0 引言
目前我国正处于经济的快速发展时期,油气资源需求量与日俱增,油气资源供给已成为我国社会经济发展的重要障碍。虽然在整体上我国的油气储量比较丰富,但是从油气资源的实际探明储量,储采比数据来看,相对匮乏的油气资源难以满足我国处于快速工业化经济增长周期的油气资源需求[1]。随着油气勘探开发技术的发展,构造型油气藏的探明度不断提高,从而使发现大型整装油田的可能性降低,隐蔽型、裂缝型、深层等复杂油气藏已成为我国油气勘探开发的主要对象[2]。复杂油气藏具有地表条件复杂,构造复杂、储层厚度薄且分散、埋藏深等特征,造成地震记录中有效信号能量弱,噪声干扰发育,信噪比普遍较低,严重制约地震波场的准确偏移成像和有效目标的检测识别。因此,为了适应复杂地区、复杂油气藏勘探的需要,能更加全面和有效地利用地震资料,噪声衰减问题依然是地震资料处理的关键问题之一[3,4,5]。常规地震资料处理中使用的去噪技术有小波变换去噪、f-x域预测滤波[6,7]、KL变换[8,9]、SVD分解[10]等,f-x预测滤波会对相干信号进行增强,但由于高频段信噪比比较低,求取的预测算子受噪声影响较大,从而使得滤波后的高频段有效信号更易发生畸变,降低信号的保真度;KL变换与SVD分解主要利用相邻道信号在相同时刻的相关性,所以对水平同相轴具有较好的去噪效果,而处理倾斜或者弯曲同相轴时效果并不明显。这些方法为达到提高信噪比的目的,大多利用了信号的空间相干特性,但牺牲横向分辨率,容易使倾斜和弯曲同相轴受到影响,因此会模糊和压制一些细微的信号结构,如小断裂、细河道等,甚至还可能引起较大断距的断层两侧同相轴的错误连接,给精细的地震结构解释带来诸多不便。
对地震信号进行稀疏表示可以有效地揭示地震信号的本质特征,有利于形成对地震信号更为清晰和直观的描述和认识。信号的稀疏表示就是在变换域上利用尽量少的基函数重构逼近原始信号,从而获得原始信号简洁而有效的表达形式。目前常用的变换方法主要有小波变换[11]、Ridgelet变换[12]、Curvelet变换[13]等。信号处理中,通常也将常用的变换称作稀疏表示字典,将变换中的原子称作字典原子。小波变换具有很强的去数据相关特性,通过小波变换将信号能量被投影在少数小波系数上,而噪声能量却分布于整个小波域内,因此可对小波系数进行阈值处理以达到去噪目的。然而,地震数据不仅是关于时间的一维信号,还与波场记录的空间位置有关,通常情况下地震数据为二维甚至为高维信号。Candes和Donoho[13]构造出第二代Curvelet变换,他们直接在频域定义Curvelet原子的表达形式,并且给出第二代Curvelet变换的快速离散算法[14]。由于Curvelet变换在捕捉波前面方面具有独特优势,很快被广泛地应用到地震数据处理和解释问题中,如噪声衰减[15,16,17]、数据规则化[18]和多尺度相干分析[19]等等。Curvelet及Ridglet等变换虽然具有对复杂高维结构精细刻画能力,但由于其变换原子固定不变的特点,仍不具备根据待处理复杂地震数据自适应地调整字典原子以增加稀疏表示的能力。Olshausen等[20]提出了采用机器学习的方法来自适应地构造过完备字典,对待处理数据进行有效地稀疏表示。但是这种自适应学习字典由于没有固定的结构和快速算法,算法复杂度很高,不适合处理大规模地震资料处理。Rubinstein等[21]提出了一种基于双重稀疏概念的学习字典,在固定字典和自适应学习字典之间找到一个平衡点,一定程度上弥补了固定基函数和自适应学习字典的不足,吸收了两种字典的优点。笔者将这种双重稀疏字典引入到高维地震资料的噪声压制中,选取能够较好地对地震资料进行稀疏表示的过完备离散余弦变换作为训练基字典,采用OMP(orthogonal matching pursuit)算法进行稀疏编码,通过稀疏K-SVD算法进行字典学习,选取待处理的地震资料特征明显的部分作为训练样本,得到能够匹配地震资料的双重稀疏字典。通过3D模型及实际资料算例的结果表明,与基于Curvelet变换的去噪结果对比,基于双重稀疏表示的方法不仅可以有效压制地震资料随机噪声,而且在3D资料处理中能更好地保持有效边缘结构。
1 基于双重稀疏表示的信噪分离方法
1.1 双重稀疏字典构造
双重稀疏字典认为过完备学习字典本身就具有稀疏性,因此定义过完备学习字典D中的每个原子(即列向量)都可以用一个已知的基字典Φ来进行稀疏表示,此时的学习字典D为具有稀疏结构的字典,其字典结构可以表示为:
其中,矩阵A是原子表示矩阵,该模型认为原子表示矩阵A就也具有一定的稀疏性,即D中任意一列可用少数基字典Φ列向量及矩阵A的对应列表示,其中矩阵A对应列的非零元素个数是固定的(若用αi表示院子表示矩阵中的第i列,则有‖αi‖0≤p,p为常数)。
双重稀疏字典中,训练基字典A的选择至关重要,其决定了该双重稀疏字典对信号进行处理的效果,因此训练基字典A的选择在整个字典学习过程中变得至关重要。由于通过学习得到的学习类字典没有结构性而计算复杂度很大,因此双重稀疏字典一般选具有可快速实现的固定字典作为训练基字典。为了更好地适应待处理地震资料,通常需要选择一个具有一些先验数据信息的字典。
双重稀疏字典模型通过训练样本数据来调整原子表示矩阵A而使其具有自适应性及稀疏性。此外,由于基字典Φ可以是任意一个存在的固定字典,所以双重稀疏字典模型可以看成是对现存固定字典的一种自适应性的扩展。和学习字典相比,双重稀疏字典由于具有了稀疏性,所以计算复杂度更低,对于训练样本的数量要求更低。此外,双重稀疏字典模型在字典学习的过程中具有正则化功能,可以减少过度拟合和及不稳定性。由于训练双重稀疏字典比训练学习字典需要的样本数据要少很多,当可使用的样本数据很少时,该双重稀疏字典的效果更加有效。
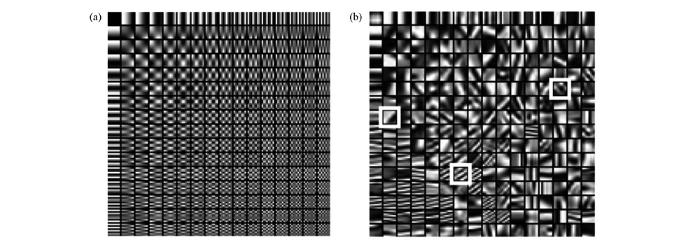
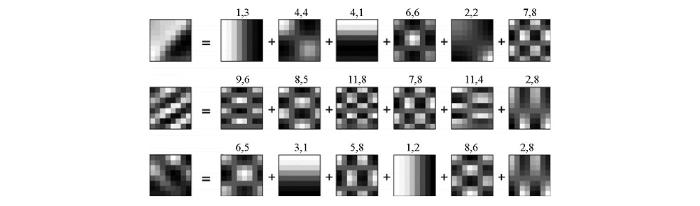
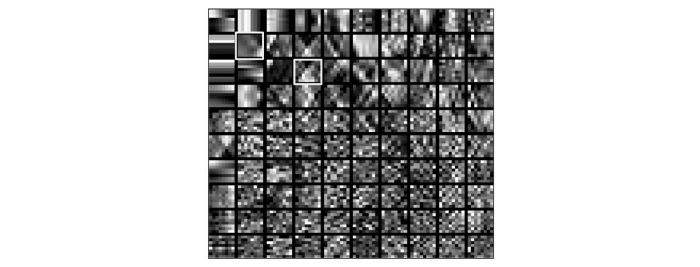
笔者采用稀疏K-SVD算法并采用OMP方法进行稀疏编码来训练得到双重稀疏字典[21,22]。图1为文献[22]给出的典型双重稀疏表示字典例子,其中图1a为训练双重稀疏字典中选定的基字典(大小为8×8过完备离散余弦字典),图1b为采用大小为8×8的样本数据块经过稀疏K-SVD训练后得到双重稀疏字典。通过图1a和图1b的对比可以看出,经过训练后得到的双重稀疏学习字典的具有了明显的结构特征。提取图1b中3个白色方框中的原子,对这3个原子进行放大得到图2中的稀疏原子分解图。在训练该字典的过程中,原子表示矩阵的稀疏度设定为6,即要求每个训练得到的稀疏字典D的原子都是由过完备离散余弦变换字典Φ中的6个原子组成,如图2所示,构成双重稀疏字典原子的系数由左到右逐渐变大,每个基字典原子上的索引为其在图1a中的离散余弦变换字典所在的位置。图2表明,稀疏字典的结构性通过过完备离散余弦变换字典中的原子获得,其自适应性通过基字典原子表示系数A进行调整。
图1
图2
1.2 基于双重稀疏表示的信噪分离方法
在本文中,采用以下模型来表示含噪地震数据:
其中,Y为实际观测得到的含噪地震数据,X为理想的不含噪地震数据,V为标准差为σ的零均值加性均匀高斯白噪声。噪声衰减就是尽可能从含噪数据Y中恢复出理想数据X,信号X在变换域的系数越稀疏(即信号X可用双重稀疏字典稀疏表示),所得到的去噪效果越好。去噪流程图如图3所示。
图3
对系数表示进行阈值处理的过程中,阈值处理主要分为硬阈值和软阈值两种。硬阈值处理为:
软阈值处理为:
式(3)和式(4)分别为和阈值δ相关的软阈值函数和硬阈值函数,其中c表示数据进行变换后的系数。文中对变换系数采用软阈值处理。
基于变换的去噪问题通常可以表示成具有稀疏限制的优化问题:
其中,D为冗余字典(此文中表示双重稀疏字典),γ为信号X在变换域的系数表示,ε为和噪声水平相关的误差限。系数表示γ的l0范数表明非零元素的个数,通过最小化该范数可以得到理想的去噪结果。
双重稀疏字典通过稀疏K-SVD算法训练得到,即已经得到原子表示矩阵A,上述优化问题可转化为求取下列最小化问题。
通过正交匹配追踪的方法来求得系数表示
2 算例
2.1 模型算例
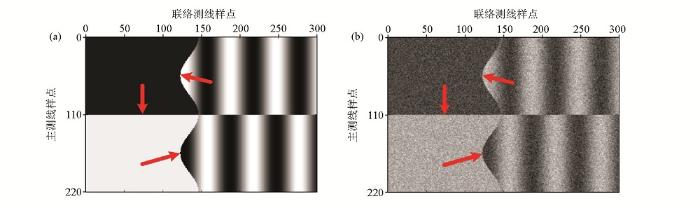
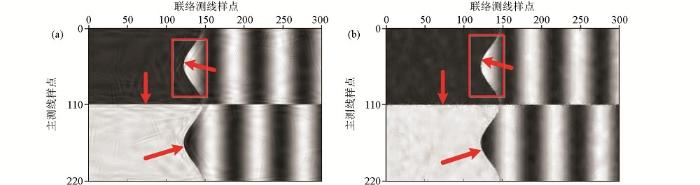
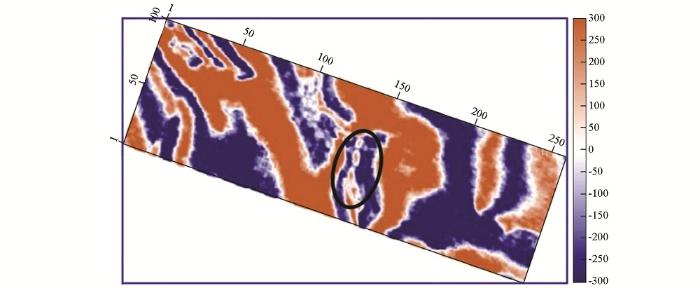
选取不含噪的合成地震记录模型作为原始的三维地震数据,某时间切片如图4a所示。对合成数据加入白噪声,信噪比为3 dB。为含噪地震数据的对应时间切面。该合成模型沿着主测线、联络测线和垂直方向上分别有220、300、80个采样点,采用两种同频,沿着不同方向传播的平面波组成,在两个平面波相交的地方产生弯曲的倾斜断层,与此同时,该模型还有一个与倾斜断层相交的垂直断层。
图4
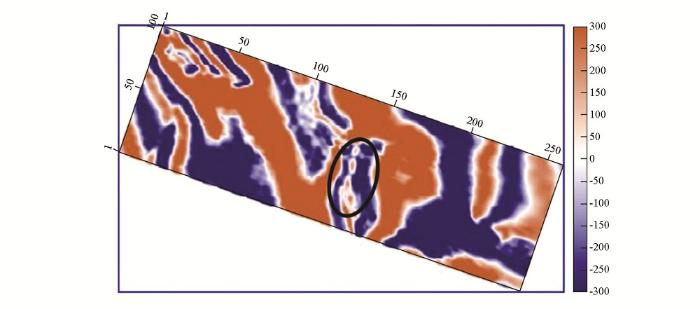
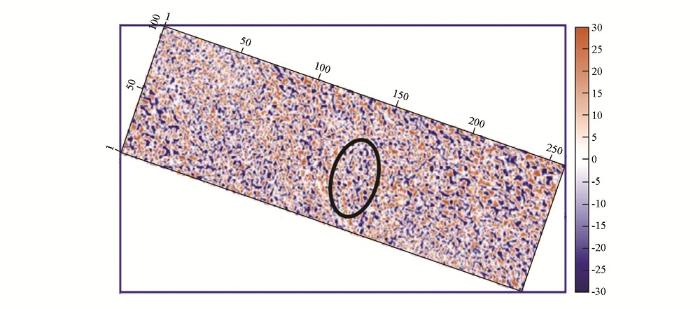
通过采用3D稀疏K-SVD去噪算法处理该含噪三维合成模型数据的具体参数如表1所示。采用的训练基字典都为过完备的离散余弦变换字典(ODCT),选取8×8×8的立体数据块作为训练样本数据体的大小,在3D稀疏K-SVD算法中,过完备字典的大小为512×1 000。由于此处采用双重稀疏字典模型,原子表示矩阵的稀疏度选为16,即在原子的系数表示中,系数表示中非零元素的个数至少为16。选取的训练样本数为80 000,既能有效地降低训练成本,又能保证训练的效果,而且迭代次数为15就可以满足相应的收敛要求。
图5
图6
2.2 实际资料算例
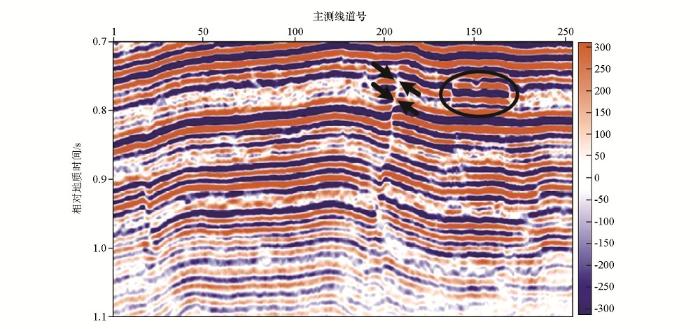
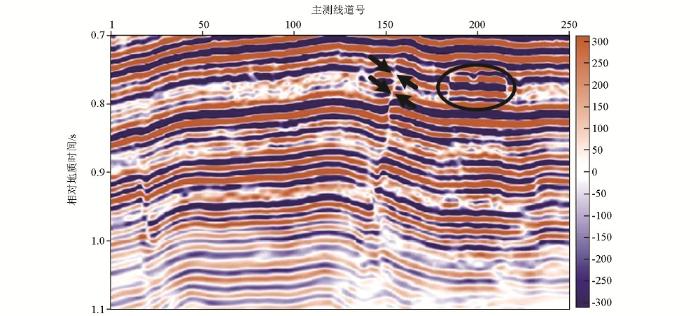
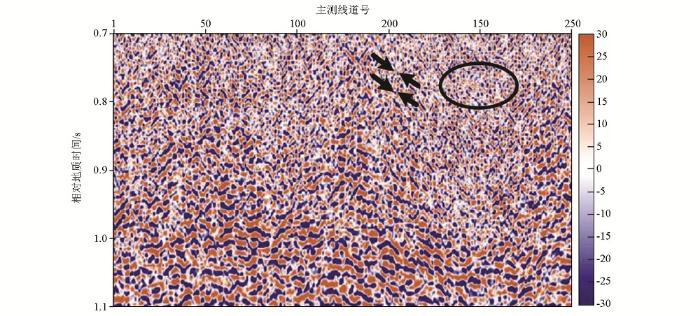
将基于双重稀疏字典稀疏表示的地震资料随机噪声衰减方法用于某油田三维地震资料的噪声衰减中。由于基于Curvelet的去噪方法整体信噪比提高不如稀疏K-SVD去噪方法,而且会引入剪切波感干扰,所以在对实际资料的进行处理中,仅3D稀疏K-SVD方法。该三维数据体中,具有几条河道砂体沉积特征,因而要求对此数据处理中采用的去噪算法具有有效的边缘结构保持能力,否则很容易引起细小结构的损失和压制。图7是该三维地震资料的一个Crossline方向剖面,Inline的值为900。图8为3D稀疏K-SVD去噪结果Crossline方向剖面。Crossline方向剖面中,圆圈标明的区域为细小河道结构,箭头所示位置为断层结构。图9为3D去噪方法去除的噪声Crossline剖面图,从噪声剖面对比中可以看出, 3D稀疏K-SVD方法明显衰减噪声,而且对断层结构和细小河道结构的损伤很小。
图7
图8
图9
图10
3 结论
图11
图12
文中介绍了双重稀疏字典模型和相应的字典训练算法,通过稀疏K-SVD算法训练双重稀疏字典,得到了兼具结构性和自适应性的学习字典,能更好地匹配待处理数据。介绍了基于双重稀疏字典的随机噪声衰减模型,通过和基于Curvelet变换的去噪结果相对比,以及本文方法处理算例的对比表明,该方法不仅可以有效压制地震资料随机噪声,而且在3D资料处理中能更好地保持断层边缘结构。
参考文献
中国石化油气勘探十年回顾与展望
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-6809.2009.03.001
URL
[本文引用: 1]

回顾了中国石化十年来油气资源储量和产量增长情况以及油气勘探方面取得的重大成果与认识,展望了中国石化未来十年油气资源勘探前景。
Seismic attributes:a historical perspective
[J].DOI:10.1190/1.2098670 URL [本文引用: 1]
Emerging and future trends in seismic attributes
[J].DOI:10.1190/1.2896620 URL [本文引用: 1]
Coherence and curvature attributes on preconditioned seismic data
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.3575281
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Seismic data are usually contaminated with both random and coherent noise, even when the data have been properly migrated and are multiple-free. Seismic attributes are particularly effective at extracting subtle features from relatively noise-free data. Certain types of noise can be addressed by the interpreter through careful structure-oriented filtering or postmigration footprint suppression. However, if the data are contaminated by multiples or are poorly focused and imaged due to inaccurate velocities, the data need to go back to the processing team.
用 f-x域预测技术消除随机噪音
[J].针对<em>f-x</em>域预测技术的局限性和实际地下构造的复杂性,本文提出了<em>f-x</em>域预测与二维滤波并用的办法,使反射信号畸变尽可能小。考虑到<em>f-x</em>域预测技术对随机干扰的压制程度不太理想,本文根据信号的可预测性和随机干扰的不可预测性,应用信噪比的模对预测值作自适应加权处理,提高<em>f-x</em>域预测技术压制随机干扰的能力。这两项对<em>f-x</em>域预测技术的改进在理论数据和实际地震记录上均见到了明显的效果。
Improving the performance of f-x prediction filtering at low signal-to-noise ratios
[J].
DOI:10.1046/j.1365-2478.1997.00347.x
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The conventional method of f filtering for random noise reduction suffers from three drawbacks. Firstly, the wavenumber response of the filter does not peak exactly at the wavenumbers of the signal components. Secondly, the amplitude of the filter response is less than one at the signal component wavenumbers, causing attenuation of the signal. Finally, sidelobes in the filter response cause noise at wavenumbers well separated from the signal components to leak into the filtered output. Singular value decomposition (SVD) of the data matrix shows that the problems may be reduced by using a transient-free formulation of the data matrix; that is, minimizing the squared errors over a finite data length rather than minimizing the expected value of the squared errors under the assumption of an infinite length of available data. Using the transient-free formulation, noise-free signal can be predicted perfectly, unlike the conventional method. The SVD analysis of the transient-free case shows that the noise-reduction performance may be improved further at all signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs). This is achieved because in the noise-free case, the correlation matrix is rank-deficient. For noisy data, an estimate of the correlation matrix is made by selecting appropriate eigenvectors to construct the filter. The use of selected eigenvectors ensures stability, thus permitting the use of much longer filters than the usual methods, with a consequent improvement in SNR gain. Conventional techniques for estimating the effective rank of the correlation matrix focus on variations in the size of the eigenvalues, selecting only the largest. It was found that these methods severely overestimate the effective rank. Furthermore, in synthetic tests it was found that some eigenvectors corresponding to noise may have eigenvalues larger than some of the signal eigenvectors. The eigenvector selection is therefore based on the observation that the phase of a noise eigenvector has a random walk appearance, whereas the phase of the signal eigenvectors varies in a smooth manner. Statistical criteria permit the selection of the signal eigenvectors in a robust way. Tests on synthetic data show that the SNR gain may typically be 10 dB for the selected eigenvector method, as opposed to 5 dB to 0 dB at different input signal-to-noise ratios for the other methods. The optimal filter lengths were about twice the optimal lengths found for the conventional method. Tests on real stacked data also show considerable improvement in performance. Care must be taken in areas of complicated structure, particularly when strongly curved events are present, to select sufficient eigenvectors, but this may be achieved at the price of a slight loss in noise reduction.
Signal-to-noise ratio enhancement in multichannel seismic data via the Karhunen-Loeve transform
[J].
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2478.1987.tb00800.x
URL
[本文引用: 1]

ABSTRACT The Karhunen-Lo ve transform, which optimally extracts coherent information from multichannel input data in a least-squares sense, is used for two specific problems in seismic data processing. The first is the enhancement of stacked seismic sections by a reconstruction procedure which increases the signal-to-noise ratio by removing from the data that information which is incoherent trace-to-trace. The technique is demonstrated on synthetic data examples and works well on real data. The Karhunen-Lo ve transform is useful for data compression for the transmission and storage of stacked seismic data. The second problem is the suppression of multiples in CMP or CDP gathers. After moveout correction with the velocity associated with the multiples, the gather is reconstructed using the Karhunen-Lo ve procedure, and the information associated with the multiples omitted. Examples of this technique for synthetic and real data are presented.
Local singular value decomposition for signal enhancement of seismic data
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.2435967
URL
[本文引用: 1]

ABSTRACT Singular value decomposition (SVD) is a coherency-based technique that provides both signal enhancement and noise suppression. It has been implemented in a variety of seismic applications - mostly on a global scale. In this paper, we use SVD to improve the signal-to-noise ratio of unstacked and stacked seismic sections, but apply it locally to cope with coherent events that vary with both time and offset. The local SVD technique is compared with f-x deconvolution and median filtering on a set of synthetic and real-data sections. Local SVD is better than f-x deconvolution and median filtering in removing background noise, but it performs less well in enhancing weak events or events with conflicting dips. Combining f-x deconvolution or median filtering with local SVD overcomes the main weaknesses associated with each individual method and leads to the best results.
Cycle-Octave and related transforms in seismic signal analysis
[J].
DOI:10.1016/0016-7142(84)90025-5
URL
[本文引用: 1]

High-resolution seismic methods are needed especially in oil and gas field development. They involve the use of backscattered energy rather than that of reflected signals, and make it interesting to look for representations of seismic traces in the time-frequency domain. One such representation was introduced by D. Gabor in 1946 into signal analysis; it is based on the consideration of a family of “elementary wavelets” that can be obtained from one “basic wavelet” by shifts in time and in frequency. We present here a different representation, in which frequency shifts are replaced by dilations. The resulting “voice transform” and “cycle-octave transform” are briefly described from the mathematical point of view and illustrated by numerical examples.
New tight frames of curvelets and optimal representations of objects with C2 singularities
[J].DOI:10.1002/cpa.v57:2 URL [本文引用: 2]
Fast discrete curvelet transforms
[J].
Simply denoise:Wavefield reconstruction via jittered undersampling
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.2841038
URL
[本文引用: 1]

We present a new, discrete undersampling scheme designed to favor wavefield reconstruction by sparsity-promoting inversion with transform elements localized in the Fourier domain. The work is motivated by empirical observations in the seismic community, corroborated by results from compressive sampling, that indicate favorable (wavefield) reconstructions from random rather than regular undersampling. Indeed, random undersampling renders coherent aliases into harmless incoherent random noise, effectively turning the interpolation problem into a much simpler denoising problem. A practical requirement of wavefield reconstruction with localized sparsifying transforms is the control on the maximum gap size. Unfortunately, random undersampling does not provide such a control. Thus, we introduce a sampling scheme, termed jittered undersampling, that shares the benefits of random sampling and controls the maximum gap size. The contribution of jittered sub-Nyquist sampling is key in formulating a versatile wavefield sparsity-promoting recovery scheme that follows the principles of compressive sampling. After the behavior of the jittered-undersampling scheme in the Fourier domain is analyzed, its performance is studied for curvelet recovery by sparsity-promoting inversion (CRSI). The findings on synthetic and real seismic data indicate an improvement of several decibels over recovery from regularly undersampled data for the same amount of data collected.
Coherent and random noise attenuation using the curvelet transform
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.2840373
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Abstract This paper discusses an effective approach to attenuate random and coherent linear noise in a 3D data set from a carbonate environment. Figure 1 illustrates a seismic inline section from a noisy 3D seismic cube. Clearly, the section in Figure 1 is corrupted by undesirable random noise and coherent noise that are linear and vertically dipping in nature.
The surface wave suppression using the second generation curvelet transform
[J].
DOI:10.1007/s11770-010-0257-x
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In this paper, we develop a new and effective multiple scale and strongly directional method for identifying and suppressing ground roll based on the second generation curvelet transform. Making the best use of the curvelet transform strong local directional characteristics, seismic frequency bands are transformed into scale data with and without noise. Since surface waves and primary reflected waves have less overlap in the curvelet domain, we can effectively identify and separate noise. Applying this method to pre-stack seismic data can successfully remove surface waves and, at the same time, protect the reflected events well, particularly in the low-frequency band. This indicates that the method described in this paper is an effective and amplitude-preserving method.
Nonequispaced curvelet transform for seismic data reconstruction:A sparsity-promoting approach
[J].
DOI:10.1190/1.3494032
URL
[本文引用: 1]

We extend our earlier work on the nonequispaced fast discrete curvelet transform (NFDCT) and introduce a second generation of the transform. This new generation differs from the previous one by the approach taken to compute accurate curvelet coefficients from irregularly sampled data. The first generation relies on accurate Fourier coefficients obtained by an l
基于Curvelet变换的多尺度分析技术
[J].
DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2009.05.004
URL
Magsci
[本文引用: 1]

为了更好地描述断层和断裂系统,本文将三维相干体技术与第二代Curvelet变换相结合,基于Curvelet变换良好的多尺度特性和局部滤波功能.提出了多尺度相干体分析方法,并给出了简单的计算公式.该方法在曲波域中给出不同的重构系数,得到突出不同频带的地震数据体,然后再利用相干体算法得到分频相干体.将本文提出的方法应用到实际地震数据中,突出了特定频带范围的地质异常体,提高了解释精度,有助于实现地质目标的精细解释.
Emergence of simple-cell receptive field properties by learning a sparse code for natural images
[J].DOI:10.1038/381607a0 URL [本文引用: 1]
Optimally sparse representation in general (nonorthogonal) dictionaries via l1 minimization
[J].
DOI:10.1073/pnas.0437847100
URL
PMID:16576749
[本文引用: 2]

Given a dictionary$D = \lbrace\underline d_k\rbrace$of vectors$\underline d_k$, we seek to represent a signal S as a linear combination$\underline S = \Sigma_k\>\gamma(k)\underline d_k$, with scalar coefficients (k). In particular, we aim for the sparsest representation possible. In general, this requires a combinatorial optimization process. Previous work considered the special case where D is an overcomplete system consisting of exactly two orthobases and has shown that, under a condition of mutual incoherence of the two bases, and assuming that S has a sufficiently sparse representation, this representation is unique and can be found by solving a convex optimization problem: specifically, minimizing the 1norm of the coefficients$\underline\gamma$. In this article, we obtain parallel results in a more general setting, where the dictionary D can arise from two or several bases, frames, or even less structured systems. We sketch three applications: separating linear features from planar ones in 3D data, noncooperative multiuser encoding, and identification of over-complete independent component models.
Double sparsity: Learning sparse dictionaries for sparse signal approximation
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TSP.2009.2036477
URL
[本文引用: 2]

An efficient and flexible dictionary structure is proposed for sparse and redundant signal representation. The proposed sparse dictionary is based on a sparsity model of the dictionary atoms over a base dictionary, and takes the form D = A, where is a fixed base dictionary and A is sparse. The sparse dictionary provides efficient forward and adjoint operators, has a compact representation, and can be effectively trained from given example data. In this, the sparse structure bridges the gap between implicit dictionaries, which have efficient implementations yet lack adaptability, and explicit dictionaries, which are fully adaptable but non-efficient and costly to deploy. In this paper, we discuss the advantages of sparse dictionaries, and present an efficient algorithm for training them. We demonstrate the advantages of the proposed structure for 3-D image denoising.