中国陆域冻土区浅表烃类地球化学特征及其成因分析
Geochemical characteristics and genesis of hydrocarbons in superficial soil in continental permafrost regions in China
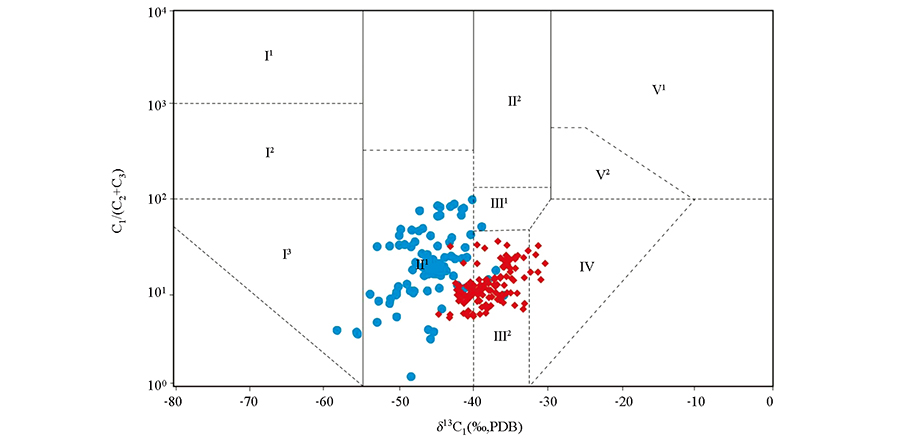
Ⅰ1 —生物气;Ⅰ2—生物气和亚生物气; Ⅰ3—亚生物气;Ⅱ1—原油伴生气;Ⅱ2—油型裂解气;Ⅲ1—油型裂解气和煤成气;Ⅲ2—凝析油伴生气和煤成气;Ⅳ—煤成气;Ⅴ1—无机气;Ⅴ2—无机气和煤成气;
 —羌塘盆地检测点;
—羌塘盆地检测点;  —祁连山地区检测点
—祁连山地区检测点Ⅰ1—biogas;Ⅰ2—biogas and sub-biogas;Ⅰ3—sub-biogas;Ⅱ1—oil-associated gas;Ⅱ2—oil cracking gas;Ⅲ1—oil cracking gas and coal gas;Ⅲ2—condensate oil-associated gas and coal gas;Ⅳ—coal gas;Ⅴ1—inorganic gas;Ⅴ2—inorganic gas and coal gas;
 —detection point of Qiangtang Basin;
—detection point of Qiangtang Basin;  —detection point of Qilian mountain
—detection point of Qilian mountain