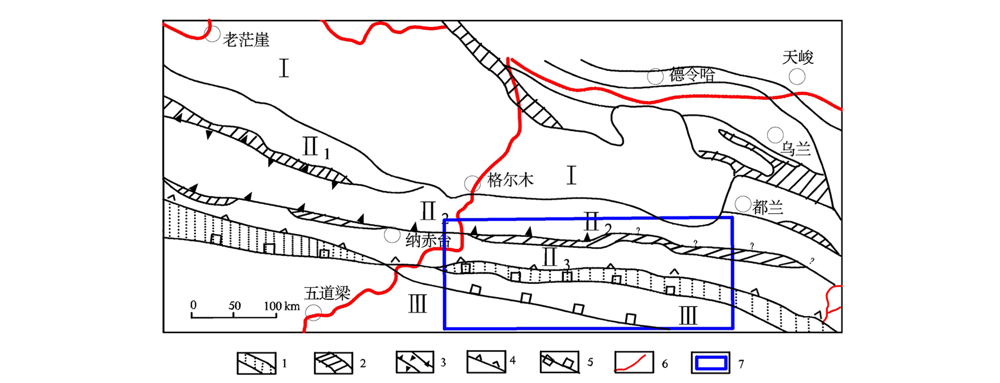
马氏距离法在东昆仑东段多元异常圈定中的对比试验
The application of Mahalanobis distance to the delineation of multivariate outliers in the East Kunlun Mountains
1—主缝合带;2—次缝合带;3—新元古代-早古生代结合带俯冲方向(一侧有齿者为单向俯冲,两侧有齿者为双向俯冲);4—晚古生代-早中生代缝合带俯冲方向;5—A型俯冲带;6—公路;7—研究区位置;Ⅰ—柴达木地块;Ⅱ—东昆仑造山带;Ⅱ1—东昆北早古生代弧后裂陷带(昆北带);Ⅱ2—东昆中岩浆弧带(昆中带);Ⅱ3—东昆南构造-混杂岩带(昆南带);Ⅲ—巴颜喀拉造山带(北巴带)
1—main structure zone; 2—secondary structure zone; 3—Neoproterozoic-early Paleozoic combined belt subduction direction(one-way subduction with teeth on one side and two-way subduction with teeth on both sides); 4—subduction direction of late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic suture belt; 5—A type subduction zones; 6—high way; 7—location of study area; Ⅰ—Qaidam massif; Ⅱ—East Kunlun orogenic belt; Ⅱ1—East Kunbei early paleozoic back-arc rife (Kunbei belt); Ⅱ2—East Kunzhong magmatic arc zone(Kunzhong belt); Ⅱ3—East-Kunnan tectonomagmatic belt(Kunnan belt); Ⅲ—Bayan Kara orogenic belt (Beiba belt)