0 引言
为揭示牛营子凹陷构造演化特征和地层展布规律,探索适合应用于辽西地区规模小、构造复杂凹陷的高效、低耗的地球物理方法,中国地质调查局沈阳地质调查中心联合江苏省有色金属华东地质勘查局八一四队,在牛营子凹陷采用广域电磁法开展地质探测工作。通过本次研究,了解了该区域由浅及深的电阻率变化规律,丰富了燕辽沉降带东部的勘探层系,首次揭示出燕辽沉降带东段牛营子凹陷中元古界蓟县系高于庄组之下隐伏着一套厚度较大的低阻地层,并得到钻孔验证。此次工作印证了广域电磁法在构造复杂的小型凹陷具有极佳的适用性,并为该地区后续油气勘探工作的开展奠定了基础。
1 区域地质和地球物理概况
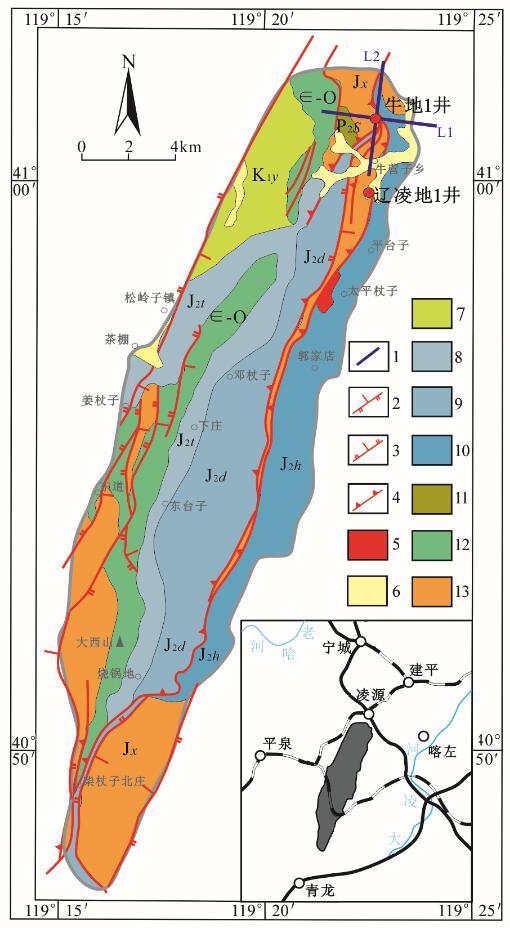
图1
图1
牛营子凹陷地质概图
1—测线位置;2—正断层;3—逆断层;4—逆冲推覆构造;5—侵入岩;6—第四系;7—白垩系义县组(K1y);8—侏罗系髫髻山组(J2t);9—侏罗系邓杖子组(J2d);10—侏罗系海房沟组(J2h);11—二叠系石盒子组(P2s);12—寒武系-奥陶系并层(∈-O);13—中-新元古界并层
Fig.1
Geological sketch of Niuyingzi depression
1—line position;2—normal fault;3—reverse fault;4—thrust fault;5—intrusive rock;6—Quaternary;7—Cretaceous Yixian formation;8—Jurassic Tiaojishan formation;9—Jurassic Dengzhangzi formation;10—Jurassic Haifanggou formation;11—Permian Shihezi formation;12—Cambrian-Ordovician strata;13—Mesoproic-Neoproterozoic strata
根据牛营子地区实测物性标本提出该地区电性分层方案,如表1所示。侏罗系北票组泥砂互层夹煤线,海房沟组砾岩夹煤层与寒武系、奥陶系、中-新远古界碳酸盐岩地层有明显的电阻率差异:泥岩、砂岩电阻率一般小于220 Ω·m(均值约为130 Ω·m),表现为低阻,碳酸盐岩地层电阻率一般大于 2 000 Ω·m(均值约为6 300 Ω·m),表现为相对高阻。侏罗系泥、砂互层地层呈低阻的电性特征,中元古界碳酸盐岩地层呈高阻电性特征,二者差异明显,这是使用广域电磁法勘探的良好物性前提,如有侏罗系泥岩、砂岩层存在则在电阻率断面上会呈现出明显的低阻特征。
Table 1 Statistical table of physical parameters
| 地-电分层 | 代号 | 主要岩性 | 标本数 | 电阻率范围/(Ω·m) | 电性特征 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 侏罗系土城子组 | J3t | 粉砂岩、含砾粉砂岩 | 37 | 102~172 | 低阻 |
| 侏罗系髫髻山组 | J2t | 安山岩、角砾熔岩 | 62 | 562~846 | 次低阻 |
| 侏罗系海房沟组 | J2h | 复成分砾岩、砂岩、页岩夹煤线 | 32 | 163~220 | 低阻 |
| 侏罗系北票组 | J1b | 泥岩、砂岩夹煤线 | 27 | 110~130 | 低阻 |
| 奥陶系 | O | 灰岩、白云岩 | 29 | 5100~9150 | 高阻 |
| 寒武系 | ∈ | 泥晶灰岩 | 24 | 2073~6304 | 次高阻 |
| 青白口系 | Qb | 灰岩、白云岩 | 50 | 6367~13497 | 高阻 |
| 洪水庄组 | Jxh | 粉砂质泥岩、钙质页岩 | 32 | 192~231 | 低阻 |
| 长城系—蓟县系雾迷山组 | Ch-Jxw | 白云岩、灰岩、砂岩 | 185 | 1496~9672 | 次高阻 |
| 太古宇 | Ar | 斜长角闪岩、变粒岩、片麻岩 | 67 | 3208~3906 | 次高阻层 |
| 岩体 | γ | 花岗岩 | 65 | 5226 | 次高阻体 |
2 工作原理及方法
广域电磁法因场源不同分为电流源广域电磁法和垂直场源广域电磁法。本次研究的地质体碳酸盐岩与泥岩、砂岩层电阻率差异显著,因此采用电流源广域电磁法进行勘探。该方法采用一对接地电极形成电流源作为人工接地场源,测量电磁场中的某个电磁场分量,从而计算广域视电阻率,达到探测不同埋深地质目标体的目的。
均匀地表之水平电偶极源激励的电场x 分量可表示为
广域电磁视电阻率可定义为
式中:
测线布置如图1所示。2条测线长都是5 km,总长度10 km,L1线垂直构造带,L2线与L1线过牛地1井呈“十”字交叉,点距100 m,总物理点102个。仪器采用中南大学研发的广域电磁仪,测量频率是3、5、6、7、9、11频组,频率范围是 0.015 625~8 192 Hz,发射总电流80 A,发射电压700~800 V,1线的收发距离为17.8 km,2线的收发距离为15.1 km。
3 广域电磁法探测有效性分析
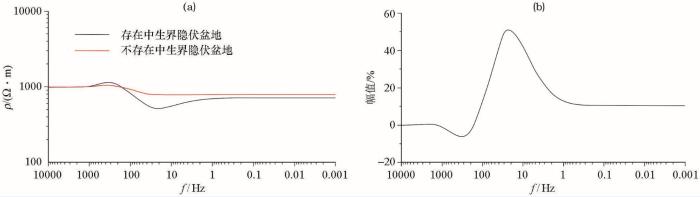
根据区内的物性资料统计,以中生代隐伏盆地为目标层,大体可分为三个电性层,自上而下分别为:①中新元古界长城系—蓟县系,岩性以白云岩、灰岩为主,为高阻层,厚度约1 000 m;②中生界侏罗系北票组,岩性为砂岩、泥岩及煤层,为中低组层,厚度约为500 m;③古生界寒武系—奥陶系,岩性以灰岩为主,为中高阻层,厚度约为800 m。
图2
图2
广域电磁法正演曲线视电阻率曲线对比(a)及异常幅值(b)
Fig.2
The wide filed apparent resistivity curve comparison(a) and the abnormal amplitude (b)
4 资料处理及解释
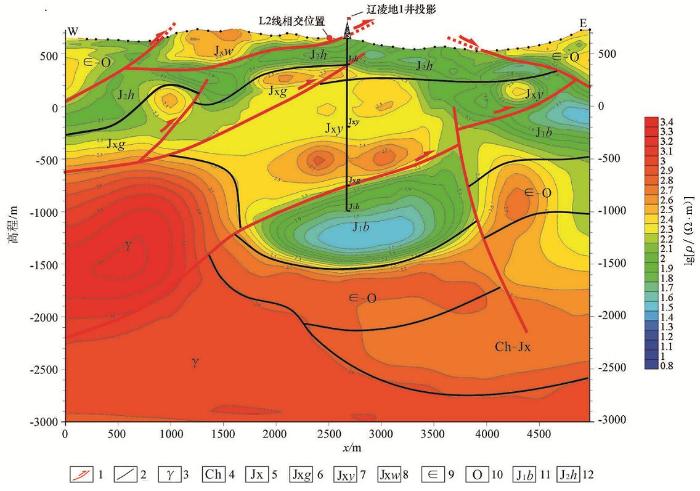
图3
图3
牛营子凹陷L1测线广域电磁法视电阻率反演解释剖面
1—逆冲推覆构造;2—地层界线;3—花岗岩体;4—长城系;5—蓟县系;6—蓟县系高于庄组;7—蓟县系杨庄组;8—蓟县系雾迷山组;9—寒武系;10—奥陶系;11—侏罗系北票组;12—侏罗系海房沟组
Fig.3
The apparent resistivity inversion profile of wide fieldelectromagnetic sounding of L1 line in Niuyingzi depression
1—thrust fault;2—stratigraphic boundary;3—granitic pluton;4—Changchengian;5—Jixianian;6—Jixianian Gaoyuzhuang formation;7—Jixianian Yangzhuang formation;8—Jixianian Wumishan formation;9—Cambrian;10—Ordovician;11—Jurassic Beipiao formation;12—Jurassic Haifanggou formation
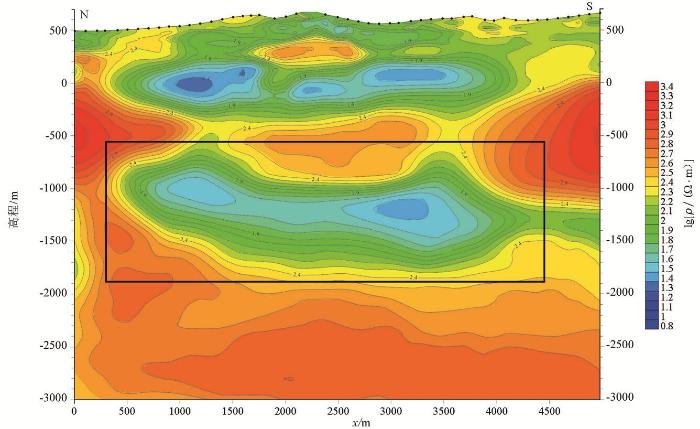
图4
图4
牛营子凹陷L2测线广域电磁法视电阻率反演解释剖面
Fig.4
The apparent resistivity inversion profile of wide fieldelectromagnetic sounding of L2 line in Niuyingzi depression
为100~150 Ω·m,显示为低阻,是第四电性层;海拔-1 600~-2 300 m的电阻率值为 1 500~3 000 Ω·m,显示为高阻,为第五电性层。
L1测线上地表至海拔高程300 m范围的电阻率值为800~1 200 Ω·m,显示为次高阻,是第一电性层;海拔高程300~-100 m的电阻率值为150~250 Ω·m,显示为低阻,是第二电性层;海拔-100~-900 m的电阻率值为1 000~3 000 Ω·m,显示为高阻,是第三电性层;海拔-900~-1 600 m的电阻率值整体来看,电阻率断面分层清晰且构造上能很好地反演出双重逆冲构造样式。结合之前地质工作和岩石标本电性测试数据,认为第一电性层为中元古界蓟县系雾迷山组灰岩和白云岩,第二电性层为中生界侏罗系海房沟组组砾岩、砂岩、粉砂岩,第三电性层为中元古界蓟县系杨庄组和高于庄组灰岩、白云岩,第四电性层为中生界侏罗系北票组泥岩、砂岩,第五电性层为古生界碳酸盐岩。
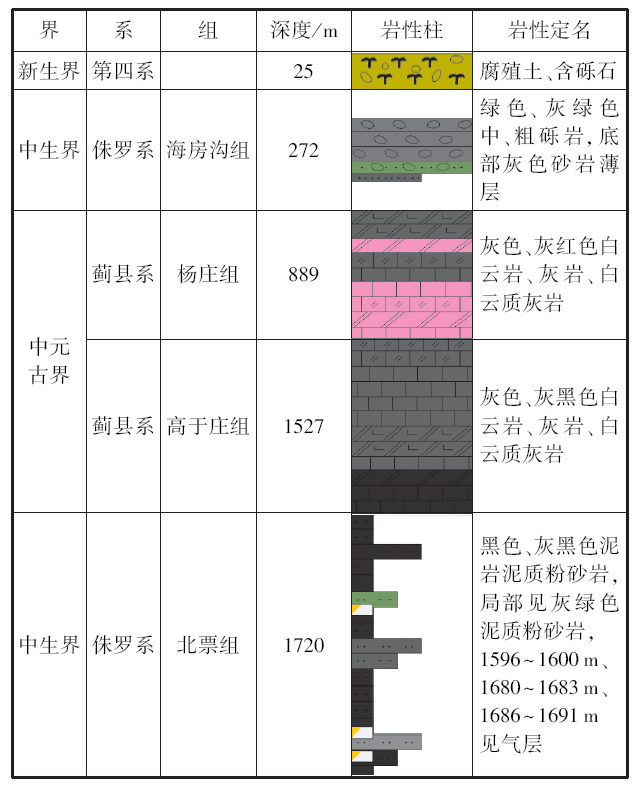
该电阻率断面纵向上电阻率变化梯度大,特别是海拔-900~-1 600 m的第四电性层,低阻特征明显,电性特征与上下岩层差异大。该低阻层推测为北票组泥岩,之前在牛营子凹陷区域地质调查和基础油气调查过程中未见有北票组大套的厚层泥岩,燕辽沉降带东部中新元古界碳酸盐岩推覆体下亦未发现过此套泥岩。为确定中新元古界碳酸盐岩推覆体下侏罗系北票组泥岩存在与否,以L1广域电磁法反演电阻率解释剖面图作为主要依据,结合地表露头观察及实测剖面,部署了一口地质井——辽凌地1井。该井在1 527 m钻穿上覆中元古界推覆体,钻遇该套低阻泥岩层,如图5所示。
图5
从图可以看出辽凌地1井于广域电磁剖面与L1线广域电磁法反演电阻率解释剖面图的对应性极好,说明广域电磁法在牛营子凹陷这种构造复杂的小型凹陷有极佳的适用性,很好地印证了广域电磁法在本地区油气勘探的有效性。
5 结论
运用广域电磁法在辽西牛营子凹陷开展探测研究,将该方法首次应用于燕辽沉降带东部构造复杂且被中元古界碳酸盐岩推覆体覆盖的小规模凹陷,取得了良好的效果。
本次探测丰富了燕辽沉降带东部的勘探层系,首次揭示了燕辽沉降带东段牛营子凹陷中元古界蓟县系高于庄组之下隐伏着一套厚度较大的低阻北票组地层,并得到钻孔验证,将该地区原有的中新元古界单一勘探层系拓展为中新元古界黑色碳酸盐岩地层和中生界北票组泥岩两套油气勘探层系。
广域电磁法是圈定牛营子凹陷下伏北票组烃源岩分布范围和埋深的有效探测手段,此次工作对今后在同类型盆地开展油气工作具有参考意义。
参考文献
凌源—宁城盆地中元古代早期盆地构造演化过程研究
[J].凌源-宁城地区位于燕辽沉降带东部(如图1),在中新元古界时期沉降缓慢、地层发育齐全、厚度巨大,且变质作用较小,具有较好的生烃潜力和油气勘探价值。
Study on tetonic evolution process of early mesoproterozoic in Lingyuan—Ningcheng basin
[J].
Early mesozoic deformations of the eastern Yanshan thrust belt,borthern China
[J].
DOI:10.1007/s00531-009-0417-5
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The Yanshan thrust belt (YTB) is located at the northern edge of the North China plate. Because of the intense thicking and subsequent delamination of the lithosphere in north China, geologists have been focused on the Late Mesozoic deformation in the Yanshan belt. The Yanshan belt has been regarded as part of a stable craton from the Proterozoic to the early Mesozoic. In this paper, the authors present that the Yanshan area was deformed during the early Mesozoic. This deformation could be related to ocean basin closure along the northern margin of North China, or related to the collision between the north China and Yangtze Plates along the Qinling-Dabie ultrahigh pressure belt. Three stages of early Mesozoic deformation are identified in the eastern Yanshan at Lingyuan County. The first stage is characterized by westward thrusting (D1), the second stage comprises a top-to-east thrust system (D2), and the third stage comprises extensional gravity-induced collapse and landsliding (D3). The timing of these evens is constrained by both the crosscutting relationships of faults and the isotopic dating of volcanic rocks and gravels. The D1 and D2 events took place in the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic, whereas D3 event occurred at the end of the Middle Jurassic. The Dengzhangzi formation was deposited during the D1-D2 period and recorded a rapid uplift, erosion, and deposition sequence. These early Mesozoic contractional deformations in the YTB were probably related to the closure of ancient Asian ocean and ancient Qinling ocean. The later crustal extension was caused by gravitational collapse of the eastern China plateau during early Mesozoic.
Carboniferous-Permian sedimentation on the northern margin of north China: implications for regional tectonics and climate change
[J].
DOI:10.2747/0020-6814.47.3.270
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The Late Paleozoic collision between the North China continental block and the Altaid arc terranes of Mongolia represents one of the earliest and most fundamental tectonic events in the ongoing construction of Asia. New detrital zircon provenance data from Carboniferous-Permian nonmarine strata on the northern margin of North China imply that the northern margin of the North China block constituted a continental margin arc prior to this collision (~400-275 Ma) and that collision took place via south-directed subduction beneath North China.
Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the Yanshan fold and thrust belt, with emphasis on Hebei and Liaoning provinces
[J].
Yanshanian compression and extension in the Yan-shan area(in Chinese with English abstract)
[J].
Tectonics if the Mesozoic wide extensional basin system in the China-Mongolia border region
[J].
DOI:10.1046/j.1365-2117.2003.00209.x
URL
[本文引用: 1]

he China-Mongolia border region contains many late Mesozoic extensional basins that together constitute a regionally extensive basin system.Individual basins within the system are internal ly composed of a family of sub-basins filled with relatively thin sedimentary piles mostly less than 5 km in thickness.There are two types of sub-basins within the basins,failed and combined,respectively. The failed sub-basins are those that failed to continue developing with time.In contrast,the combined ones are those that succeeded in growing by coalescing adjacent previously isolated subbasins. Thus,a combined sub-basin is bounded by a linked through-going normal fault that usually displays a corrugated trace on map view and a shallower dip on cross-section.Along-strike existence of discrete depocenters and alternation of sedimentary wedges of different types validate the linkage origin of combined sub-basins.Localized high-strain extension resulted in large-amount displacement on linked faults,but contemporaneously brought about the cessation of some isolated fault segments and the formation of corresponding failed sub-basins in intervening areas between active linked faults.Some combined sub-basins might have evolved into supradetachment basins through time,concurrent with rapid denudation of footwall rocks and formation of metamorphic core complexes in places.A tectonic scenario of the broad basin system can be envisioned as an evolution from early-stage distributed isolated sub-basins to late-stage focused combined or/and supradetachment sub-basins bounded by linked faults,accompanied by synchronous cessation of some early-formed sub-basins. Initiation of the late Mesozoic extension is believed to result from gravitational collapse of the crust that had been overthickened shortly prior to the extension.Compression,arising from collision of Siberia and the amalgamated North China-Mongolia block along the Mongol-Okhotsk suture in the time interval from the Middle to Late Jurassic,led to significant shortening and thickening over a broad area and subsequent extensional collapse.Pre-and svn-extensional voluminous magmatism must have considerably reduced the viscosity of the overthickened crust,thereby not only facilitating the gravitational collapse but enabling the lower-middle crust to flow as well.Flow of a thicker crustal layer is assumed to have occurred coevally with upper-crustal stretching so as to diminish the potential contrast of crustal thickness by repositioning materials from less extended to highly extending regions.Lateral middle-and lower-crustal flow and its resultant upward push upon the upper crust provide a satisfying explanation for a number of unusual phenomena,such as supracrustal activity of the extension,absence or negligibleness ofpostrift subsidence of the basin system,less reduction of crustal thickness after extension,and non-compression-induced basin inversion,all of which have been paradoxical in the previous study of the late Mesozoic basin tectonics in the China-Mongolia border region.
广域电磁法在湘西北页岩气探测中的应用
[J].将广域电磁法应用于湘西龙山地区的碳质页岩探测,揭示了该区碳质页岩的含碳量较高,相对上、下地层显示为低阻的特征。采用自主研发的“重磁电三维反演成像解释一体化系统”进行广域电磁法数据处理,获得了地下电性体真实的电阻率特征,基本查明龙山地区碳质泥页岩层位的电性分布规律。表明广域电磁法是获取碳质页岩分布范围和埋深的有效探测手段。
Shale gas detection with wide field electromagnetic method in north-western Hunan
[J].
广域电磁法在南华北盆地长山隆起页岩气资源潜力评价中的应用
[J].
DOI:10.11720/wtyht.2017.2.28
URL
[本文引用: 1]

采用广域电磁法在南华北盆地长山隆起地区进行探测,基本查明了工作区内基底起伏、埋藏深度和地层在空间上的主要分布,揭示了低阻区域的埋藏深度和厚度,从而确定了寻找页岩层的有利地段,解释结果得到钻孔验证,取得了较好的地质效果。勘探成果为确定页岩气开采"靶区"和"甜点区"提供了极为有用的地质地球物理信息,同时验证了广域电磁法探测页岩气赋存地层的有效性。
Shale gas potential assessment of Changsan uplift area in southern north China basin by using wide field electromagnetic method
[J].
用广域电磁法勘查深层地热资源
[J].
DOI:10.11720/wtyht.2017.4.14
URL
[本文引用: 1]

使用广域电磁法勘查了江苏省仪征市捺山地区的深层地热资源,查明了工区的第一热水储层和第二热水储层,钻遇储层出水量大、温度高。勘查结果显示广域电磁法是一种高效的深层地热能资源地球物理勘查方法,具有深度大、分辨率高、野外数据采集快等优点,勘查深度超过1 500 m,是深层地热能资源勘查主要的地球物理勘查方法。
Exploration of deep geothermal energy resources with wide field electromagnetic method
[J].
广域电磁测深法研究
[J].根据水平电流场源和垂直磁场源在半均匀空间地面的电磁场解析表达式,定义了广域视电阻率,建立1种新的频率域测深方法即广域电磁测深法。研究结果表明:采用广域电磁测深法可以在过渡带进行测量,即以较小的收发距探测到较大的深度;广域电磁法包括E-Ex广域电磁测深和E-Ez广域电磁测深等方式,每种方式各有其特点,而且都只测量1种物理量;广域电磁法与2n序列伪随机电法相结合还可以发展成2n序列伪随机信号-广域电磁法,不但探测深度大,而且效率高,广域电磁法可用于寻找火山岩油气藏、深部金属矿和工程电法勘探。
Wide field electromagnetic sounding methods
[J].
Petrogenesis of the Middle Devonian Gushan diorite pluton on the northern margin of the North China block and its tectonic implications
[J].
广域电磁法在保靖页岩气勘探中的应用
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2016.04.003
URL
[本文引用: 1]

在我国南方地区,复杂的地形和地下构造限制了常规地震勘探方法在页岩气勘探中的使用,如何充分、合理地发挥非地震勘探方法的技术优势,是页岩气勘探中必须面对的问题。为此在湖南保靖地区使用广域电磁法,以龙马溪组和牛蹄塘组为目的层,进行页岩气勘探,并对勘探成果进行解释,确认了该地区页岩气目的层具有低电阻的特征,基本查明了该地区页岩气主要目的层的分布规律。勘探结果表明,龙马溪组和牛蹄塘组具有使用电磁法勘探的电性基础;广域电磁法作为一种非地震的电磁勘探方法,具有在复杂地形和地下构造地区进行页岩气勘探的能力。该结果为电磁勘探方法在页岩气勘探中的应用提供了重要依据,促进了我国南方页岩气勘探方法技术的完善。
The exploration of wide field electromagnetic mehtod on shale gas
[J].