范围.为实现对非线性多变量系统的有效控制,扩展神经网络的应有范围,本文采用PIDNN神经网络设计了多变量PIDNN神经网络(MPIDNN)控制器,并用本文作者提出的合作粒子群算法(CPSO)取代了传统BP后向传播算法,通过比较MPIDNN_CPSO、MPIDNN_CRPSO、MPIDNN_PSO和MPIDNN_BP4种控制器的控制性能,仿真结果表明,基于CPSO算法的MPIDNN控制器实现了对非线性多变量不对称系统的有效控制.与传统的BP算法相比,CPSO算法提高了控制系统的稳定性、精确性与鲁棒性.
Nonlinear control system of PID neural network based on cooperated particle swarm optimization (PSO)
[J].
基于粒子群优化的时间最优机械臂轨迹规划算法
[J].
DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1219.2011.00802
URL
Magsci
[本文引用: 1]

根据机械臂运动学约束,提出了关节空间基于粒子群优化(PSO)的时间最优3-5-3多项式插值轨迹规划算法,解决了由于多项式插值轨迹规划具有阶次高、没有凸包性质等缺点,难以应用传统优化方法进行优化的问题.粒子群算法结构简单、参数易调整的特点弥补了多项式阶插值的缺点.直接在优化目标空间搜索,巧妙地避免了粒子群计算构造自变量和因变量的映射,降低了搜索维数,简化了计算.在优化过程中,采用两个适应度函数之间切换的开关控制,使各段插值尽快收敛于运动学约束内.通过与传统3-5-3多项式插值的运动位置、速度、加速度曲线对比,证明该方法运行时间更短,稳定性和流畅性更好.
Time-optimal trajectory planning algorithm for manipulator based on PSO
[J].
A Research on particle swarm optimization and its application in robot manipulators
粒子群优化算法及其在机电设备中的应用研究
[D].
Particle swarm optimization algorithm and its application in electromechanical equipment
[D].
基于改进粒子群优化算法的电力线通信多径传输模型参数辨识
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.apm.2007.10.019
URL
Magsci
[本文引用: 1]

基于已有的电力线多径传输模型结构,以0.5~20 MHz范围内的实际低压载波通信信道测量数据为样本,将改进粒子群优化算法应用于低压载波通信信道模型的多参数辨识,通过自适应改变惯性权重提高搜索效率,同时采用模拟退火算法并自适应调整退火温度,克服了基本粒子群算法容易发生早熟收敛的缺点。对路径数为4和18的信道模型进行参数辨识的结果表明:与遗传算法相比,改进的粒子群算法可加速收敛,缩短辨识时间,同时提高了拟合精度,克服了参数的分散性,所取路径数越多,拟合效果越好。
Parameter identification of Multi-Path transmission model for power line communication based on improved particle swarm optimization
[J].
粒子群算法在时效变形参数反演中的应用
[J].以往的现场刚性承压板压缩蠕变试验中都假设岩体变形为黏弹性变形,然后推求岩体的蠕变变形公式,并结合最小二乘法反演获得蠕变参数,这种方法由于进行了黏弹性变形的假设从而无法考虑岩体的黏塑性变形,为此,采用粒子群智能算法的数值反演方法进行研究,并且提出将流变模型中控制瞬时变形和时效变形的2种参数分开反演的二次粒子群算法。研究结果表明:采用这种方法可以有效地减小反演的难度,提高了反演精度;将此方法应用于现场压缩蠕变试验的参数反演,拟合时效变形参数曲线与试验曲线较吻合,从而可获得相应的流变参数。
Application of particle swarm optimization in time-dependent parameters inversion
[J].
粒子群算法在投资组合中的应用
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-4098.2007.08.021
URL
[本文引用: 1]

投资组合面临现实证券市场中大量数据,求解组合模型是一个非线性整数规划问题,传统数学规划算法难以有效求解。为此,本文将粒子群算法应用到基于VaR的投资组合模型中,并通过上海证券交易所的实际数据进行计算机模拟,结果说明该算法所求最优投资组合是实用的和有效的。
Application of the particle swarm optimization in the Portfolio Selection
[J].
基于粒子群优化的自然电场数据反演
[J].在分析测试粒子数、速度因子、目标函数等算法参数对粒子群优化算法效果的影响规律的基础上,设计自然电场粒子群优化反演算法,并对加入不同程度白噪声模拟数据进行反演试算。研究结果表明:设计的粒子群优化算法能有效实现对自然电场数据的反演,算法具有收敛速度快、稳定、反演精度较高和抗噪音能力强等优点,可以较为准确地得到异常体的位置、形态、极化角等参数,能较好地满足生成实际要求。
Inversion of self-potential anomalies based on particle swarm optimization
[J].
电阻率层析成像的二维改进粒子群优化算法反演
[J].
DOI:10.11720/wtyht.2015.5.27
URL
Magsci
[本文引用: 1]

<p>粒子群优化算法(PSO)是通过模拟鸟群觅食过程中的社会行为而提出的一种基于群体智能的全局随机搜索算法,已有研究学者证明PSO算法是一种有效的地球物理反演方法,不依赖初始模型。此次在研究常规粒子群算法的基础上,针对常规粒子群优化算法易于陷于局部极值,后期收敛速度慢,反演精度不高等缺点,提出了一种改进的充分混沌振荡粒子群优化算法。针对粒子群算法的特点,改进速度更新公式,使粒子更快获取与当前全局最好位置的差异,增强粒子的学习能力,并用此算法在matlab2012b编程环境中对均匀半空间电阻率层析成像异常体理论模型进行了二维数值试验。结果表明,此种算法反演时不依赖初始模型,搜索空间增大,实现全局搜索,在准确性上优于标准PSO反演,成像质量优于Levenberg-Marquardt法反演。</p>
2-D improved particle swarm optimization algorithm for electrical resistance tomography inversion
[J].
粒子群算法在磁测资料井地联合反演中的应用
[J].<p>粒子群优化算法是一种新兴的高效并行优化算法,目前被广泛应用于各领域,但在地球物理反演中很少运用。磁测资料井地联合反演是结合井中与地面磁测数据的各自优势,进行地球物理反演的一种新方法。笔者以立方体为模型,通过理论模型试验和大冶危机矿山实例,将粒子群优化算法运用于磁测资料井地联合反演,取得了比较好的效果,不仅验证了粒子群算法在地球物理反演中的可行性,而且也论证了井地联合反演的优越性。</p>
The application of PSO to joint inversion of survey and borehole magnatic data
[J].
Inversion of self-potential of idealized bodies' anomalies using particle swarm optimization
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.cageo.2010.01.011
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The particle swarm optimization (PSO) method was applied to the inversion of single and multiple self-potential (SP) data anomalies caused by buried bodies with simple geometry like spheres, cylinders and inclined sheets. The inversion parameters are the depth of the body, the location of the anomaly, the electric current dipole moment, the polarization angle or the inclination angle and the half-width in the sheet-like body case. The algorithm was tested on synthetic data with single and multiple SP anomalies and applied to two experimental data from Surda area (India) and Vilarelho da Raia (Portugal). The inversion results showed good agreement with the previous results obtained using other techniques. The great advantage of the PSO method is that it is fast and does not require assumptions about the shape of the source of the SP anomaly.
Ground penetrating radar inversion algorithm based on improved particle swarm optimization
[J].
基于改进粒子群算法的路面厚度反演分析
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2579.2012.04.022
URL
[本文引用: 1]

传统公路厚度检测都是采用钻芯取样,人工测量的方法,不仅效率低,而且破坏路面结构.路面雷达是一种连续、高效、无破损的路面质量检测工具.通过对路面雷达回波信号进行反演分析,可以得到路面结构层介电常数、厚度等信息.该文采用一种改进的粒子群优化方法,建立路面结构层参数的改进粒子群反演算法,实现了结构层介电常数和厚度的反演分析.通过对比理论模型反演结果发现,该方法得到的结构层介电常数精度高于标准粒子群方法,采用该方法分析实际路面雷达回波信号,与钻芯结果对比可知,反算结果与实际钻芯测量值误差在3%以内.
Analysis of pavement thickness inversion based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm
[J].
A social learning particle swarm optimization algorithm for scalable optimization
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.ins.2014.08.039
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Social learning plays an important role in behavior learning among social animals. In contrast to individual (asocial) learning, social learning has the advantage of allowing individuals to learn behaviors from others without incurring the costs of individual trials-and-errors. This paper introduces social learning mechanisms into particle swarm optimization (PSO) to develop a social learning PSO (SL-PSO). Unlike classical PSO variants where the particles are updated based on historical information, including the best solution found by the whole swarm (global best) and the best solution found by each particle (personal best), each particle in the proposed SL-PSO learns from any better particles (termed demonstrators) in the current swarm. In addition, to ease the burden of parameter settings, the proposed SL-PSO adopts a dimension-dependent parameter control method. The proposed SL-PSO is first compared with five representative PSO variants on 40 low-dimensional test functions, including shifted and rotated test functions. The scalability of the proposed SL-PSO is further tested by comparing it with five state-of-the-art algorithms for large-scale optimization on seven high-dimensional (100-D, 500-D, and 1000-D) benchmark functions. Our comparative results show that SL-PSO performs well on low-dimensional problems and is promising for solving large-scale problems as well.
粒子群优化算法综述
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2004.05.018
URL
[本文引用: 1]

粒子群优化(PSO)算法是一种新兴的优化技术,其思想来源于人工生命和演化计算理论.PSO通过粒子追随自己找到的最好解和整个群的最好解来完成优化.该算法简单易实现,可调参数少,已得到广泛研究和应用.详细介绍了PSO的基本原理、各种改进技术及其应用等,并对其未来的研究提出了一些建议.
Summary of particle swarm optimization
[J].
The finite difference time domain method for electromagnetics with MATLAB simulations
[M].
Finite difference time domain method forward simulation of complex geoelectricity ground penetrating radar model
[J].
DOI:10.1007/s11771-005-0186-7
URL

The ground penetrating radar(GPR) forward simulation all aims at the singular and regular models, such as sandwich model, round cavity, square cavity, and so on, which are comparably simple. But as to the forward of curl interface underground or 'v' figure complex model, it is difficult to realize. So it is important to forward the complex geoelectricity model. This paper takes two Maxwell's vorticity equations as departure point, makes use of the principles of Yee's space grid model theory and the basic principle finite difference time domain method, and deduces a GPR forward system of equation of two dimensional spaces. The Mur super absorbed boundary condition is adopted to solve the super strong reflection on the interceptive boundary when there is the forward simulation. And a self-made program is used to process forward simulation to two typical geoelectricity model.
地质雷达二维时域有限差分正演
[D].
Two-dimensional time domain finite difference forward modeling of geological radar
[D].
Numerical solution of initial boundary value problems involving Maxwell's equations in isotropic media
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TAP.1966.1138693
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Maxwell's equations are replaced by a set of finite difference equations. It is shown that if one chooses the field points appropriately, the set of finite difference equations is applicable for a boundary condition involving perfectly conducting surfaces. An example is given of the scattering of an electromagnetic pulse by a perfectly conducting cylinder.
Numerical solution of initial boundary value problems involving Maxwell's equations in isotropic media
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TAP.1966.1138693
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Maxwell's equations are replaced by a set of finite difference equations. It is shown that if one chooses the field points appropriately, the set of finite difference equations is applicable for a boundary condition involving perfectly conducting surfaces. An example is given of the scattering of an electromagnetic pulse by a perfectly conducting cylinder.
隧道衬砌内空洞探地雷达探测正反演研究
[D].
Research on forward and inversion of ground penetrating radar in tunnel lining
[D].
基于反演的稳定高效衰减补偿方法
[J].
DOI:10.6038/cjg20140423
URL
Magsci
[本文引用: 1]

反<em>Q</em>滤波方法是提高地震数据分辨率的一种有效途径,可以用来补偿振幅和校正相位.常规的反<em>Q</em>滤波方法一般基于波场延拓理论,具有不稳定性或振幅补偿不足的缺点.本文基于波场延拓的正<em>Q</em>滤波方程,借鉴反演的思想以及正则化策略提出了一种新的衰减补偿方法,该方法稳定、精确,利用该方法可最终得到高分辨的地震记录.该方法仅计算有效频带内的频率分量,提高了计算效率.模拟数据以及实际数据处理验证了本文方法的有效性.
A stable and efficient attenuation compensation method based on inversion
[J].
Pseudo-full-waveform inversion of borehole GPR data using stochastic tomography
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.2755929
URL

Not Available