0 引言
地—井瞬变电磁法是在钻孔上方或钻孔附近的地面上发射,用接收探头在钻孔中逐点测量发射电流关断后地下地质体中感应的瞬变电磁二次场,它不是测井方法,而是一种地—井物探方法。用该方法测量时,接收探头与勘查对象距离较近,受导电覆盖层和电磁干扰小,故较地面TEM更易发现深部的隐伏矿体;该方法可在钻孔周围一定范围内,最大限度地发现井旁及井底矿体,还可对钻孔已见的良导目标体进行定位并追踪其延伸方向。
在国外,地—井TEM方法的研究始于20世纪70年代,80年代获得快速发展,90年代初期三分量仪器便得以商品化,目前该方法在加拿大、澳大利亚等国已被广泛应用。近二十多年来,国内在地—井TEM方法上亦开展了较多的研究工作,研究内容主要集中在方法理论方面,国内地—井TEM工作所使用的仪器设备均需从国外进口,但进口设备的高价格以及下井设备的高风险,制约了该项技术的开展和应用。为此,依托国土资源部公益性行业科研专项经费项目,我们从仪器设备、测量方法技术、处理解释软件等方面进行了系统的研究,希望能推动该方法技术在国内走向实用化。
1 IGGETEM4.0三分量地—井TEM系统
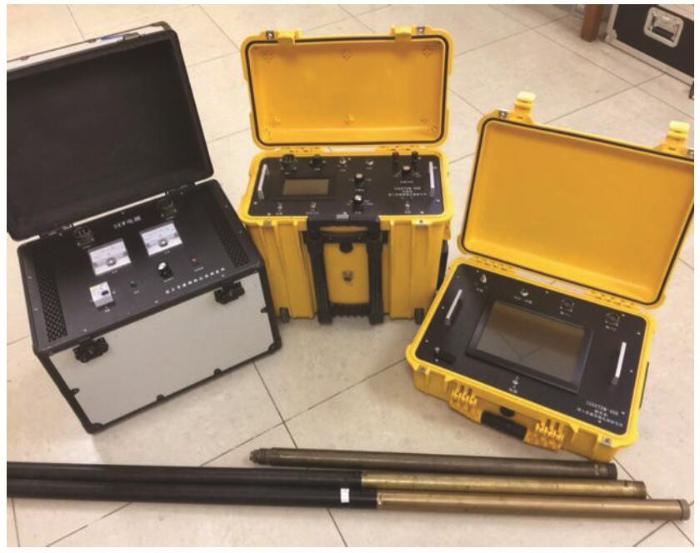
图1
图1
三分量TEM整流器、发射机、接收机及探头
Fig.1
Rectifier, transmitter, receiver and probes of the thre-component TEM system
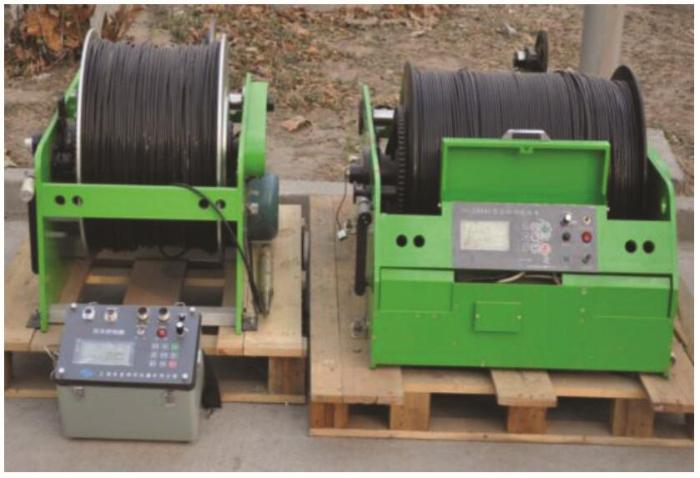
图2
图2
1 000 m、2 000 m塑胶电缆专用绞车
Fig.2
Special winches for 1 000 m and 2 000 m plastic cables
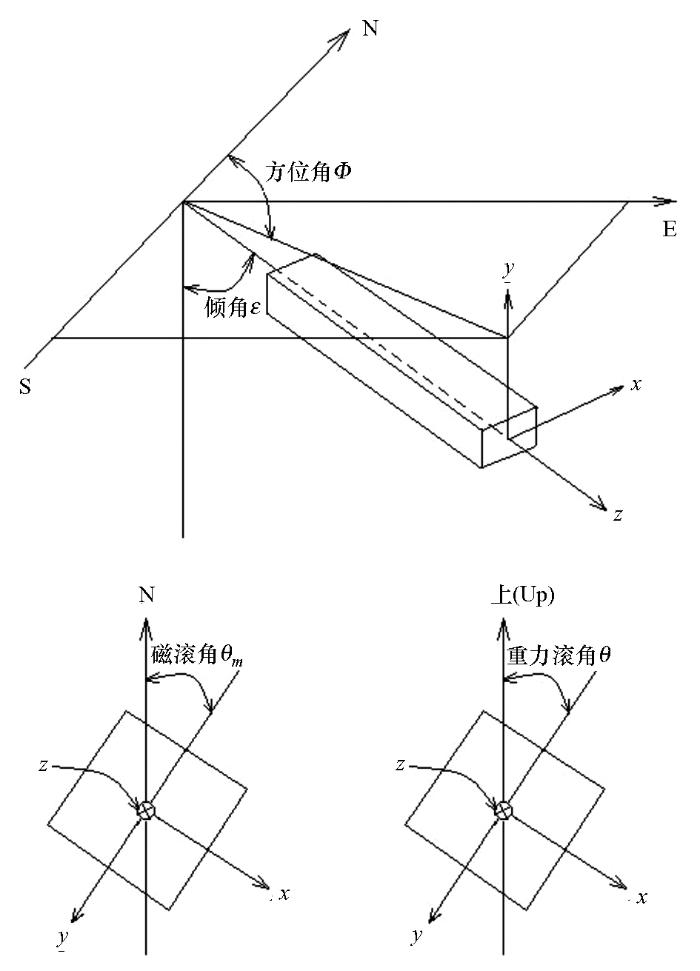
2 三分量坐标系的确定
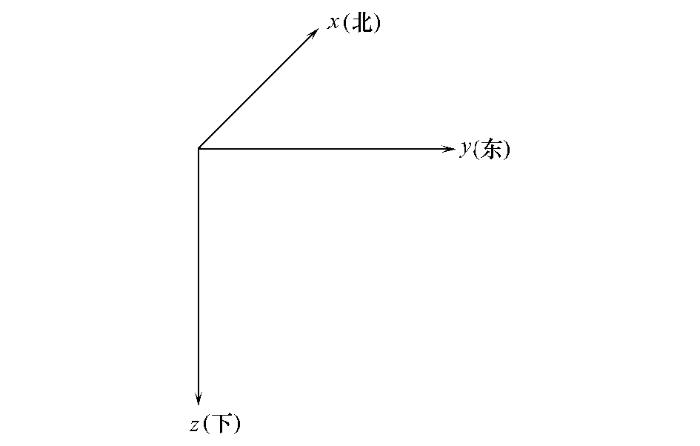
地—井TEM坐标系目前尚不统一,本文定义的坐标系如图3所示。如此定义坐标系的理由有三:x为北、y为东,这样可使其与大地坐标的北(x)、东(y)一致,亦即与地形图的坐标一致;z为下,与瞬变电磁教科书的多数示意图中的磁场方向一致;x、y、z三个分量的正方向适用于右手定则(右手笛卡尔坐标系)。
图3
3 探头角度系统偏差的测定
TEM探头在井中是可以自由转动的,即探头中的x、y线圈的方向是不可控的,探头在井中各测点的转角、倾角及方位角等参数由安装在同一探头中的定向器给出。在安装探头中的TEM线圈和定向器时,难以使得TEM线圈的北(x)、东(y)与定向器相应的北、东轴完全一致,为此,每个探头成为产品之前均须通过实际测量,测定出TEM线圈的x、y线圈的法线方向与定向器北、东轴的角度偏差。
为测得这些角度数据,制作了专门装置。装置上包含一个与该装置固定在一起的可发射磁场的线圈,当该线圈的角度被确定时,通过旋转探头使TEM线圈接收的值达到最大或最小的方式确定出TEM线圈的角度,而此时同时读取测向器的重、磁参数并计算出相应角度,TEM线圈的角度与测向器相应角度之差便是我们需要的角度偏差值。
TEM线圈的北、东、下各轴与测向器相应轴的夹角在下文中计作:φx、φy、φz。角度偏差测定的具体装置情况及具体测量过程可参见参考文献[3]。
4 三分量的校正运算
4.1 井中定向器角度的计算
各厂家的定向器其坐标系定义不尽相同,由定向器测量结果计算的滚角、倾角、方位角的表达式便不同。文中用图3中的地—井TEM坐标系来定义定向器的x、y、z坐标,在此坐标系下,整理的各角度的计算公式如下。
1)由重力参数计算重力滚角θ:
2)由磁性参数计算磁滚角θm:
3)由重力参数计算倾角ε:
4)由重力、磁性参数计算的方位角ϕ:
Hx'=
Hy'=
Hz'=
cosϕ=
sinϕ=
tanϕ=
上述各式中,Hx、Hy、Hz、gx、gy、gz分别为测向器测得的磁性及重力参数;g、Hx'、Hy'、Hz'、
图4
4.2 TEM三分量的校正计算
TEM探头测得的分别是x、y、z各线圈法线方向上的感应电动势的值,为将全井的观测结果校正至图3的地—井TEM坐标系,推导出校正计算公式。
1)倾角ε<3.0度时的校正计算:
Vxy0=(
Vz=Vz0·cos(ε-φz)+Vxy0·sin(ε-φz) ,
Vx=Vx0·cos(θm-φx)-Vy0·sin(θm-φy) ,
Vy=Vx0·sin(θm-φx)+Vy0·cos(θm-φy) 。
2)倾角ε>=3.0度时的校正计算:
Vx=
Vy=
Vz=Vz0·cos(ε-φz)+
上述各式中:Vx0、Vy0、Vz0为实测的感应电动势数据;φx、φy、φz分别为TEM线圈的北、东、下轴至测向器相应轴的夹角(逆时针为正,顺时针为负);
5 数据处理
地—井瞬变电磁数据处理内容包括:数据编辑、滤波,三分量校正运算,异常识别及分析处理。
6 应用效果
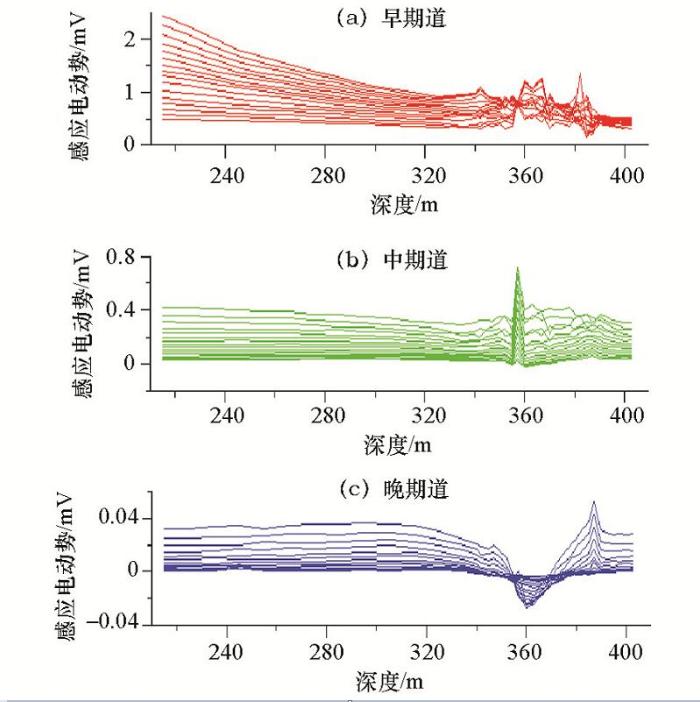
运用自行研制的IGGETEM4.0地—井瞬变电磁仪器系统,在新疆哈密白石泉506钻孔中开展了测量工作,下述三组图分别为x、y、z三个分量的感应电动势剖面。
图5
图5
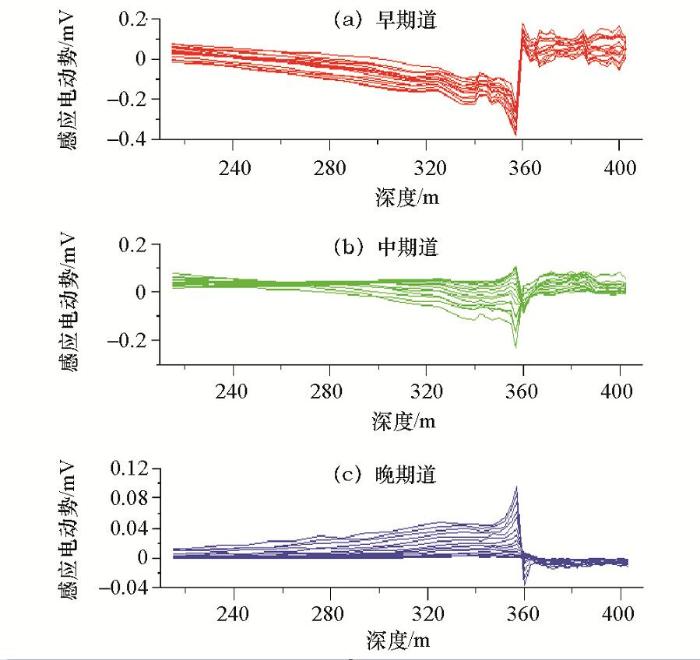
白石泉506钻孔x分量早、中、晚期感应电动势剖面
Fig.5
X-component profiles of induced electromotive force in early,middle and late stages of Baishiquan 506 borehole
图6
图6
白石泉506钻孔y分量早、中、晚期感应电动势剖面
Fig.6
Y-component profiles of induced electromotive force in early, middle and late stages of Baishiquan 506 borehole
图7
图7
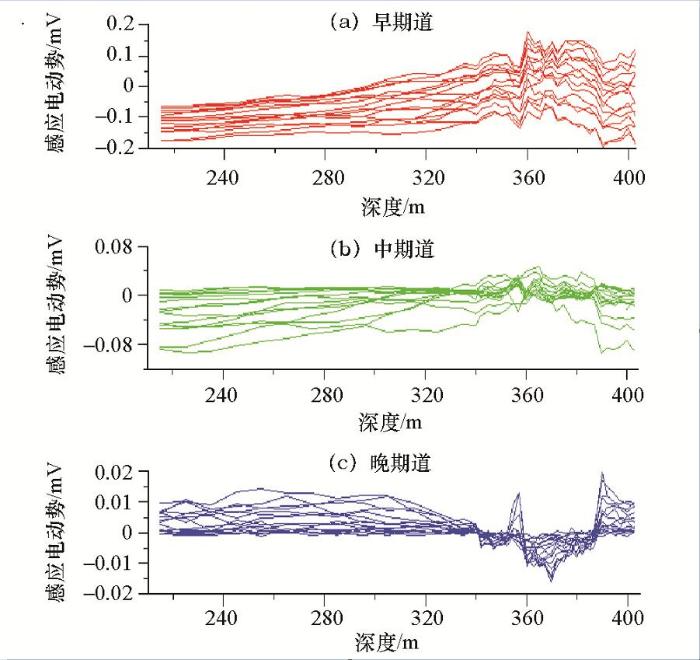
白石泉506钻孔z分量早、中、晚期感应电动势剖面
Fig.7
Z-component profiles of induced electromotive force in early, middle and late stages of Baishiquan 506 borehole
z方向:在360 m深度处,早期为弱的正异常,钻孔在该处穿过低阻体(边缘);晚期为负异常,表明钻孔旁侧有低阻体,由异常衬度可见,该低阻体规模较大。
x、y方向:由早期x、y感应电动势剖面曲线可见,钻孔穿过低阻体,该低阻体向南倾斜,其主体位于钻孔西侧偏北;由晚期x、y感应电动势剖面曲线可见,钻孔旁侧有较大规模的低阻体,该低阻体向北倾斜,其主体位于钻孔东侧偏南。
在x、y、z的中期道,由于钻孔所穿过低阻体异常(正异常)与钻孔东侧较远处的低阻体的异常(负异常)反向,两种异常在中期道相互抵消,故中期道感应电动势相对早、晚期而言异常不够明显。
7 结论与建议
经实际勘查工作检验,这套地—井瞬变电磁法系统性能稳定,测量结果是正确的;经多次测试,开发的三分量校正计算软件,计算结果正确,研制的数据处理程序可基本满足勘查工作的需要。
这套自主研发的地—井瞬变电磁法系统已基本接近实用,并初步形成为一套较完整的应用技术,建议对该系统做进一步的完善并加大推广使用的力度,以使我国可更快、更好、更广泛地开展地—井瞬变电磁法的勘查工作。
致谢:在地—井瞬变电磁法系统的实用化应用中,得到了新疆地质矿产勘查开发局第六地质大队、青海省第三地质矿产勘查院、内蒙古国土资源勘查开发院的大力支持,在此表示感谢。
参考文献
瞬变电磁 (TEM)数据组合滤波
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2002.z1.036

随着TEM方法理论的不断进步,其正反演计算及解释在理论上已基本成熟,为取得良好的勘测效果,如何从观测数据中去除干扰,获得良好、可靠的原始信息变得至关重要,故就此问题进行探讨.
TEM data composite filter
[J].
TEM井中磁探头的校准装置及校准方法:发明专利证书号第2231480号
[P].
中国地质科学院地球物理地球化学勘查研究所
.
Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration
地—井瞬变电磁资料矢量交会解释方法
[J].
DOI:10.11720/wtyht.2015.3.23
URL
Magsci

<p>以往地—井瞬变电磁法资料解释研究主要为定性解释。本文在瞬变电磁等效涡流的理论基础上,通过研究等效场矢量的空间特征,发现感应二次场矢量的方向与一次场强度、观测点距离及观测时间均无关,只与观测点的方位有关,经简单的修正,二次场特征矢量就可以交会于异常中心位置。研究的地—井瞬变电磁矢量交会法是一种新的定量解释方法,该方法通过绘制每个测点的特征矢量,根据异常区矢量交会于一点的规律,确定异常中心位置。分别采用理论模型和实测资料对该方法进行了验证,结果表明矢量交会法能够对井旁盲矿中心位置进行较准确地定位。</p>
A study of vector intersection for borehole transient electromagnetic method
[J].
电性源地—井瞬变电磁法三分量响应特征分析
[J].地-井瞬变电磁法是在地面发射,井(钻孔)中接收的装置形式,能够利用已有钻孔使接收探头深入地下更加接近矿体,获得更加可靠的目标体信息.文中针对复杂地形地区矿区深部找矿面临的实际问题,提出了电性源地-井瞬变电磁法的思路,并以FDTD正演模拟来研究均匀半空间瞬变场的空间分布以及一维、三维模型钻孔中的三分量瞬变响应特征,以期获得理论模型三分量响应特征规律,为实际勘查提供参考.理论模型计算结果表明,电性源地-井TEM方法三分量瞬变响应曲线对于电性界面、异常体具有良好的反应.
Analysis of three component TEM response characteristic of electric source dill hole TEM
[J].
大地介质影响下地—井瞬变电磁的正演模拟分析
[J].对大地介质影响下地-井瞬变电磁响应特征规律进行了研究.基于时域有限差分法和Mur吸收边界条件对不同观测方式('定源-异井位观测'和'方位观测')下典型地电模型(均质半空间和含浅部低阻层的半空间介质)中三维体的地-井瞬变电磁响应进行了正演模拟,认为观测所得响应是围岩背景场与目标体异常场共同作用的结果,提出大地介质会影响观测结果的观点.研究结果表明:围岩背景场越强,总响应的异常特征越弱;随着观测延时的增加,背景场对总响应的影响减弱;受导电介质影响的观测曲线在剖面形态和衰减特征上与高阻围岩的典型解释模型存在差别.研究结果为相关资料解释工作提供了理论依据.
Forward simulation of surface-borehole TEM in geological medium effect
[J].
地—井瞬变电磁法三维正演研究
[J].
DOI:10.13810/j.cnki.issn.1000-7210.2015.03.025
URL
Magsci

地—井瞬变电磁法是一种使用较多的瞬变电磁法工作装置。鉴于现今国内外对其正演研究还比较少, 在此实现了基于一维解析法和矢量有限单元法的地—井瞬变电磁法一维和三维正演。通过对比层状介质的一维解析解和水平板状体地电模型的数值解, 验证了矢量有限单元法用于模拟地—井瞬变电磁法的有效性; 通过对低阻块状体地电模型进行三维正演, 分析总结了矩形回线源激发瞬变电磁场随时间和深度变化的扩散规律。
Three-dimensional forward modeling for surface-borehole transient electromagnetic method
[J].
Discovery of a largescale porphyry molybdenum deposit in tibet through a modified TEM Exploration Method
[J].uring the last decade,there have been many exploration achievements in the Tibetan Gangdese metallogenic bell.The Sharang area of the Tibetan region is covered by a lowtemperature mineralized alterable clay that is considered to be a low-grade ore.Although small intervals of rich molybdenum(Mo) mineralization have been discovered,the ore deposit scale is limited and the condition of deep ore is still unknown.To explore these deeper targets,a modified large-loop TEM system was used in the Sharang area.The TEM receiver configuration is redesigned and the late-time resistivity equation of large-loop TEM has also been defined.During data processing,two regions with low resistivity anomalies were discovered.The interpreted results indicate that the main ore deposit is buried 200 m beneath the surface,and extends 600 m vertically.The total anomalous area associated with the ore deposit is estimated at 3.77 km~2.The interpretation results are consistent with drilling data acquired after the geophysical survey.The results show that it is the first ultra-large porphyry molybdenum deposit that has been found in Tibet.
Numerical simulation analysis of surface-to-borehole TEM based on the finite difference method
On smoke rings produced by a loop buried in a conductive half-space
[J].
DOI:10.1190/geo2015-0002.1
URL

The transient electromagnetic (TEM) response of a wire loop at the surface of the earth has been studied in detail for several decades. When current in the loop is rapidly switched off, an identical system of current, commonly referred to as a moke ring, is induced in the conductive subsurface and diffuses downward and outward into the earth. What has not been studied as thoroughly is the response of a loop buried within a conductive medium, as might be the case in the marine environment or when TEM prospecting systems are placed in mine tunnels or horizontal boreholes. We have examined the TEM response of a horizontal wire loop buried within a conductive half-space. Expressions were derived for the azimuthal electric field and corresponding vertical and radial magnetic fields. Our results showed that when the loop is far from the earth-air interface, a single smoke ring system diffuses radially outward from the transmitter, while the electric field and corresponding current density decays away in the vertical direction. As the loop approaches the interface, the smoke ring system diffuses radially at early times, but gradually, the complex image of the loop in the air produces a system of secondary azimuthal electric fields, which, when combined with the primary field, adds a vertical component to the field diffusion. At late times, the field behavior reduces to the well-known surface case and the maximum current system diffuses downward at a constant angle of 26 with respect to the plane of the loop. We concluded that it was the effect of the interface that produces the downward migration of a smoke ring system, whereas the outward migration is mainly generated by the primary field.
Inversion of surface and downhole electromagnetic data for a 3D earth
Modelling of drill-hole TEM response from multiple targets covered by a conductive overburden
[J].
DOI:10.1071/eg996141
URL

A number of transient electromagnetic (TEM) analogue modelling projects have been carried out at CSIRO to compile suites of model responses for surface, drill-hole and airborne surveys. The drill-hole modelling described in this paper has been carried out to determine the response of targets in free space and covered by overburden. The objective of this modelling was specifically to investigate the effect of inductive interaction between a conductive overburden and electrically-isolated targets beneath it, and to examine the effect of current channelled from the overburden into a target in electrical contact with it. For the experiments discussed here, a model consisting of two parallel plate targets with a dip angle of 45 and covered by a conductive overburden was employed. Measurements were made both with and without the overburden present. The modelling results show that for cases of simple conductors without overburden, the characteristics of the drill-hole TEM responses can be understood in terms of the geometrical relationship between the transmitter loop, the drill-hole receiver probe, and the conductive targets. However, the modelling experiments demonstrate that the presence of a conductive overburden can significantly alter the drill hole response. Inductive interaction between the overburden and targets can be large enough to cause polarity reversals of the drill-hole response of the targets. Additionally, when the upper target is in electrical contact with the overburden, current channelling produces a galvanic current that may suppress or enhance peaks in the drill-hole profiles. When interpreting field data with the use of superposition of responses from various components of a given model, unexpected polarity reversals and enhanced or suppressed peak responses in the field data could be explained by these two effects.
Inversion of array induction logs and its application
[J].
DOI:10.1007/s12182-007-0005-x
URL

With the help of the modified geometrical factor theory, the Marquardt method was used to calculate the true electrical parameters of the formation from array induction logs. The inversion results derived from the assumed model and some practical cases show that the rebuilt formation profile determined by 2-ft resolution array induction logs is reasonable when the formation thickness is greater than 1 m, which thus indicates that the inversion method is reliable and can provide quantitative information for the discrimination of oil/gas or water zone.
Three componet DHEM surveying at balcooma
[J].
DOI:10.1071/EG996077
URL

http://library.seg.org/doi/pdf/10.1071/EG996077